ACS- Young
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
FYI: Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is a broad term that describes what?
unstable angina (UA)
myocardial infarction
ST segment elevation MI (STEMI)
non-ST segment elevation MI (NSTEMI)
What is the etiology of ACS?
idk how imp
atherosclerosis (cholesterol excess, inflammation, endothelial dysfunction aka stress of blood flow on endothelial lining)
RFs for endothelial dysfunction?
idk how imp
HTN
age
male
tobacco use
DM
obesity
dyslipidemias
What is the cause of ACS?
erosion, rupture, or fissure of unstable atherosclerotic plaque
What happens after a plaque ruptures?
idk how important
thrombogenic parts of plaque exposed
causes platelet adhesion to site
binding causes changes in platelet shape and platelets active
ADP binds to platelet P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors
cross linking of platelets
gives the clot a white appearance
Compare a white vs. red clot:
“white clot” | “red clot” |
|
|
What is the patient presentation for ACS?
what is specific to STEMI?
what is specific to NSTEMI?
in general:
midline, anterior chest discomfort (at rest, severe new onset, increasing angina at least 20 min in duration)
pain may radiate to shoulder, down left arm, to back or jaw
may have n/v, sweating, SOB
STEMI—> unremitting chest discomfort
NSTEMI—> rest angina OR new angina (<2m) OR angina w/ increased frequency duration or intensity
How is unstable angina diagnosed?
How is MI diagnosed?
unstable angina: 10-20 min, may or may not be relieved by nitroglycerin (NTG)
MI: >30 minutes, unrelieved by rest or NTG
What segment is the main area of focus in evaluation of chest pain?
a. PR interval
b. QRS complex
c. PR segment
d. ST segment
e. QT interval
d.
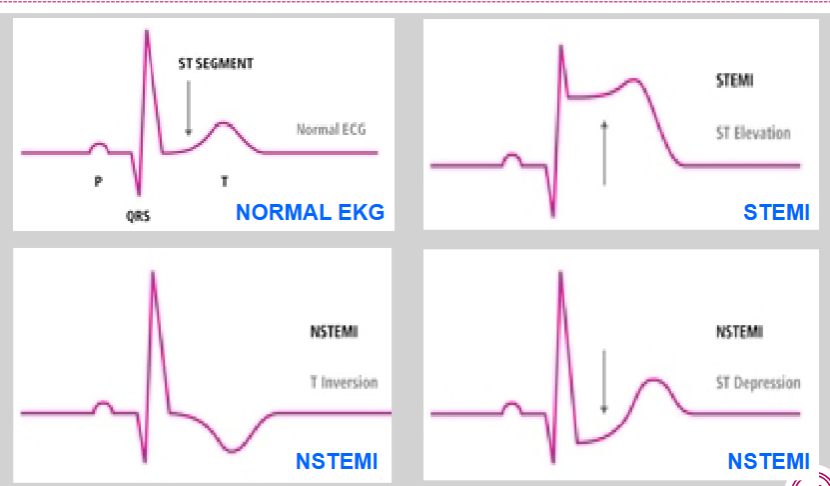
How does the EKG look in NSTEMI vs. STEMI?
idk how imp lowkey
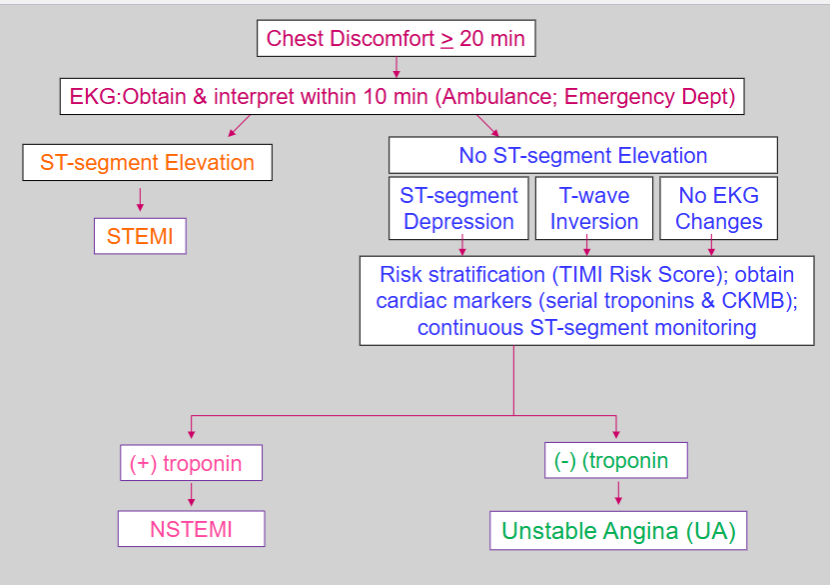
What is the general algorithm to determining whether a STEMI, NSTEMI, or unstable angina occurred?
chest discomfort for ≥20 min
EKG obtained and interpreted
What are the main markers to differentiate between a NSTEMI and UA?
UA: normal troponin or CK MB
NSTEMI: increased troponin, increased CK MB
What is troponin?
What does it reflect?
idk how imp
troponin—> Components of contractile apparatus of myocardial cells and expressed almost exclusively in the heart
Reflect injury leading to necrosis, but not the mechanism
PRACTICE:
A pt. presents with crushing chest pain for 40 minutes, his initial EKG reveals ST segment depression, and his troponin is positive, what is his diagnosis?
a. UA
b. NSTEMI
c. STEMI
d. chronic stable angina
b. NSTEMI
What is the acronym for ACS early management?
MONA-B (NOT IN THIS ORDER THO)
M= morphine
O= oxygen
N= nitroglycerin
A= aspirin
B= b-blocker
For ACS early management:
What is given to relieve acute chest pain?
How many doses can be given?
After how many doses do you call 911?
nitroglycerin
x3 doses to relieve acute CP
after 1 dose… if pain is unrelieved—> call 911
When should caution be used with nitroglycerin?
What are the C/I to nitroglycerin?
caution:
inferior wall MI
RV infarction
C/I:
sildenafil, vardenafil, or avanafil use in past 24 hrs
may pos give 12 hrs after avanafil
tadalafil use in past 48 hrs
For ACS early management:
what type of aspirin should be given?
effect of aspirin?
what to give in aspirin allergy?
1 dose of NON-ENTERIC COATED aspirin
effect: reduces recurrence of MI and death
aspirin allergy: use clopidogrel
For ACS early management:
when is oxygen indicated?
for oxygen saturation <90%
respiratory distress
high risk fts. for hypoxemia
For ACS early management:
what is given for pain relief?
indication?
effect?
hold for what?
morphine
for unrelieved chest pain despite nitroglycerin and maximally tolerated anti-ischemic medications
effect: vasodilation—> hold for hypotension
For ACS early management:
what is the most widely studied beta-blocker?
used in what pts.?
effects of b-blockers?
C/I to b-blocker use.
most widely studied—> metoprolol
used in pts. undergoing primary PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention)
effects: decreases myocardial ischemia, reinfarction, and frequency of ventricular dyysrhythmias
C/I: hypotension, low output state, signs of HF, risk factors for cardio shock
PRACTICE:
Which medication should NOT be used with an inferior MI?
a. aspirin
b. clopidogrel
c. nitroglycerin
d. morphine
c.
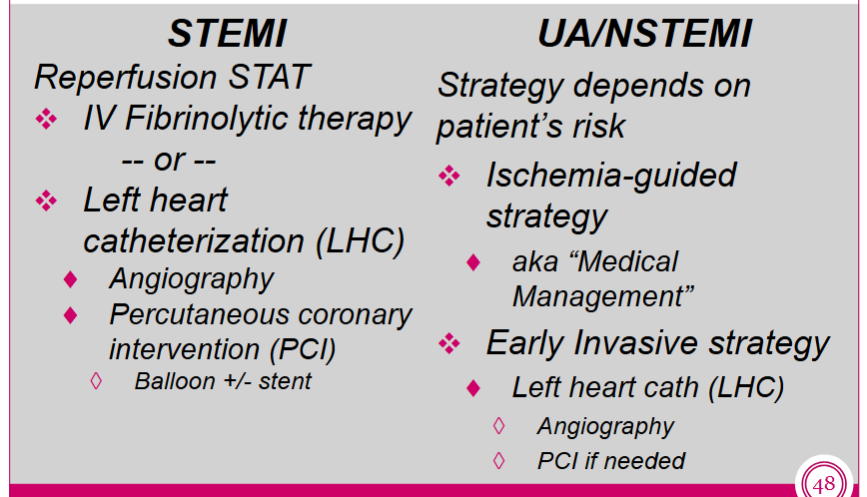
What are the general management strategies to ACS?
STEMI
UA/NSTEMI
just a general overview lowkey
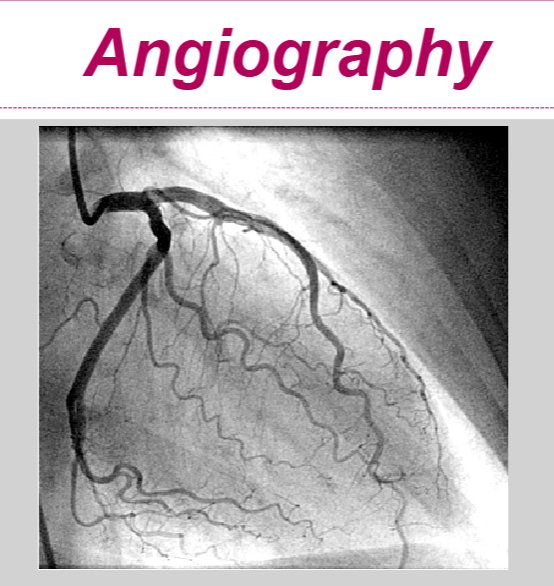
Describe left heart catheterization:
invasive or noninvasive procedure?
requires what?
what is an angiography?
invasive procedure—> to assess patency of coronary vessels and hemodynamic parameters of cardiac fxn
requires IV contrast and fluoroscopy
angiography—> assesses for coronary artery blockages
If appropriate… a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is done during a left heart catheterization. What is a PCI?
PCI—> procedure to open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries
balloon angioplasty ± stent placement
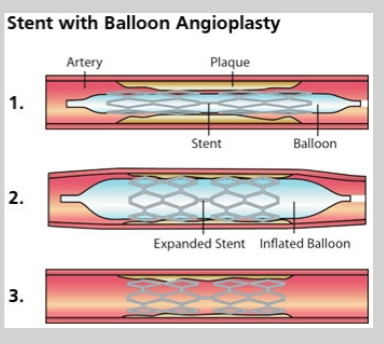
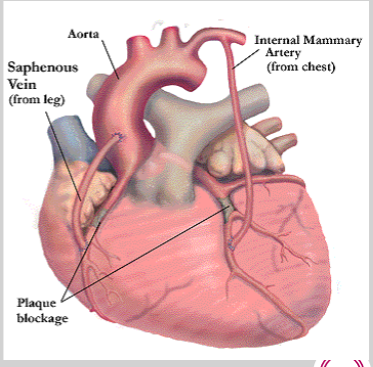
What is a CABG?
coronary artery bypass grafting
grafts used as detour around blocked portion of coronary artery
Heparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, and bivalirudin are all examples of…
a. antiplatelets
b. fibrinolytics
c. anticoagulants
c. anticoagulants
aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitors, and glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors are all examples of…
a. antiplatelets
b. fibrinolytics
c. anticoagulants
a. antiplatelets
Match the class to its drugs:
Class | Drug Examples |
Unfractionated heparin | |
LMWH | |
Direct thrombin inhibitor | |
Factor Xa inhibitor |
drugs: fondaparinux, bivalirudin, enoxaparin, heparin, dalteparin
Class | Drug Examples |
Unfractionated heparin | heparin |
LMWH |
|
Direct thrombin inhibitor | bivalirudin |
Factor Xa inhibitor | fondaparinux |
What must be monitored on heparin?
aPTT or ACT
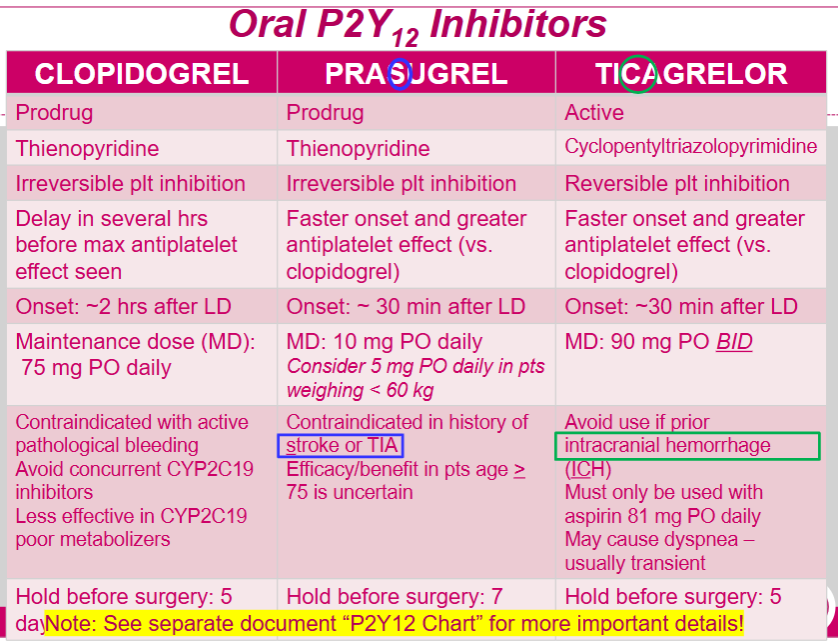
What P2Y12 inhibitors are oral? which are IV?
oral: clopidogrel (plavix), prasugrel (Effient), ticagrelor (Brillinta)
IV: cangrelor
MOA of P2Y12 inhibitors:
idk how imp
block P2Y12 component of ADP receptors on platelet surface—> prevents activation of GPIIb/IIIa receptor complex—> reduces platelet aggregation
Any head trauma needs to go to the ED to be evaluated. Intracranial hemorrhage can be fatal and risk is higher with…
antiplatelet and anticoagulants
When is prasugrel C/I?
Stroke or TIA
tip: praSugrel= C/I in Stroke
When should ticagrelor be avoided?
prior intracranial hemorrhage
FYI comparison of the oral P2Y12 inhibitors:
What drugs are glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
tirofiban (aggrastat)
eptifibitide (integrilin)
Monitor what while on Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors?
monitor CBC and for s/sx of bleeding (bc of bleeding and thrombocytopenia risk)
What is the “gold standard” for STEMI?
left heart catheterization (LHC)
angiography
PCI
balloon ± stent
PCI recommended triage strategy for STEMI
PCI is preferable to fibrinolytic therapy for a STEMI if done within _____ minutes.
120
When is fibrinolytic therapy preferred over PCI for a STEMI?
early presentation (if ≤12 hrs from s/sx onset= use fibrinolytics)
AND
anticipated first medical contact (FMC)-to-device system time >120 minutes (ex: can’t get to the hospital within 120 minutes to do a PCI)
If fibrinolytics are going to be given for a STEMI, they should be given within ____ minutes of hospital arrival.
30
Examples of fibrinolytics:
tenecteplase
reteplase
alteplase
What are the absolute and relative C/I to fibrinolytic therapy?
i would just focus on the absolute…
absolute:
any prior ICH (intracerebral hemorrhage)
known cerebrovascular lesion (these lesions can rupture= bad)
known malignant intracranial neoplasm (aka bad brain cancer)
ischemic stroke within 3 months
(exception: acute ischemic stroke within 3 hrs)
suspected aortic dissection
active bleeding or bleeding diathesis
relative:
Pregnancy
History of chronic, severe, poorly controlled hypertension
Severe uncontrolled hypertension on presentation
SBP >180 mm Hg or DBP >110 mm Hg
Traumatic or prolonged (> 10 min) resuscitation or major surgery (within < 3 weeks)
Recent internal bleeding (within 2 to 4 weeks)
Current use of anticoagulants
Higher the INR = Higher risk of bleeding (warfarin)
Active peptic ulcer
History of prior ischemic stroke (>3 months), dementia, or known intracranial pathology not covered in absolute CI
Streptokinase: Exposure (> 5 days) or prior allergic reaction
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is an ABSOLUTE contraindication to using fibrinolytic therapy for STEMI?
a. stroke >3 months ago
b. current anticoagulant use
c. severe uncontrolled HTN
d. suspected aortic dissection
d.
Fibrinolytics are only an option for what ACS?
ONLY FOR STEMI—> NOT FOR UA/NSTEMI
For antithrombic therapy in STEMI pts.
what is used for primary PCI?
what is used WITH fibrinolytics?
what is used for a PCI after fibrinolytics?
primary PCI
aspirin
P2Y12 inhibitor
anticoagulant (heparin, bivalirudin)
glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors
with fibrinolytics
aspirin
clopidogrel
anticoagulant (heparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux)
PCI after fibrinolytics
aspirin
clopidogrel
anticoagulant (heparin, enoxaparin)
glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors
With Ticagrelor, you CANNOT exceed WHAT dose of aspirin?
know this.
100 mg
Management strategy for UA/NSTEMI depends on the patient’s risk.
What is done for low risk?
What is done for high risk?
low risk: ischemia-guided strategy
aka medical management—> using meds only
high risk: early invasive strategy
left heart catheterization (LHC)
angiography
PCI if needed (balloon angioplasty ± stent placement)
What medications can be used for low risk pts. with NSTEMI/UA?
aspirin
P2Y12 inhibitor + aspirin
clopidogrel or ticagrelor
anticoagulants
UFH
enoxaparin
fondaparinux
What are the 4 components to the early invasive strategy for high risk pts. with NSTEMI/UA?
anticoagulant (UFH, enoxaparin, bivalirudin)+ aspirin + P2Y12 inhibitor ± GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor
note: cannot given GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor with bivalirudin
After an angiography is done to determine coronary anatomy for the early invasive strategy (aka high risk pts. with NSTEMI/UA)… what 3 pathways can be followed?
continue medication management
PCI
CABG
After the placement of a stent, REGARDLESS of STEMI or NSTEMI, what is required?
must know the doses
DUAL ANTIPLATELET THERAPY (DAPT) x 1 year
aspirin + P2Y12 inhibitor
aspirin (continued indefinitely)—> 75-324 mg PO daily
P2Y12 inhibitor (usually continued for a year)
clopidogrel 75mg PO daily
prasugrel 10mg PO daily
ticagrelor 90mg PO BID
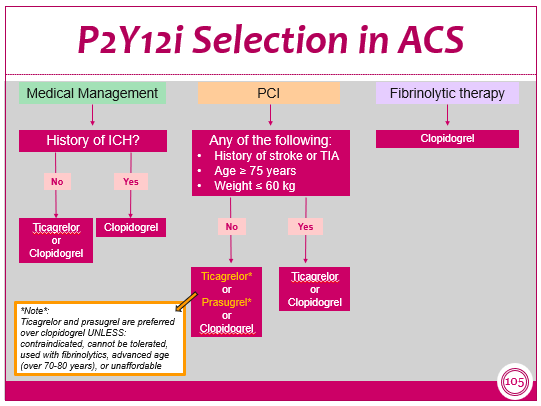
What is the process for selecting a P2Y12 inhibitor?
FYI
For pts. who undergo PCI with history of AF or VTE who require chronic anticoagulation… what anticoagulants are preferred? what type of therapy is preferred?
preferred—> DOAC > warfarin
preferred—> dual antithrombotic therapy (DAT)
DOAC+ clopidogrel
What is triple antithrombotic therapy?
what risks are associated?
what drugs can’t be given?
triple antithrombotic therapy= anticoagulant + P2Y12 + aspirin
high bleeding risk
cannot give ticagrelor or prasugrel (bleed risk)
For ACS, what drug is given regardless of stent or medical therapy and reduces incidence of recurrent MI and death?
aspirin
Are statins given for ACS pts. even if their cholesterol is at goal?
yes
What is the indication for non-DHP CCBs in ACS?
If continuing or frequently recurring ischemia WITH CI to BB therapy OR BB & nitrates used optimally
What’s the acronym for medications at discharge for ACS secondary prevention?
SPABA ± MRA
S= statins
P= P2Y12 inhibitor
A= aspirin
B= beta-blockers (if c/i= CCB)
A= ACE inhibitors
MRA=
for pts. post MI with EF <40%, DM, or symptomatic HF