the nucleus
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
approx what % of the cytoplasm does the nucleus occupy ?
10
who first observed the nucleus and how ?
Leeuwenhoek (1719) using light microscope with increased mag
who coined the term nucleus ?
Brown (1831)
average size of nucleus
2 - 10 um
the relationship between volume of cytoplasm and nucleus is…
linear
example of cell with non-spherical nucleus
neutrophils
example of cell with multiple nuclei
hepatocytes, osteoclasts
nucleolus
condensed area of chromatin, site of ribosome synthesis
granules
rRNA being packaged with cytoplasmic proteins
nucleoplasm
viscous part of nucleus
chromatin
condensed DNA
chromosomes
chromatin ready for cell division
nuclear envelope
membrane barrier between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm
what is the space in between the 2 membranes of the nuclear envelope called ?
perinuclear space
nuclear lamina
protein lining which binds to chromatin and nuclear components
what is the function of the nuclear lamina ?
mechanical support, chromatin organisation, regulation of cell division, stabilises nuclear pore complexes
nuclear pore complex
protein complex that allows for movement of materials in and out of nucleus
where would you find more NPCs
in more active cells
how are chromosomes formed ?
negative DNA wrapped around positive histone proteins to form chromatin, then wound into loops to form chromosomes
gene
sections of chromosomes which code for specific characteristics
how does the presence of a nucleus allows eukaryotes to have a higher level of gene regulation ?
it separates the processes of transcription and translation
transcription factors
proteins involved in process of converting/transcribing DNA into RNA
how is mRNA modified pre-translation ?
splicing to remove introns, capping and addition of poly-A tail
active nuclear import
selective movement of large proteins and rNA via NPC
passive nuclear export
free diffusion of small molecules
NPC components
cytosolic filaments, cytosolic ring, pore ring, nuclear ring, nuclear basket
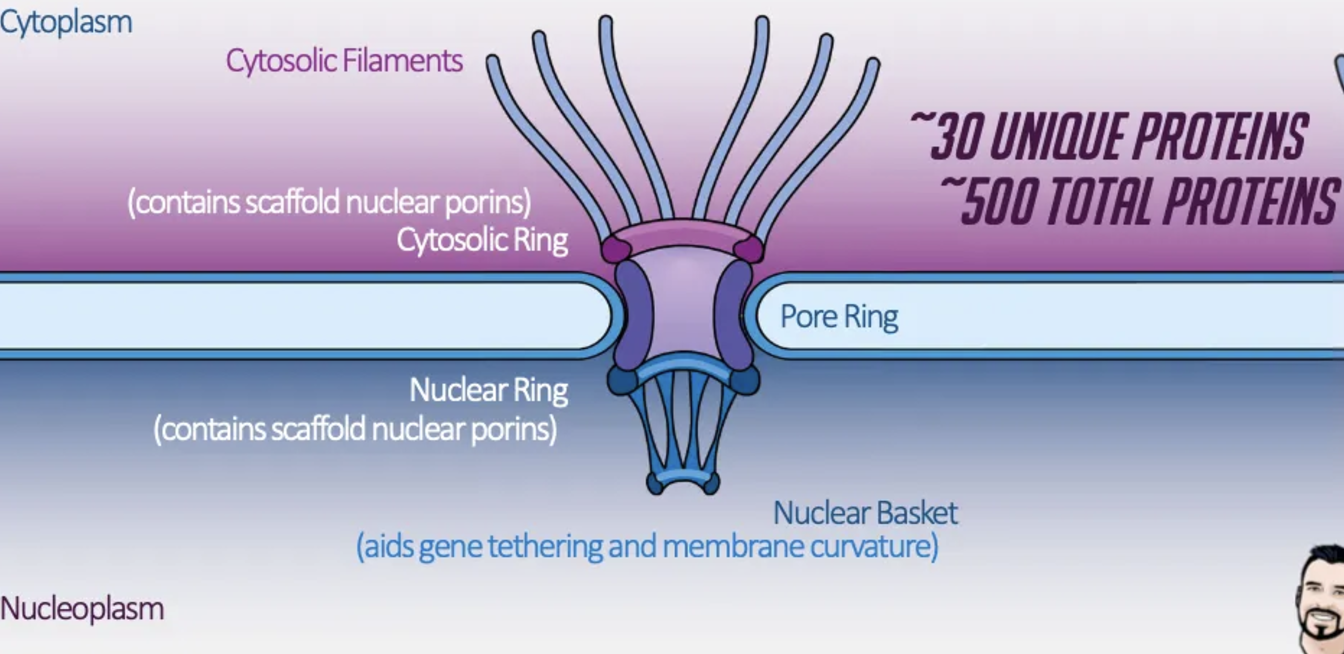
where would you find scaffold nuclear porins ?
in the cytosolic and nuclear rings
nuclear basket
aids gene tethering and membrane curvtaure
which protein recognises the specific signal sequence on cargo-proteins and transports them from cytoplasm into nucleus ?
importins
what causes the release of cargo once translocated into the nucleus ?
binding of RanGTP
how is RanGTP recycled ?
RanGTP-exporting complex translocated back into cytosol where RanGAP hydrolyses GTP to GDP (inactive) NTF2 translocate RandGDP back into nucleus where GEF phosphorylates GDP back to GTP re-activating Ran
approx. how many unique proteins form the NPC ?
30
which protein is responsible for the exchanging of GDP for GTP on the Ran protein found within the nucleus ?
RanGEF
Ran
monomeric G protein
Ran is only functional in what state ?
GTP bound
RanGAP is found in high concentrations in…
cytoplasm
RanGEF is found in high concentrations in…
nucleoplasm
where are granules and fibrils found ?
nucleolus
proto-eukaryotic model
evolutionary theory based on a progressive increase in complexity without need for endosymbiotic stage
proteins destined for the cytoplasm contain a specific sequence known as a..
nuclear export signal
what is the main function of the eukaryotic nucleus ?
control gene expression within cell