Amino Acids and Amides
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are amines
Derived by replacing 1 or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia with organic groups
Uss of quaternary ammonium compounds
production of cationic surfactants
Detergents/fabric softeners/ hair conditioners
How to name secondary amines
name the two alkyl chains
Add prefixes for additional groups
Add suffix amines
→ N-substituted
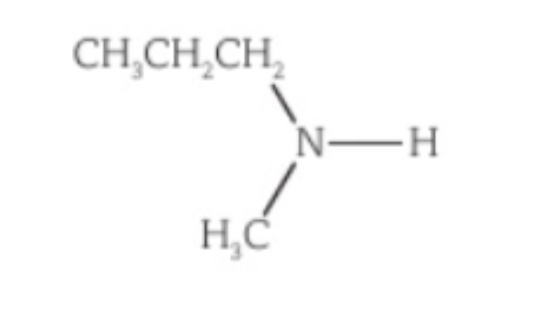
Name this amine
N-methylpropylamine
Why are amines basic
Lone pair of electrons on N can for dative bonds with H+ ion → proton acceptor
Name the salts formed when amines are neutralised by acids
alkylammonium chloride
Alkylammonium nitrate
Alkylammonium sulphate
What are two ways that amines can be produced
nucleophillic substitution
→ excess ammonia primary amine is major product
→ excess halogenoalkane successive substitution leads to a mixture of primary/secondary/tertiary amines
reduction of nitriles- LiAlH4 in dry ether/ H2 + nickel catalyst at high temperatures
How can aromatic amineS be produced
Sn + concentrated HCl + NaOH (heat under reflux) → phenylamine
Why are primary aliphatic amines stronger bases than ammonia or aromatic amines
alkyl groups are electron releasing (positive inductive effect)
More electron density on the nitrogen atom
→ number of alkyl groups attached to nitrogen increase, the base strength increases
What are amides and how do you name them
Functional group CONH2
Suffix- amide
Root depends on number of carbon atoms in parent chain
Alkyl chain attached to nitrogen N-substituted
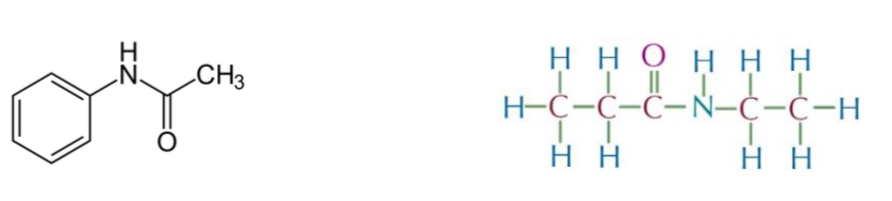
Name the following:
N-phenylethanamide + N-ethylpropanamide
Why are amides not basic
C=O bond highly electronegative
greater power to draw electrons toward it so lone pair of the amide nitrogen less available to accept protons
What is a zwiterrion
Dipolar ion produced in an internal acid-base reaction