Paper 2 SL
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
discuss possible exceptions to cell theory
skeletal muscle fibers are larger/have many nuclei / are not typical cells
fungal hyphae are (sometimes) not divided up into individual cells
unicellular organisms can be considered acellular because they are larger than a typical cell / carry out all functions of life
some tissues / organs contain large amounts of extracellular material
vitreous humor of eye / mineral deposits in bone / xylem in trees / other example
ovary: produces
eukaryotic cells have intracellular and extracellular components
state the functions of one names extracellular component
plant cell wall / cellulose / interstitial
prevents the entry of pathogens
maintains the shape of plant cells
prevents excessive entry of water to the cell
explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes
small cells have larger ratio (than larger cells) / ratio decreases as size increases
surface area / membrane must be large enough to absorb nutrients / oxygen / substances needed
cell size is limited (by SA / Volume ratio) / cells divide when they reach a certain size
outline differentiation of cells in a multicellular organism
differentiation is development in different / specific ways
cells carry out specialized functions / become specialized
each cell contains all the genetic information for the production of the complete organism
each cell becomes a specific type of cell dependent on which DNA segment becomes active
describe the importance of stem cells in differentiation
stem cells are undifferentiated cells
stem cells can differentiate in many / all ways = are pluripotent / totipotent
differentiation involves expressing some genes but not others
stem cells can be used to repair / replace tissues / heal wounds
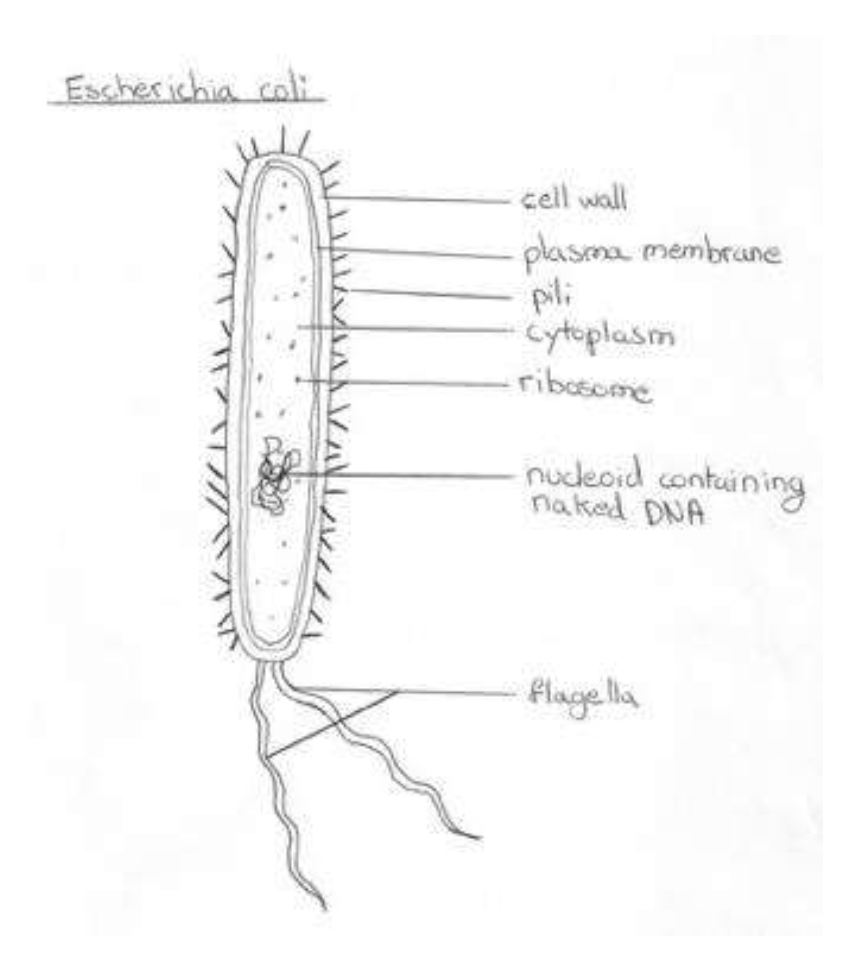
draw a label diagram to show the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli
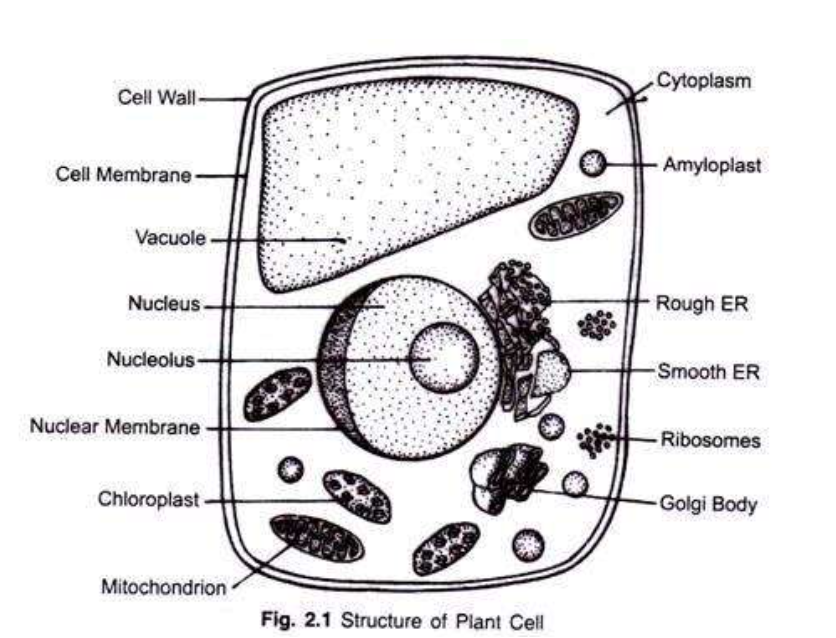
draw a labelled diagram to show the organelles which are found in the cytoplasm of plant cells
draw a labelled diagram showing the ultra-structure of a liver cell
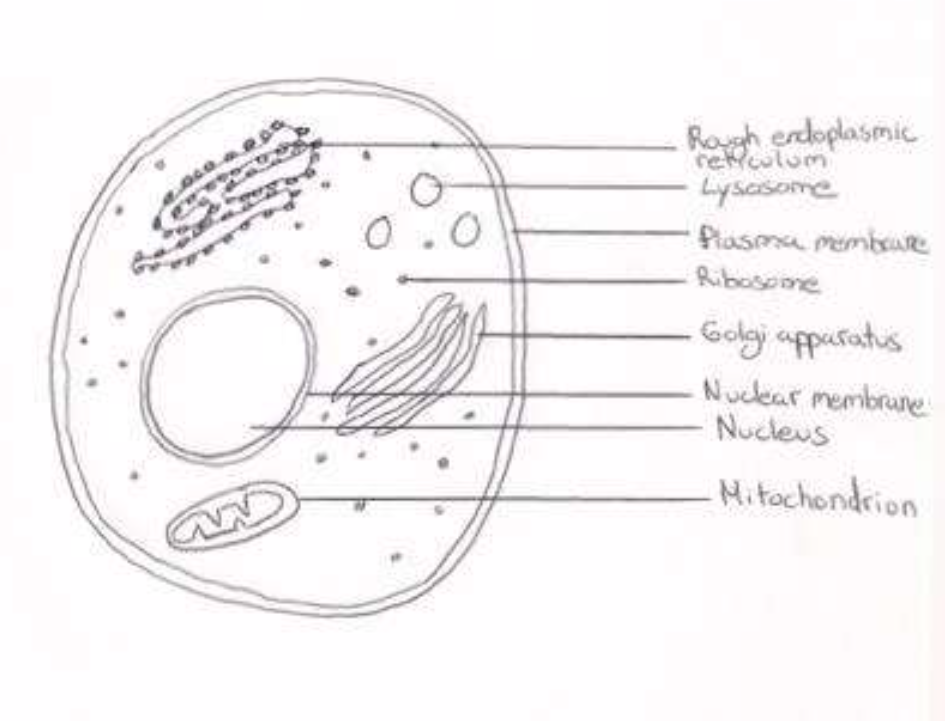
state one function of each of the following organelles: lysosome, Golgi apparatus, rough endoplasmic reticulum, nucleus, mitochondrion
lysosome: hydrolysis / digestion / break down of materials
Golgi apparatus: synthesis /sorting / transporting / secretion of cell products
rough endoplasmic reticulum: site of synthesis of proteins (to be secreted) / intracellular transport of polypeptides to Golgi apparatus
nucleus: controls cells activities / mitosis / replication of DNA / transcription of DNA (to RNA) / directs protein synthesis
mitochondrion: (aerobic) respiration / generates ATP
distinguish between the structure of plant and animal cells
plant cells
have cell walls, animal cells do not
have plastids / chloroplasts, animal cells do not
store starch
fixed / more regular shape
animal cells
have centrioles, plant cells do not
have cholesterol in the cell membrane, plant cells do not
store glycogen
more rounded
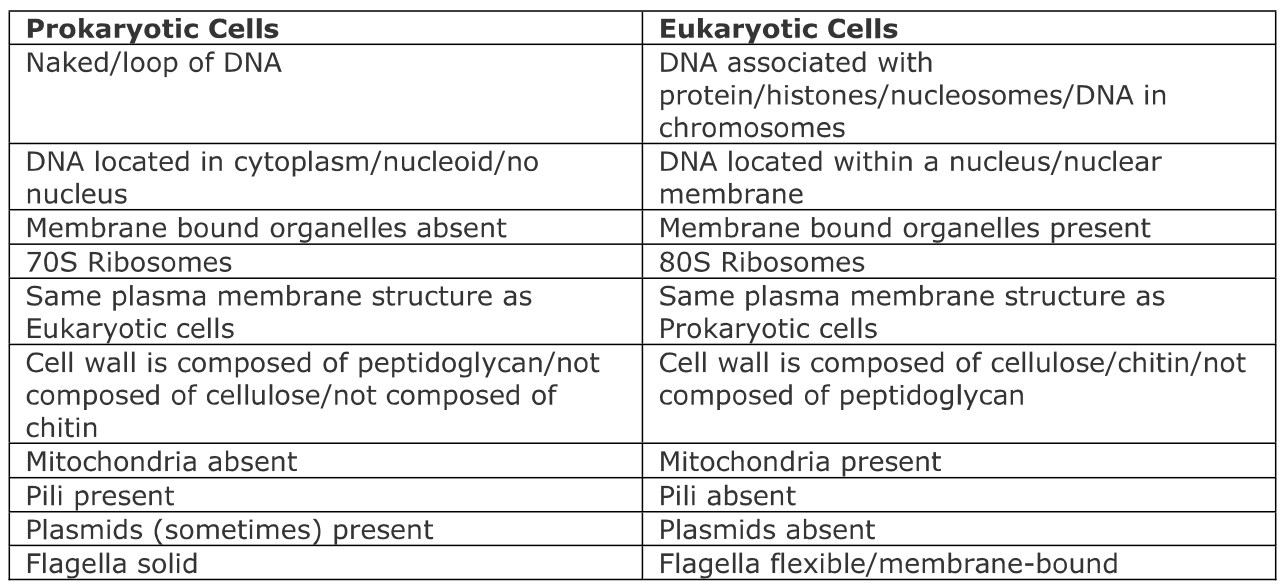
using a table, compare the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
draw a diagram to show the structure of a cell membrane
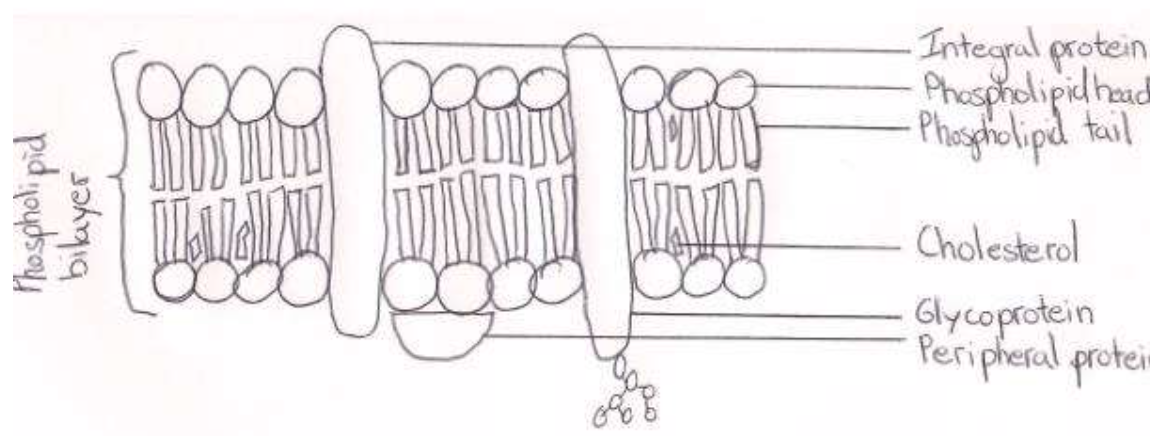
explain how the structure and properties of phospholipids help to maintain the structure of cell membranes
phospholipid structure
hydrophobic tail / head
head made from glycerol and phosphate
tail made from two fatty acids
saturated / unsaturated fatty acid (in tail)
arrangement in membrane
phospholipids form a bilayer
heads face outside the membrane / tails face inside the membrane / hydrophobic interior / hydrophilic exterior of membrane
phospholipids held together by hydrophobic interactions
phospholipid layers are stabilized by interaction of hydrophilic heads and surrounding waters
phospholipids allow for membrane fluidity / flexibility
explain the role of vesicles in transportation of materials within cells
vesicles are membrane bound packages / droplets
formed by pinching off / budding off a piece from a membrane
can carry proteins
transported to Golgi apparatus for processing
targeted to / transported to specific cellular organelles
fuse with the membrane of organelle so contents of your vesicle
join the organelle
transported to the plasma membrane
fuses with plasma membrane
fuses with platana plasma membrane releases / secret contents
distinguish between active and passive movements of materials across plasma membraned, using name exampled
passive: oxygen across alveoli
active transport: glucose absorption in ileum
passive: does not require energy
active transport: requires energy / ATP
passive: down concentration gradient
active transport: against concentration gradient
passive: no pumps needed
active transport: requires protein pumps
outline, with an example, the process of exocytosis
vesicles carry material to plasma membrane
vehicle fuses with membrane
(by joining of) phospholipid bilayers
aided by the fluidity of the membrane
material released / expelled from the cell
membrane flattens
outline for processes that occur in a cell during interphase, including those needed to prepare for mitosis
DNA replication
DNA transcription
enzyme / protein synthesis
cell respiration
growth
organelles replicated
outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationship between amino acids and dipeptides
condensation / dehydration synthesis: water produced (when two amino acids joined)
hydrolysis: water needed to break bond
dipeptide → amino acids - hydrolysis
amino acids → dipeptide - condensation occurs
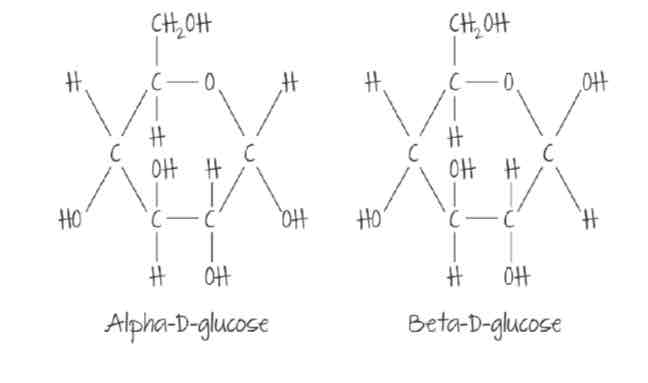
draw a molecule of a-d-glucose and B-d-glucose
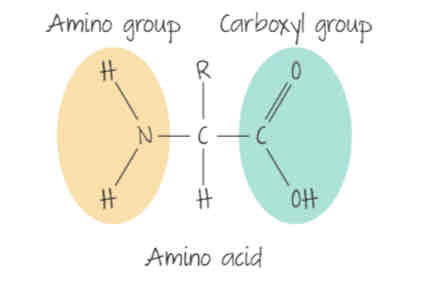
draw an amino acid
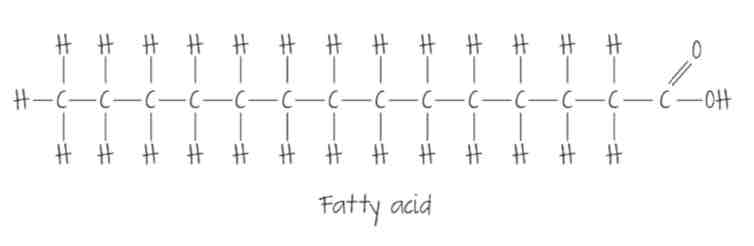
draw a fatty acid
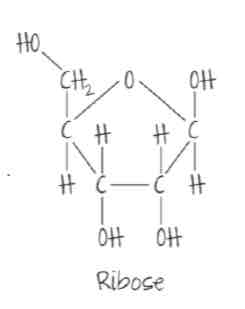
draw a molecule of ribose
outline the thermal, cohesive and solvent properties of water
water has a high specific heat capacity
a large amount of heat cause a small increase in temperature
water has a high latent heat of vaporisation
a large amount of heat energy is needed to vaporise / evaporate water
hydrogen bonds between water molecules make them cohesive / stick together
water → high surface tension / explains how water rises up xylem
water molecules are polar
this makes water a good water solvent
describe the significance of water to living organisms
surface tension → allows some organisms (insects) to move on water’s surface
polarity / capillarity / adhesion - helps plants transport water
ice floats - lakes / oceans do no not freeze, allowing life under the ice
buoyancy- supports organisms
structure - turgor in plant cells / hydrostatic pressure
habitat - place for aquatic organisms to live
describe the use of carbohydrates and lipids for energy storage in animals
carbohydrates
stored as glycogen in liver
short-term energy storage
more soluble in water for easier transport
lipids
stored as fat in animals
long-term energy storage
lipids are insoluble in water so less osmotic effect
list three functions of lipids
heat insulation
protection of internal organs
water proofing / cuticle
structural component of cell membranes
functions of the male parts of the reproductive system
penis: penetrates the vagina to deposit semen close to the cervix
urethra: transfers semen during ejaculation and passage of urine during urination
seminal vesicle: produces a sugar-rich fluid that provides sperm with a source of energy to help them move
sperm duct: transfers sperm during ejaculation
epididymis: stores sperm until ejaculation
testis: sperm and testosterone production