4.1-4.3 anatomy powerpoints
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
what has gray matter; genetic information, energy generation, homeostasis
soma
telencephalon
cerebral cortex and limbic system
diencephelan
thalamus, hypothalamus
mesencephalon
midbrain
metencephalon
pons, cerebellum
myelencephalon
medulla
_____ trimester: suck/swallow, motor movements (kicking), blinking, senses (startle at loud noises)
____ trimester: brain triples in weight during last trimester (growing those gyri!), myelination, more senses (response to light), diaphragmatic movements (“practice breathing”)
2nd
3rd
After age ____: synaptic pruning: more highways, fewer ____(adults have ½ the synapses as infants/toddlers)
2
backroads
what is the receptor of transmitted signal from previous neuron
dendrite
white matter; travels across nervous system, can be a meter in length!
axon
where transmission happens to the next neuron at the synapse (synaptic cleft)
axon terminal
fatty covering that speeds up transmission down axon
myelin
nervous tissues in your brain and spinal cord
CNS
nervous tissue in your body
peripheral nervous system
A neuron that exists from your brainstem and travels to your face is called
cranial nerve
A neuron that exists from your spinal cord and travels to your fingers or toes is called
spinal nerve
cell bodies (signal generation) has what kind of matter
grey matter
axons (signal travel & transmission)
white matter
In your brain, grey matter is _____and white matter is internal; in your spinal cord, _____matter is internal and _____matter is external
In your brain, grey matter is external and white matter is internal; in your spinal cord, grey matter is internal and white matter is external
true or false: there are more neurons than glial cells
false: 4x as many glial cells
what kind of tissue inside nervous system
•surround neurons, holding them in place, insulate neurons, supply nutrients and oxygen, make myelin, make cerebrospinal fluid, maintain homeostasis, clean up (eat) dead neurons
connective tissue
what kind of glial cell transports oxygen from blood to the brain
astrocytes
which glial cells create mylein
oligodendrocytes
which glial cells eat dead cells and bad organisms; synaptic pruning; injury repair
microglia (NOM NOM MICROGLIA)
true false: (glial cells) astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia are all in the PNS
FALSE—> CNS
what type of cells repair damage to neurons
Schwann cells
what type of cells supply nutrients and cushion neurons
satellite cells
where do schwann and satellite cells live (CNS or PNS)
the PNS
involuntary is to _____ as somatic is to ____
autonomic as somatic is to voluntary
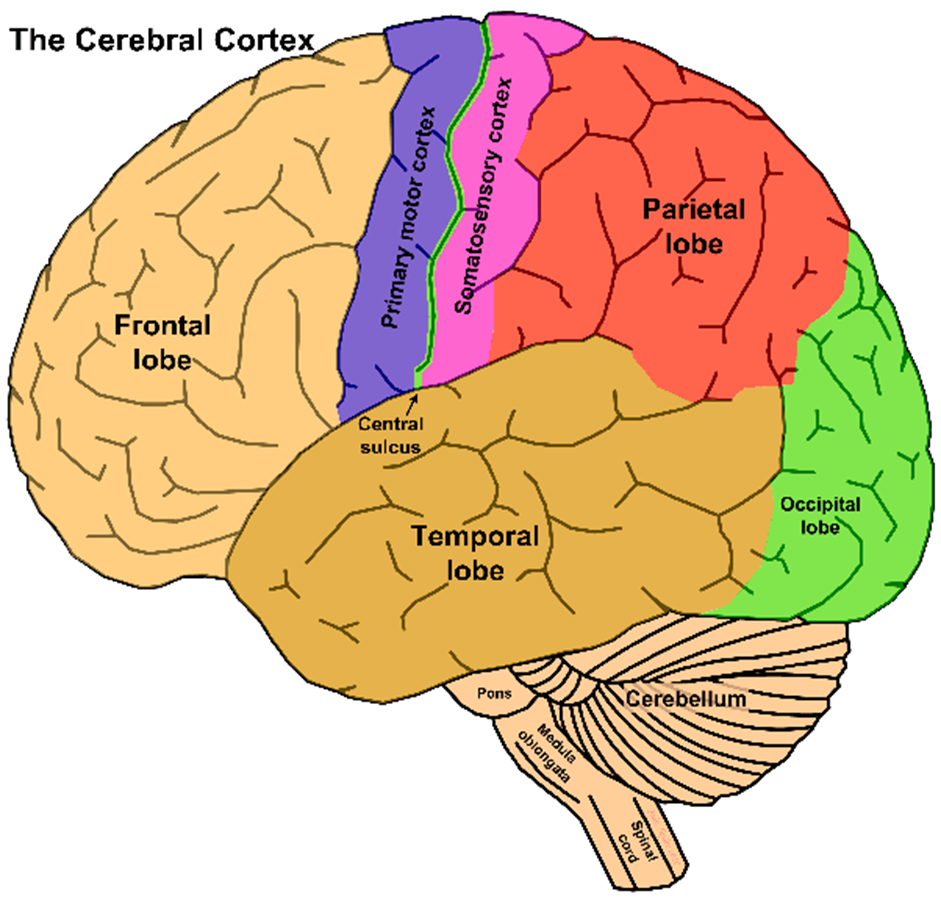
what separates the 2 hemispheres
what does longitudinal fissure separate
what separates the frontal and parietal lobe
what is the central sulcus
what separates the frontal and temporal in anteriror
temporal/parietal in posterior
lateral fissure
which lobe is
abstract processes including reasoning, problem solving, personality; also movement
frontal
which lobe is:
somatic sensation (body sensation) including touch, pressure, pain, temperature
parietal lobe
what lobe is auditory reception (hearing), language
temporal
what lobe is auditory reception
temporal
what lobe is visual reception
occipital
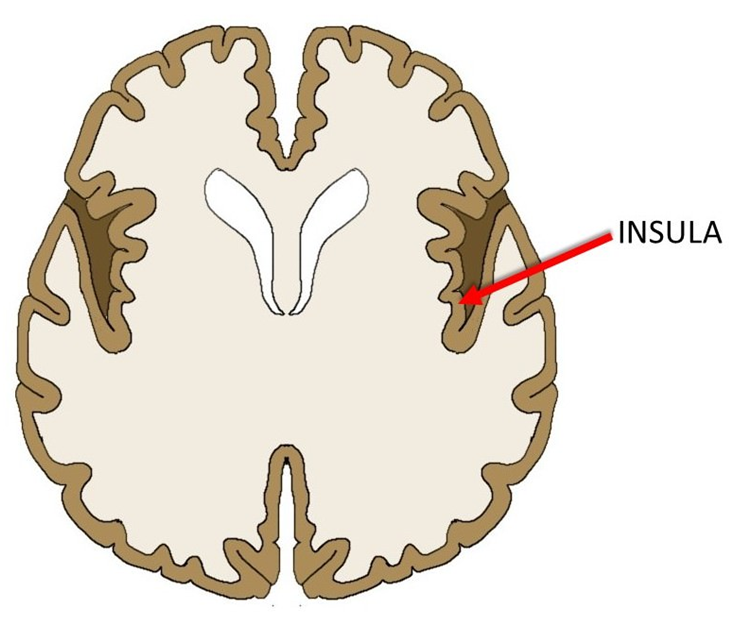
gustation (taste), emotion, cravings, empathy
insula
where is the insula
inside the _____
lateral fissure
Inhibition of motor movements, “background” muscle tone, postural stability, motor learning
basal ganglia
Coordination, precision & fine motor correction, distance, speed of motor movements
cerebellum
In around 90-95% of people, language is centered in the ____ hemisphere
less likely for _____
left
less likely for lefties
White matter structure right above the subcortical structures – connects the hemispheres
corpus callosum
•All sensory information (hearing, vision, body, etc) except for smell
•Call center
•Consciousness/alertness
thalamus
what connects the thalamus to the limbic system
the hypothalamus
what does the hypothalamus not controls
1. Hormones
2. Body temperature
3. Hunger
4.Language
5. Attachment behaviors (parenting, relationships)
6. Fatigue
7. Sleep
Executive functions
4 and 8
what system is made up of
•Amygdala
•Basal ganglia
•Hippocampus
limbic system
white matter structure that connects the hemispheres
corpus callosum
internal structures that create cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
ventricles
•Sensory relay station
•“Call center”
•All sensory information goes through here except ____!
•___to ___ connection
•Also associated with consciousness and _____
thalamus
•Sensory relay station
•“Call center”
•All sensory information goes through here except _smell___!
•Body to brain connection
•Also associated with consciousness and alertness
hypothalamus
Connects _____ with _____ system
•Controls hormones, body temperature, hunger, attachment behaviors (parenting, relationships), fatigue, sleep
•_______– secretes hormones from pituitary gland
hypothalamus
•Connects thalamus with limbic system
•Controls hormones, body temperature, hunger, attachment behaviors (parenting, relationships), fatigue, sleep
•Metabolic – secretes hormones from pituitary gland
•Almond shaped clusters in each hemisphere – _____lobe
•____ responses (fear, anxiety, aggression)
•Biting ppl emotions
•Also associated with _____-making
•fast _____ making
•Also associated with _____(through connection to hippocampus)
Almond shaped clusters in each hemisphere – temporal lobe
•Emotional responses (fear, anxiety, aggression)
•Biting ppl emotions
•Also associated with decision-making
•Reflex decision making
•Also associated with memory (through connection to hippocampus)
•Memory
•Spatial orientation & navigation
•“The caterpillar” or “the seahorse” – curled up in the temporal lobe
•Connected to ______ and _____bulb
•Why smells trigger really strong emotions
•Implicated for _______ disease
hippocampus
Memory
•Spatial orientation & navigation
•“The caterpillar” or “the seahorse” – curled up in the temporal lobe
•Connected to __amygdala__(emotion) and _olfactory___ bulb (smell)
•Why smells trigger really strong emotions
•Implicated for Alzheimer’s disease
•Inhibition of motor movements, “background” muscle tone, postural stability
•____learning (learn steps to do something)
•Connected with _____cortex
•Procedural learning and ____formation (also reward)
•Makes (what neurotransmitter) ____
•Strongly interconnected to ___cortex and ___(sensory-to-motor adjustments… fine motor movement)
•Implicated in _____ disease, _____disease
•But also the cerebellum
•“The wrap” – wraps around the thalamus
basal ganglia
•Inhibition of motor movements, “background” muscle tone, postural stability
•Motor learning (learn steps to do something)
•Connected with premotor cortex
•Procedural learning and habit formation (also reward)
•Makes dopamine
•Strongly interconnected to motor cortex and thalamus (sensory-to-motor adjustments… fine motor movement)
•Implicated in Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease
•But also the cerebellum
•“The wrap” – wraps around the thalamus
Inhibition of motor movements, “background” muscle tone, postural stability, motor learning
basal ganglia
Coordination, precision & fine motor correction, distance, speed of motor movements
cerebellum
•Basal ganglia (striatum) + Cerebellum
•Chorea – jerky involuntary movements
•High chance of passing it to children
huntington’s disease
•Basal ganglia (substantia nigra)
•Everything a little slurred, quiet, not crisp/clean
•Late disease and relatively effective treatment
•Tremor, rigid posture, “shuffling” walk
Parkinson’s disease
what makes up the brainstem
midbrain and pons
Recall: below the foramen magnum
•Atlas, axis
•Associated with movement and sensation of the body
•5 levels are what
•Recall: below the foramen magnum
•Atlas, axis
•Associated with movement and sensation of the body
•5 levels: cervical (neck, arms, shoulders, diaphragm), thoracic (chest), lumbar (legs), sacral (bowel, bladder), coccyx (tailbone)
Peripheral Nervous System
•Recall: central vs. peripheral only means, is it inside your brain/spinal cord, or does it leave your brain/spinal cord?
•Cranial nerves: leave from the _____
•A big topic in this class!
•Spinal nerves: leave from the ___ cord
•Sensory receptors (at level of muscle)
•Recall: central vs. peripheral only means, is it inside your brain/spinal cord, or does it leave your brain/spinal cord?
•Cranial nerves: leave from the brainstem
•A big topic in this class!
•Spinal nerves: leave from the spinal cord
•Sensory receptors (at level of muscle)
spinal cord
In the brain: grey matter _____, white matter _____
•In the spinal cord: white matter ______, grey matter _____
•Functions to transmit information from the brain to the body (______) and from the body to the brain (______)
•Ventral column: ____
•Dorsal column: _____
spinal cord:
•In the brain: grey matter outside, white matter inside
•In the spinal cord: white matter outside, grey matter inside
•Functions to transmit information from the brain to the body (_motor_) and from the body to the brain (__sensory__)
•Ventral column: motor
•Dorsal column: sensory
what nervous system is “fight or flight”
sympathetic
what nervous system is “rest and digest”
parasympathetic
•Speech = _____
•_____ lobe
•_____ cortex
•“______area”
•Brodmann area 44 & 45
motor
Frontal lobe
•Premotor cortex
•“Broca’s area”
•Brodmann area 44 & 45
•Hearing = _____
•___ lobe
•_____ _____cortex
•Brodmann area 41 & 42
sensory
___temporal___ lobe
primary auditory cortex
Brodmann area 41&42
•Language = ______
•______ lobe
•_____ ______cortex
•“_____ area”
•Brodmann area 22
symbolic
temporal lobe
auditory association cortex
wernicke’s area
what is the white matter pathway connecting Broca’s & Wernicke’s areas
Arcuate fasciculus
•Arcuate fasciculus (white matter pathway connecting Broca’s & Wernicke’s areas)
•Supramarginal & angular gyri – parietal lobes, integrate vision, touch, & hearing
they both _______
integration
•Parietal lobe (Brodmann area 40)
•Integrates tactile information – sounds in words (phonological processing), rhyming, sounding out words (decoding)
supramarginal gyrus
•Parietal lobe (Brodmann area 39)
•Integrates vision/visual information
•READING AND WRITING
•Associated with dysgraphia and dyscalculia
angular gyrus
•_____area
•Motor speech production
•Part of the premotor cortex
•______area
•Comprehension of speech
•Part of auditory association cortex
•___ ____cortex
•Receives sensory information from ear
•____ _____
•Association pathway, connects Broca’s and Wernicke’s area through supramarginal & angular gyri
•______ gyrus
•Interprets tactile information for phonological processing, music
•_____ gyrus
•Interprets visual information for reading & writing
•Broca’s area
•Motor speech production
•Part of the premotor cortex
•Wernicke’s area
•Comprehension of speech
•Part of auditory association cortex
•Primary auditory cortex
•Receives sensory information from ear
•Arcuate fasciculus
•Association pathway, connects Broca’s and Wernicke’s area through supramarginal & angular gyri
•Supramarginal gyrus
•Interprets tactile information for phonological processing, music
•Angular gyrus
•Interprets visual information for reading & writing
•Remember that the insula is deep inside the ____ fissure
•“What’s near what” matters in the brain: these are shorter neural connections
•So speech, language, and hearing are located in cortex that is associated with emotion
•Remember that the insula is deep inside the lateral fissure
•“What’s near what” matters in the brain: these are shorter neural connections
•So speech, language, and hearing are located in cortex that is associated with emotion