HSCI 100 Respiratory
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
2 parts of respiratory system
upper respiratory tract:
nasal cavity
pharynx
Glottis
Larynx
lower respiratory tract:
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Lung
Diaphragm
Pathway of air
Inhale:
nose/mouth → trachea → Bronchus → Bronchiole → Alveolus in lung → (diffusion) blood capillary
Exhale:
blood capillary (diffusion) → nose/mouth → trachea → Bronchus → Bronchiole → Alveolus in lung
Nasal turbinates
bony structures that help filter, warm, and humidify air (critical for efficient gas exchange)
mucosa
can become swollen due to allergies or infections, leading to nasal
congestion and breathing difficulties
Epiglottis
When you swallow, the larynx moves up against the epiglottis to close off the opening to the trachea
Trachea
A “tube” connecting the larynx with
the primary bronchi
Lined with cilia and goblet cells that produce mucus
keeping lungs clean
Cilia move trapped debris upward toward the throat to
be swallowed or expelled
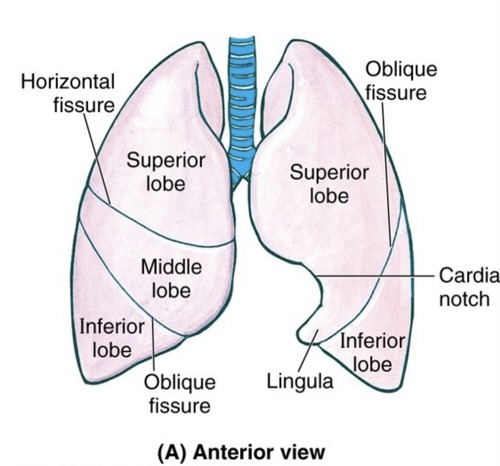
Lungs
The bronchi, bronchioles, and
alveoli beyond the primary
bronchi make up the lungs
The right lung has 3 lobes while the left lung has 2 lobes.
Each lung is enclosed by a pleura(membrane).
The pleura help keep lungs
expanded and inflate
The alveoli
small sacs where oxygen enters the bloodstream and carbon
dioxide is expelled
lined with surfactant preventing their collapse - it breaks
the surface tension created by water molecules
Inspiration/Inhalation
1) diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
2) the diaphragm flattens and the move ribcage moves upward and outward
3) volume of lungs increase
4) a partial vacuum is generated within the lungs, and air flows in
5) With muscle relaxation, expiration happens due to volume lessening
breathing Nervous control
-voluntary and involuntary
-Input signals from blood chemistry
-autonomic respiratory control centers in the brain send out nerve
impulses to contract muscles for inspiration.
– Sudden infant death syndrome is thought to occur
when these centers stop sending out signals
breathing: chemical control
chemoreceptors are sensitive to (CO2) levels that change blood pH
– Hyperventilating pushes the reactions to the right – alkalosis results
(pH goes up).
– Hypoventilating pushes the reaction to the left – acidosis results (pH goes down).
– The drop in pH [ H+] is perceived by chemoreceptors which trigger an increase rate and depth of breathing. This is why you cannot hold your breath forever: involuntary control overrides voluntary control of breathing.
Exchange of gases, O2 and CO2, in the body
exchange of gas is dependent on diffusion
partial pressure = amount of pressure each gas exerts
O2 and CO2 will diffuse from the space of higher
partial pressure to the space of lower partial
pressure
External respiration
-exchange of gases betwen alveoli(lungs) and capillaries where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide is removed
Internal respiration
-gas exchange between tissue capillaries and cells throughout the body
-oxygen is delivered to cells and carbon dioxide is collected as a waste product
The movement of O2 and CO2 in the body
At lungs:
CO2 capillary > CO2 air
O2 air > O2 capillary
At tissue:
CO2 cells > CO2 capillary
O2 capillary > O2 cells
Lower respiratory tract disorders
Pneumonia: infection of lungs with thick fluid build up
Tuberculosis: bacterial infection that leads to tubercles
Pulmonary fibrosis: when lungs thicken and scar usually due to buildup from inhaled particles
Emphysema: chronic, incurable disorder in which alveoli are damaged and thus the functional surface area for gas exchange is reduced. Most common cause is smoking
Asthma
-bronchial tree becomes irritated causing breathlessness, wheezing and coughing. Can be triggered by allergic or hyperactive immune response.
Bronchitis
bronchi become inflamed due to infection
Lung cancer
uncontrolled cell division in the lungs that is
often associated with smoking- deadliest of all cancers
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
-emphysema, asthma and chronic bronchitis
-frequently recurring disorders