Biology: Homeostasis, nerves and reflex arcs terms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Nerve Impulse
An electrical signal that passes along nerve fibre in response to a stimulus and serves to transmit a record of sensation from a receptor or an instruction to act to an effector
What is the difference between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system?
The central nervous system contains the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of everything else of the nervous system.
What is a voluntary action?
An action completed with conscious thought and under our own will
What is an involuntary action?
An action completed without conscious thought
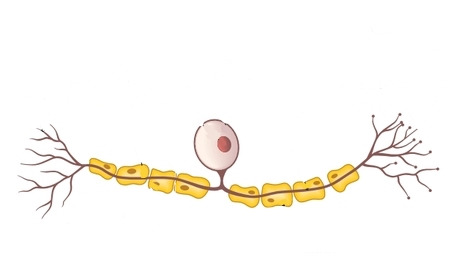
Name the neurone shown
Sensory neuron
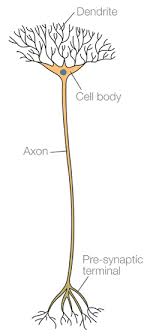
Name the neurone shown
Relay neuron
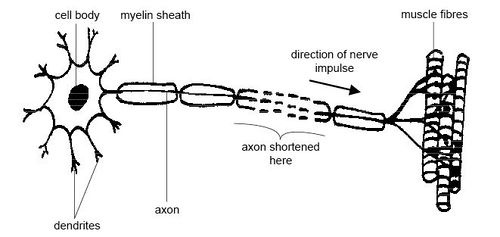
Name the neurone shown
Motor neuron
Describe the reflex arc
Stimulus detected by a receptor. Impulse passed along sensory neurone to relay neurones in the CNS. Impulse passed along motor neurone to effector. Effector brings about the response
What is a reflex action?
A rapid (involuntary) response to a stimulus by an effector (muscle or gland).
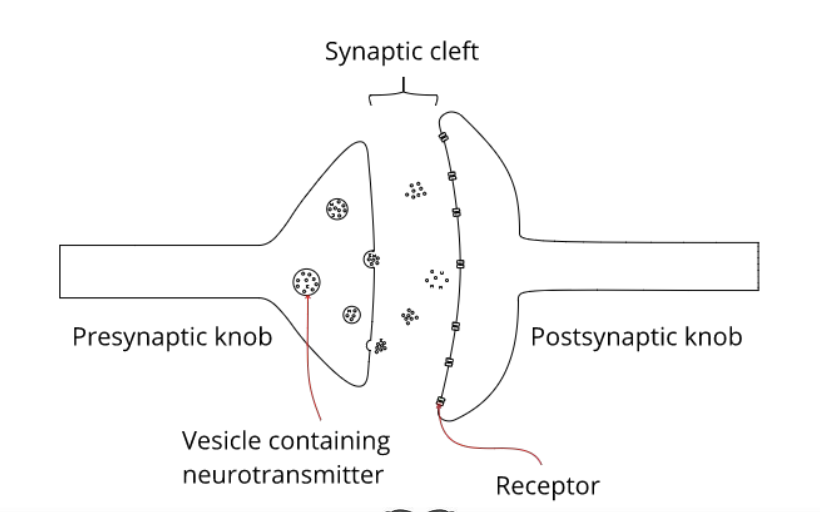
What is a synapse?
A small gap at the end of a neurone that allows a signal to pass from one neurone to the next.
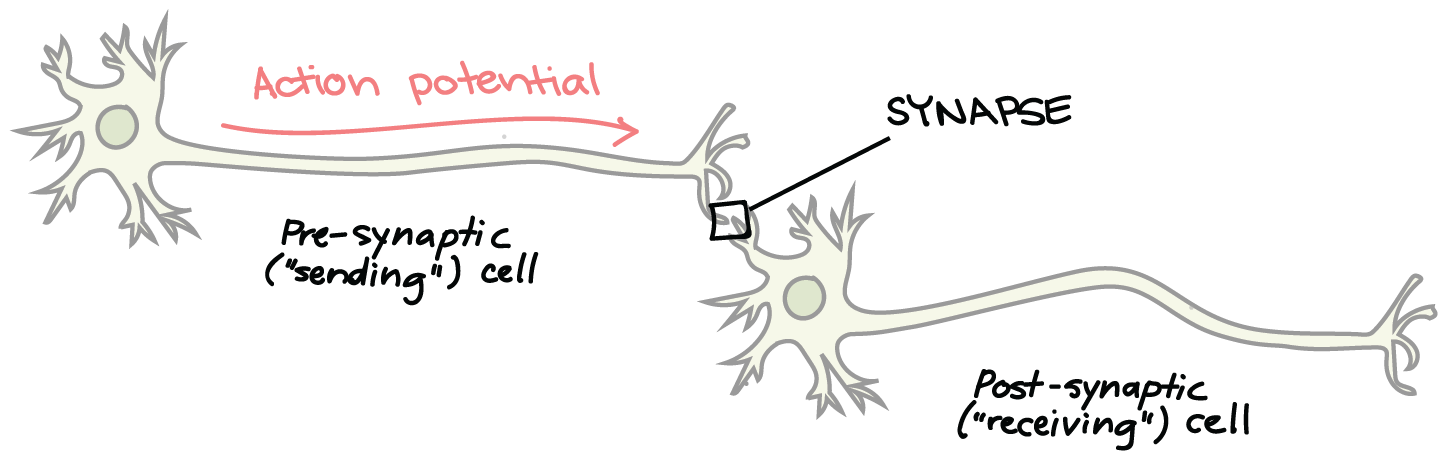
Label this diagram of a synapse
What are sense organs?
Groups of cells that detect changes in the environment
What is a hormone?
Chemicals that coordinate different functions in your body by carrying messages through your blood to your organs, skin, muscles and other tissues.
What is homeostasis?
Homeostasis is how the body keeps conditions inside it the same. Scientists describe it as the maintenance of a constant internal environment.
What are receptors?
The receptor senses the change in the environment, then sends a signal to the brain which in turn generates a response that is signaled to an effector
What are effectors?
Any organ or tissue that receives information from the integrating center and acts to bring about the changes needed to maintain homeostasis.
What is a negative feedback loop?
It is the process where a change in a condition from a set level causes a series of action that return the conditions to the set level
What is positive feedback loop?
Positive feedback occurs to increase the change or output: the result of a reaction is amplified to make it occur more quickly
Pancreas
Monitors blood sugar levels, produces insulin and glucagon
Pituitary gland and Hypothalamus
Monitor blood temperature and water levels
Skin
Responds to changes in core temperature
Kidneys
Respond to changes in water levels in the blood, excrete urea.
Lungs
Removes waste CO2 and some water
vasodilation
Vasodilation is when the capillaries close to the surface of the skin become wider, so more blood flows through them and more heat is lost from the skin
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is when the capillaries close to the surface of the skin become narrower. When this happens, the blood flows through deeper vessels instead and less heat is lost from the skin
Brain
Allows us to make a conscious response
Spinal Cord
Allows us to make a reflex (unconscious) response
Sensory Neuron
Detect a stimulus and then transfer this stimulus to the brain or spinal cord. The main job of a sensory neurone is to transmit nerve impulses, so these neurones are long
Relay Neurons
Connects one neurone to the next
Motor Neurons
Transfer nerve impulses from the brain or the spinal cord to the muscles or glands. This type of neurone can be very long
Reflex Arc
It is the neural pathway that controls an automatic, involuntary response to a stimulus, often as a protective mechanism.