revision of the abdomen
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
How would you define the region of the abdomen?
Below diaphragm (physical barrier) and above the inlet of the pelvis (space)
At what level is the transpylonic plane?
L1
At what level is the transtubular line?
L5
At what level is the subcostal plane?
L2-3
At what level is the transumbilical plane?
L3/4
At what level is the oesophagus?
C6 - T11
What does the pylorus do?
connects and controls flow between stomach to duodenum
What is the location of the pancreas?
Epigastric and L hypochondriac
posterior to the stomach
Level T1-2
What is the location of the liver?
right upper quadrant (R hypochondriac to L hypochondriac)
What is the location of the kidneys?
retroperitoneal from T12 - L4
** R kidney lower than left
What is the location of the spleen?
LUQ (L yphypochondriac)
Posterior to the stomach and anterior to the left hemidiaphram
Rib 9-11
Where does the abdominal aorta bifurcate?
L4
At what level is the interspinous plane?
Midsacrum
Which organs are intraperitoneal?
S: Stomach
A: Appendix
L: Liver
T: Transverse colon
D: First part of the duodenum
S: Small intestines (jejunum and ileum)
P: Tail of the pancreas
R: Upper third of the rectum
S: Spleen
S: Sigmoid colon
SALTD SPRSS
Which organs are reteroperitoneal?
S: Suprarenal (adrenal) glands
A: Aorta/IVC
D: Duodenum (except the proximal 2cm, the duodenal cap)
P: Pancreas (except the tail)
U: Ureters
C: Colon (ascending and descending parts)
K: Kidneys
E: (O)esophagus
R: Rectum
SAD PUCKER
What are Ascites and how are they formed?
Ascites is the build-up of fluid in the space between the lining of the abdomen and abdominal organs.
results from high pressure in certain veins of the liver (portal hypertension) and low blood levels of a albumin
What is an omentm?
a fold of peritoneum connecting the stomach with other abdominal organs
what is a ligament (in the abdomen)
Links organ to organ or organ to abdominal wall
What is an aponeurosis?
A fibrous connective tissue that connected muscle to bone or fibrous tissue
What arteries supply the foregut, midgut and hindgut?
foregut: celiac trunk
midgut: superior mesenteric artery
hindgut: inferior mesenteric artery
What does the greater, lesser and gastrosplenic omenta connect
Stomach to TRANSVERSE COLON
Stomach to LIVER
Stomach to SPLEEN
What does a mesentary do?
Connects intestine wall to posterior abdominal wall
What does the abdominal aorta bifurcate into?
the right and left common iliac arteries
What structures does the foregut give rise to?
oesophagus
stomach
liver
gallbladder
bile ducts
pancreas
proximal duodenum
What structures does the midgut give rise to?
distal duodenum
jejunum
ileum
cecum
appendix
ascending colon
proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
What structures does the hindgut give rise to?
the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon
descending colon
sigmoid colon
upper anal canal
What is the portal triad made up of?
hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein and bile duct
Describe the livers dual blood supply
the hepatic artery delivers oxygenated blood from the general circulation
the hepatic portal vein delivers deoxygenated blood from the small intestine containing nutrients
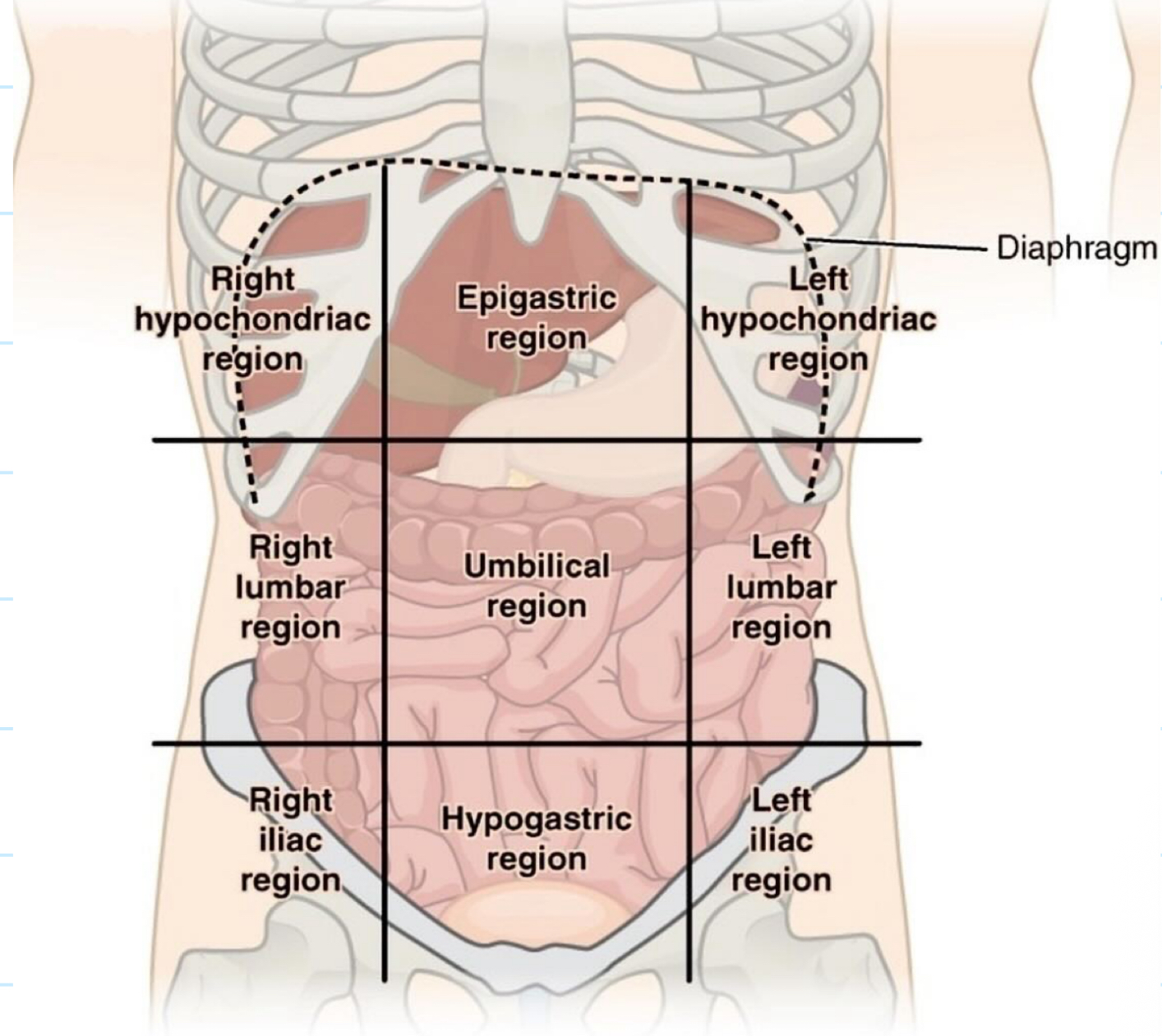
What planes/ lines/ landmarks make up the 4 quadrants of the abdomen?
Vertical line: midline (line down from jugular notch to the pubic symphysis)
Horizontal line: transumbilical plane
What lines/planes/ landmarks form the lines in the 9 section abdominal model?
Horizontal: Midclavicular line
Vertical superior: subcostal plane L2-3
Vertical inferior: transtubercular plane (supracristal plane) L4 → highest point of iliac crest
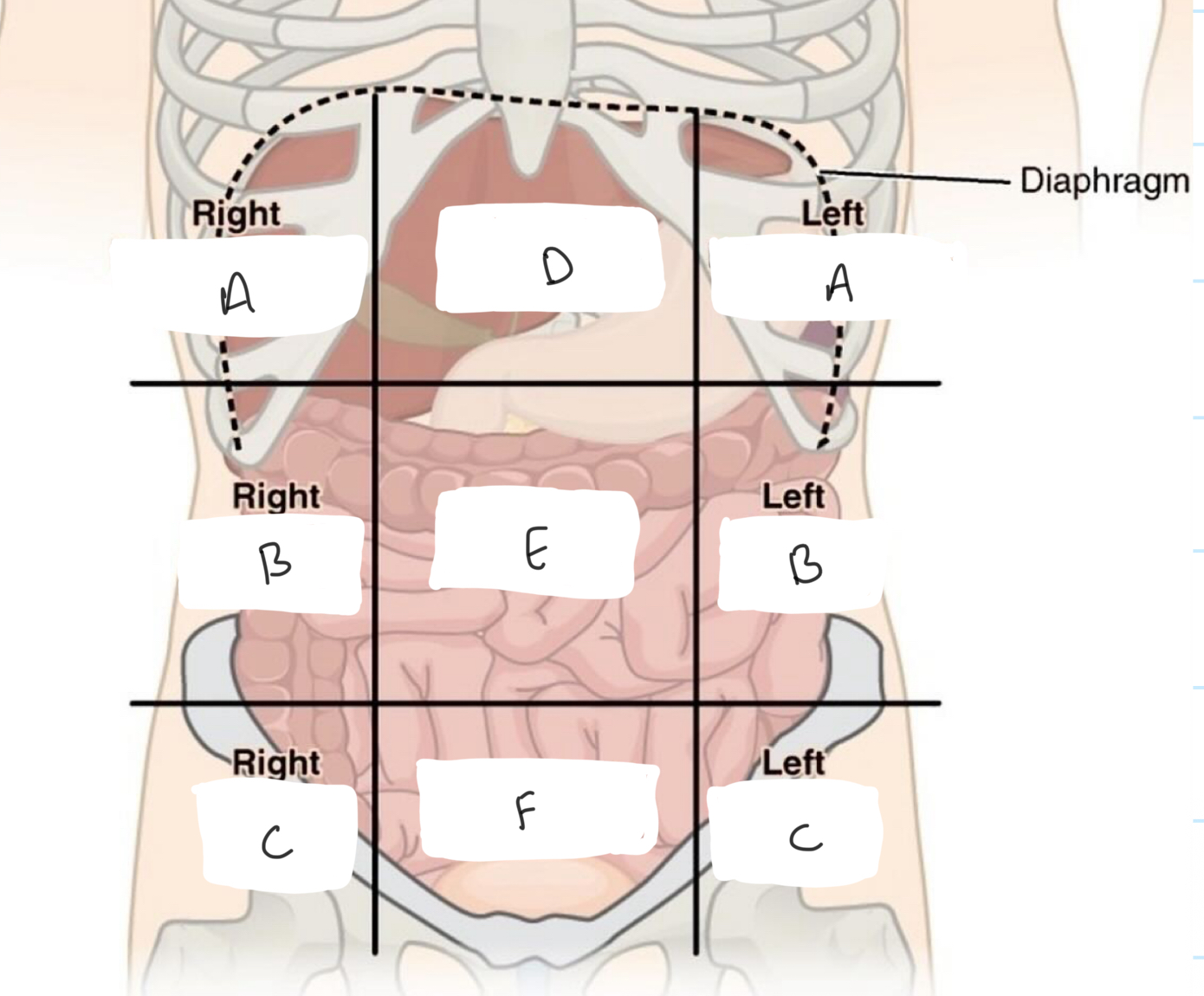
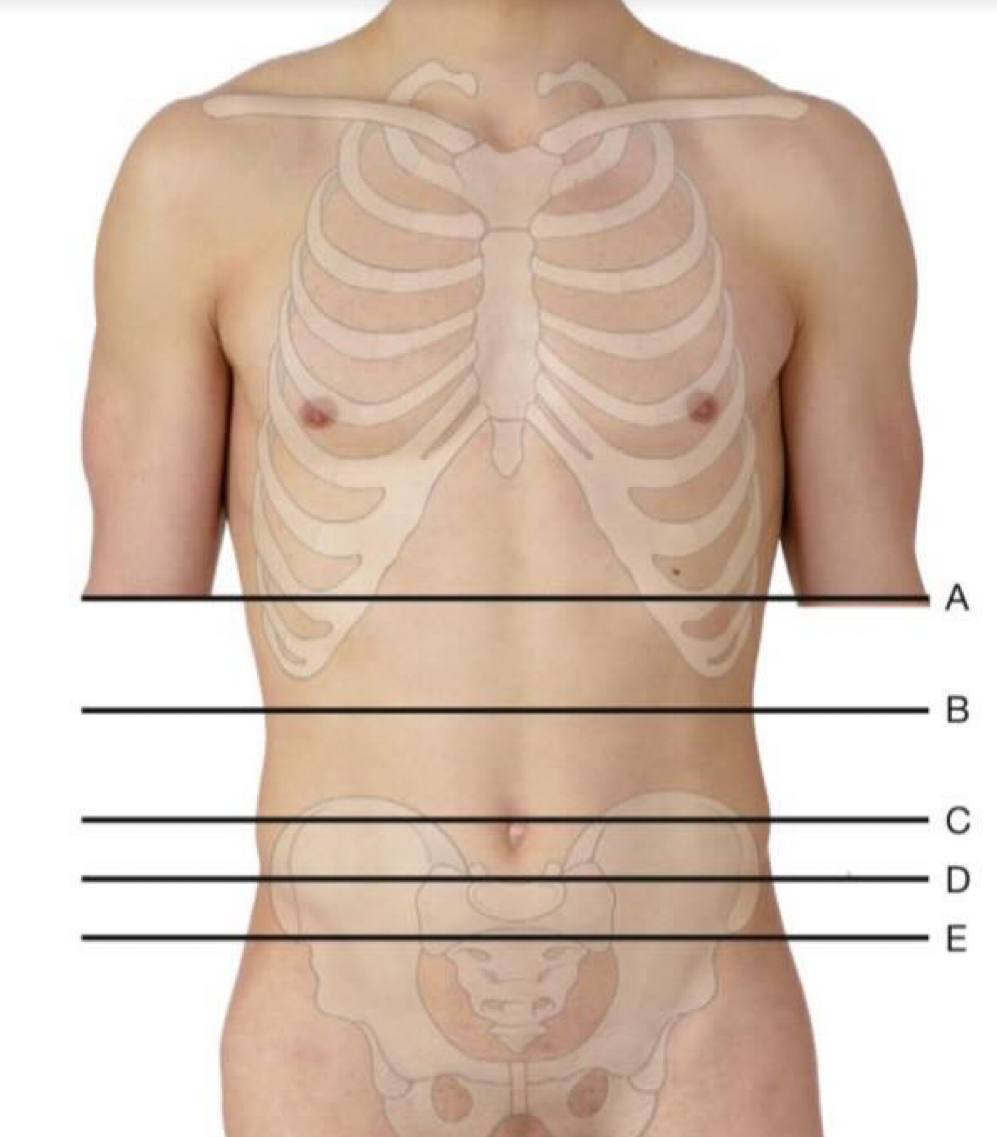
A. Transpyloric plane L1
B. Subcostal plane L2-3
C. Transumbilical plane L3/4
D. Transtubercular plane/ supracristal plane L5
E. Interspinous plane: midsacrum
Describe the boundaries of the inguinal canal
Anterior wall – aponeurosis of the external oblique, reinforced by the internal oblique muscle laterally.
Posterior wall – transversalis fascia.
Roof – transversalis fascia, internal oblique, and transversus abdominis.
Floor – inguinal ligament