cell bio 1
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
What do living things do?
Maintain homeostasis
Growth and development
Maintain PH levels/acidity
Cellular respiration
Who discovered Cell Theory?
Robert Hooke (English Scientist in1665)
Who laid bases for Cell Theory?
Botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann in Germany
Cell Theory
says that cells are the universal building blocks for all living things.
1500
Light microscope was invented
1665
Hooke identifies cells
1839
Schleiden and Schwann’s cell theory
1950s
Electron microscope invented
Polar covalent bond made of
partial positive + (oxidized) and partial negative charge - (reduced)
Elements in the cells
About 25 elements are essential to life (known to be)
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen make up 96% of all living matter.
Trace elements
elements that are only needed in small amounts
O (oxygen), C (carbon), H (hydrogen), N (nitrogen), C (calcium), P (phosphorus), P (potassium).
chemical bonds
Weak or strong electrical attraction that holds atoms in the same vicinity
molecule
a grouping of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
covalent bonds
atoms share electrons.
Two types of covalent bonds
Can be nonpolar (equal sharing, ex, CH4)
Can be polar (unequal sharing, ex, H2O)
Ionic bonds
electrons are transferred
Creates ions
Cations = positive
Anions = negative
Opposites attract!
Compounds formed by ionic bonds are called ionic compounds or salts.
Whether an atom forms a covalent or ionic bond depends
electronegativity of the atom involved.
electronegativity
attraction of an atom for electrons. The more electronegative an atom is, the stronger it pulls electrons to the nucleus.
When two atoms are very unequal in electronegativity, the more electronegative one may strip away electrons, forming an ionic bond.
Electronegativity increases as you move from left to right across the periodic table until you reach the noble gases (these are inert/chemically unreactive)
In water, ionic bonds get…
Because the ions are separated and shielded from each other by water molecules. The sphere of water molecules around each dissolved ion is called the hydration shell.
Important because all organisms familiar to us are mostly water, and most cells are *70-95% Water.
Many things dissolve in water, like molecules such as proteins. Water is a universal solvent/solvent for life.
weaker bonds
Two molecules in a cell contact each other → may stick together temporarily because of chemical bonds weaker than covalent bonds. Have brief contact.
hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds, which are strongly bound to one electronegative atom, are also attracted to another electron-donating atom.
Van der Waals interactions
attraction of positive and negative regions of molecules that are caused by the motion of electrons. Electrons are in constant motion, so they accumulate by chance in one part of a molecule. These changing regions of partial charge enable atoms and molecules to interact and form bonds.
These interactions are very weak and only occur when molecules or parts of the same molecules are in proximity.
Hydroxyl
Compound name: Akohols
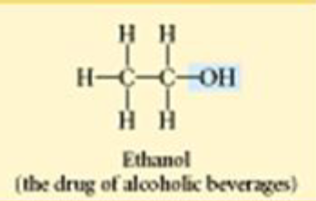
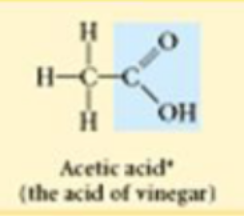
Carboxyl
Carboxylic acids
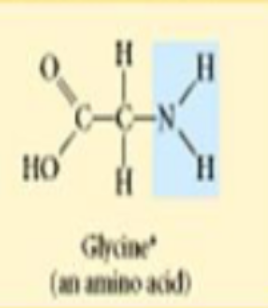
amino
amines
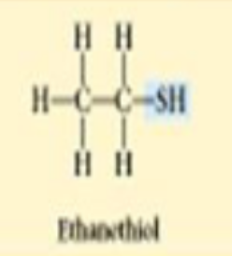
sulfhydryl
thiols
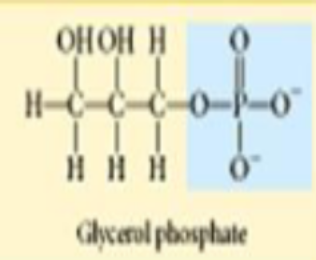
phosphate
organic phosphates
Stanley Miller (1953)
studied —> Demonstrate spontaneous formation of organic compounds in primitive Earth conditions
Cells are…?
organic and 70-95% water
How many Macromolecules classes are there?
four.
What are the four classes of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
How are macromolecules arranged?
chainlike molecules
Macromolecules are arranged in chainlike structures that are called…?
polymers.
A polymer is…?
long molecule consisting of similar/identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
sugars are the subunit of…
polysaccharides and oligosaccharides
Fatty acids are the subunit of…
fats and membranes lipids
amino acids are the subunit of…
proteins
nucleotides are the subunit of…
nucleic acids (DNA, RNA)
How many carbons are in ribose and glucose?
5,6
carbohydrates can exist as…
linear structure, but sugar monomers form rings in water.
isomer
same chemical formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms.
small changes are important…
like when molecules act as ligands for proteins.
Deoxyribose
a five-carbon sugar found in DNA.
Disaccharide
sugar formed by two monosaccharides and a glycosidic bond.
example of disaccharides
Sucrose
sucrose is made of
glucose and fructose
A monosaccharide has how many carbons?
6
cellulose
a polysaccharide made by some organisms, such as plants. Humans can’t digest.
polysaccharide
made of many monosaccharides linked together
Amylose, amylopectin, glycogen are all…
polysaccharides
Humans (and animals) make which polysaccharide…
Glycogen (energy storage)
Monosaccharides are linked by…
glycosidic bonds
A glycosidic bond has what type of bond?
covalent bond (shares electrons)
Lipids are made of what…
fatty acids
fatty acids have a…
hydrophilic carbon acid head
hydrophobic hydrocarbon tail
triglycerides
Composed of one glycerol and three fatty acids.
Fatty acids link to glycerol by dehydration synthesis.
These are commonly called fat molecules (triglycerides).
There are how many types of fatty acids?
Unsaturated fats
Saturated fats
Saturated fats
Fully saturated with hydrogens (no double bonds).
Long, straight (linear) tails.
Pack closely together → solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated fats
Not fully saturated with hydrogens (one or more double bonds).
Double bonds cause a bend (kink) in the tail.
Cannot pack closely → liquid at room temperature (e.g., corn oil).
Omega - 3 fatty acid is a…
A type of polyunsaturated fatty acid (has multiple double bonds).
three types of omega-3 fatty acids
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
18 carbons
3 double bond
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
20 carbons
5 double bonds
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
22 carbons
6 double bonds
What is cholesterol?
A steroid.
Are steroids…?
lipids characterized by carbon skeleton consisting of four fused rings.
Many hormones are produced from…
cholesterol.
nucleotides are…
building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
nucleotide components are
Phosphate group(s)
Sugar
Nitrogenous base
There are two types of nitrogenous bases…
pyrimidines
purines
pyrimidines (single ring)
Cytosine, thymine, uracil
DNA: cytosine, thymine
RNA: cytosine, uracil (uracil replaces thymine
purine (double ring)
Adenine and guanine
Different sugars in each nucleotide. DNA contains…
deoxyribose
Different sugars in each nucleotide. RNA contains…
ribose
function of nucleotides…
Energy transfer by breaking phosphate groups (e.g., ATP).
Form coenzymes when combined with other groups.
Act as small intracellular signaling molecules in the cell.
Enzymatic proteins
ex: digestive enzymes
structural proteins
ex: silk fibers, collagen, feathers, hair keratin.
storage proteins
ex: ovalbumin in egg whites
transport proteins
ex: hemoglobin
hormonal proteins
ex: insulin
receptor proteins
ex: receptors in nerve cell membranes
contractile and motor proteins
ex: actin and myosin in muscles
defensive proteins
ex: antibodies combating bacteria and viruses.
proteins are…
polymers made of amino acid subunits
A polymer of amino acids is called…
polypeptide
polypeptide can range from how many amino acids?
a few to over 1,000
polypeptides have a what sequence?
unique.
protein consists of one or more…
polypeptides
polypeptides can be folded into…
a specific shape (conformation)
all amino acids have…
Amino group (–NH₂)
Central carbon
Hydrogen atom
Carboxyl group (–COOH)
What truly makes each amino acid different…?
The R group, or side chain.
How many common amino acids are in cellular proteins?
twenty (you’re twenty???)
families of amino acids are grouped into families according to whether their side chains are…
acidic, basic, uncharged polar, nonpolar
acidic side chains
aspartic acid, glutamic acid
basic side chains
lysine, arginine, histidine
why are basic side chains basic?
because it positive charge stabilized by resonance.
uncharged polar side chains
asparagine, glutamine, serine, threonine,tyrosine
uncharged polar side chains have…
have hydroxyl group as a side chain
nonpolar side chains
alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, proline, methionine, tryptophan, glycine, cysteine, phenylanine
all amino acids have…
weak acids and bases
acids
release protons (hydrogen ions) when dissolve in water. increase H+ concentration.