Cognitive Psychology - Memory - Hacking your Memory
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the effect of multitasking on a laptop during class? (Sana et al., 2013)
Students multitasking on a laptop during class may learn 11% less.
What is the effect of taking notes on a laptop?
Fast but encourages verbatim notes rather than summary, leading to shallow processing, although it prevents mind-wandering.
What are the benefits of note-taking?
Promotes deep and elaborative encoding of material.
Provides external storage of lecture information not on slides.
Supports later study and revision.
What is elaboration in learning?
Actively relating incoming material to prior knowledge through semantic processing.
What is a mnemonic?
A deliberate strategy, such as mental imagery or keywords, to enhance memory of verbal material.
What is Elaborative Interrogation?
Explaining why a fact or concept is true. Effects are larger when elaborations are precise and self-generated.
What is Self-Explanation?
Relating new information to existing knowledge.
What is a Keyword Mnemonic?
Associating words using mental imagery.
What did Van Kesteren et al (2014) find about schemas in education?
People’s memory judgments depended on reactivation, NOT schemas. Despite being partially correct, they underestimated the role of prior knowledge.
How can students use schemas effectively in university learning? (Putnam, 2016)
Connect new material to prior learning.
Do readings and review key ideas before lectures.
Preview slides to understand main messages and identify areas needing clarification.
What are the limitations of improving encoding through mnemonics?
Mnemonics require effort, suitable material, and are less effective for long-term learning.
Why are self-generated cues effective for memory?
When we use our own hobbies and interests we create semantically related cues. Since they match personal cognitive context, they are more diagnostic and easier to remember (Tullis & Finley, 2018).
What is the Testing Effect? (Roediger & Karpicke., 2006, Thomas et al., 2020)
Testing enhances concept development and generalisation.
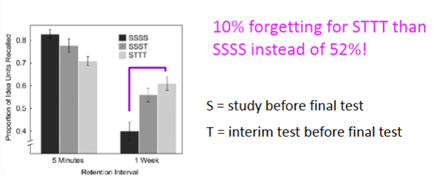
What did Thomas et al (2020) find about testing for different question types?
MCQs: Quizzing improved performance by 12-14% over studying.
SAQs: Quizzing improved performance by 13-21%.
Feedback during quizzing was not significantly better than quizzing alone.
What are the least useful and most useful revision strategies?
Least Useful: Summarisation, imagery, re-reading.
Useful: Elaborative Interrogation, Self-Explanation, Interleaved Practice.
Most Useful: Testing yourself.
Other strategies should be combined with testing for the best effect.
How does imagery impact memory retention?
While less useful during initial learning, imagery can improve long-term retention during revision.
What is the Spacing Effect in revision?
Revisiting information after a break enhances memory, with expanded spacing being most effective for long-term retention.
What did Conway et al (1997) find about episodic and semantic memory in academic learning?
Immediately after lecture: Students recalled episodic details (specific lectures).
Delayed (exam): Students relied on semantic memory, showing generalised knowledge.
Suggests a shift from Episodic → Semantic Memory & Generalisation.
What did Harand et al (2012) find about memory semanticisation?
Episodic memories transform into semantic memory over time, with repeated retrieval and sleep supporting this process.