immunology final questions
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dr park :((((((
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What is the role of HLA-Cw6 in psoriasis pathogenesis?
b) presenting self-peptides to CD8+ T cells
HLA-Cw6 positive psoriasis patients are more likely to:
b) have early-onset, severe, plaque/guttate disease
MHC class I molecules primarily present which type of peptides?
b) endogenous peptides to CD8+ T cells
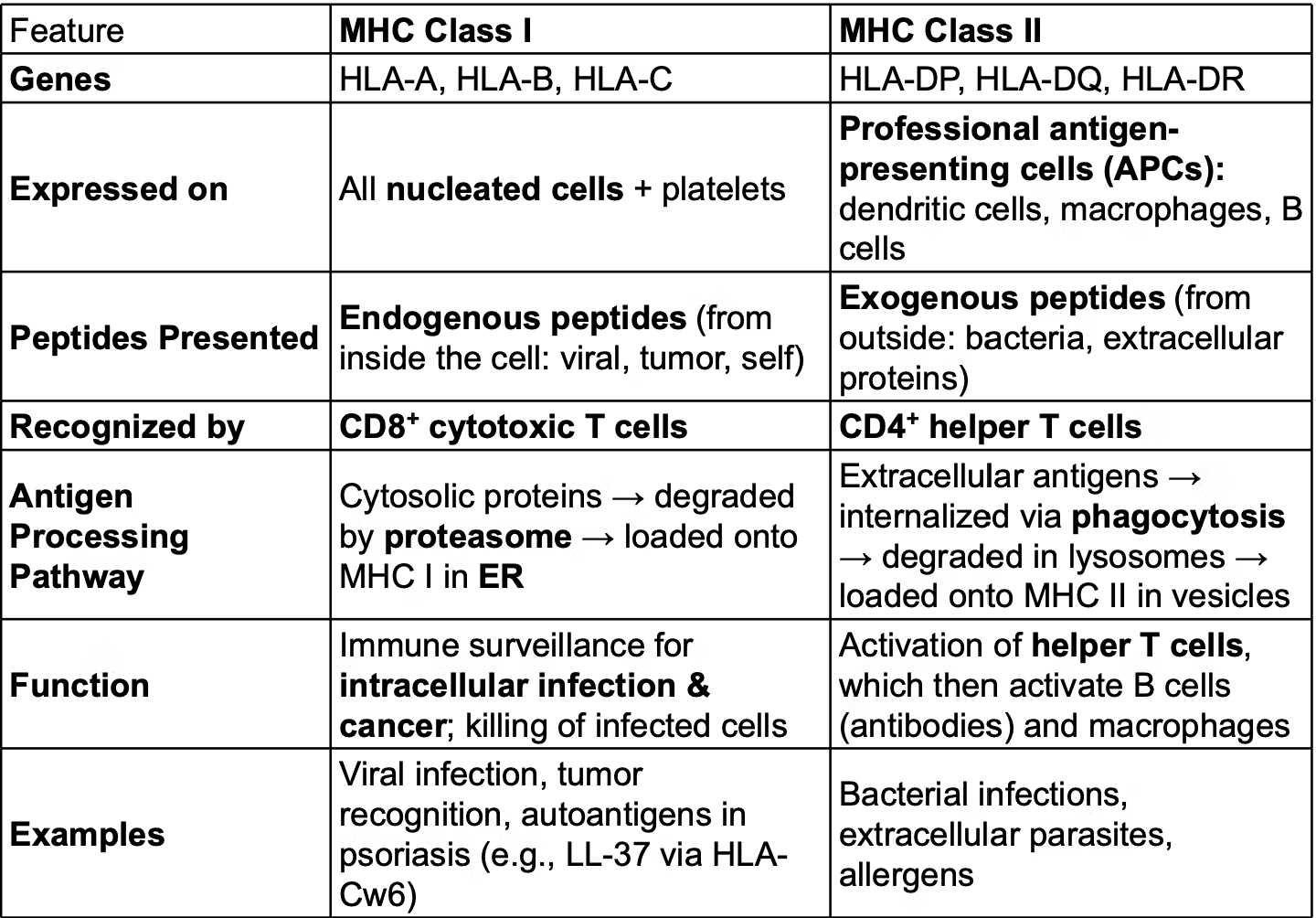
MHC I vs II
MHC I:
all nucleated cells
endogenous peptides
CD8+ cytotoxic T cells
proteasome loaded into ER
monitoring for intracellular infection and cancer
MHC II:
APCs (antigen-presenting cells)
endogenous peptides
CD4+ helper T cells
activate helper T cells
Which of the following features is more typical of psoriatic arthritis than rheumatoid arthritis?
c) involvement of enthesitis
A 35-year-old man presents with diffuse swelling of his right index finger (“sausage digit”) and nail pitting. He has a history of psoriasis. Which feature best distinguishes psoriatic arthritis from rheumatoid arthritis?
c) dactylitis and DIP involvement
A 38-year-old woman with chronic plaque psoriasis develops joint pain. She is HLA-Cw6 positive. Which autoantigen is most often presented to CD8+ T cells in her disease?
b) LL-37
What is the most important pathological consequence of activated neutrophils in Lupus?
b) release of nuclear antigens that stimulate DCs
Why the other answers were wrong:
What is the most important pathological consequence of activated neutrophils in Lupus?
a) increases antigen presentation via
MHC I→ increases antigen presentation via MHC IIc)
enhancedphagocytosis of apoptotic cells → decreased phagocytosis of apoptotic cellsd)
production of IL-17→ this is in PsAe)
decreasein type I interferon levels → increase in type I interferon levels
In lupus, monocytes/macrophages contribute to chronic inflammation primarily by:
b) producing pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-ɑ
What finding is the earliest innate immune abnormality that sets the stage for lupus pathogenesis?
b) defective clearance of apoptotic cells
Defective clearance of apoptotic cells in lupus mainly promotes autoimmunity by:
b) presenting self-antigens to autoreactive lymphocytes
In lupus, a reduction in regulatory T cell (Treg) activity leads to:
b) suppression of Tfh cell activity
What is the primary immune pathway involved in acute gout inflammation?
b) NLRP3 inflammasome activation in innate immune cells
Which immune system arm plays the dominant role in acute gout?
b) innate immunity
Which adaptive immune cell type is most often found in chronic gout lesions?
a) Th17 CD4+ T cells