1.) Preliminary Planning
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Overview
Defines the scope of a project, which determines the complexity of the planning process & the professionals involved in design & implementation.
Explains the process of concept development for hotels, chains, restaurants, & institutions.
Discusses the decision-making process regarding menu, market, management, money, & method of execution.
Introduces the elements of a feasibility study
Scope of a Project
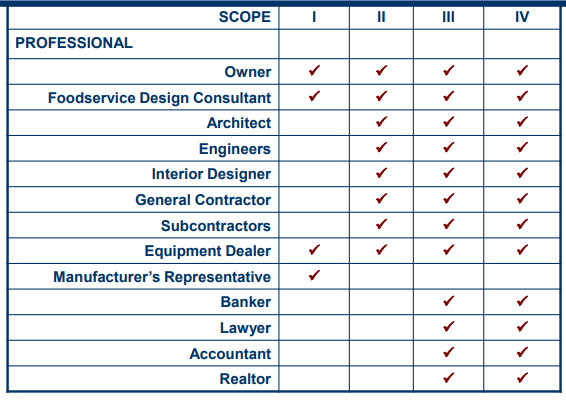
Level I: equipment addition/replacement or renovation of small area (example: new dish machine).
Level II: renovation of a significant portion of a facility (example: renovation of serving area).
Level III: complete renovation or new construction of a facility.
Level IV: development of a prototype restaurant for a chain.
Scope of a Project
Level I:
equipment addition/replacement or renovation of small area (example: new dish machine).
Scope of a Project
Level II:
renovation of a significant portion of a facility (example: renovation of serving area).
Scope of a Project
Level III:
complete renovation or new construction of a facility.
Scope of a Project
Level IV:
development of a prototype restaurant for a chain.
Professionals Involved in a Project
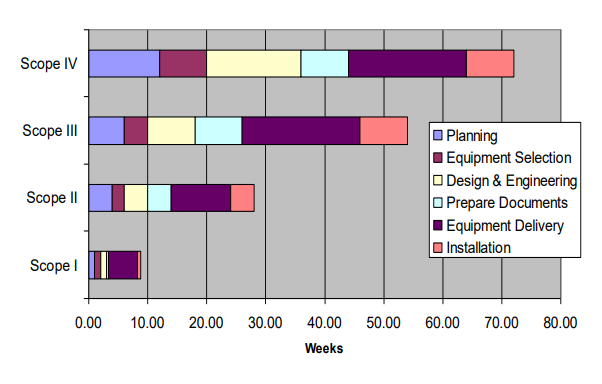
Project Time Lines by Scope
Concept Development
Concept: the overall plan for how the operation will meet the needs & expectations of the target market.
Concept is expressed in many ways, including menu, theme, décor, hours of operation, form of service, pricing, & location.
Examples of broad concepts include fine dining, theme, casual, fast-casual, quick-service, ethnic, & family.
Concept development is critical for design because it provides direction to planners – it is critical for operational success as well!
The Five “M”s of Concept Development
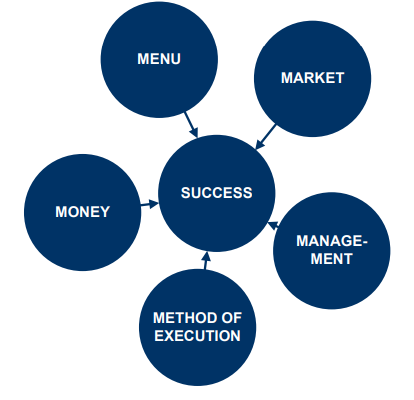
The Five “M”s: Market Questions
To whom is the food operation being marketed?
Is the market large enough to generate sales & produce a profit?
How will the market be identified?
What level of competition exists?
What method will be used to communicate to this market?
Will the potential customer want or need the food product?
Will a quality assurance plan be developed that will encourage the customer to return because of superior service and/or product quality?
Will internal marketing successfully sell the customer additional services or products after he or she arrives at the food facility?
The Five “M”s: Menu has an impact on …
Amount of space required.
Service area size & design.
Types & capacities of cooking equipment.
Size of the dishwashing operation.
Size of storage areas.
Number of employees.
Amount of investment.
The Five “M”s: Money
Successful capitalization of a food facility includes funds for:
Planning costs.
Building construction or renovation.
Equipment (fixed).
China, glassware, utensils.
Furniture & fixtures.
Décor.
Start-up & operating costs.
A two-step process: estimating the necessary investment & identifying sources; then, when design is complete & actual costs are known, securing commitments from investors.
The Five “M”s: Management
Who will operate the facility, & what skills/ experience must he/she have?
Who will assist this person in covering the long hours that are usually required to operate a foodservice facility?
What level of pay will this person receive?
Will this person be rewarded in some way for excellent sales & profit results?
How will the owners set operational policies & communicate these to the management staff?
The Five “M”s: Method of Execution
Production approach: cooking “from scratch” or using “convenience” (partially prepared) items.
Control systems: production management systems (menu, recipe, inventory, costing); sales management systems (cash control); & service systems (reservations).
Personnel: labor staffing & scheduling, time keeping, payroll, etc.
Production approach:
cooking “from scratch” or using “convenience” (partially prepared) items.
Control systems:
production management systems (menu, recipe, inventory, costing); sales management systems (cash control); & service systems (reservations).
Personnel:
labor staffing & scheduling, time keeping, payroll, etc.
Feasibility: Two Related Approaches
Market Feasibility
Will the sales revenues be great enough to generate a reasonable profit?
Emphasis on the income statement & revenue sources.
Financial Feasibility
Will the profits generated by the operation be sufficient to satisfy investors’ expectations for financial return?
Emphasis on the balance sheet & retained earnings.
Market Feasibility
Will the sales revenues be great enough to generate a reasonable profit?
Emphasis on the income statement & revenue sources.
Financial Feasibility
Will the profits generated by the operation be sufficient to satisfy investors’ expectations for financial return?
Emphasis on the balance sheet & retained earnings.
Market Feasibility
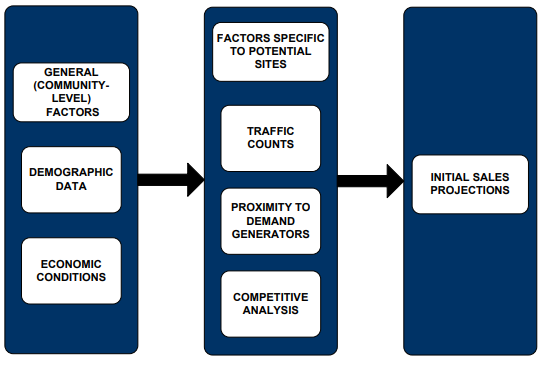
Calculating Projected Sales
• Step 1: Estimate Customer Counts & Capacity.
# of seats X turnover for each meal period.
• Step 2: Estimate Average Check.
Use menu mix & price projections.
• Step 3: Multiply Customer Counts by Average Check.
• Step 4: Prepare a Sales Projection for the Year.
Financial Feasibility: Balance Sheet
Estimating Assets:
Operating capital.
Accounts receivable.
Land, building, furniture & fixtures.
Inventory (food & supplies).
-
Estimating Liabilities:
Accounts payable.
Short-term debt.
Long-term debt.
Owners’ Equity.
Estimating Assets:
Operating capital.
Accounts receivable.
Land, building, furniture & fixtures.
Inventory (food & supplies).
Estimating Liabilities:
Accounts payable.
Short-term debt.
Long-term debt.
Owners’ Equity.
Financial Feasibility: Income Statement (Pro Forma Profit & Loss)
Estimates of the following:
Cost of goods sold, involving menu pricing & recipe costing.
Labor costs, involving projections of staffing levels, wages & salaries, benefits.
Marketing costs.
Utilities.
Occupancy costs (example: rent).
Repairs & maintenance.
General & administrative.
-
These estimates result in a projected profit/loss for the operation.
Feasibility Analysis
The net income – “the bottom line” – from the income statement is transferred to retained earnings on the balance sheet.
Investors receive return on their investments through either dividends paid from retained earnings or through growth in the value of their equity.
Market & financial feasibility studies work together to demonstrate that investment in the foodservice facility will generate the desired financial return.
The Go/No-Go Decision
If the project looks financially sound, the market is identified, a need for the foodservice exists, & the capital is obtainable, the decision to go ahead can be made.
If one or more elements are uncertain, there are three alternative courses to explore.
-
Correct the problem area that has been identified.
Abandon the project & look for another place to invest the funds.
Delay the decision until the final go/no-go decision point.
Site Selection & Planning
Includes the calculation of foot traffic, automobile counts, & distance to travel as a part of the feasibility study process.
Other considerations:
Visual recognition.
Convenience.
Code restrictions.
Environmental issues.
Agency Approvals
Typical approval agencies involved in foodservice projects include:
Zoning board.
Health department.
Municipal engineers (water, sewer, gas, & electrical).
City planner.
Fire marshal.
Liquor control board.
Telephone company.
State or federal agencies (on state or federal projects).