PT7711- Rotator Cuff Tears
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
16-30 y/o; eccentric; irritable; surgical
Traumatic rotator cuff tears:
- In younger population (________________).
- MOI usually involves fall with arm in a compromised posiiton, forceful ___________________ load, forceful distraction.
- Symptoms tend to be more obvious and will likely be more ____________________.
- Although MOI is present, there may have been some damage already.
- Typically, this patient is _____________________ for RC repair.
40 y/o; 30%; rotator cuff tendinopathy; rehab; reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (rTSA)
Atraumatic rotator cuff tears:
- >__________________ with history of shoulder pain (RC tendinopathy) → ~___________________ of people >60 y/o have a RC tear.
- Will present with many of the same signs and symptoms as ____________________.
- May have weakness with pain or weakness without pain presentation.
- Typically, this patient will do just as well with _____________________. → If this fails, then likely will have _____________________.
Drop arm, ER lag sign, horn blower's, painful arc, empty can
What are the special tests for rotator cuff tears?
- Age >65 y/o
- Night pain when rolling
- Positive painful arc
- Positive ER lag sign (and infraspinatus MMT)
- Positive drop arm
- Positive empty can
What is the clinical prediction rule for chronic rotator cuff tear?
Normal rotator cuff
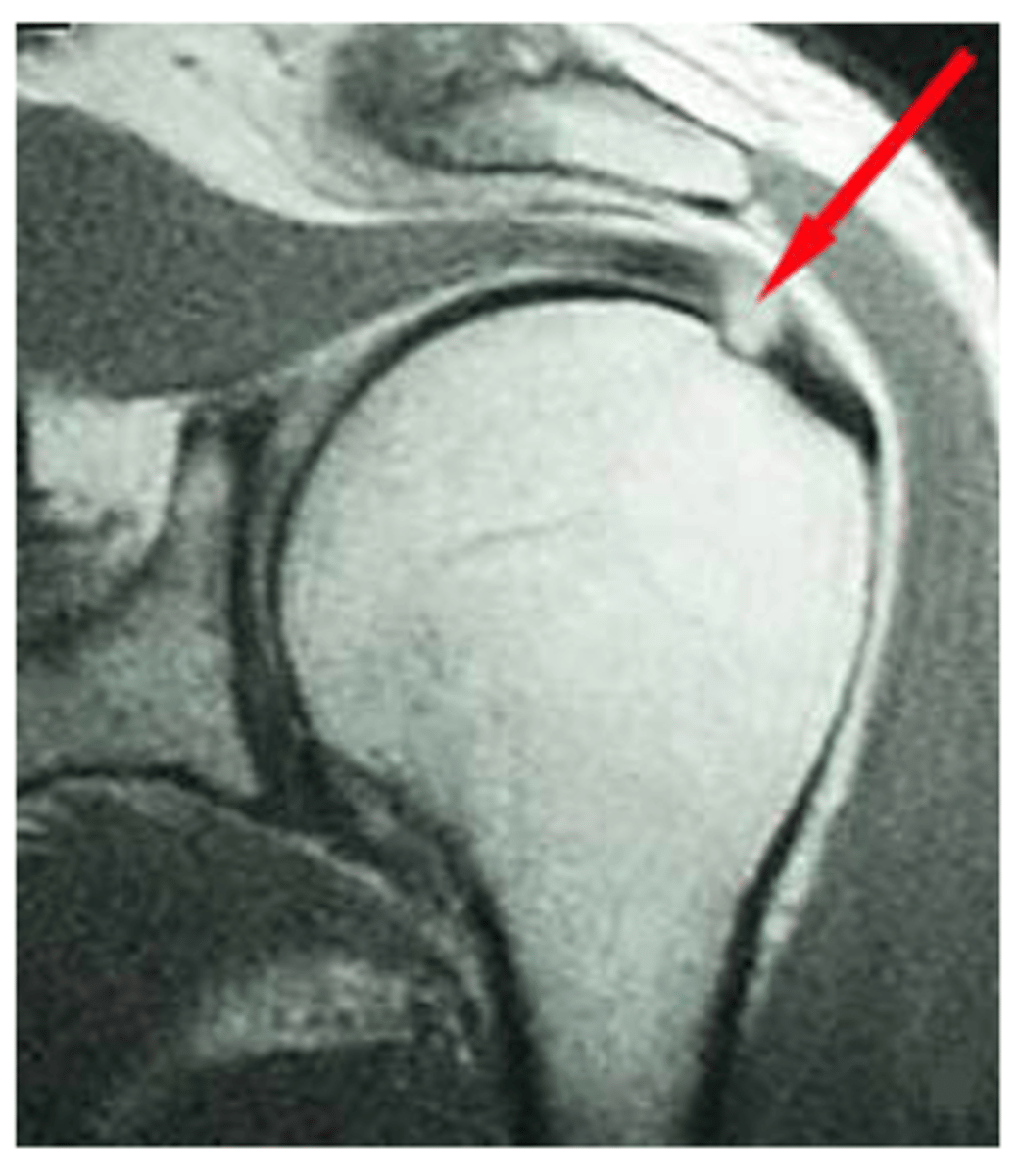
What does this image show?
Full-thickness supraspinatus tear
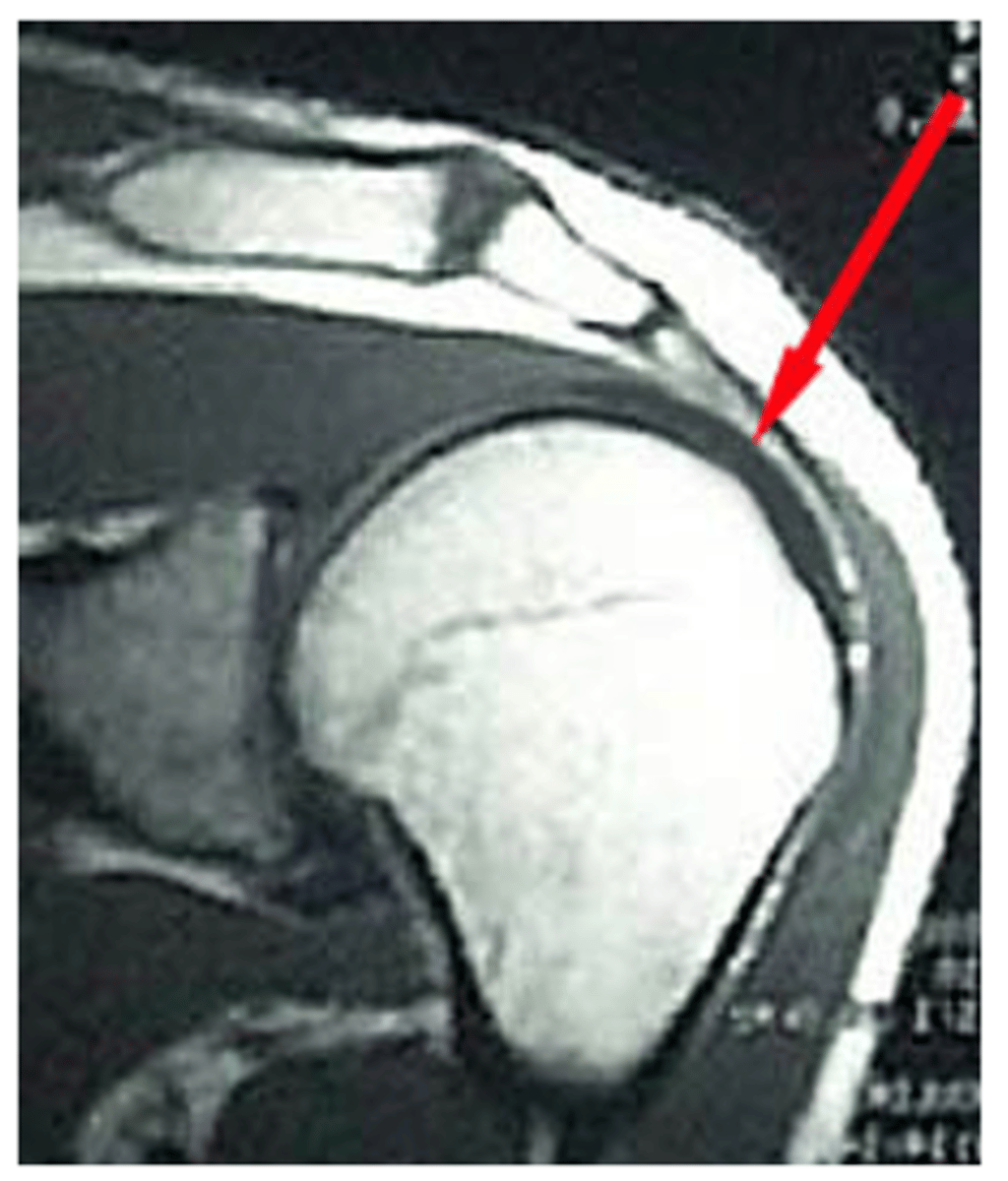
What does this image show?
Partial-thickness supraspinatus tear
What does this image show?
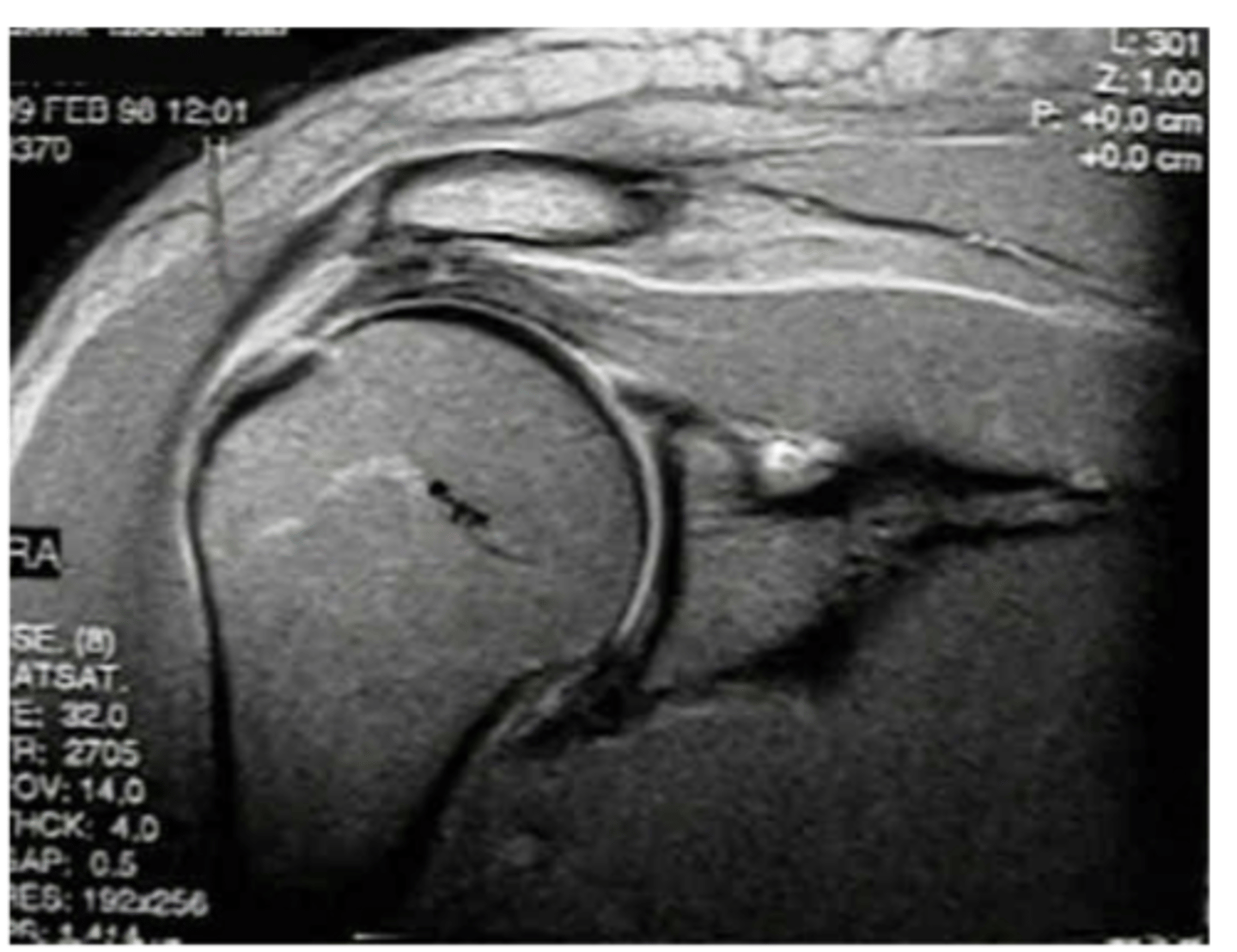
Bursal
If rotator cuff tear is on top, it's on _____________________ surface.
Contrast arthrogram of rotator cuff tear
What does this image show?
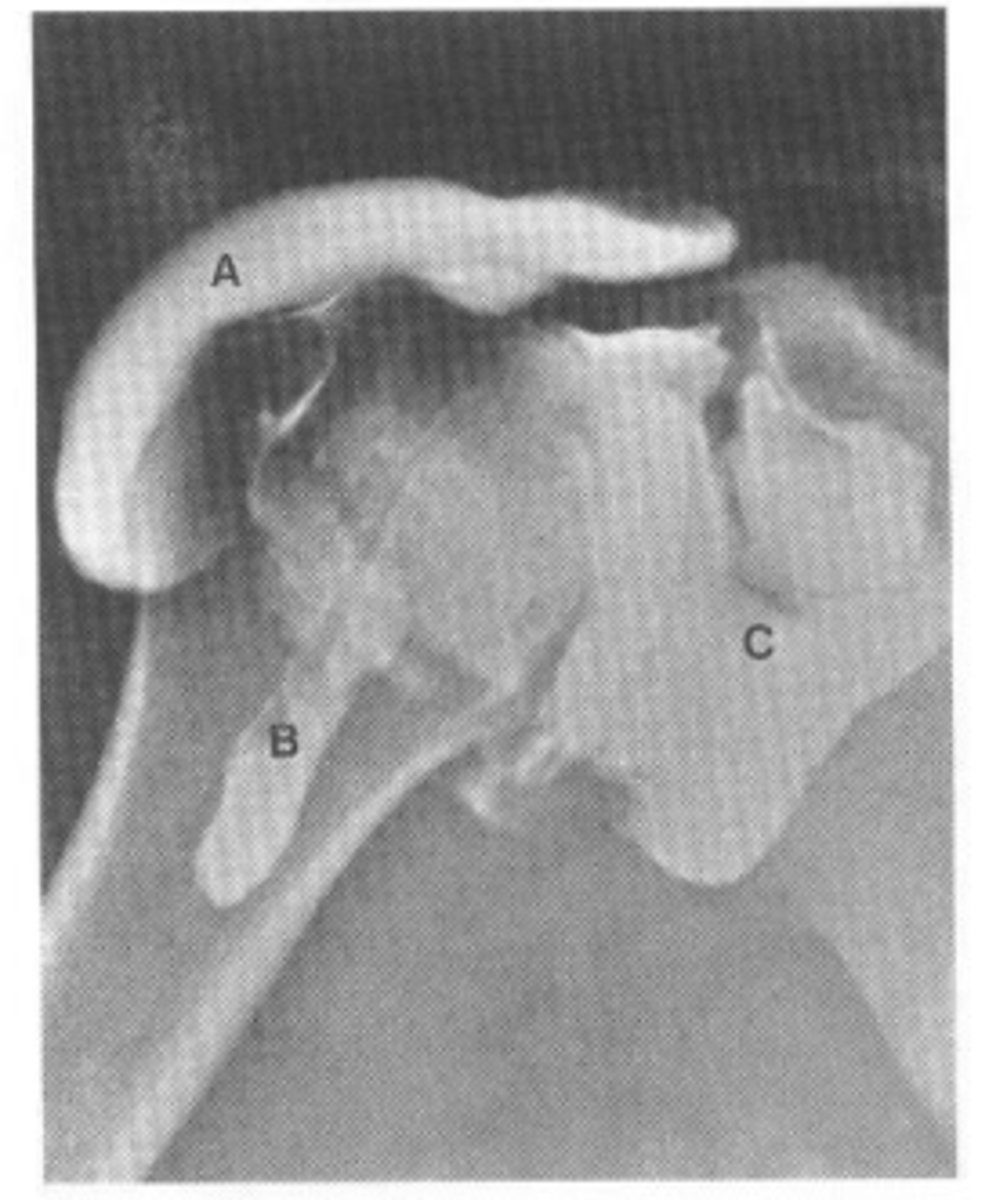
Central tendon
Axial MR localizer through the supraspinatus muscle demonstrating placement of cursors parallel to the _____________________ (arrow).
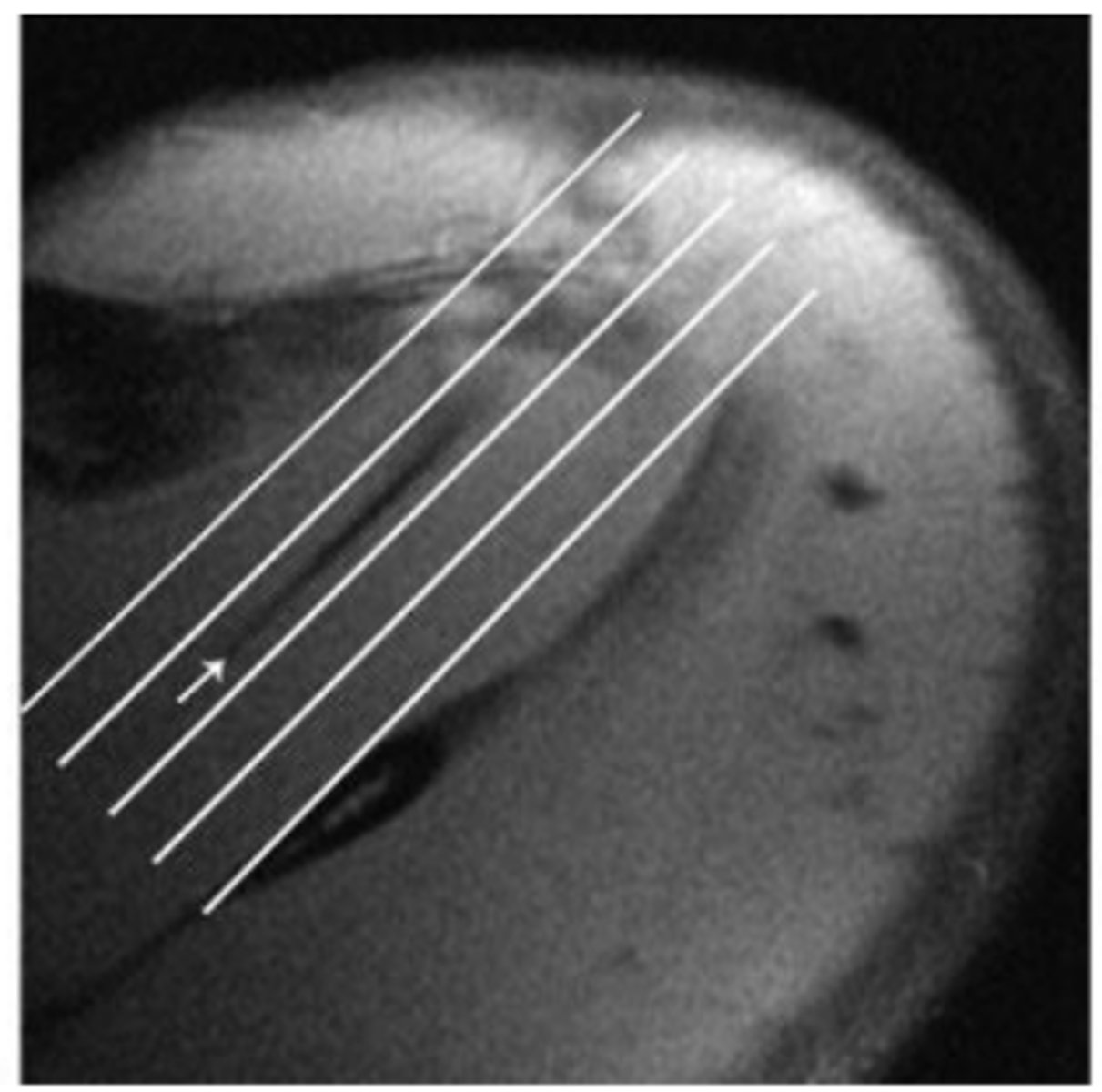
Oblique coronal
Resulting _____________________ image allows assessment of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons in continuity.
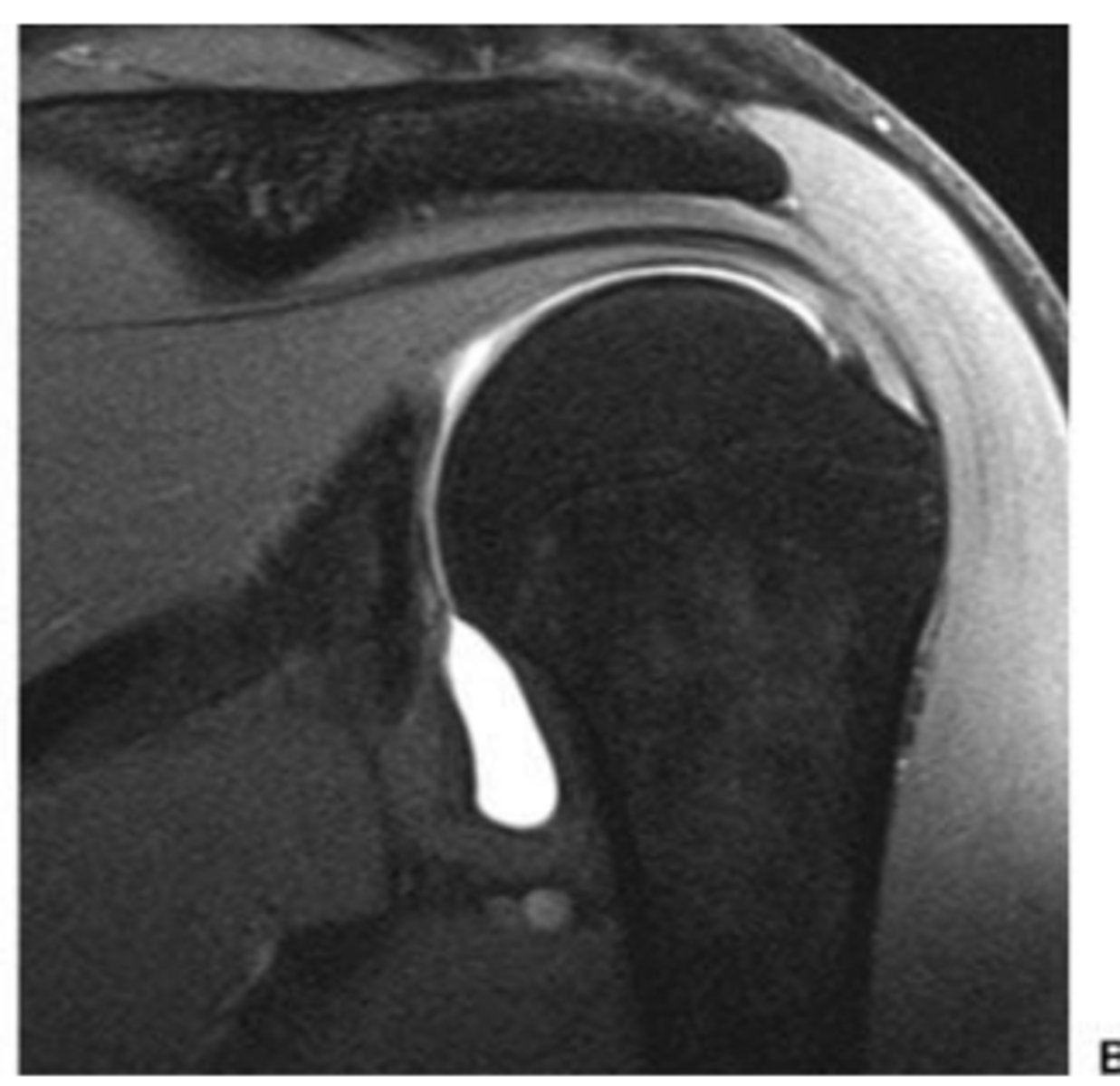
Thickening of supraspinatus tendon
What does the short white arrow show?
Small amount of fluid present in subacromial-subdeltoid bursa
What do the long white arrows show?
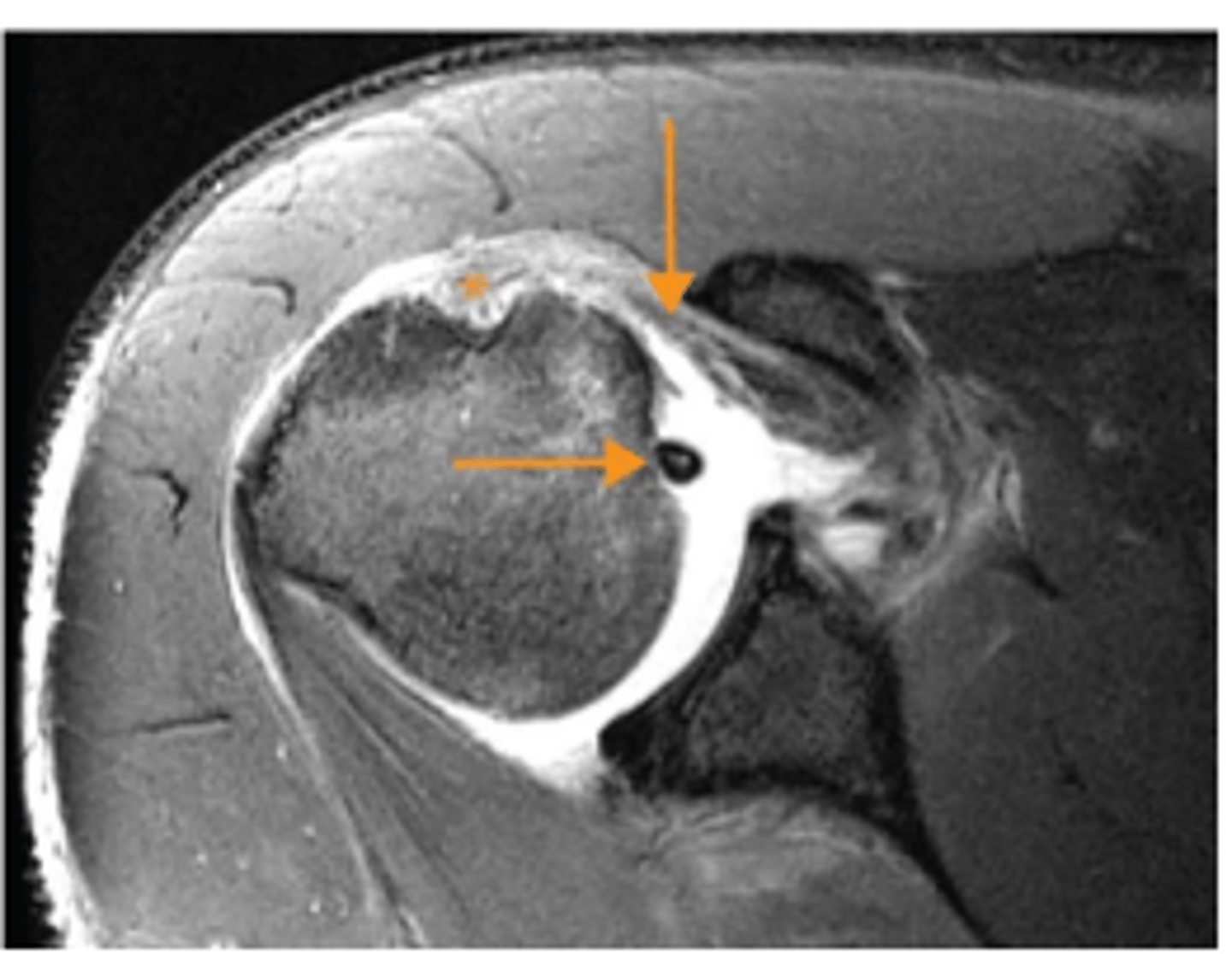
Supraspinatus intramuscular ganglion cyst
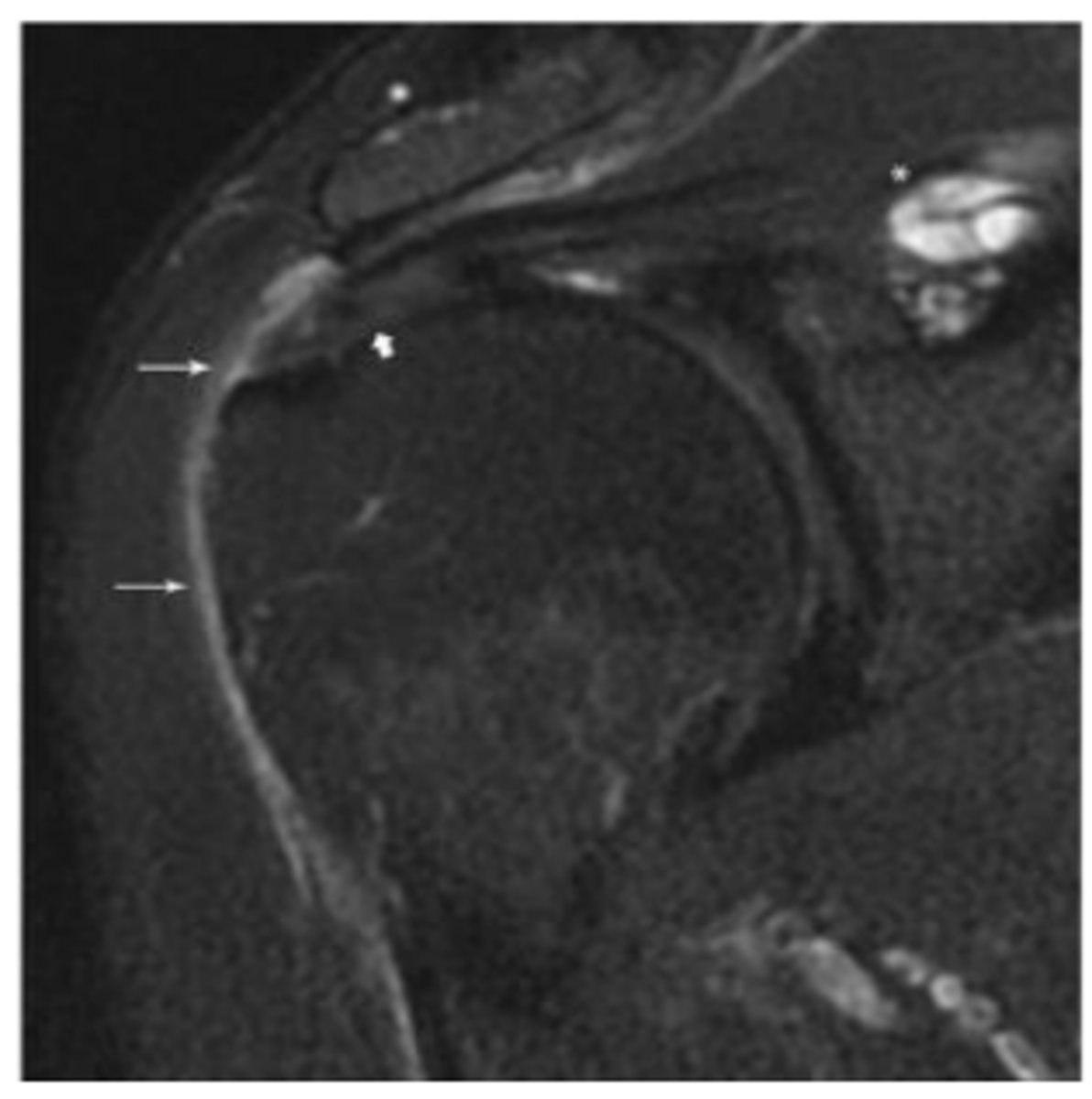
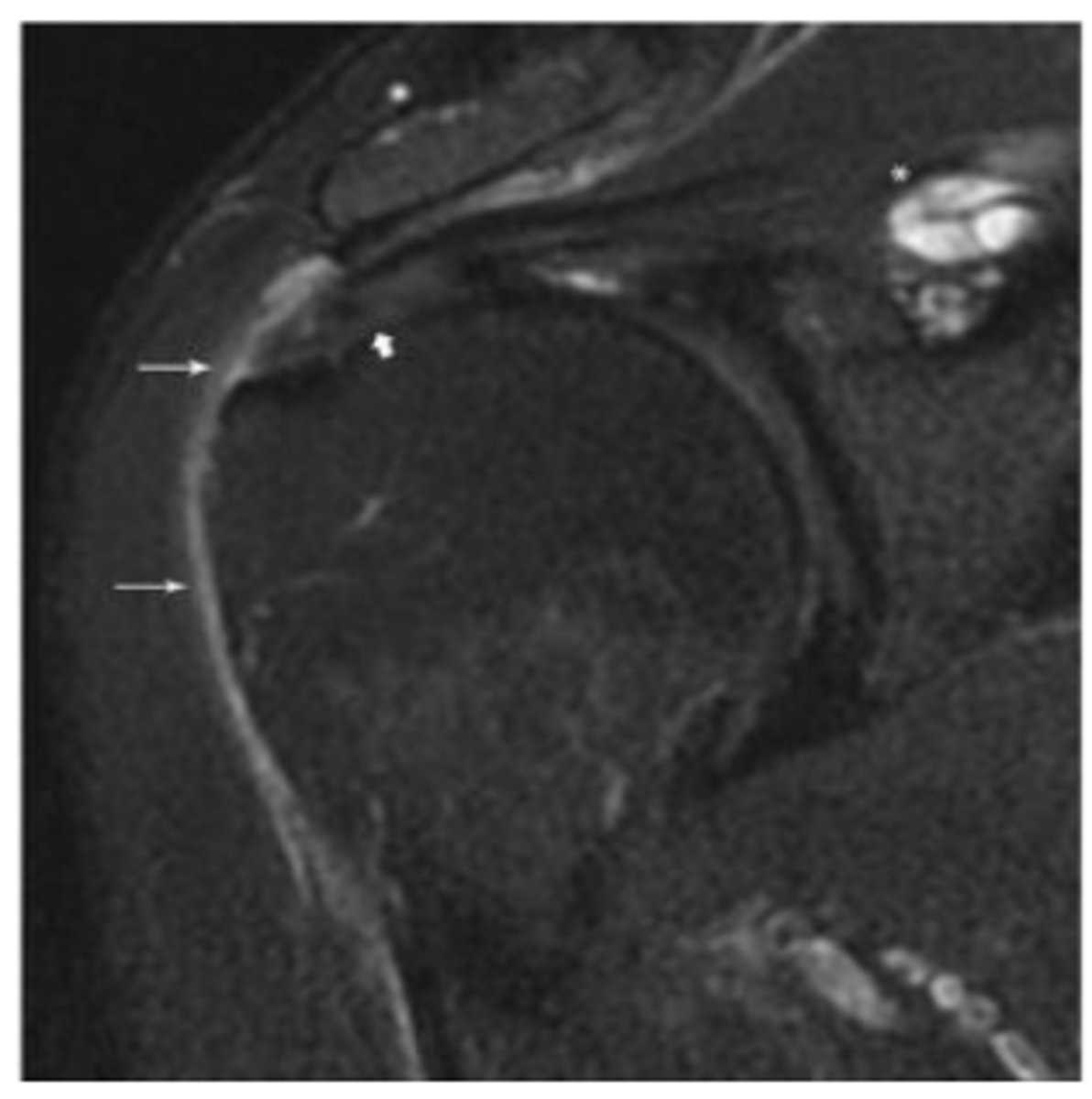
What does the asterisk show?
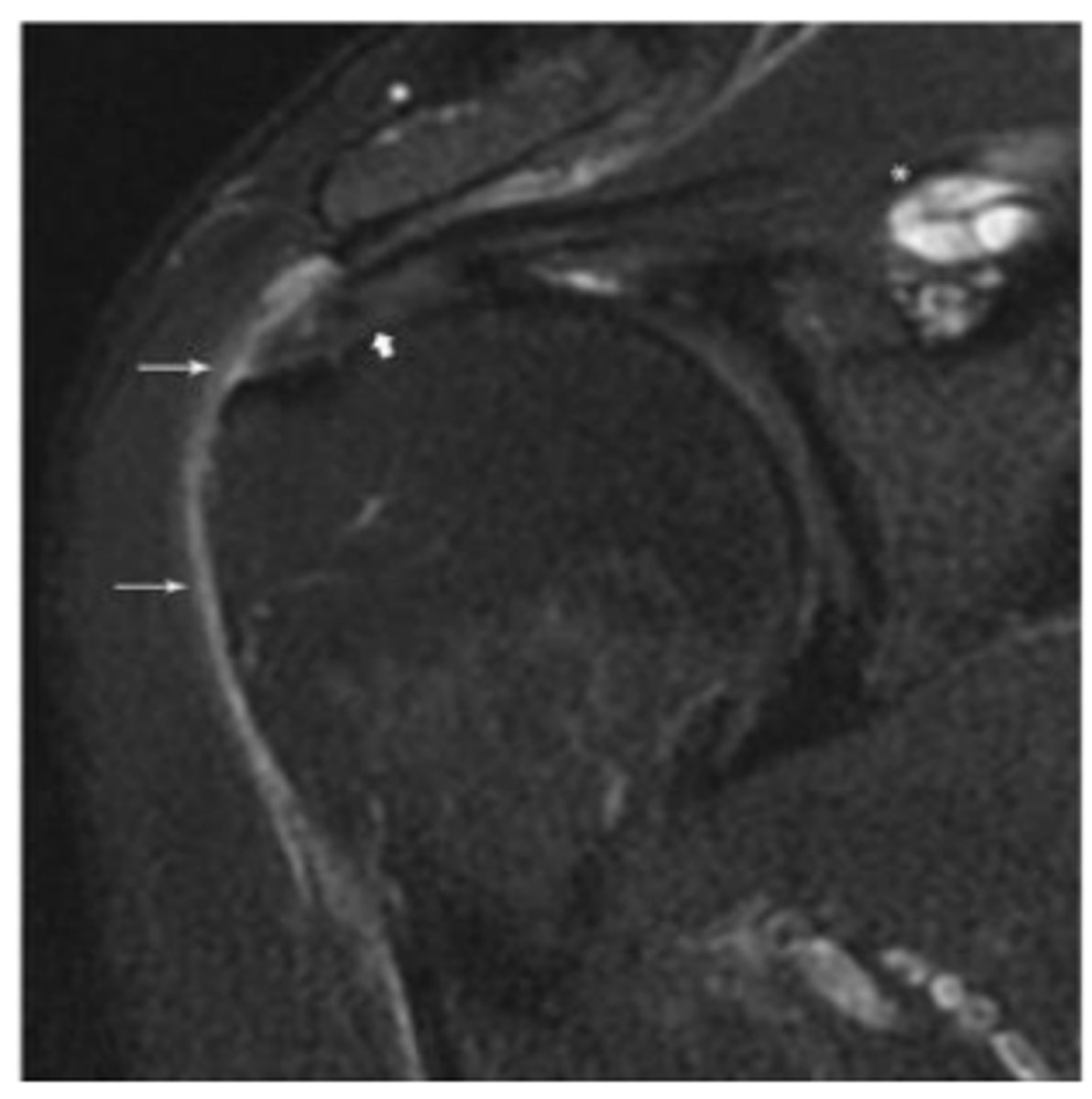
Minimally retracted full-thickness tear
What does the short arrow show?
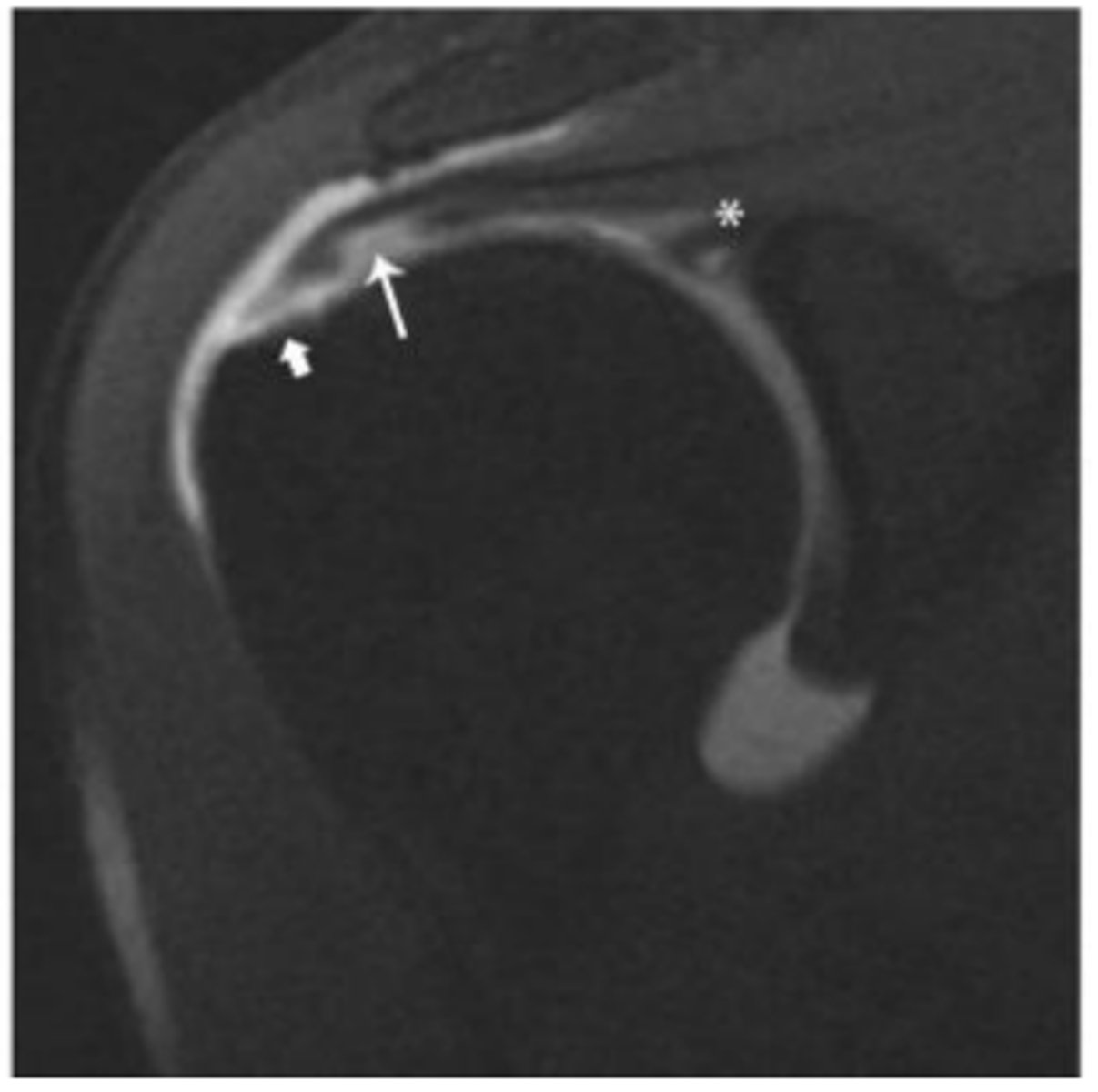
Articular surface component with delamination
What does the long arrow show?
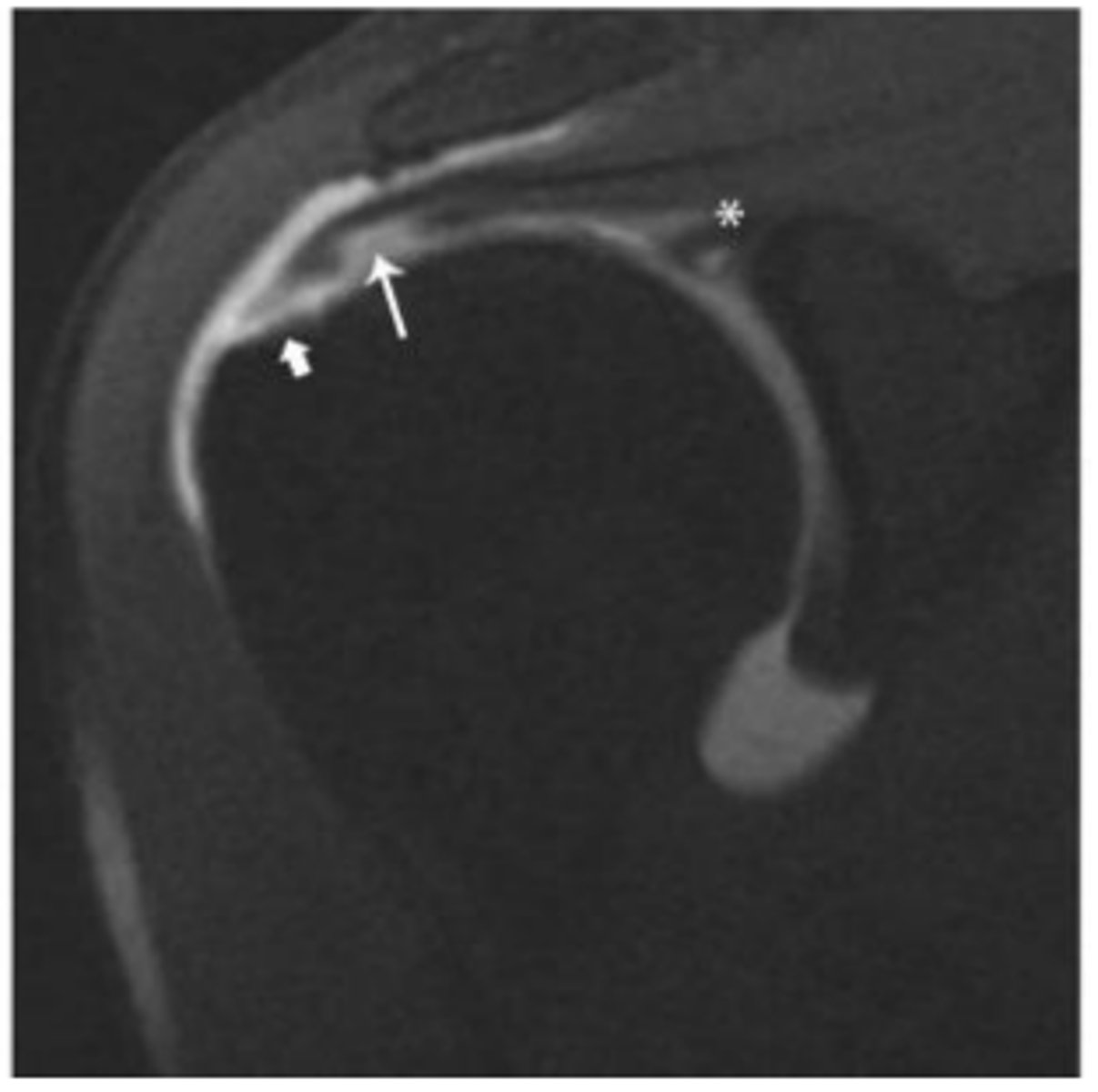
SLAP tear
What does the asterisk show?
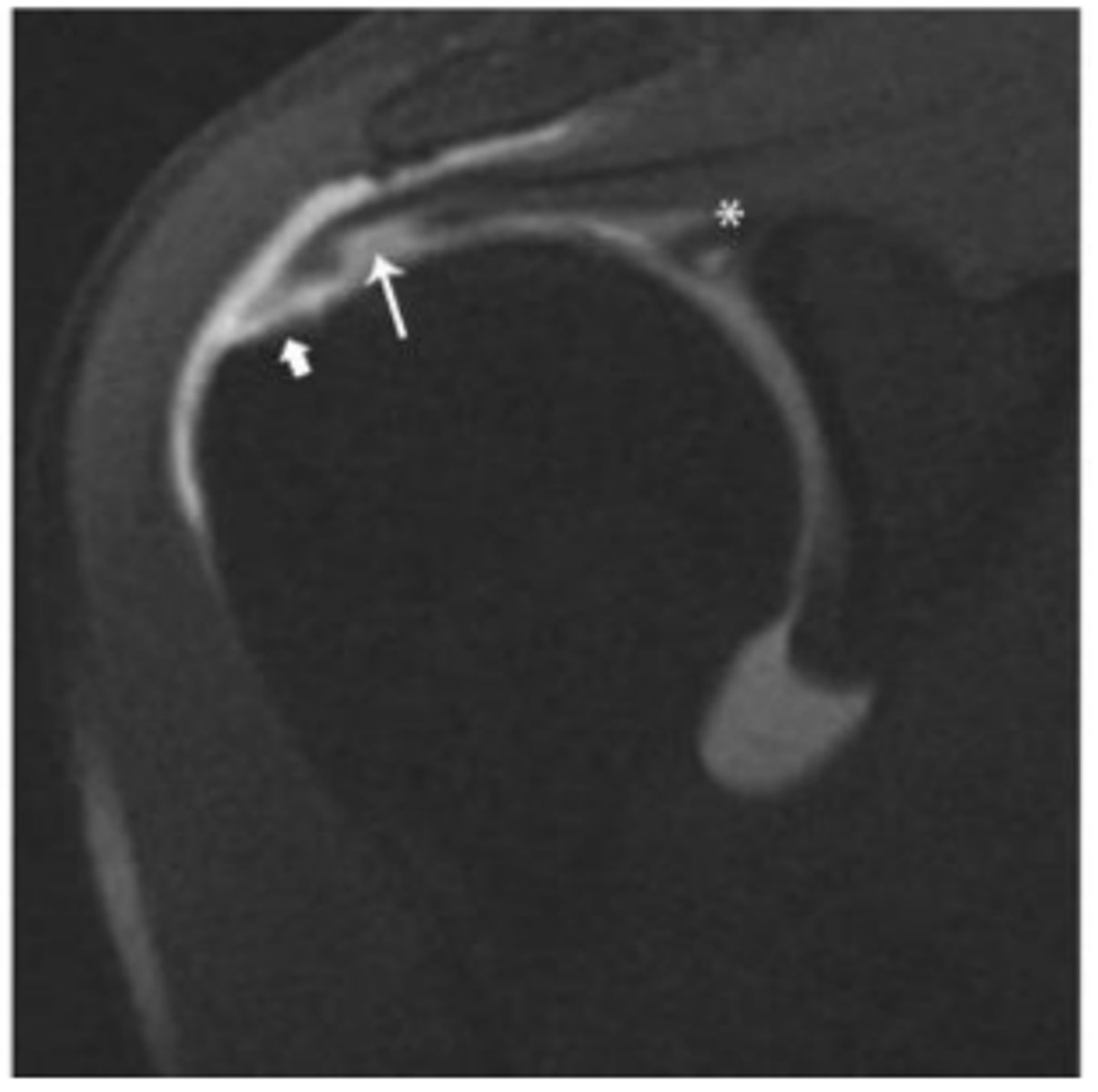
0-1 cm
Small tear.
1-3 cm
Medium tear.
3-5 cm
Large tear.
>5 cm
Massive tear.
Supraspinatus tendon
What does the asterisk show?
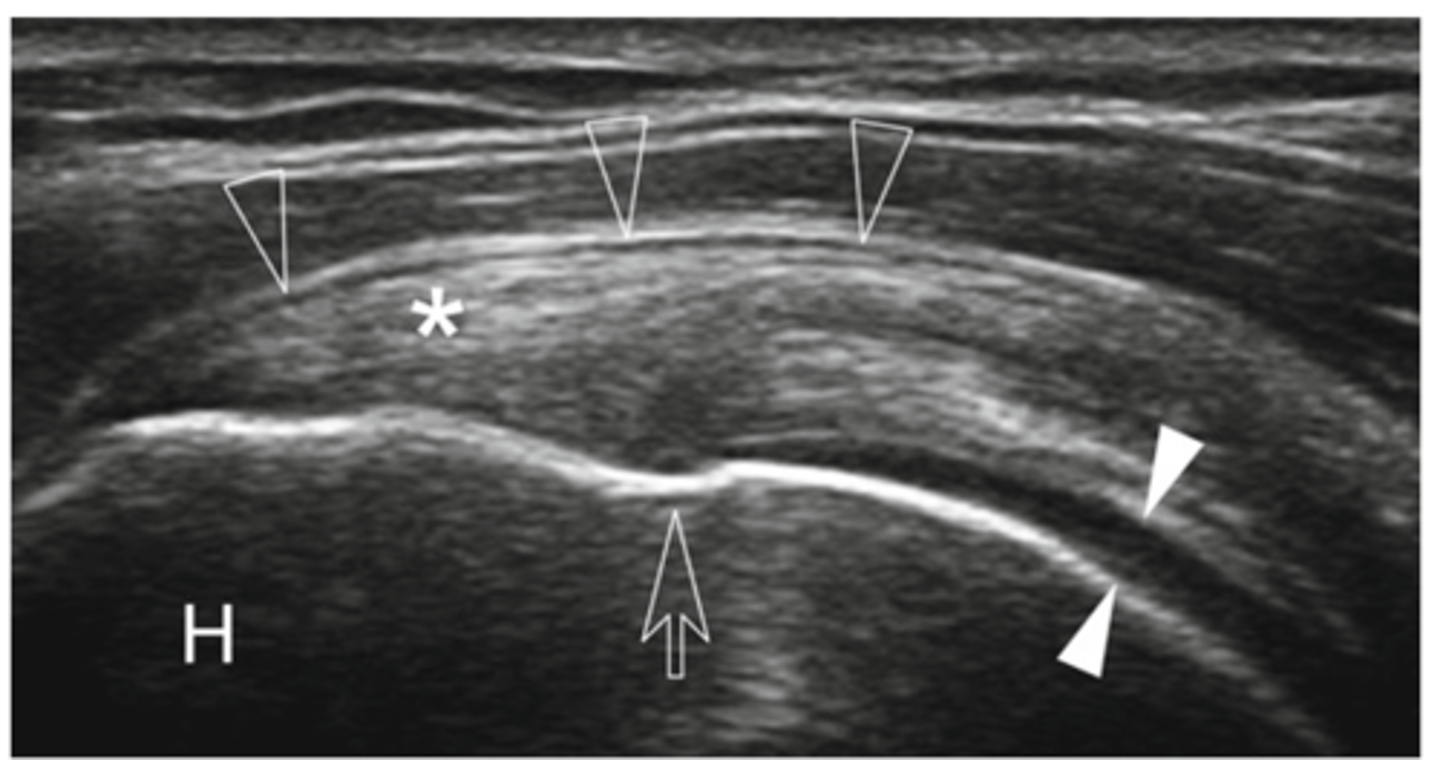
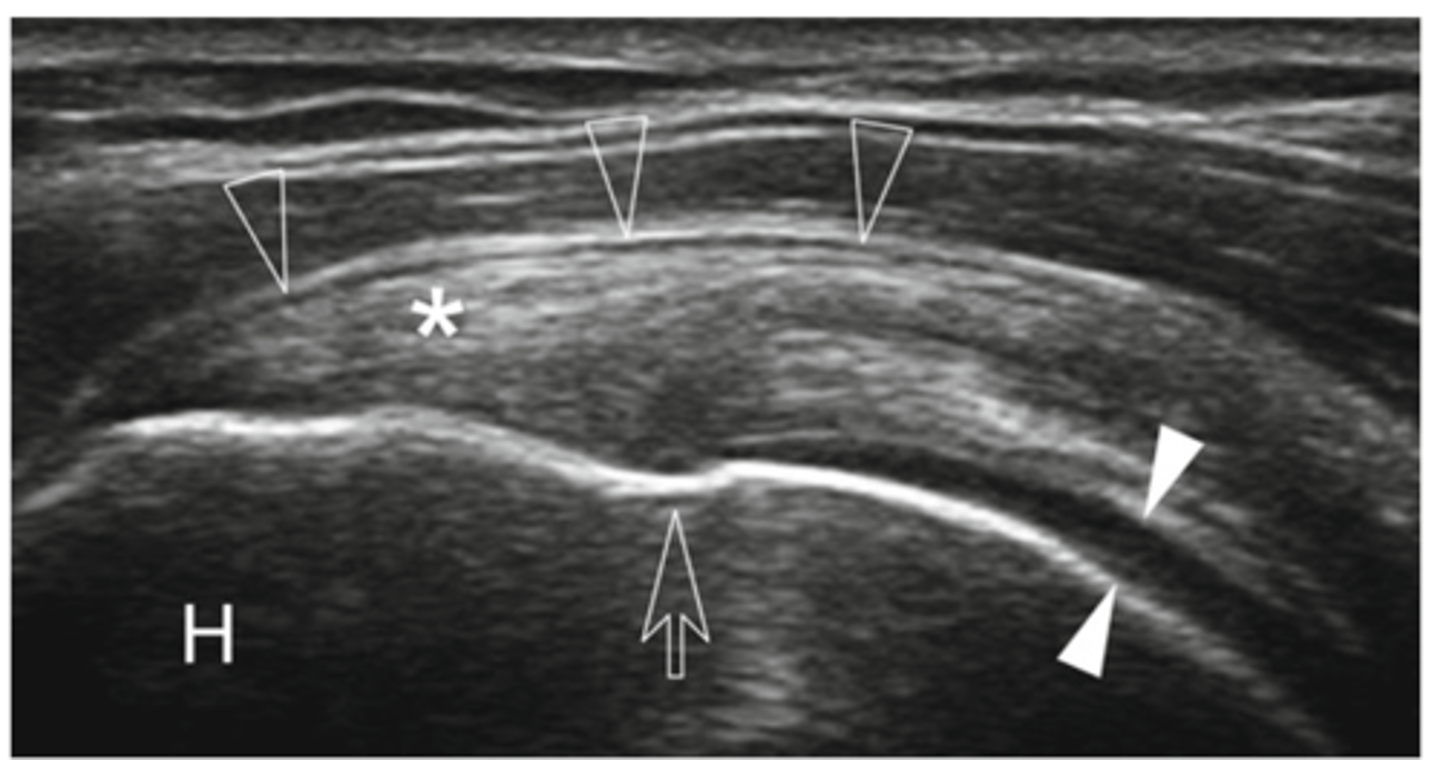
Cartilage
What do the white arrowheads show?
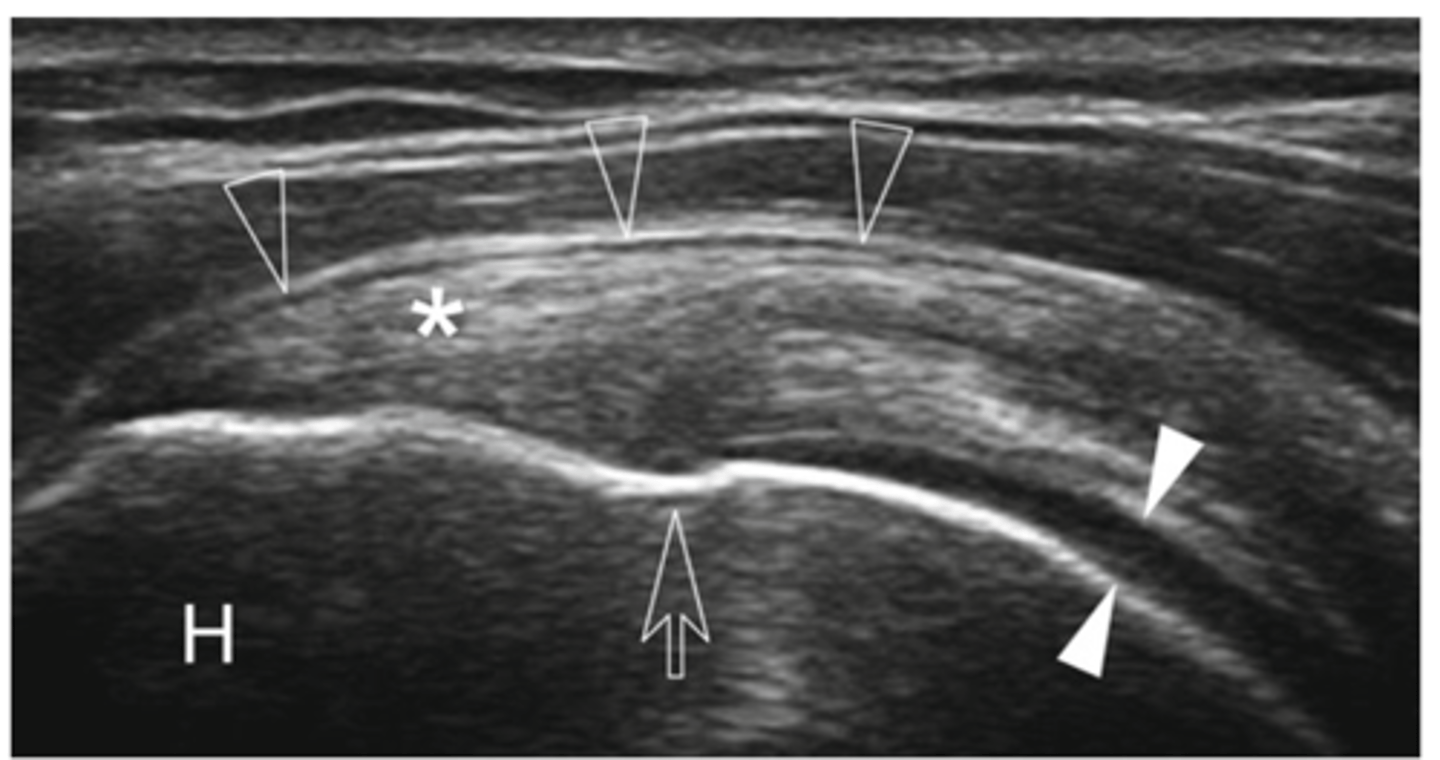
Bursa
What do the empty arrowheads show?
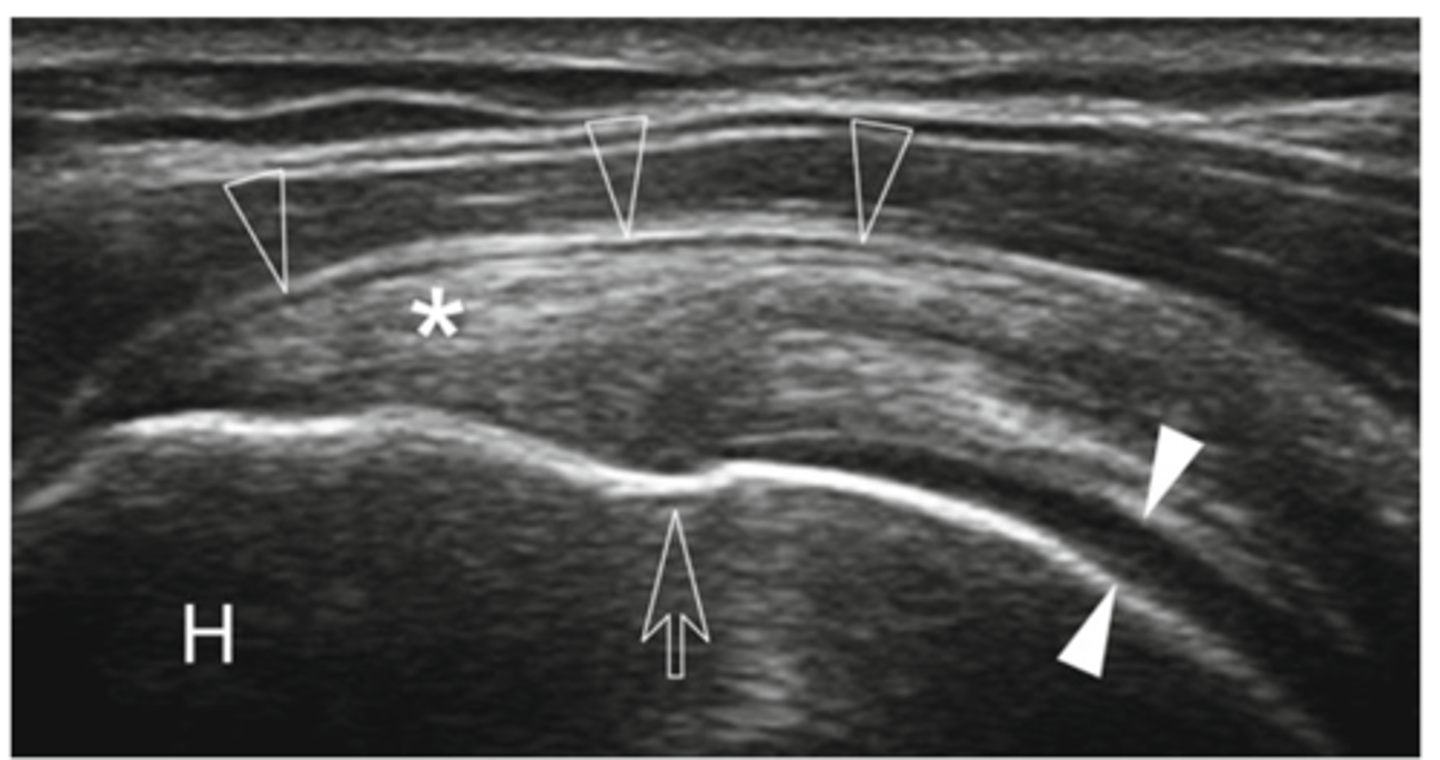
Greater tuberosity
What does the H show?
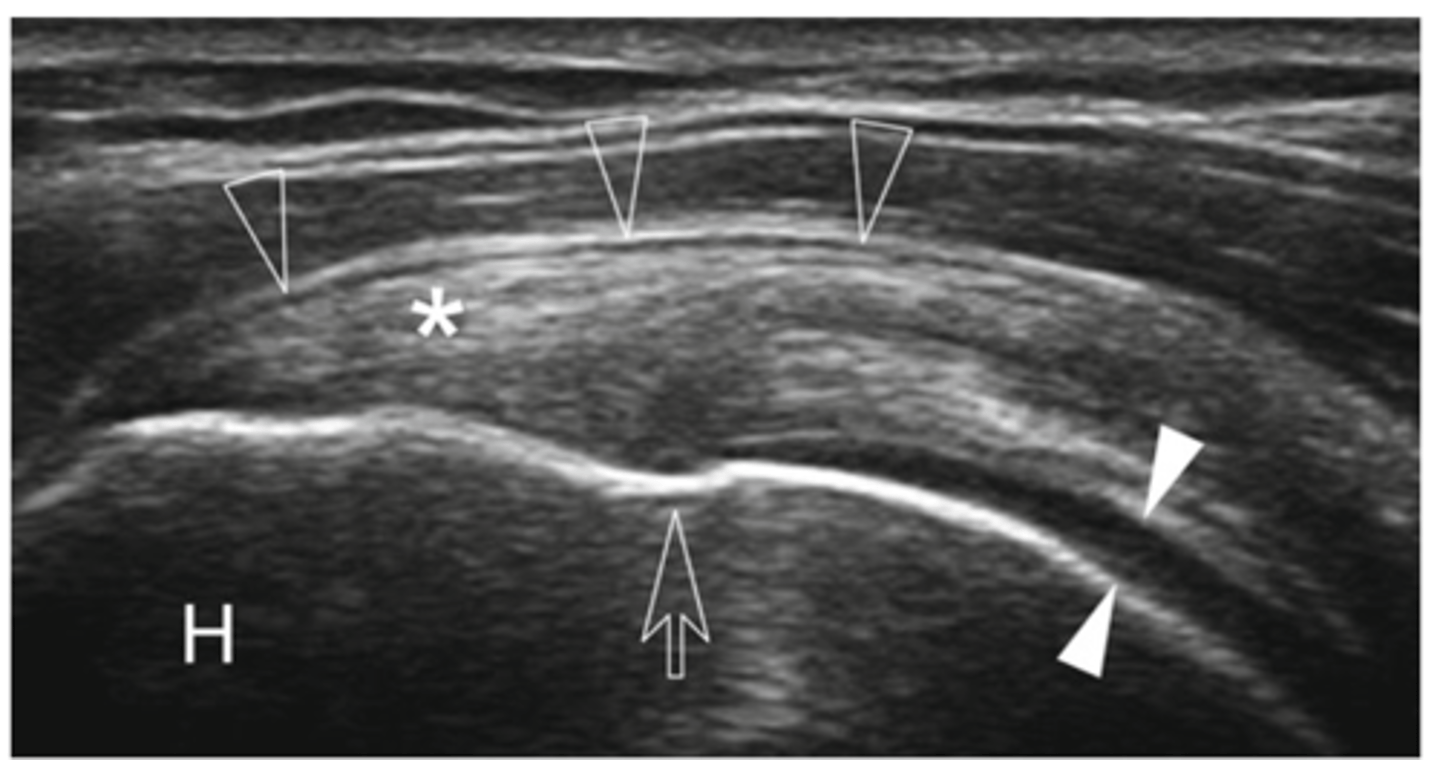
Enthesis
What is the white line going through the center of the image (indicated by empty arrow)?
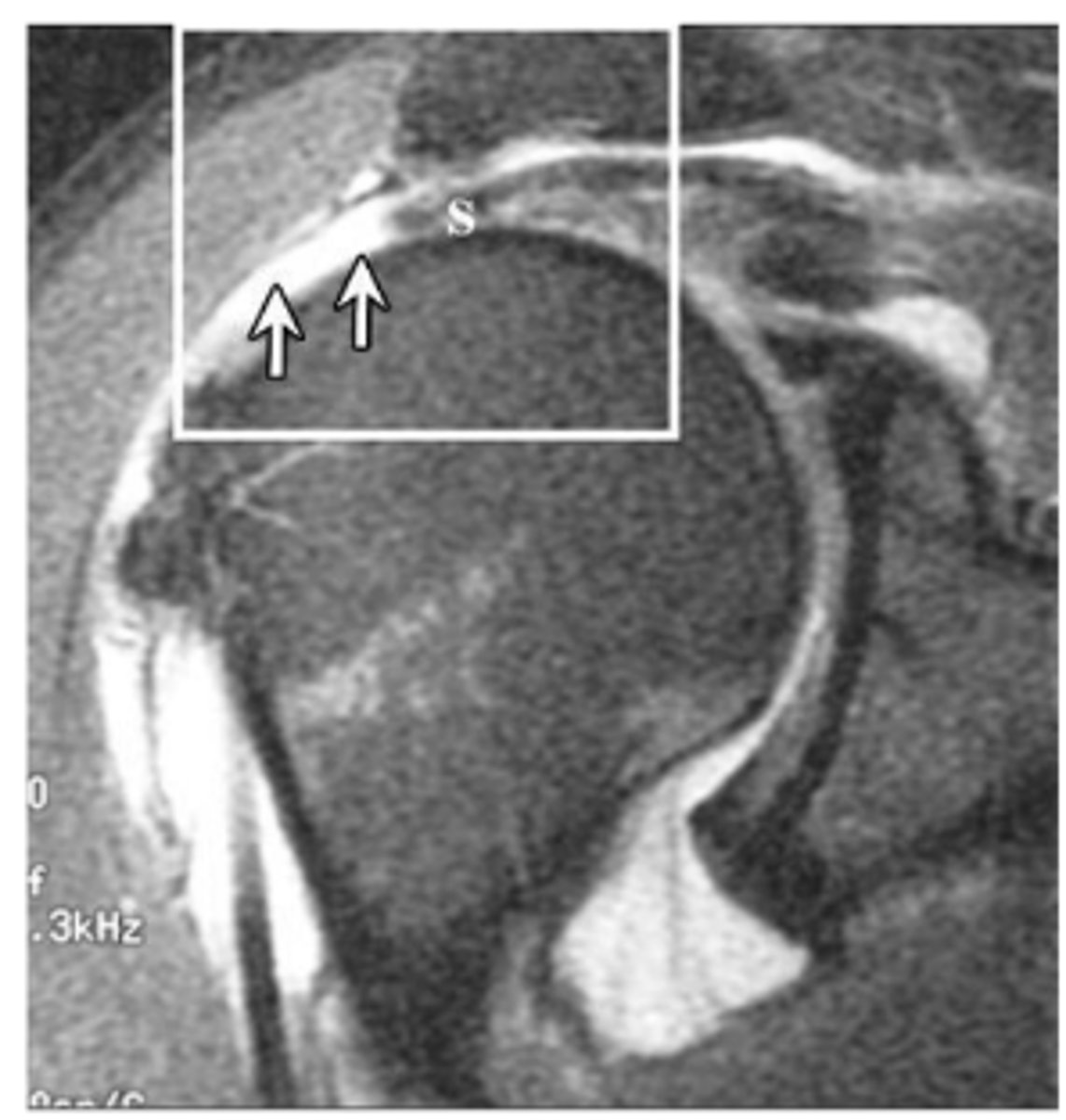
Supraspinatus tear
What does the MRI image show?
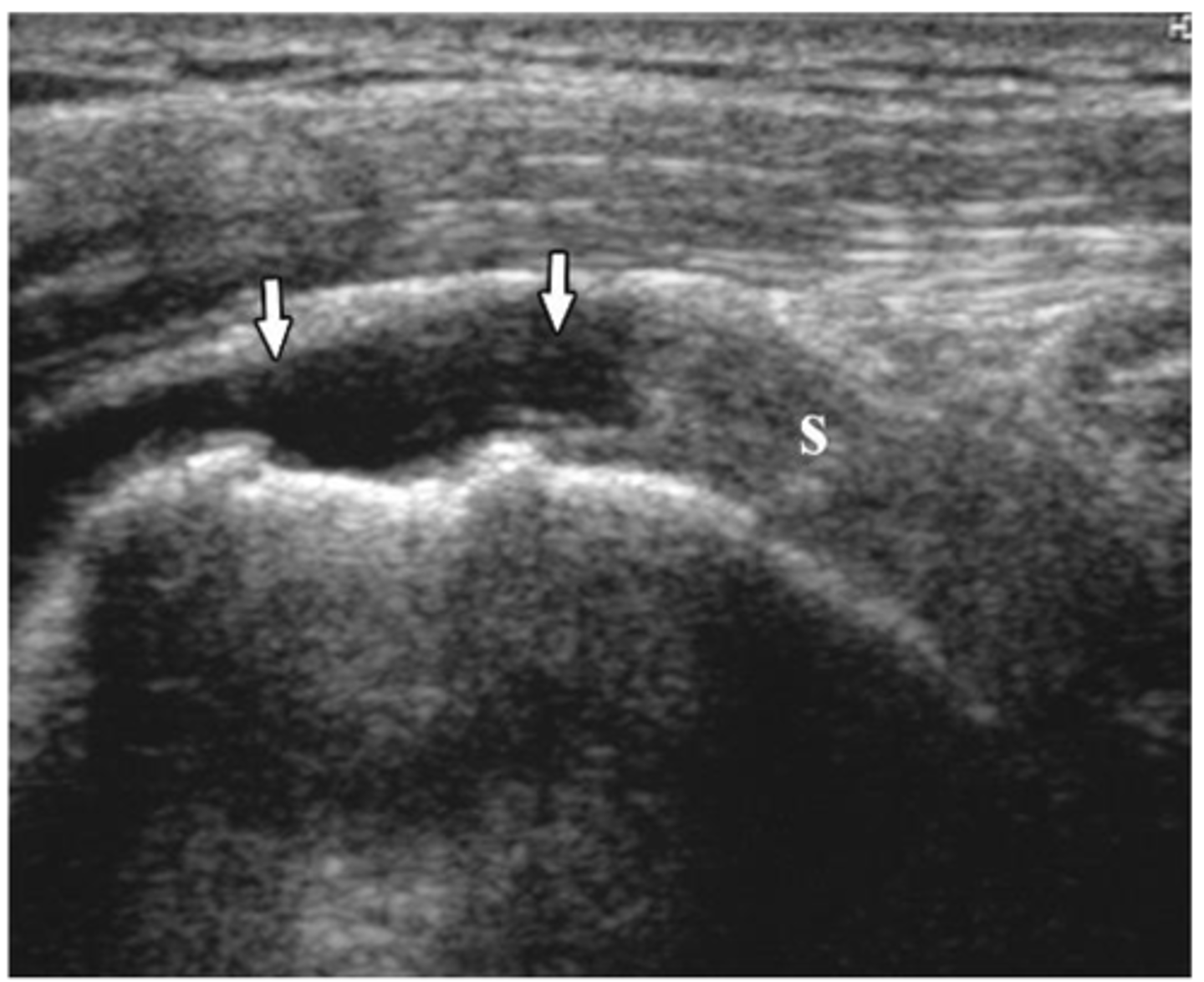
Hypoechogenicity indicative of supraspinatus tear.
What does the ultrasound image show?
More than one
With massive tears, there is _____________________ tendon involved.
Retraction
Usually, a significant amount of ______________________ occurs in the presence of massive tears.
- Simple
- Mattress
- Combination
- Single row vs. double row
What are the four different types of suture patterns?
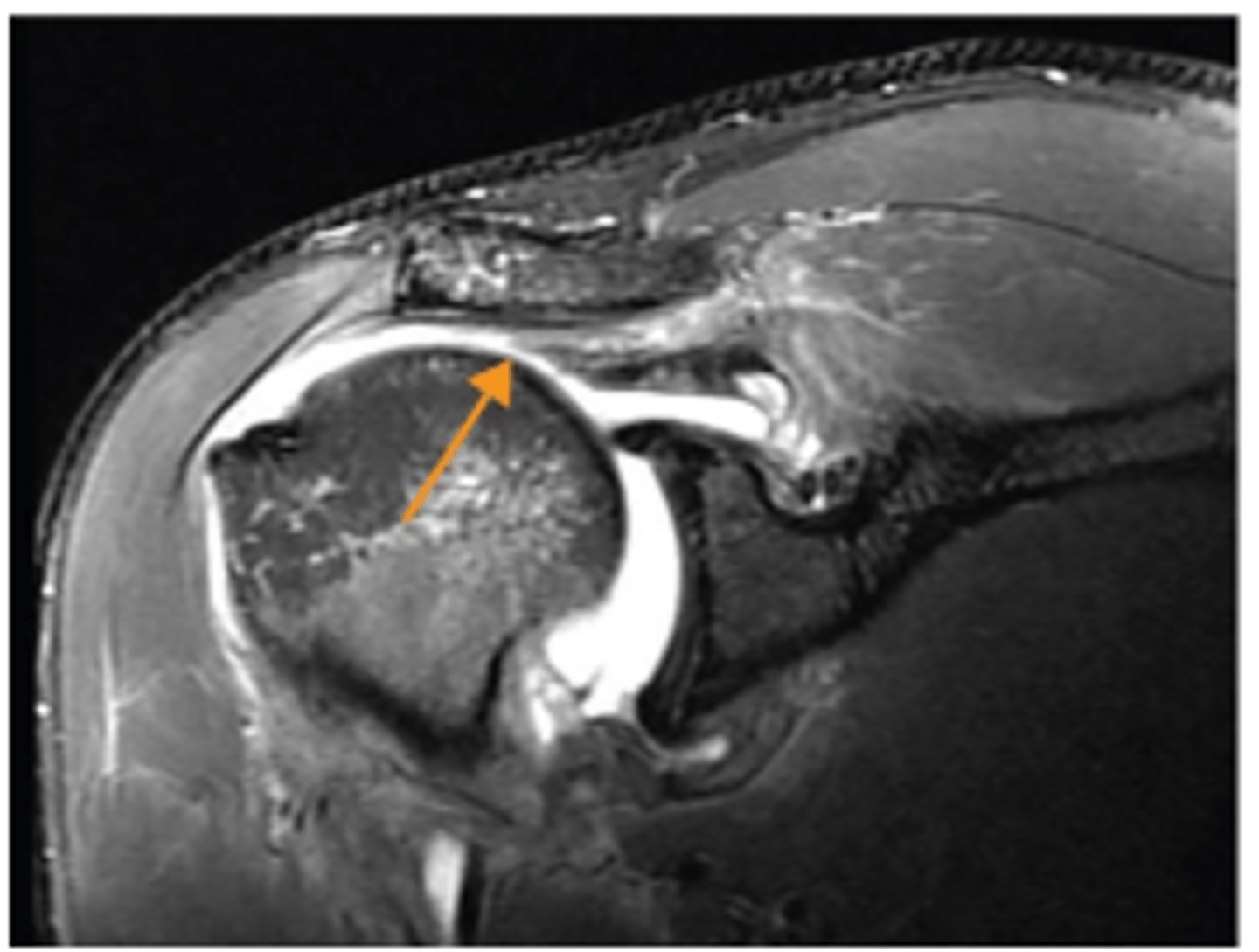
Full-thickness supraspinatus tear
What does the arrow show?
Superior migration
What is happening to humeral head in image?
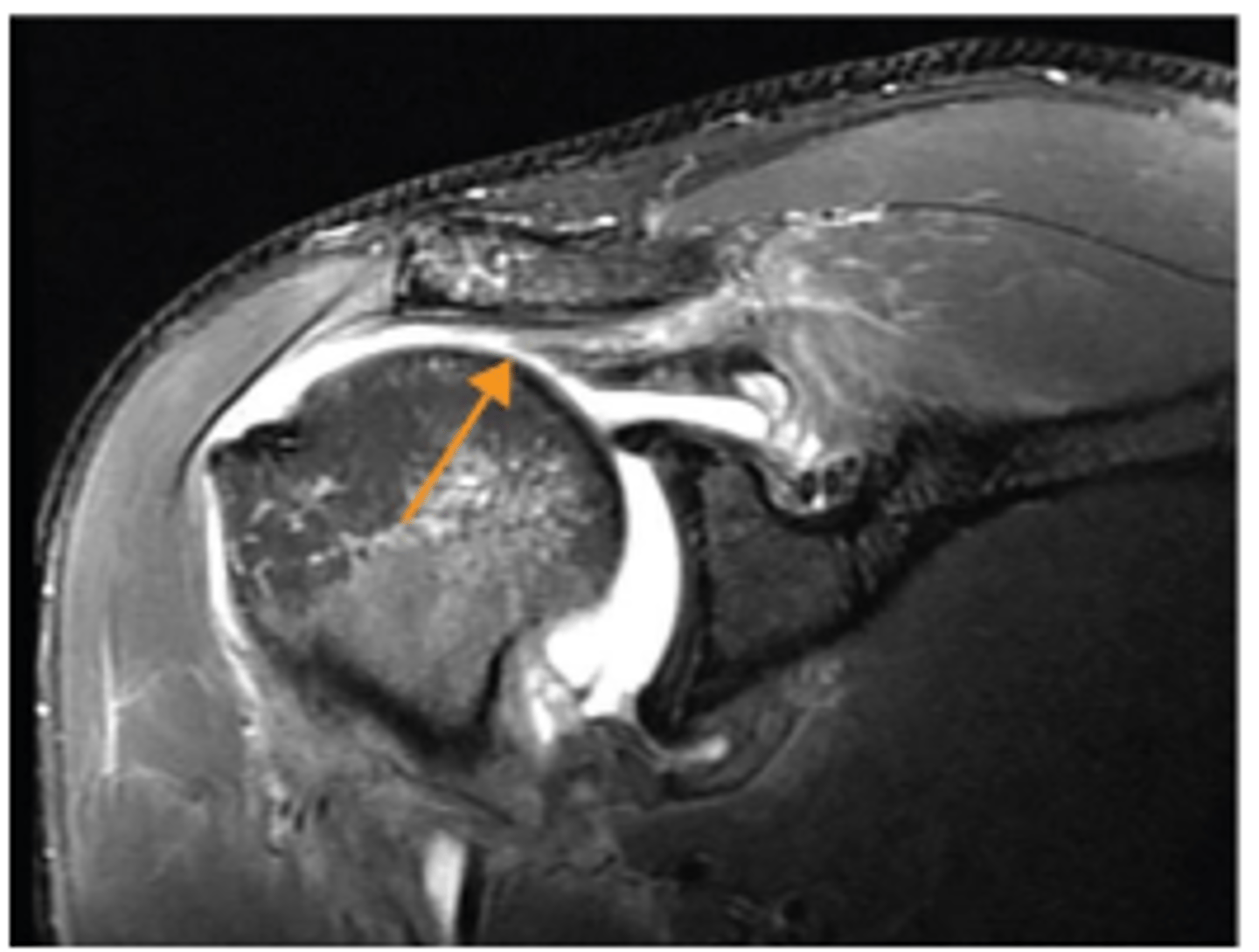
Full-thickness tear of infraspinatus
What does the arrow show?
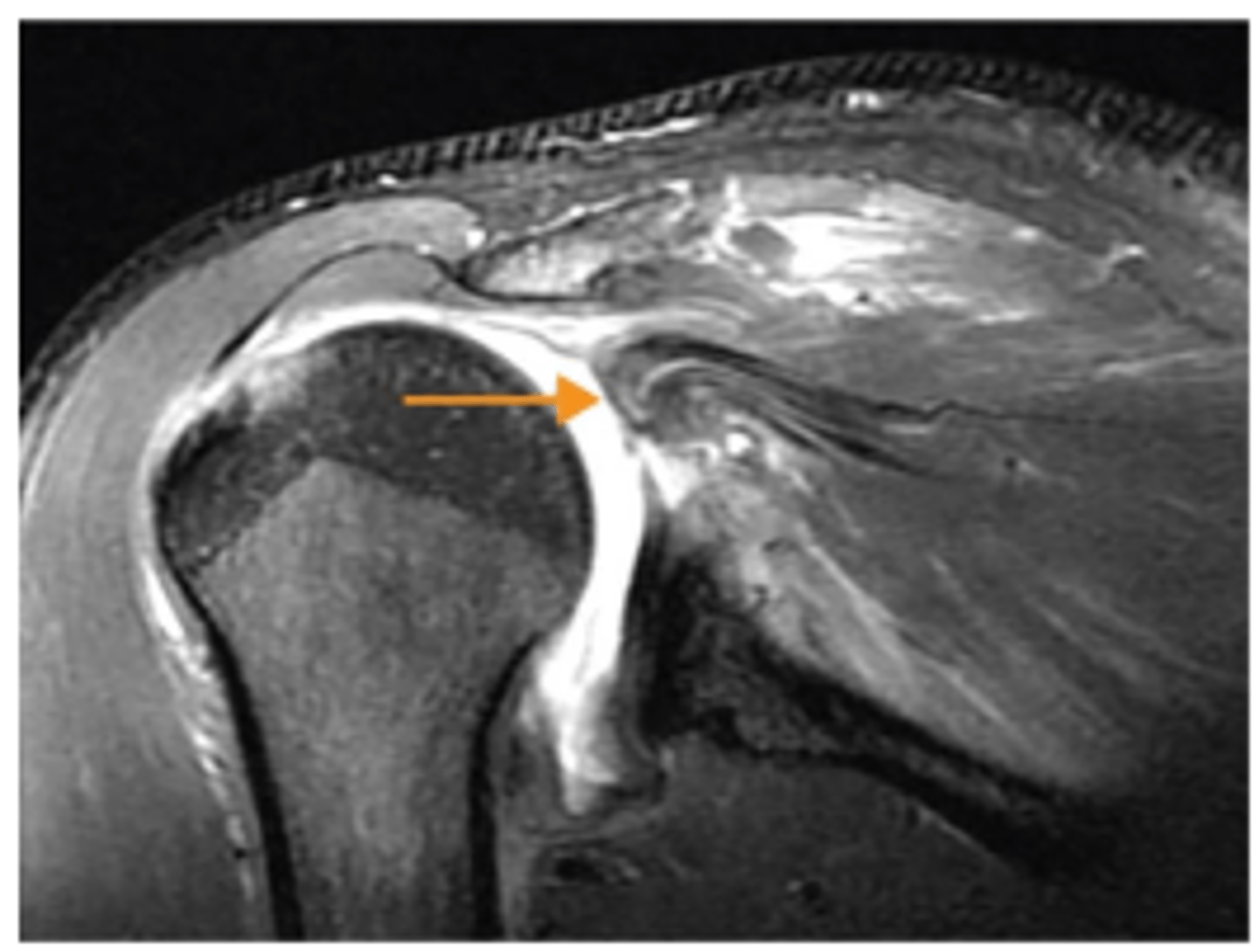
Biceps long head tendon was dislocated into joint space inside the reverse Hill-Sachs humeral head defect
What does the horizontal arrow show?
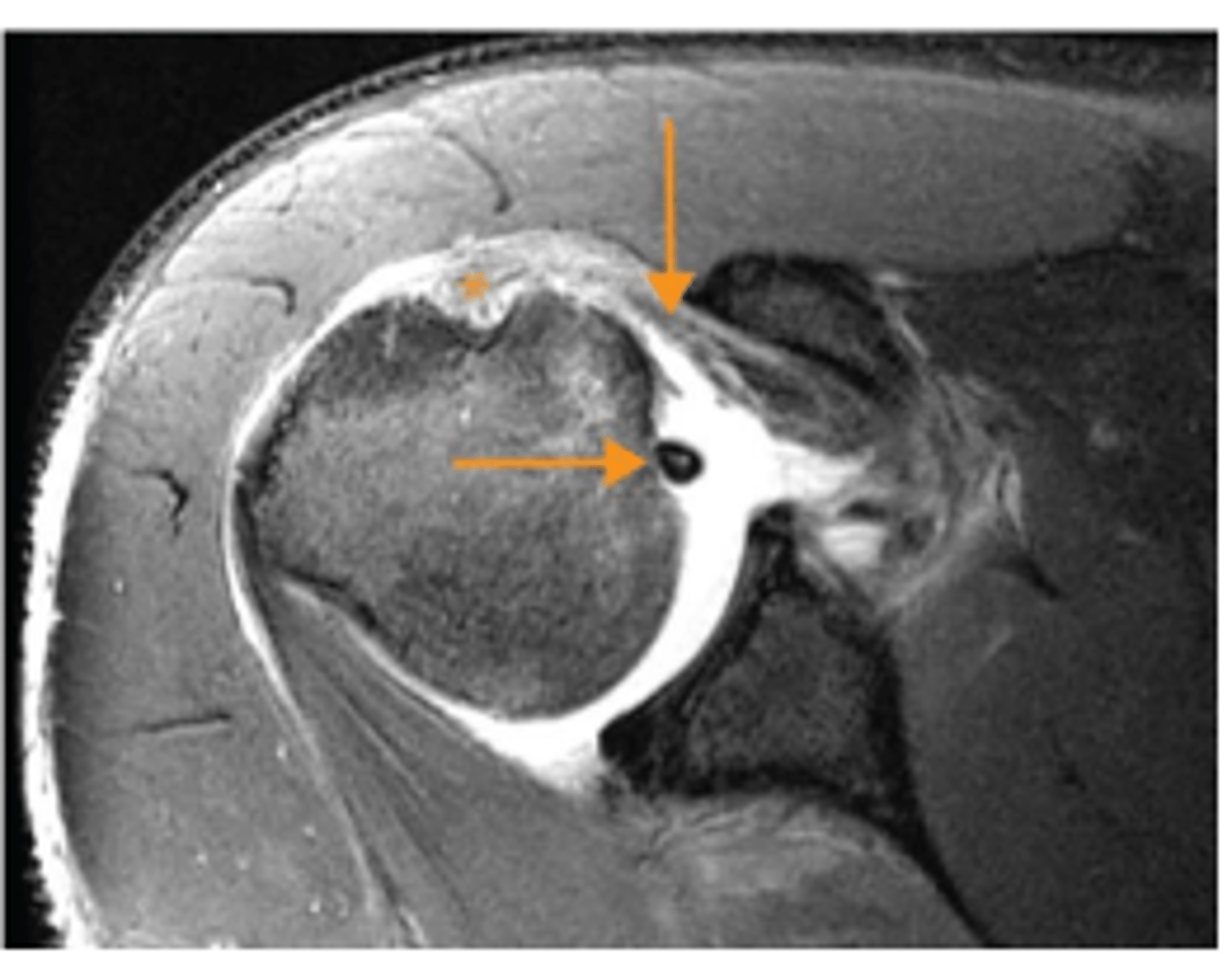
Subscapularis tear
What does the vertical arrow show?
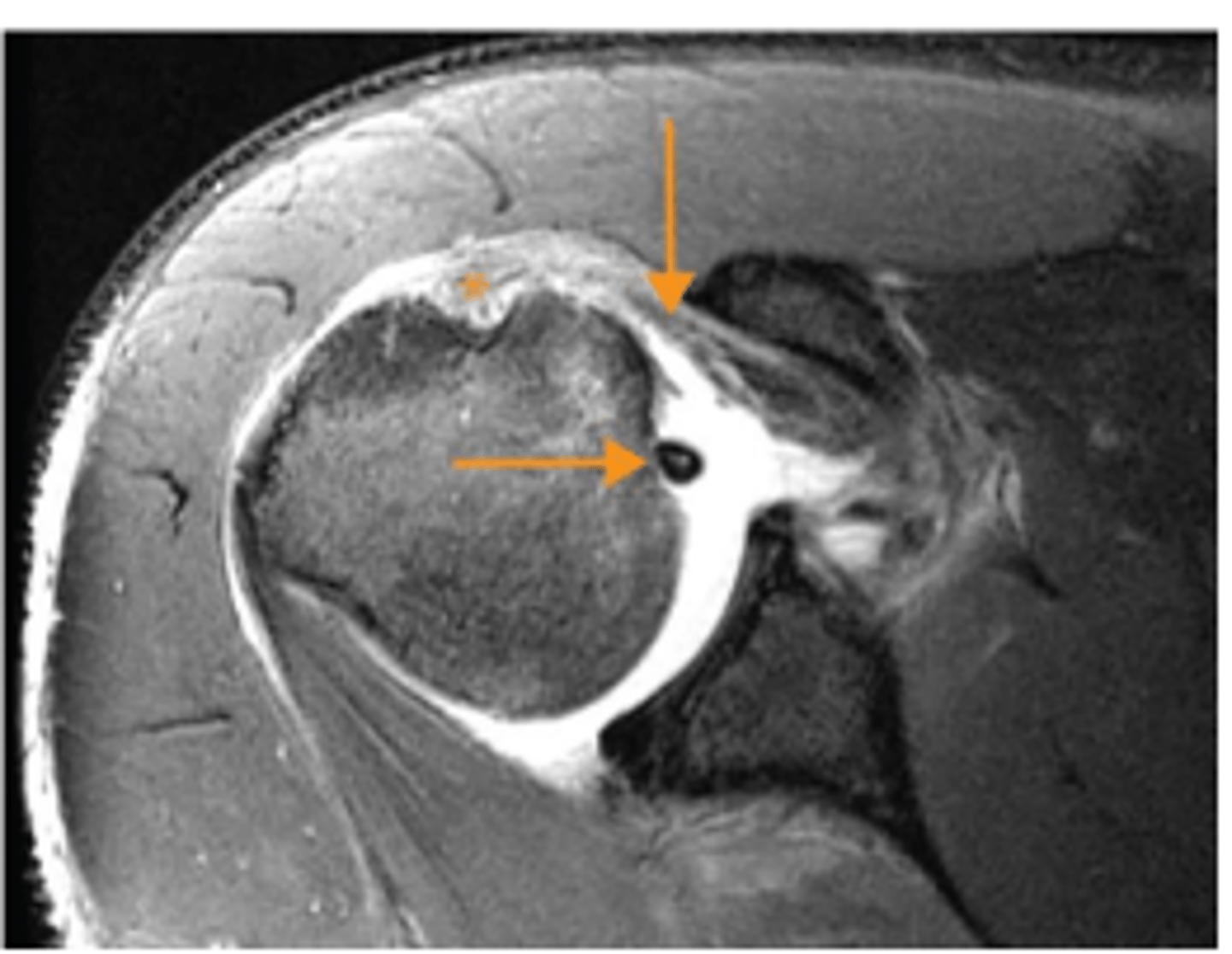
Empty bicipital groove
What does the asterisk show?
Horizontal adduction, flexion, IR
21 y/o running back that sustained a posterior GH dislocation.
- Was reduced on the field
- AROM limited to ~80%; PROM full
- Imaging revealed tear of supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis.
- Also had a reverse Hill-Sach's lesion from a posterior Bankart lesion and bicipital tendon dislocation.
What would you expect ROM protocol for this patient to include? Specifically, what motions would be contraindicated?
Active contraction contraindicated d/t rotator cuff repair
21 y/o running back that sustained a posterior GH dislocation.
- Was reduced on the field
- AROM limited to ~80%; PROM full
- Imaging revealed tear of supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis.
- Also had a reverse Hill-Sach's lesion from a posterior Bankart lesion and bicipital tendon dislocation.
What would you expect protocol for this patient to include, specifically regarding active contraction?
Surgical s/p 2-3 weeks; 4-6 week maximal protection phase
21 y/o running back that sustained a posterior GH dislocation.
- Was reduced on the field
- AROM limited to ~80%; PROM full
- Imaging revealed tear of supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis.
- Also had a reverse Hill-Sach's lesion from a posterior Bankart lesion and bicipital tendon dislocation.
What would you expect protocol for this patient to include, specifically regarding time frame?
Tenodysis
Takes biceps tendon off labrum and attaches to humerus so biceps can no longer prevent superior translation of humeral head.
- Tear type
- Degree of tear
- Partial or full-thickness tear
- Tear size
What factors influence progression of rehab?
0-4; 6-8; PROM; isometrics; mobilization
Maximal Protection Phase:
- ________________ weeks; ________________ weeks depending on the size of the tear.
- Early _____________________ as long as the patient tolerates it and is in line with repair. → IR/ER at 45-90 abduction; scaption, flexion, abduction
- Submax _____________________
- ____________________ of the elbow, wrist/hand, and GH/ST joints
- Weight-bearing Codman's
4-8; 4; PROM
Moderate Protection Phase:
- Lasting __________________ weeks.
- Begin ~ week __________________ s/p surgery (depending on size of tear).
- Want to see steady, progressive _____________________ improvement.
125; 60; 60; 90
At 4 weeks (start of Moderate Protection Phase):
- Flexion >___________________
- ER >_________________
- IR >__________________
- Abduction >___________________
Full; 10-12
By the end of Moderate Protection Phase, patient should have __________________ PROM. → Usually ___________________ (sometimes 14) week point.
10-14; Sharpey's fibers; AROM; functional; using
Minimal Protection Phase:
- Takes over at the end of Moderate Protection Phase (~_________________ weeks s/p surgery).
- __________________ are not considerable until ~12 weeks.
- At beginning of phase, work on full _____________________, gradual increase in strength (it should be _______________________ for household activities), and functional use of UE (dressing, opening doors, etc.).
- Note: If the patient is not __________________ the arm for daily things due to pain, etc. then not ready for the minimal phase).
80-90%
Most patients will have good prognosis s/p surgical rotator cuff repair. ____________________ of strength back in 1 year.
Impingement; overuse; deceleration
Bicipital Tendinitis MOI:
- Secondary to ____________________
- Occur directly through _____________________ during overhead movement with ______________________ component

Excursion; transverse
Bicipital Tenidinitis Pathomechanics:
- Probably due to large ______________________
- Laxity of ______________________ ligament
Coracohumeral ligament
An important restraint of the biceps tendon.
Bicipital groove; painful arc; overhead; deltoid; Yeargason's; Speed's
Signs and Symptoms of Bicipital Tendinitis:
- Tender to palpation over the biceps tendon in _____________________
- ______________________ on flexion or elbow ("sawing test")
- Pain with ____________________ use, pain at end range
- Decreased pain with rest, increased pain with activity
- Radiating pain to biceps muscle belly or _____________________ insertion (like impingement)
- Pain with rolling onto shoulder at night
- Pain with muscle activation and passive muscle stretch
- Full AROM and PROM
- Normal GH glides, if there is isolated biceps tendinitis
- Positive _____________________ or ____________________ test
- Often mimics rotator cuff (key tests would be specific muscle tests for biceps or supraspinatus; try not to bring in abductors when testing Speed's or Yeargason's)
- Similarity to RC tendinopathy
1-2 days; anterior; lateral; empty; painful arc; MMT; palpation; impingement; empty can
Signs and Symptoms of Bursitis:
- Gradual (over ___________________ Hertling/Dutton) onset of pain, often severe, onset may not correlate with a recently finished activity
- Intense, constant, dull, throbbing pain
- Pain with most movements in ___________________ and ___________________ shoulder
- Decreased AROM and PROM (noncapsular pattern) with pain or maybe full ROM with mid-range pain or end range pain (variable presentation)
- ___________________ end feel or end range pain
- Positive ___________________
- Pain with ____________________
- Pain with ____________________
- Positive _____________________ tests
- Positive _____________________ test
1. Supraspinatus
2. Infraspinatus
3. Subscapularis
Which rotator cuff tendons are typically repaired?
1. Active ER
2. Active abduction
3. Active IR
4. All AROM because rotator cuff is always stabilizing!
5. PROM that would elongate or pinch the structure
What movements would be limited (contraindicated during maximal protection phase) for rotator cuff repairs?
3-4 weeks for minimal tears (much longer for tears >5 cm)
How long do you need to wait till patient is ready for AROM?