Cleft Palate and Craniofacial Abnormalities
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Movements of the velum, posterior pharyngeal wall, and lateral pharyngeal walls during VP closure.
The velum elevates and moves posteriorly, the posterior pharyngeal wall move anteriorly and lateral pharyngeal wall moves medially to close against the velum.
What is the purpose of VP closure during speech?
To separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity, to help produce more speech sounds.
What happens to sounds when there is a gap in VP closure?
Hypernasality
Nasal Sounds
/m/, /n/, /ŋ/
Causes of clefts?
Genetic disorders, Chromosomal disorders, Viruses, Teratogens, Mechanical Interference
Ages in embryologic development do lip and palate fuse?
Lip - 7 weeks, Palate - 9 weeks
Complete, incomplete, unilateral, bilateral
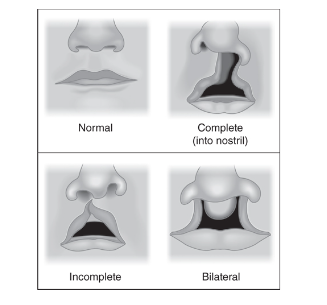
Problems that can occur due to cleft palate.
Velopharyngeal insufficiency (speech & resonance affected), feeding problems, Eustachian tube malfunction, hypernasality, glottal stops
Glottal Stops
A speech sound produced by briefly closing the vocal cords (glottis)
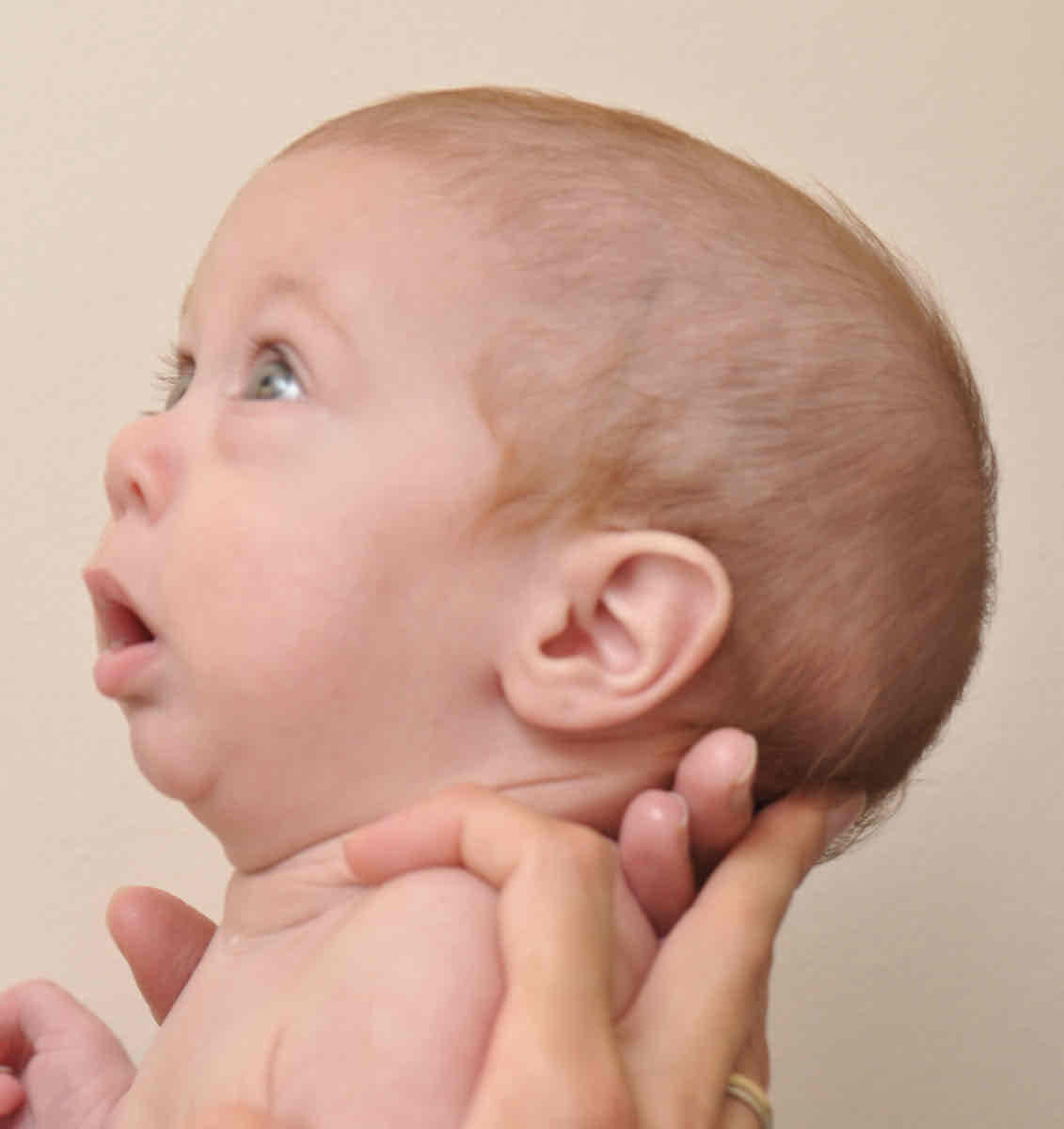
Pierre Robin
underdeveloped mandible, Retracted and elevated tongue into the pharyngeal airway, Cleft of the hard and soft palate, Digital anomalies (fingers & toes), Conductive hearing loss, Severely delayed language
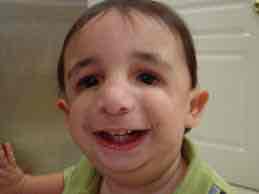
Trencher Collins
Underdevelopment of cheekbones, Underdevelopment of mandible, malformation of external ear and ear canal, Conductive hearing loss, Cleft palate, Normal intellectual and language development
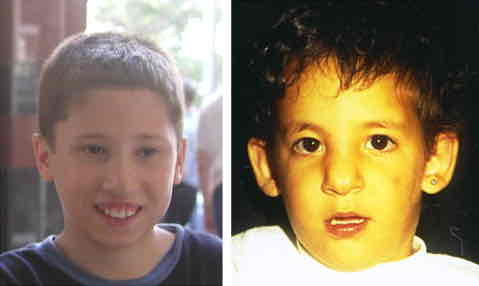
Velocardiofacial
Small stature, Broad, flattened nose and underdeveloped cheekbones, Delayed onset of expressive language and persistent language difficulties, Cognitive behavior is concrete, sometimes with perseverative behaviors, May not be detected until later in life
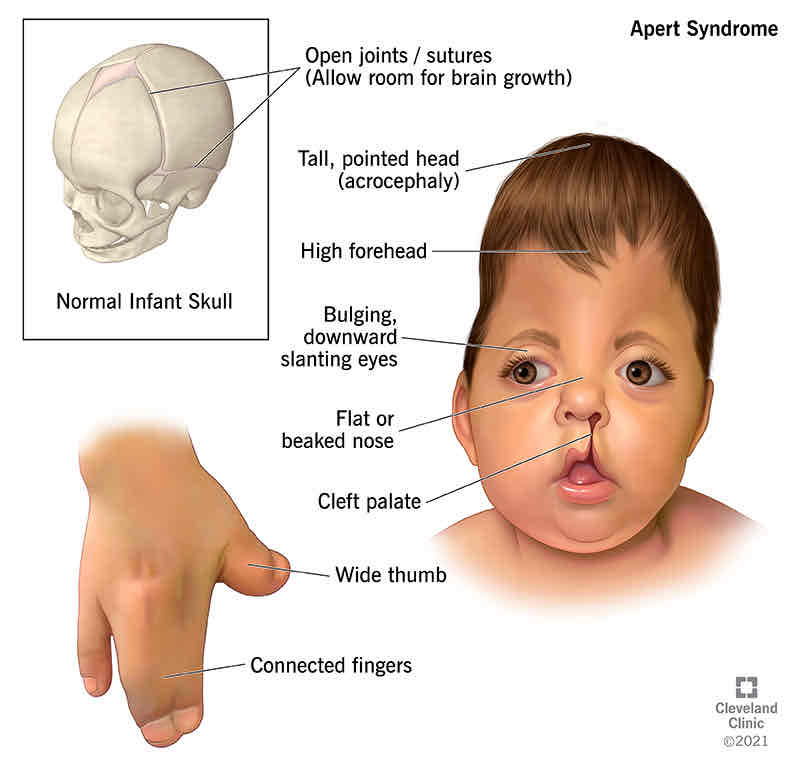
Apert
Craniosynostosis = premature closing of skull sutures with forehead disfigurement, Syndactyly = webbing of fingers and toes with bone fusion, High, narrow palate; clefted only 30% of the time, Conductive hearing loss, Expressive language development typically delayed, Intellectual disability often
Difference between velopharyngeal insufficiency and velopharyngeal incompetence
Velopharyngeal insufficiency - Anatomical defects (not enough tissue), Velopharyngeal incompetence - Neurophysiological disorder (not enough movement)
Hypernasality
abnormal nasal resonance during the production of oral sounds
Nasal Emission
When there is an attempt to build up intraoral air pressure for consonants while there is a leak in the system
Obligatory errors
occur when structure is insufficient to support accurate articulation,
Compensatory errors
occur when articulation placement is altered in an effort to maintain normal manner, due to abnormal structure
Velopharyngeal mislearning
learned misarticulations that cause nasal emission and sometimes hypernasality, despite normalized/repaired velopharyngeal structure and physiology
Nasometry
-What method allows for measurement of the acoustics of speech?
Videofluoroscopy
-What methods allow for observation of the structures?
-What are the 3 main treatments for cleft and VPI?
Surgery, Prosthetics, Speech Therapy
-At what ages are the lip and palate typically repaired?
Cleft Lip repair done between 10 and 12 weeks (3 months), Cleft palate done between 9 and 12 months
Palatal obturator
a removable device that covers an open palatal defect
Speech bulb
A removable device that fills in the velopharyngeal space
-Why would a child wear nose plugs during therapy or at home?
So air doesn’t come out their nose. Help them learn how to make sounds correctly so that when they do get surgery they are better at pronouncing sound.
Goals for speech therapy
correct speech sound placement and production.