CHM 104 Unit 3 Study Guide
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
activation energy
amount of energy needed to break bonds to allow new bonds to form
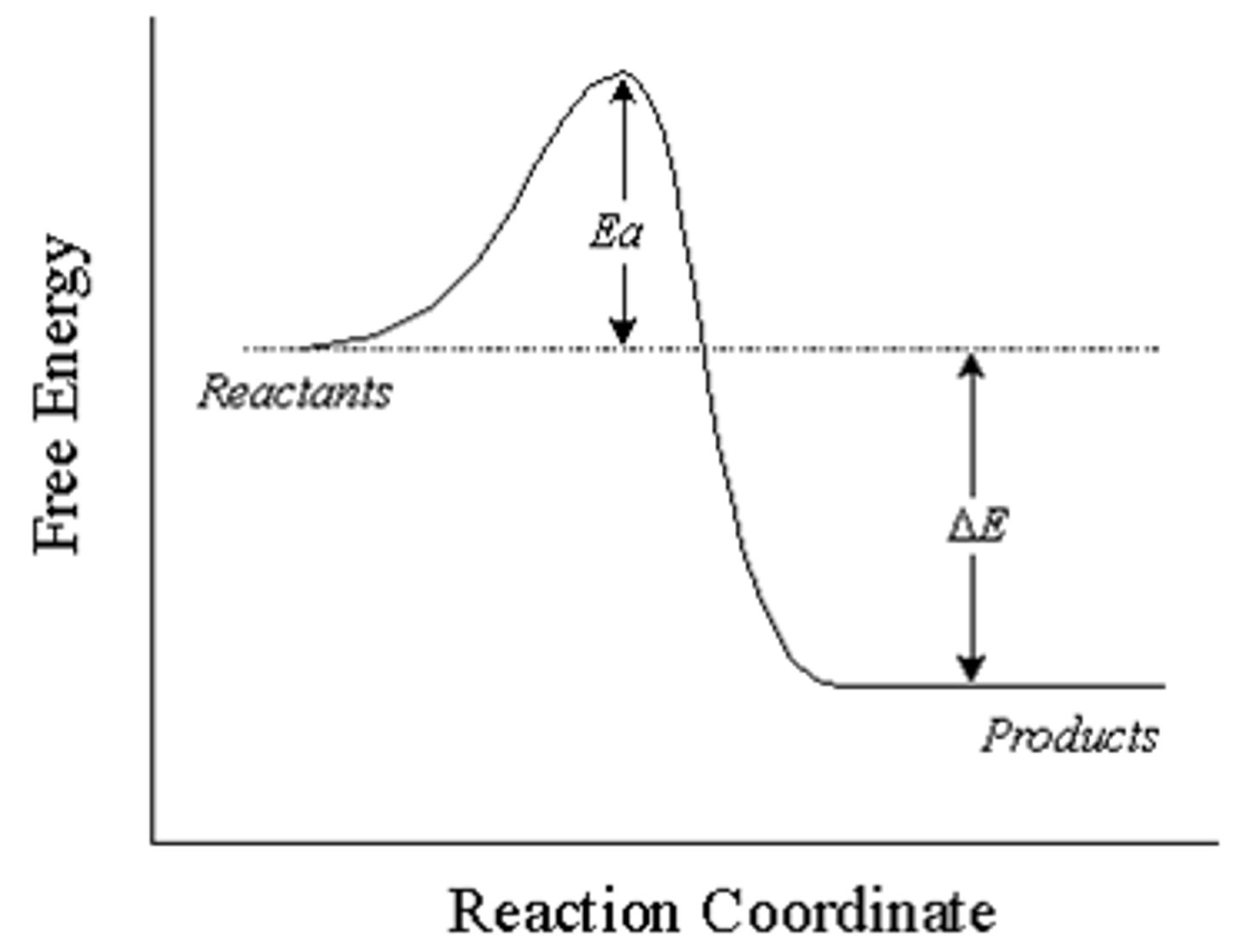
exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
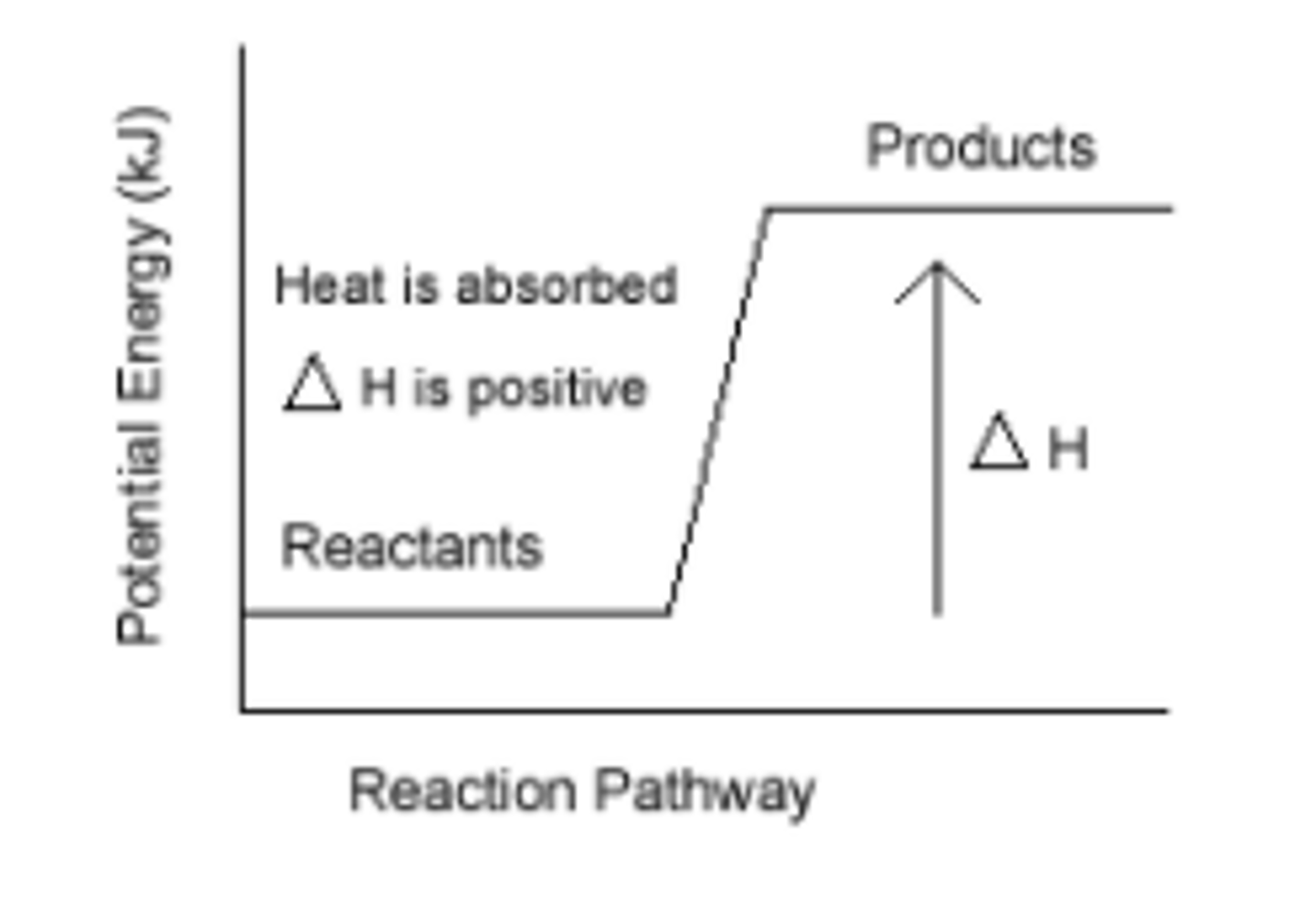
endothermic reaction
A reaction in which energy is absorbed
fat calorie content
9 calories per gram
protein calorie content
4 calories per gram
carb calorie content
4 calories per gram
Adding the proper catalyst will...
speed up reaction rate
Decreasing temperature will...
slow down reaction rate
Decreasing volume will...
speed up reaction rate
Increasing pressure will...
speed up reaction rate
enzyme
a molecule which improves conditions for a reaction
synthesis
A + B -> AB
decomposition
AB -> A + B
exchange reaction
A + BC -> AB + C
double exchange reaction
AB + CD -> AD + BC
reaction which gains oxygen
oxidation
reaction which loses hydrogen
oxidation
reaction which loses electrons
oxidation
reaction which becomes more positive
oxidation
reaction which loses oxygen
reduction
reaction which gains hydrogen
reduction
reaction which gains electrons
reduction
reaction which becomes more negative
reduction
monosaccharide
a single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose
glucose, fructose, galactose
monosaccharides
"simple sugar"
monosaccharide
disaccharide
2 monosaccharides bonded together
sucrose, lactose, maltose
disaccharides
oligosaccharide
composed of 3-10 monosaccharides bonded together
polysaccharide
long chain of hundreds to thousands of monosaccharides
starch, cellulose, glycogen
polysaccharides
pentose
a monosaccharide with 5 carbons
What is the most abundant monosaccharide in nature?
glucose
D-glucose
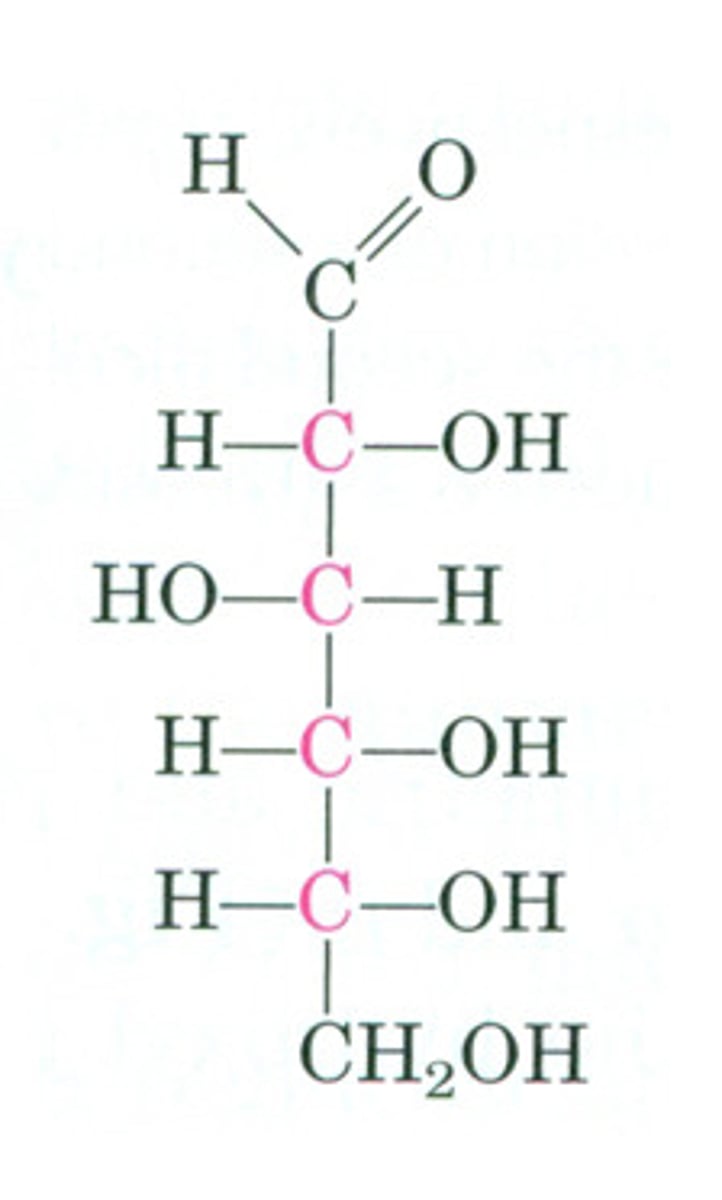
chiral carbon
a carbon atom that is bonded to four different atoms or groups
D- carbohydrate configuration
OH- on the last chiral carbon is on the right
L- carbohydrate configuration
OH- on the last chiral carbon is on the left
alpha monosaccharide
aldehyde and the OH- on the last chiral carbon are in opposite configurations
beta monosaccharide
aldehyde and the OH- on the last chiral carbon are in the same configuration
amylose
makes up ~20% of starch; glucose storage in plant cells
amylopectin
makes up ~80% of starch; glucose storage in plant cells
glycogen
energy storage in animals
cellulose
plant structure; not digestible by humans, but does assist in small and large intestines
chitin
insects' and crustaceans' exoskeletons
How many amino acids are found in the human body?
20
How many essential amino acids are there?
10
essential amino acid
an amino acid that the body cannot make and must obtain from food
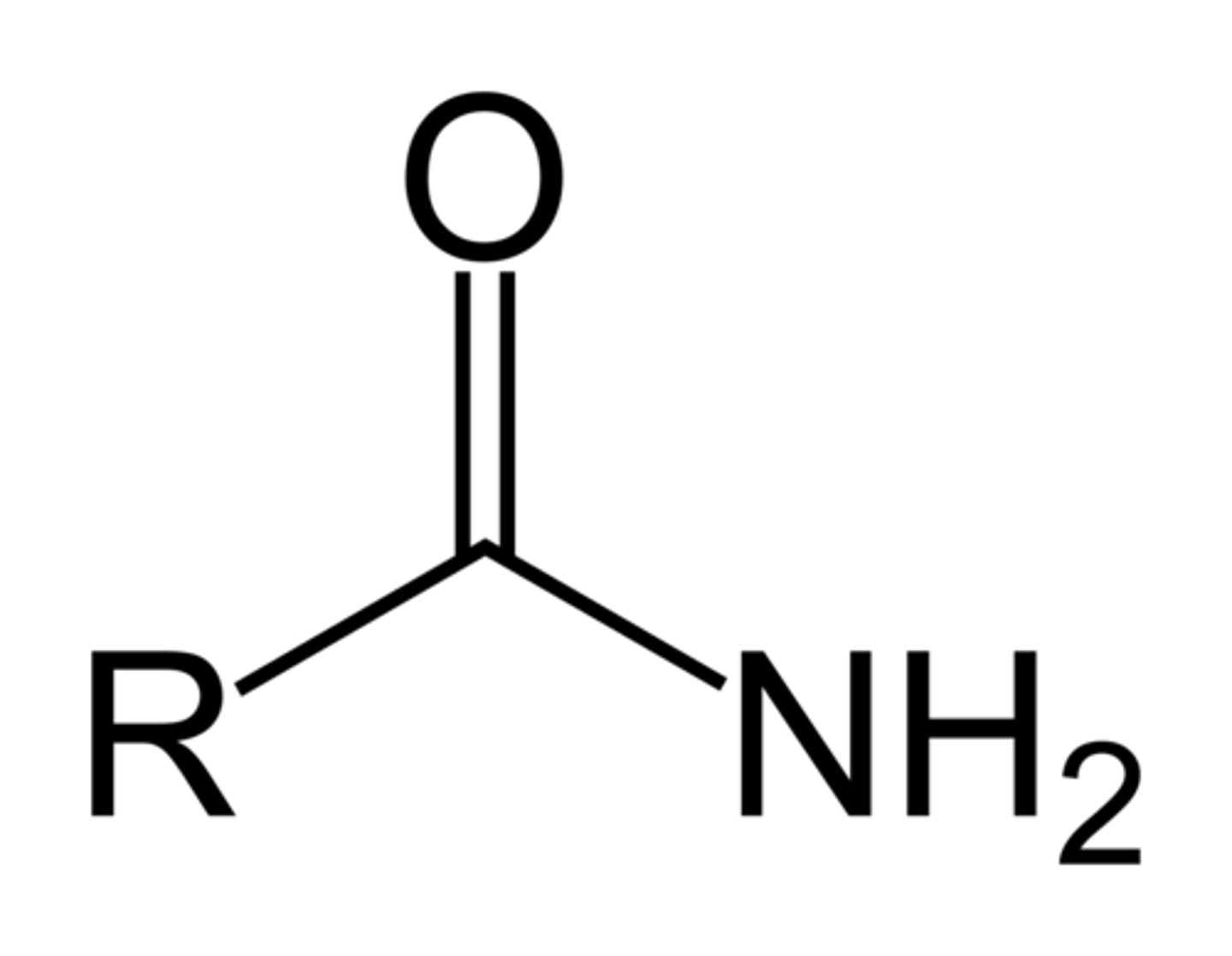
amide
non-polar amino acid
side chain is exclusively H & C
polar amino acid
uneven distribution of electrons
polar basic amino acid
uneven distribution of electrons; more negative
polar acidic amino acid
uneven distribution of electrons; more positive
primary amino acid structure
a sequence of amino acids
secondary amino acid structure
alpha helix or beta pleated
tertiary amino acid structure
interactions of side chains
quarternary amino acid structure
polypeptide chains reacting with each other
enantiomer
isomers that are mirror images of each other