HSCI 100 Reproductive System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Scrotum
Sacs that hold the testes
– Help regulate the temperature of the testes: 37oC is too warm and
inhibits spermatogenesis
Testes
Paired organs that produce sperm and male sex hormones
– Composed of seminiferous tubules where sperm are produced
continuously from puberty and includes process of meiotic cell division
– Sertoli cells help nourish sperm and regulate the
process of sperm production
– Leydig cells, between seminiferous tubules. Produce the male
hormones (androgens, e.g. testosterone
Epididymis
stores and matures sperm
Most sperm do not survive
Spermatogenesis
- Process of making sperm in Homo sapiens males
– From meiosis, all 4 haploid cells generate sperm
– A continual process after puberty
– A healthy male produce an avg 100 million sperm daily, and an ejaculate contains between 40 and 300 million sperm
Oogenesis
– Process of making eggs in females
– During meiosis 1 egg and 3 polar bodies are formed
– Polar bodies hold discarded chromosomes and disintegrate
– Female Homo sapiens are born with all their follicles
– 6-7 million follicles in fetuses, reduced to 1-2 million at birth
and to 400,000 ova) by puberty
– Normally 1 egg per month is released and ~400 during the
entire reproductive cycle
follicles
contains an unfertilized egg
Sperm production
Sperm are produced within the seminiferous tubules of the testes
• Sertoli cells help nourish sperm and regulate spermatogenesis
• Sperm are stored and mature in the epididymis
(spermiogenesis, cell differentiation
pathway)
Sperm anatomy
3 parts:
– Head: covered by a cap called the acrosome which stores enzymes needed to penetrate the egg
– Middle piece: contain mitochondria to make energy (ATP)
– Tail: A flagellum that provides movement for the sperm
3 glands that contribute to semen
Seminal vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Seminal vesicles
produces a fluid with fructose that provides energy to sperm
Prostate gland
produces an alkaline fluid to help buffer the acidic pH in the vagina
– May enlarge with age and this cuts off flow from the urethra
– Most of the time benign and curab
Bulbourethral glands
produces a clear fluid that lubricates the urethra
negative feedback
regulatory mechanism that helps maintain homeostasis by adjusting hormone levels
The endocrine control of male reproduction is regulated by negative feedback mechanisms involving testosterone and inhibin, which inhibit the release of hormones (GnRH, LH, and FSH) from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland when their levels are sufficient.
Penis
-Erection: A response to visual, auditory, olfactory, or
tactile stimuli
This stimulus causes a release of NO which causes the arteries to relax, triggering a signal transduction cascade that produces
(cGMP) which activates protein kinase G(PKG).
PKG phosphorylates target proteins and ion
channels, which lead to:
– Inhibition (Ca²⁺) entry into the smooth muscle cell.
– Sequestration of intracellular Ca²⁺ by the ER
– Opening of potassium (K⁺) channels, causing the cell membrane to hyperpolarize.
Cavernous bodies (made of erectile tissue) fill with blood,
compressing veins and slowing
blood returns; causing an erection.
Erectile dysfunction
When Cavernous bodies don’texpand enough to compress veins.
• Viagra blocks the phophodiesterase that breaks down cGMP, prolonging erections
Female anatomy: Genital tract
Ovaries
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
Clitoris
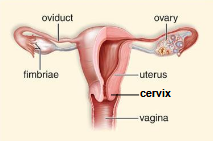
Ovaries
produce eggs and sex hormones
Fallopian tubes (oviducts)
transports egg from ovary to uterus and the site of fertilization
Uterus
site of embryo implantation and fetal development
Cervis
opening to the uterus
Vagina
organ for sexual intercourse and birth canal
Clitoris
-erectile organ and site of intense sexual feeling
-clirotal erection follows similar path to penis erection
The Ovary
-contains many follicles
-ovarian waves: when multiple follicles develop, but only one matures and lead to ovulation
-these cycles occur in avg every 29 days (‘monthly cycle’) from puberty until the end of ovarian and uterine cycles (menopause)
Ovulation is the monthly release of an immatur egg (oocyte) from the ovary when a follicle ruptures.
The Ovarian Cycle
Controlled by GnRH from the hypothalamus
Anterior pituitary secretes gonadotropic hormones; follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
Two phases:
-Follicular phase:
lasts 14 days
FSH promotes development of a follicle that secretes estrogen
Estrogen spike leads to surge in LH and ovulation on day 14
the released egg or follicle survives for around 24 hrs
- Luteal phase:
Occurs after ovulation
corpus luteum forms from the follicle that released the egg and produces progesterone to prepare the uterus for a potential pregnancy
If pregnancy does not occur, then menstruation begins
Menstruation
the regular discharge of blood and mucosal tissue from the inner lining of the uterus through the vagina
Hormonal control of the ovaries
similar to male, except it follows a monthly cycleand the ovaries make more progesterone and estrogen than testosterone
Uterine cycle
29-day cyclic event in the uterus
days 1-5: low levels of estrogen and progesterone, causing endometrium to disintergrate and menstruation occurs.
days 6-13: increase in estrogen causing the
endometrium to thicken
day 14: ovulation
Days 15-29: higher progesterone causes endometrium to further thicken in preparation for developing embryo.
If the egg is not fertilized, then the corpus luteum naturally
regresses and the endometrium breaks down
If the egg is fertilized and implants, human chorionic gonadotropin
(HCG) is made by the embryo and this maintains corpus luteum
and endometrium (n.b. hCG is what pregnancy tests detect)
Fertilization and Pregnancy
Fertilization: when a sperm and an egg combine to form a zygote
Pregnancy: begins with implantation into the endometrium, usually
6-12 days after fertilization