Aerobics Quiz 1
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What is wellness?
Process we undergo to become the best version of ourselves
What are the holistic aspects of wellness?
Mental, intellectual, financial/resource, spiritual, social, environmental, occupational
Wellness is a __ process
Fluid - not stagnant
What are the components of physical fitness?
Cardiorespiratory endurance, muscle strength, muscle endurance, flexibility, body composition
What can heart rate tell us and what is usually the result of higher fitness in terms of heart rate?
Can tell us about the stress levels in our body, our physiology, and the strength of our heart
As a result of aerobic fitness, HR is generally lower
What is the transtheoretical model of change (stages of change) and its components?
Evidence-based process - a framework for understanding how the process of change occurs
Precontemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance, termination
What is the precontemplation stage of change?
No current plans to change unhealthy behavior
What is the contemplation stage of change?
Aware of needed change, but unsure of plan
What is the preparation stage of change?
Planning to take action and is aware of the process
What is the maintenance stage of change?
Change turns into a habit and needs less conscious effort
What is the action stage of change?
Actively doing things to bring about change - motivation and commitment
What is the termination stage of change?
Healthy behavior has become normal behavior
What do SMART goals stand for?
Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-frame
What is the principle of overload?
Challenge of stress so the physiology adapts to be stronger, have more endurance, be more flexible, etc
What is the principle of progression?
Extension of overload - overload should increase gradually
10% rule - training intensity/duration of exercise should not be higher than a 10% increase per week
What are the principles of fitness?
Overload, progression, specificity, reversibility, recuperation
What is the principle of specificity?
Make sure your goals align with your training - make it muscle specific
What is the principle of reversibility?
If you don’t engage in it, you’ll lose it
What is the principle of recuperation?
Rest and recovery - exercised muscles can adapt to the stress by increasing endurance or becoming stronger
What aspect of physical fitness is the only permanent one?
Neurological motor patterns
What is the cycle of fitness?
Warmup - large, general movements to increase temp
Body of exercise
Cooldown - relax and breathe, easy rotational movements
Stretching
What is FITT?
Frequency, intensity, time, type
What does frequency mean in FITT for cardiorespiratory fitness?
The general recommendation for exercise frequency is 3-5 sessions a week to achieve near-optimal gains in cardiorespiratory fitness with minimal risk of injury
What does intensity mean in FITT cardiorespiratory fitness?
Cardiorespiratory fitness increases when the intensity is more than 50% of VO2 max; this level is often called the training threshold
Intensity + time = overload
What does time mean in FITT cardiorespiratory fitness?
In general, exercise durations most effective in increasing cardiorespiratory fitness are between 20-60 minutes
What does type mean in FITT cardiorespiratory fitness?
Any type of aerobic activity that you enjoy enough to do consistently will help increase and maintain your cardiorespiratory fitness
What is cardiorespiratory endurance?
Ability to perform aerobic exercise for a prolonged period of time
What does cardiorespiratory endurance promote?
Increase in energy availability, weight loss, and a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
What is the measurement of cardiorespiratory endurance?
VO2 max (maximal aerobic capacity) = the maximum amount of O2 the body can take in and use during exercise
What parts are included in the cardiovascular system?
2 parts to the heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, alveoli, ATP
What are the 2 parts of the heart?
Right - pumps O2-depleted blood into lungs in a pathway called the pulmonary circuit
Left - pumps O2-rich blood into tissues in a pathway called the systemic circuit
What are arteries?
Carry O2-rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body
What are veins?
Carry O2-depleted blood from the body’s tissues back to the heart
What are capillaries?
Have walls where O2 and nutrients are delivered to tissues, and CO2/waste is picked up from tissues and taken to the heart
What are alveoli?
Tiny air sacs in the lungs
What is ATP?
Is made and stored in small amounts in muscles and other cells - ATP breakdown releases energy that your muscles use to move
What is the equation for HRmax (maximum heart rate)?
206.9 - (0.67 x age)
What is the equation for HRR (heart rate reserve)?
HRmax - resting HR
What is the equation for THR (target heart rate)?
1) (0.5 x HRR) + RHR —> low
2) (0.85 x HRR) + RHR —> high
What is the training threshold?
Training intensity above which there is an improvement in cardiorespiratory fitness - the intensity is approximately 50% of VO2 max
What is target HR (THR)?
Range of HR’s that corresponds to an exercise intensity of approximately 50-85% VO2 max - range results in improvements in aerobic capacity
What is HR reserve (HRR)?
Difference between the max heart rate and the resting heart rate
What is muscle strength?
Maximum amount of force that can be generated in a single muscle or group of muscles or in a movement
What is muscle endurance?
Ability of your muscles to produce a force repeatedly for many reps/period of time
What develops first, muscle strength or endurance?
Strength
What are the benefits of muscle strength/endurance?
Toning, healthy metabolism, better bones, back health, confidence, stress management
Muscles work in ___ to allow ___
Pairs, extension
Pectorals
Biceps brachii
Rectus abdominis
External oblique
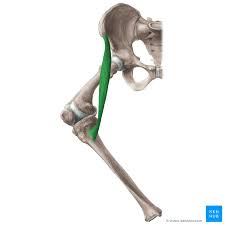
Sartorius
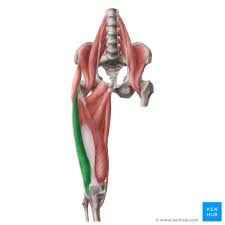
Vastus lateralis
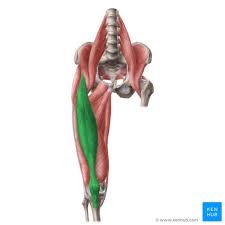
Rectus femoris
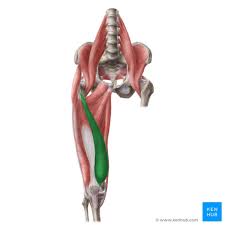
Vastus medialis
Tibialis anterior
Deltoid
Trapezius
Triceps brachii
Latissimus dorsi
Gluteus maximus
Hamstring group
Gastrocnemius
What is an isotonic muscle contraction?
Same tone - movement of a body part
What are the 2 phases of isotonic muscle contractions and what do they mean?
Concentric - muscle tenses as it shortens against resistance/gravity (positive work)
Eccentric - muscle tenses as it lengthens while controlling body movement with gravity (negative work)
What is an isometric muscle contraction?
Same length - muscular tension, but body part does not move (ex: plank)
What is an isokinetic muscle contraction?
Same speed/movement - can include concentric/eccentric actions at constant speed using a specialized machine
What is hypertrophy?
Actual change in the size of the tissue
What are the guidelines for building muscle?
Train all major muscle groups 2 times within a 7-day period to gain strength and optimize muscle fitness
Intensity - heavier load for gaining strength, lighter load for general fitness (RM: rep max - heaviest weight, 1 rep only)
Rest period - 8-12 reps, 1:1 work to rest ratio
Duration - 30-45 minutes, 8-10 exercises
What are the benefits of flexibility?
Maintain strong posture/postural alignment
Reduce risk of injury
Allows you to be stronger/toned and build endurance
Relaxation
What are the 4 types of stretching?
Dynamic, static, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation, ballistic
What is dynamic stretching?
During the warmup, not holding, warm up muscle, and rehearse movements
What is static stretching?
During the cooldown, holding, elongate muscle, and decompress tightness
What is proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation?
Physical therapy/athletic training technique that uses a combination of active stretching and isometric contraction to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion
What is ballistic stretching?
Get to a point of stretch and then force the muscle to stretch further, often by bouncing - triggers the stretch reflex which is forcing a contractive muscle to stretch and could cause tearing
What are the FITT guidelines for stretching?
Frequency - stretch every time you exercise
Intensity - feeling mild tension/discomfort
Time - hold 10-30 seconds, 2-3 reps
Type - any of the 4 types
What is the stretch reflex?
A simple, involuntary muscle contraction that occurs when a muscle is stretched
What do muscle spindles do?
Specific structure within the muscle fiber that innervates back to the spinal column to let the body know it is stretching too far
What is the golgi tendon organ?
Senses the contraction/force that is being generated in the muscle and sends a response to relax
What are the factors influencing flexibility? What are they?
Genetics - structures, limb length, etc
Ligaments - tight connective tissues, not flexible, designed to hold bones together and maintain position
Tendons - connective tissue that attaches to bone, flexible
Muscle mass - high muscle mass can limit range of motion
Body mass - high body mass can limit range of motion
What are the 2 classifications of body composition?
Lean body mass and fat mass
What is lean body mass?
Low composition of lipids - bone, muscle, tendon, ligament, vital organs, hair, skin, etc
What is fat mass?
Fat tissue - essential and storage fat
What is essential fat?
Necessary for human physiology - part of our cell membranes, nervous system, and hormone production
What is storage fat?
Can fluctuate depending on how we feel and our activity levels
Where do males carry a higher body mass vs females?
Upper body
Do males or females have a higher body water?
Males
Females have ___ higher body fat % vs males
4x
What % of essential body fat do males have?
3-5%
What % of essential body fat do females have?
10-12%
What % of body fat do healthy college aged males have?
8-19%
What % of body fat do healthy college aged females have?
21-35%
What % of body fat is considered obesity in males?
>25%
What % of body fat is considered obesity in females?
>38%
What are the concerns for obesity?
Cardiovascular/heart disease
Orthopedic issues
Diabetes
Some types of cancer
What are the concerns for low body fat %?
Changes in hormones
Muscle loss
Osteoporosis
Higher chance of depression and anxiety
What are the ways to measure body composition?
Handheld device
Hydrostatic weighing
Dual x-ray absorptiometry
Air-displacement
Full body bioelectrical impedance
BMI
How does the handheld device measure body composition?
Uses electrical current to estimate % of body fat because more fat = longer for the electrical current to go through (combined with other aspects such as age, height, etc)
How does hydrostatic weighing measure body composition?
Method of determining body composition that involves weighing an individual on land and in a tank of water
How does dual x-ray absorptiometry measure body composition?
Low radiation x-ray