MCAT Redox
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1* Alcohol (reducing agent) + PCC or CrO2/pyrimidine(oxidizing agent)
aldehyde
2* alcohol + PCC or CrO2/pyrimidine(oxidizing agent)
ketone
aldehyde + H2CrO4/KMnO4/H2O2
Carboxylic acid
alcohol + KMnO4/H2Cr2O4
carboxylic acid
benzylic alkane + KMnO4
carboxylic acid
alkene can be cleaved by O3/Zn to form
aldehyde or ketone
alkene can be cleaved by O3/H202 to form
ketone/carboxylic acid
alkyne + O3/H2O2
carboxylic acid
alkene + OsO4 or KnMnO4, -OH
diol
alkene + mCPBA
epoxide
diol + NaIO4
aldehyde
ketone + mCPBA
ester
aldehyde + LiAlH4 (reducing agent)
1* alcohol
Ketone + LiAlH4
2* a;cohol
amide + 1. LiAlH4, 2. H+
primary amine
carboxylic acid 1. LiAlH4, 2. H2O
primary alcohol
ester + 1. LiAlH4, 2. H2O
primary alcohol
How is an alcohol oxidized to an aldehyde?
PCC (anhydrous)
Jones oxidation
reaction of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
Reagents necessary for 1* Alcohol→ Carboxylic acid
CrO3( super strong oxidant), h2so4, acetone
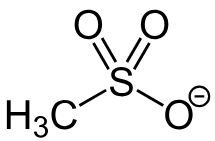
mesylate
Formation of mesylate requires
methylsulfonyl chloride + alcohol + base
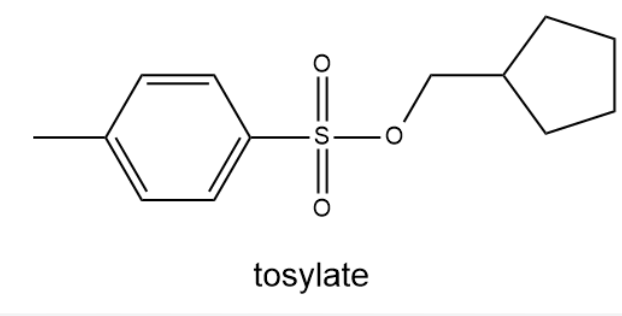
tosylate
how to form a tosylate
toulene sulfonyl chloride + alcohol
Role of mesyl and tosyl groups
make alcohol a good LG
protect alcohols
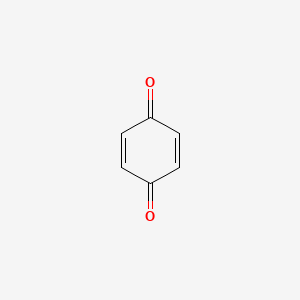
quinones
how are quinones formed
oxidation
of benzenediol
ubiquinone
biologically active quinone (Coenzyme Q)
electron carrier