4/5/6. Analytical Case Control Studies & Cohort Studies & Other Types of Studies
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what type of study?
Compares diseased individuals to non-diseased individuals – in relation to exposure status
case-control study
• Cases – have the outcome of interest
• Controls or non-cases – do not have the outcome
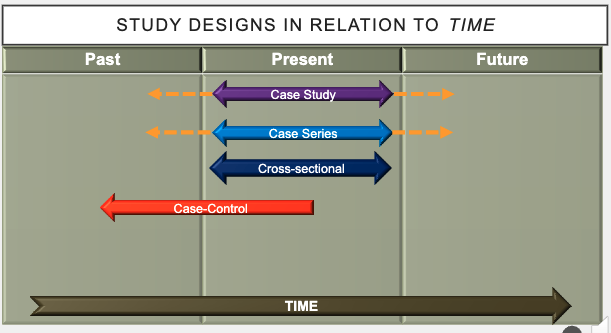
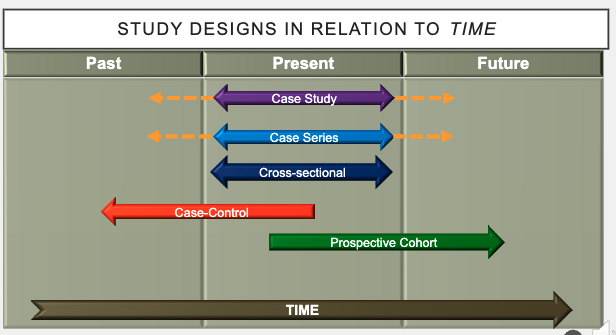
what are case control studies in relation to time?
retrospective (Start in present time and go back in time to evaluate risk factor exposure)
What type of study?
We measure the odds of disease among exposed versus odds of exposure among those with disease versus those without disease
case-control study
In case control studies, at the start of the study, the disease or outcome has not/already occurred, and cases and controls are grouped based on …?
has already occurred; the outcome/disease status
in case-control studies, has the disease/outcome already occurred at the start of the study?
yes. cases and controls are grouped based on the outcome/disease status
how are controls selected in case-control studies?
selected from same community, location, or hospital
similar characteristics as cases except for disease status
evaluate exposure info in controls in same manner as cases
In a __________ study in this sample say you want evaluate the variables that may have contributed to children wearing eye- glasses. So we can compare the children with eye-glasses (case group) to children not wearing eye-glasses (control group). We can retrospectively collect information family history, medical history, tv-watching, etc. We can then evaluate the odds of these possible risk factors to the outcome of children wearing eye-glasses (outcome could be astigmatism, myopia)
case-control
Association between exposure-outcome can be evaluated by estimating…?
odds ratios
how is odds ratio calculated?
Odds ratios are estimated based on the probability of disease among exposed individuals relative to the probability of disease among unexposed individuals.
what are the advantages of case-control studies?
• Efficient in design
• Shorter duration
• Less expensive
• Convenient for studying many exposures
• Efficient for rare diseases and for diseases with long latency period
• Measures of association can be calculated to evaluate exposure-outcome relationship (odds ratio)
what are the disadvantages of case-control studies?
retrospective nature makes it difficult to establish time sequence of exposure-outcome relationship
potential bias
what are different sources of bias?
recall bias
interview bias
reporting bias
misclassification bias
what type of bias?
Cases recall information differently when compared to controls
recall bias (can occur in case-control and cross-sectional studies)
what is the most common type of bias in case-control studies?
recall bias
• Cases remember and report their previous exposure experience differently from controls
• Ex: Moms of children with orofacial clefts recall risks more accurately
what type of bias?
Differences that occur in the recording or interpretation of information from participants
interviewer bias
what type of bias?
Ex: Those with periodontal disease are examined more frequently to evaluate oral health status versus those without
interviewer bias
what type of bias?
Those who smoke are interviewed more to evaluate oral health status versus those who do not smoke
interviewer bias
what study designs can interviewer bias occur in?
Cross-sectional, Case-control and cohort studies: Knowledge of a subject’s disease status or exposure status may lead to increased questioning by the interviewer
what type of bias?
Under-reporting of socially undesirable behaviors (Smoking, drinking)
Over-reporting (Exposure to chemicals, fluoride in water)
Cases may refuse to answer sensitive questions (Substance abuse)
reporting bias
misclassification bias is most common in what study design?
case-control studies
what type of study design can reporting bias occur in?
cross-sectional, case-control, cohort studies
what type of bias?
• Inaccurate case definitions or inclusion/exclusion criteria
• Participants are incorrectly ‘assigned’ or categorized into the wrong exposure or outcome group
• Can lead to diluted or exaggerated effects
misclassification bias
in relation to time, how are cross-sectional studies assessed?
at a point in time (slice of time)
temporality cannot be established
in relation to time, how are case-control studies assessed?
retrospectively
cohort studies are also called…?
prospective or longitudinal studies
what is a cohort?
any designated group of individuals
describe how a cohort study is designed.
1. Start with a group of people and identify an exposure.
2. Divide the cohort into exposed and unexposed groups (Smokers versus non-smokers).
3. Follow them over a period of time to observe the outcome (periodontal disease).
4. At the end of the study determine incidence of outcome among exposed versus unexposed
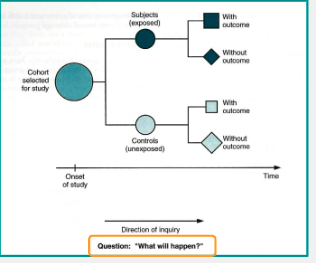
cohort study
can time sequence of events (temporality) be established in cohort study?
yes (due to prospective nature)
what measures can be calculated during cohort studies?
incidence (proportions) and incidence rates
describe cohort studies in relation to time.
prospective
what are advantages of cohort studies?
similar efficiency to RCT
more ethical than clinical trials
good for rare exposures (pesticides, cancer)
look at multiple outcomes due to single exposure
estimate incidence rates over time
establish temporality and causality
what are disadvantages of cohort studies?
NOT efficient for rare diseases
long duration (time, money)
additional resources needed
exposure status may change over time (smoking/drink patterns)
prone to loss (follow-up bias)
in case-control studies, participants are grouped by…?
disease status
in cohort studies, participants are grouped by…?
exposure status
what type of study?
• Participants are grouped by disease status
• Utilizes less time and money
• Can be used for rare diseases
• Multiple exposures can be studied
• Does not work well for rare exposures
• Prone to recall bias/information bias
case-control studies
what type of study?
• Participants are grouped by exposure status
• Long duration of follow-up so utilizes more time and resources
• Can be used for rare exposures
• Multiple outcomes can be evaluated
• May not work well for rare diseases
• Prone to loss to follow-up bias due to dropouts
cohort studies
what type of study design?
A detailed review of published articles on a particular research question
systematic reviews
in systematic reviews, what components must be clearly defined?
search criteria
inclusion/exclusion criteria
time period
what are advantages of systematic reviews?
summarize info from different sources
broadly generalized results
more reliable than individual sutides
highest quality of info
what are disadvantages of systematic reviews?
laborious
time consuming
difficult to combine info when methods and measures vary across studies
what type of study design is quantitative and formal epidemiological and used to systematically assess previous research studies to derive conclusions about that body of research?
meta-analysis
meta analysis is similar to literature review except…?
it is a statistical combination of results from 2 or more studies
what are the advantages of meta analysis?
most idea, efficient, highest quality
can combine with other study designs
highest statistical power (large sample size)
can be generalized and summary findings can be extrapolated
what are disadvantages of meta-analysis?
may not be possible in all systematic reviews
individual study biases affect results
variability in methods/approach
requires advanced statistical methods/software