PRD 146: Silver Amalgam
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
True dentalloy
GV black Produced the first commercial alloy called
Amalgam Formula
Black's Balanced Dental and 1% Zn. Plus Hg __ was incorporated into the ADA Specification for Dental Alloy in 1929
- 67% Ag
- 27% Sn
- 5% Cu
Smaller
In the 60s there were conventional low-copper lathe-cut alloys which had __ particles
lathe-cut
admixture of spherical Ag-Cu eutectic particles with conventional__
Metallic component of amalgam
- silver
- tin
- copper
- zinc
- palladium
- indium
41-51%
Besides the metallic component, how much mercury is in amalgam
Lathe cut alloy
irregularly shaped particles formed by shaving fine particles from an alloy ingot
Spherical alloy
small spheres of alloy particles produced by spraying a fine mist of liquid alloy into an inert gas environment
Admixed alloy
mixture of lathe-cut and spherical alloys
- good all around properties and is common today
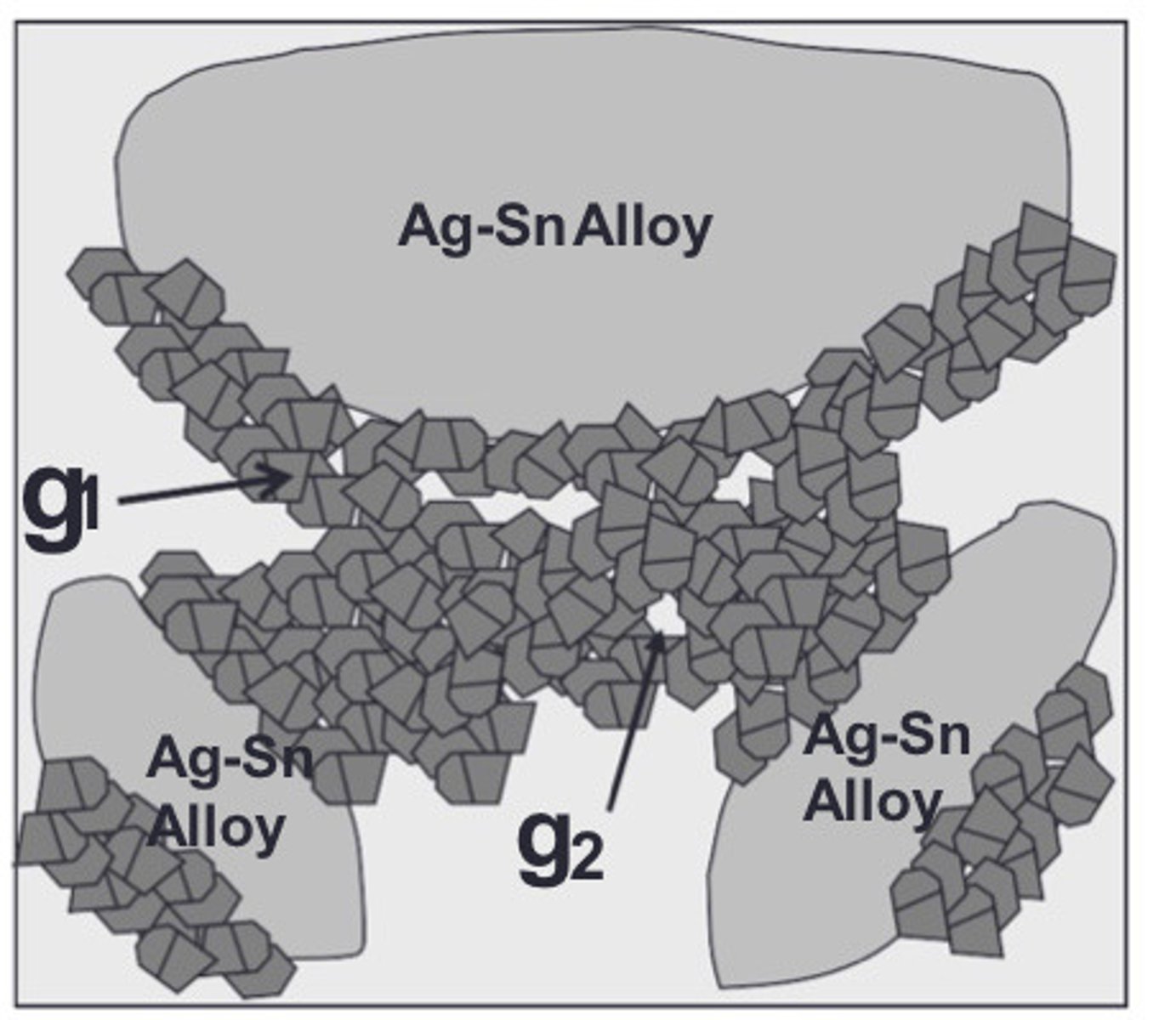
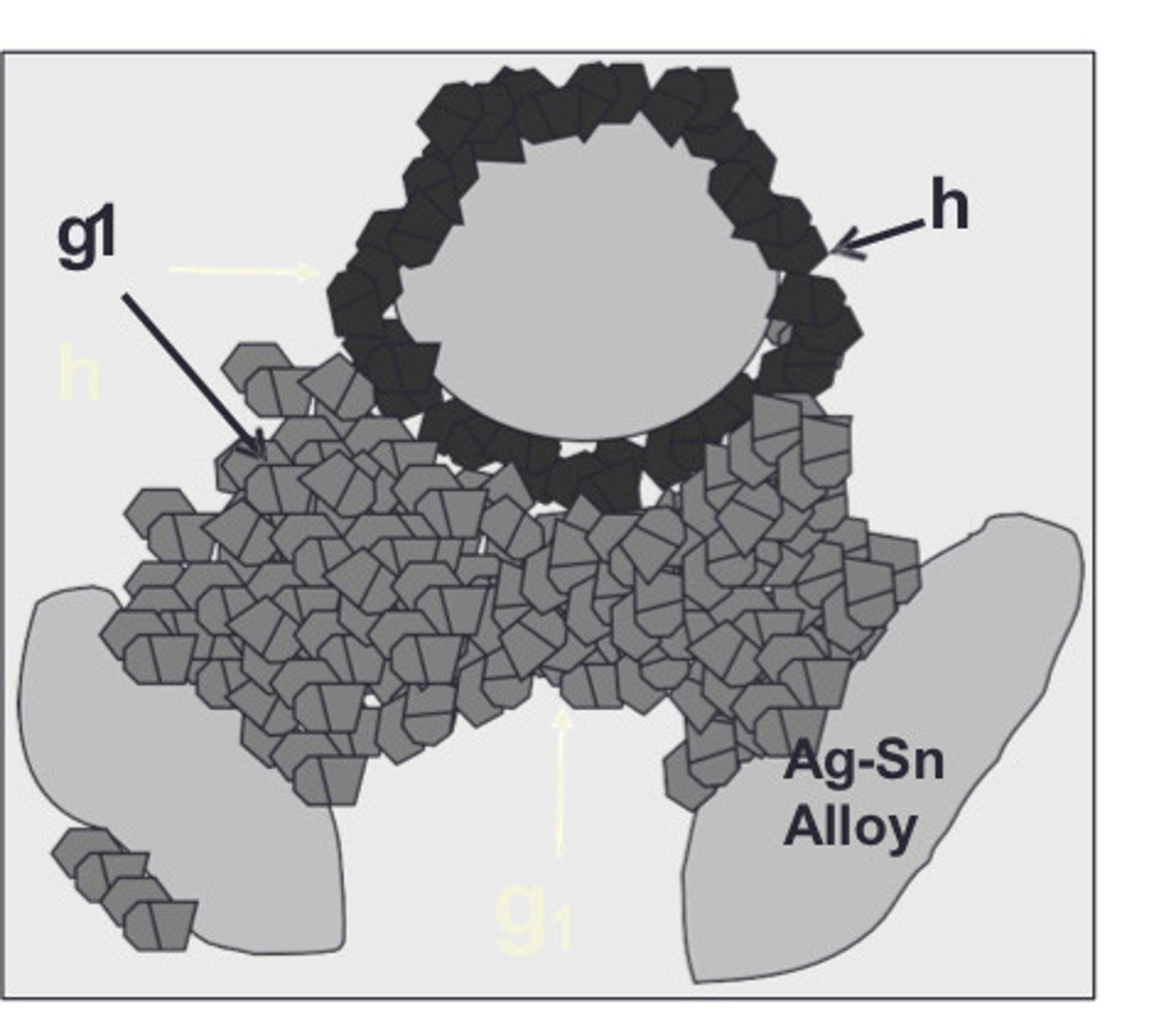
gamma 2 phase of amalgam
Tin and Mercury
CuSn now replaces gamma two with the ETA PHASE!
Weakest
The gamma 2 phase is the __ phase
Corrodes
The gamma 2 phase ___ fast and voids form
Hg
The corrosion in gamma 2 forms __ which reacts w/ more gamma
10%
The gamma copper reaction composed __ of volume
Corrosion
The volume decreases w/ time due to
gamma 1 phase
silver and mercury (admixed high copper alloys)
Gamma 2
The gamma 1 phase tries to skip the __ phase
Ivoclar Vivadent
- Palladium enriched
- admixed (dispersed phase) alloy
- high copper
Triturators
dilutions of potent powdered drugs prepared by intimately mixing them with a suitable diluents in 1:10 DILUTIONS
Silamat
The triturator used at pacific
8
The trituration should last at least __ seconds
Over trituration
• Rapid hardening
• Shortened working time
• Setting contraction(<< 1%)

Increased
Over trituration has __ compressive strength
Wet
Over trituration has a __ look
Under trituration
• Crumbly, grainy mix
• Excessive free Hg

Decreased
Under trituration has __ compressive strength
Increased
Under trituration has ___ setting expansion and corrosion
Condensation
- drives out trapped air
- adapt closely to prep wall
- press out excess mercury
- can help create tooth form
Silver amalgam properties
• Compressive Strength
• Tensile Strength
• Corrosion
• Thermal Conductivity
• Creep
20
You must wait __ hours before polishing amalgam
Mercury
During condensation it presses out excess
Compressive strength
Measures the pushing force that one needs to break or
crush a material
Enamel
The strength of amalgam is more than adequate, similar to __ (384 MPa)
Tensile strength
Maximum load that a material can support
without fracture when being stretched,
divided by the original cross-sectional area
of the material
Pupal depth
When prepping for amalgam __ is important so you have enough material for compressive/tensile strength
48 Mpa
Tensile strength of Admixed alloy
thin
Amalgam is brittle when place in __ sections. Amalgam should have sufficient bulk to resist these forces
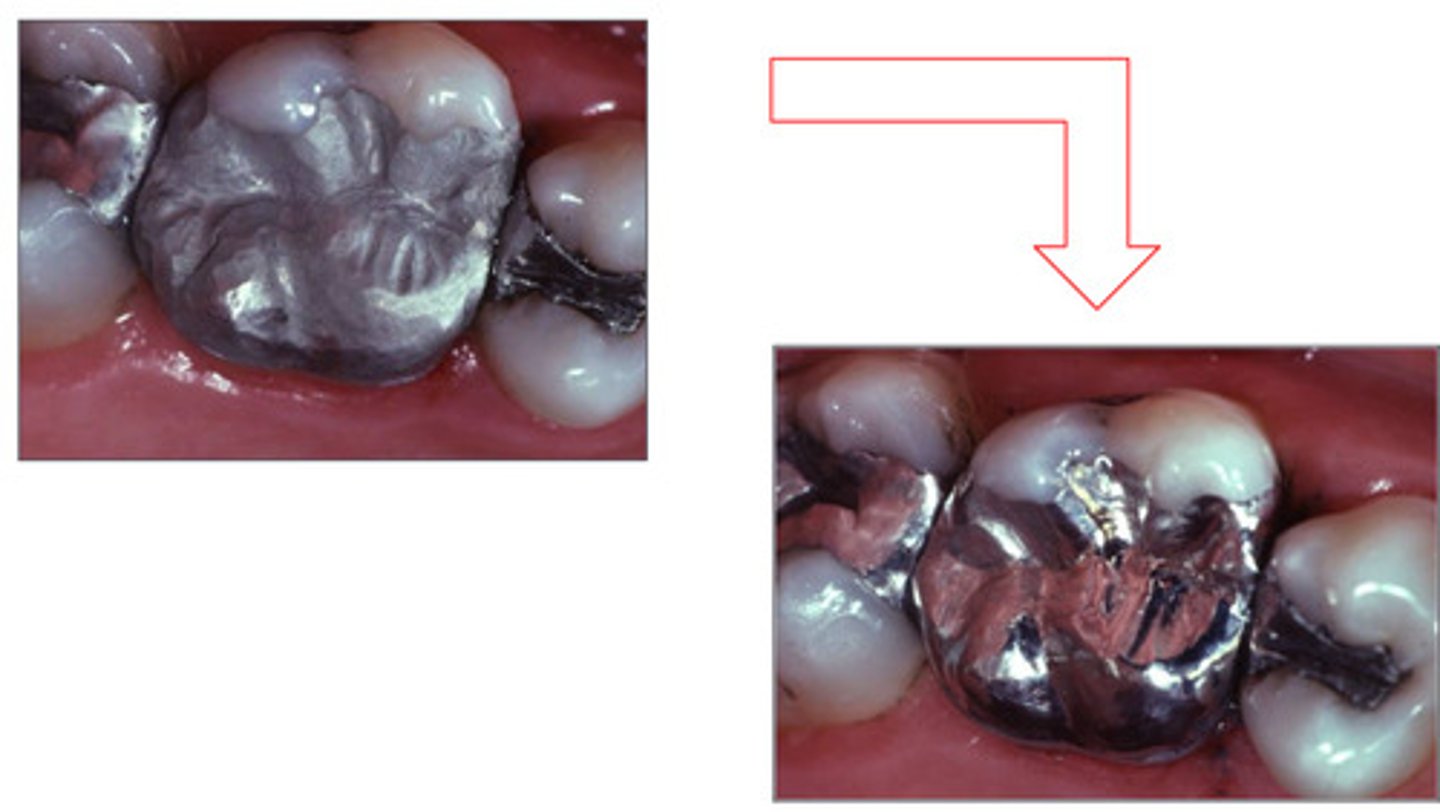
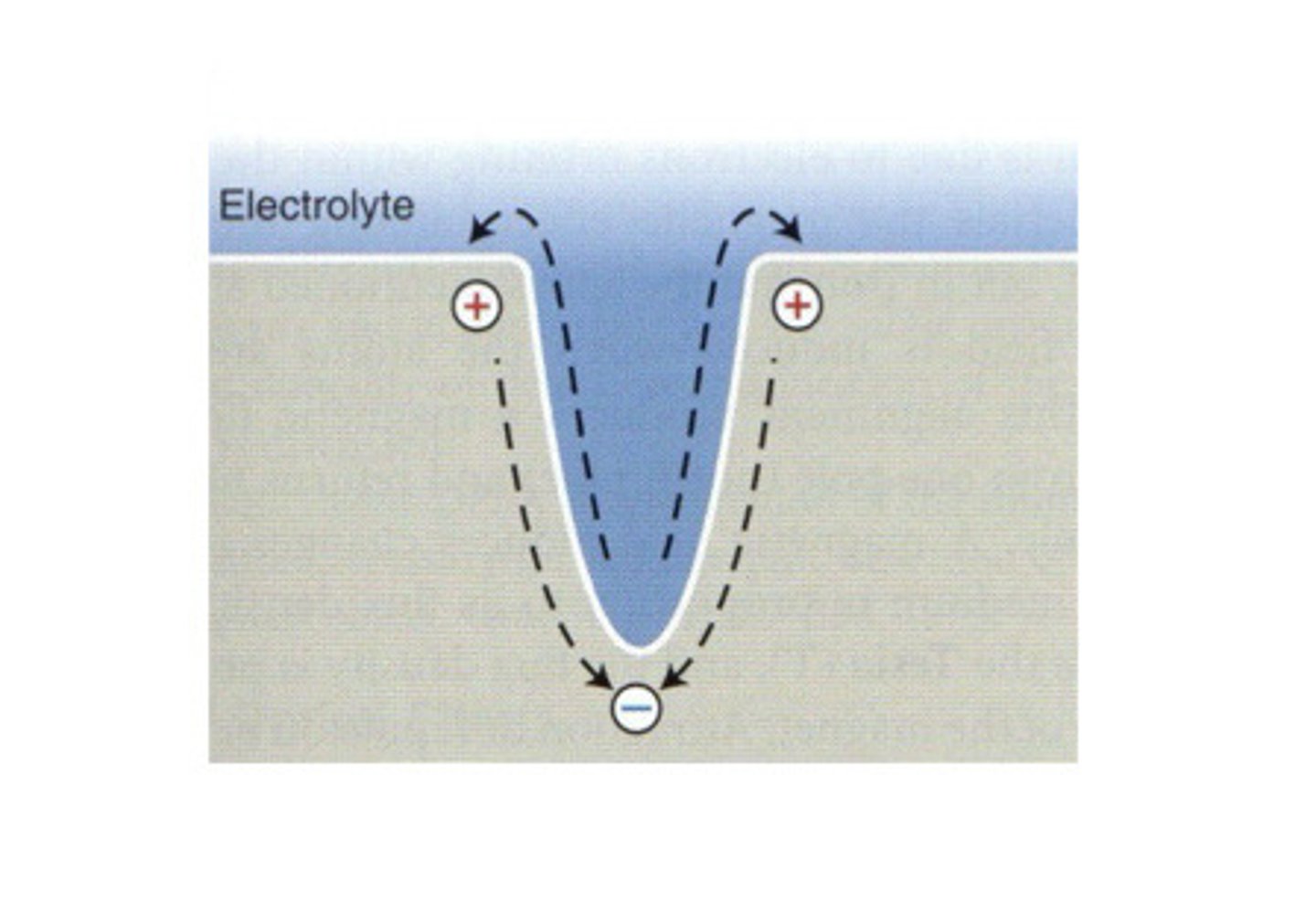
Corrosion
the deterioration of a metal as a result of
chemical reactions between it and the surrounding
environment. Both the type of metal and the
environmental conditions determine the form and rate of
deterioration.
margins
Corrosion is good for us because when it rusts, the oxidation product seals the __
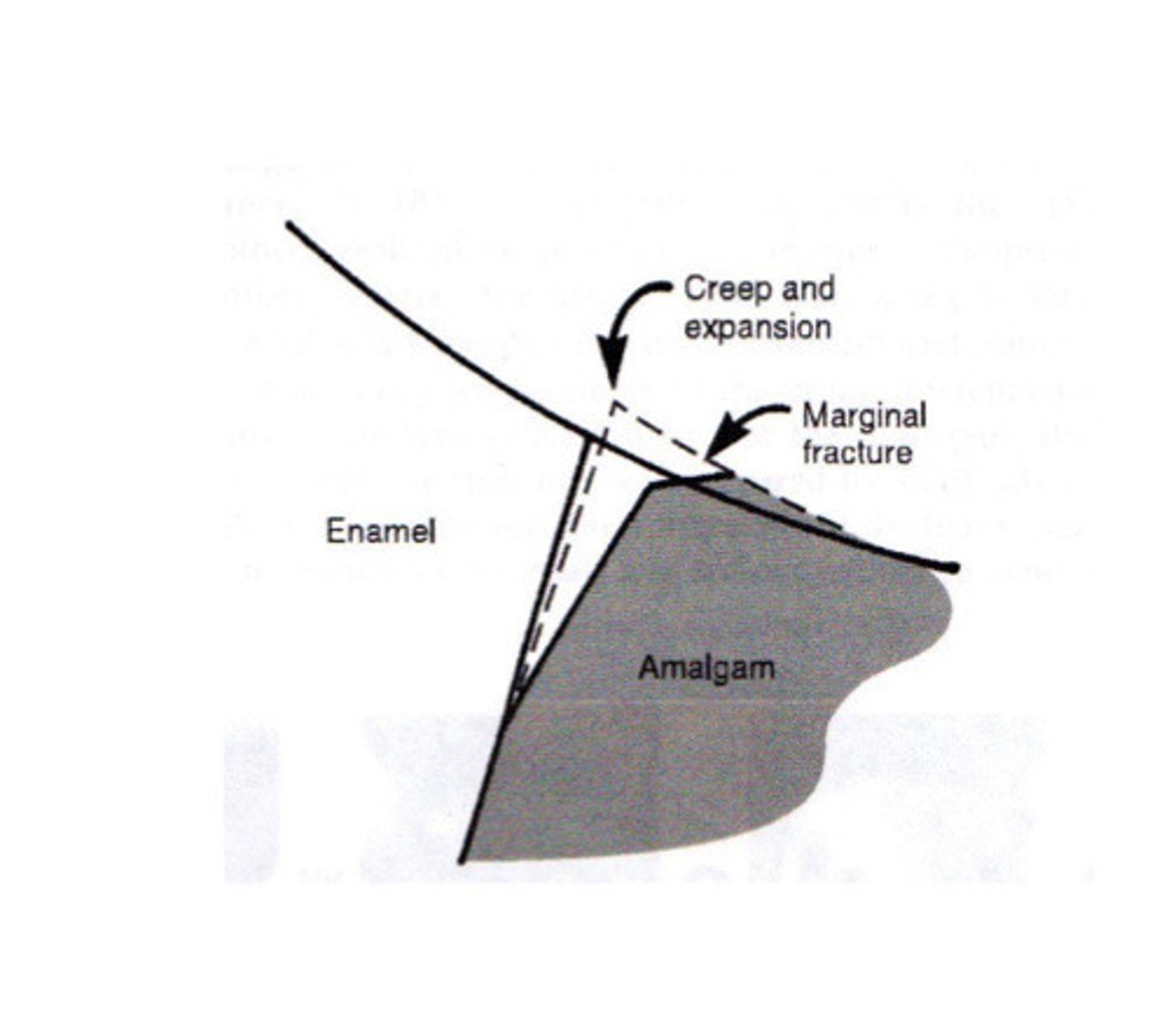
Creep
Time dependent plastic strain of a solid under a static load or constant stress
copper
Creep is Much lower in high __ alloys but still
present
10; day
The amalgam is Very fragile for the first __ hours and durable after the first __
caries
Amalgam is Resistant to recurrent __
Macromechanical retention
Amalgam is a direct restorative material that is held in place by what? (No bond to tooth structure)
Bulk
Amalgam requires __ and often chips at margins (flash and deformation)
Local
There are __ health effects on amalgam bearers and dental providers
Environment
Health effects of mercury entering the __ from dental sources
Class II lesion
Caries affecting proximal surfaces of molars and premolars
Advantages of amalgam
• Strong, durable, economical
• Easy to use
• Self sealing ability over time (corrosion)
• Wear resistance similar to tooth
• Low micro leakage with time
Disadvantage of amalgam
• Metallic color
• Does not bond to tooth- relies on mechanical retention
• Marginal breakdown
• Controversy over mercury in the alloy as a health concern
GV Black's 7 Steps of Cavity Preparation
1. establish outline form
2. obtain resistance form
3. obtain retention form
4. obtain convenience form
5. remove carious dentin
6. finish enamel walls and cavosurface margins
7. cleaning the preparation
Outline form
• Eliminate carious tooth structure
• Margins should be placed on sound tooth structure
• Leave adequate cuspal support and marginal ridge support
• Include carious fissures and grooves
• Should be able to adequately finish the restoration
• Cavosurface is smooth and fluid
• No sharp angles
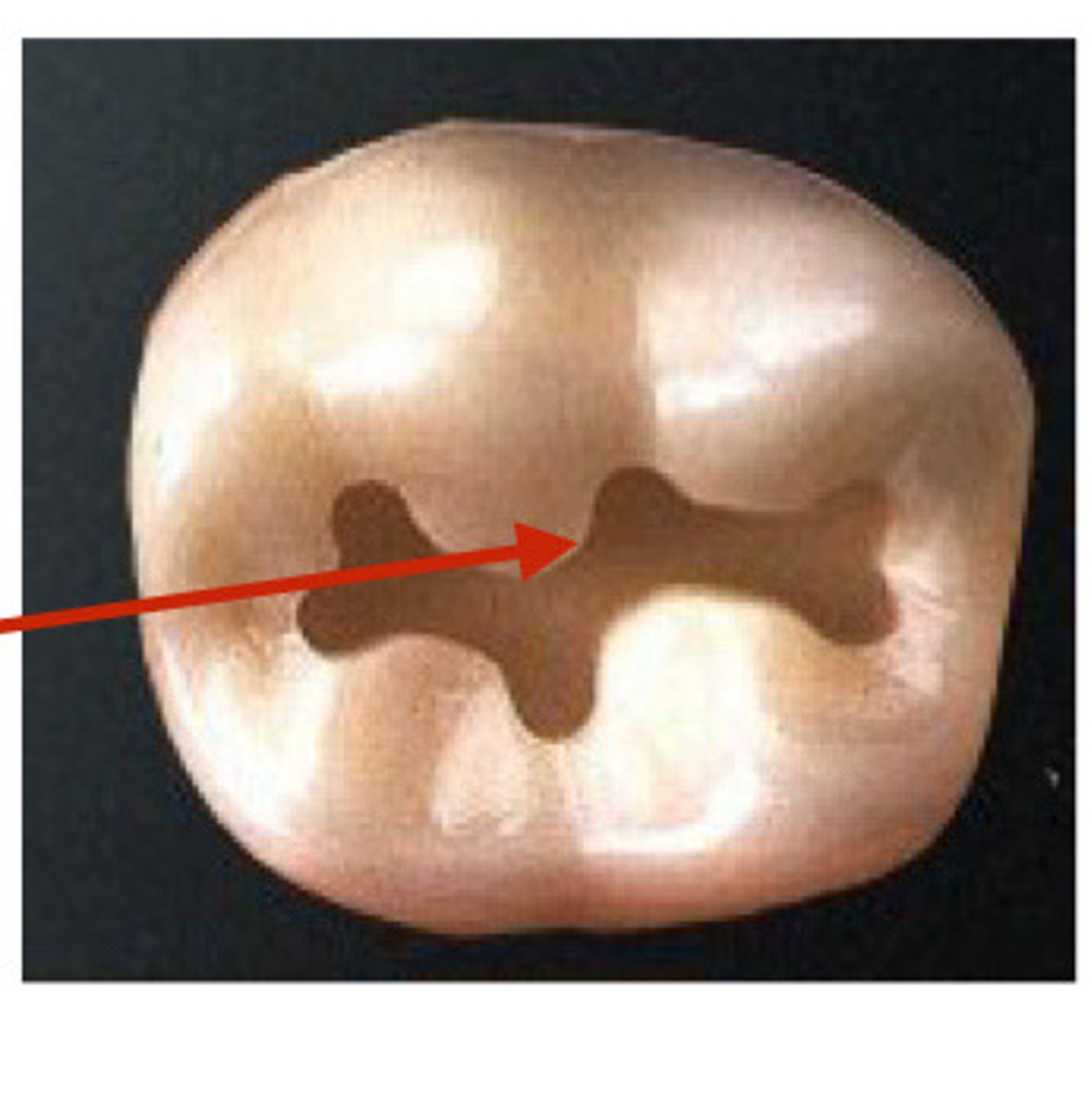
Resistance form
The shape and placement of the cavity walls that best
enables both the tooth and the restoration to withstand
occlusal forces without fracture
Occlusal pulpal depth
Amalgam requires proper __ for resistance form
Flat
For amalgam resistance form you must have __ pulpal floor perpendicular to forces of mastication
Bulk
For amalgam resistance form have sufficient __ of material
1.0mm
For resistance form the Isthmus width of __ to prevent fracture of the remaining tooth structure
Retention form
Shape or form of the cavity that best permits
the restoration to resist displacement through
tipping or lifting forces
Truncated
For retention form, Opposing walls being slightly
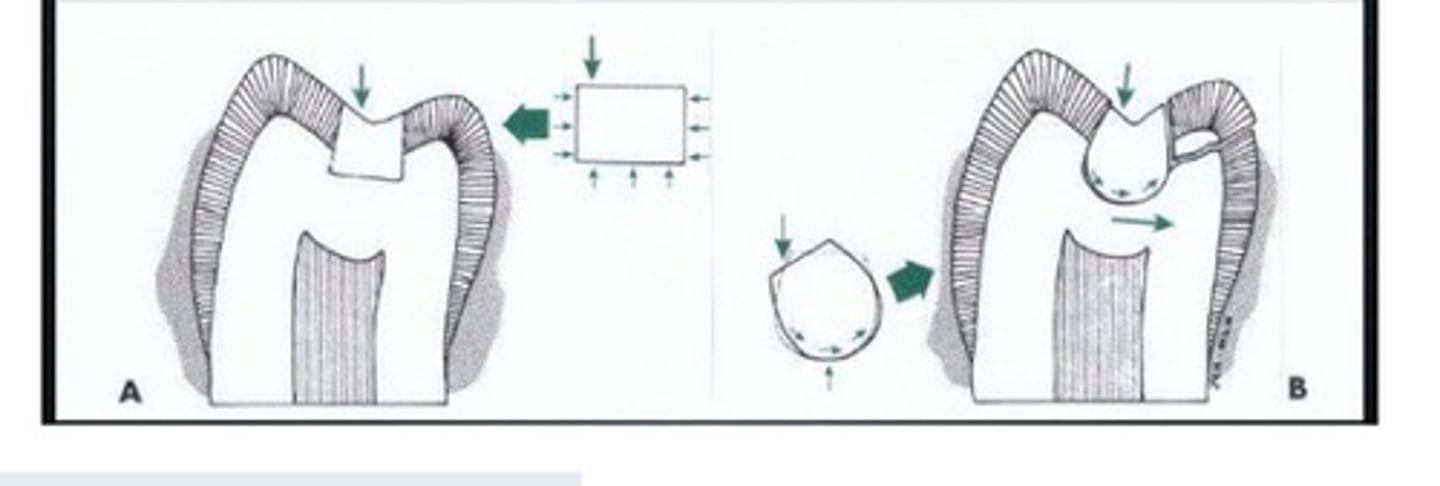
Length
Increased __ of walls will increase retention
Retention grooves
markings in the surfaces of the tooth that enhance placement and retention of the restoration
Dovetail
For retention you should have a ___
Convenience form
Shape that allows adequate preservation,
accessibility and ease of operation in preparing
and restoring the cavity preparation
DEJ
Extension of the cavity outline should ensure that all caries is removed from the peripheral __
dentin
In small sized lesions, the carious __ is usually removed during the cavity extensions
round bur
Moderate/deep lesions may require removal of carious dentin without further extension of the outline, best removed using an appropriate sized __ in a slow speed handpiece
Smoothen
__ all the walls of the preparation, no sharp angles
desiccate
Do not __ it, clean and remove debris to ensure that it is clean and ready for the restorative material
centered
Preparation should be __ on the central
development groove (outline form)
1mm
All pits and primary grooves should be removed,
__ extension into buccal and lingual grooves,
centered over the grooves (outline form)
Dovetail
Add __ on the opposite proximal wall (outline form)
1/2
Distance from marginal ridge - __ the distance from
distal pit to marginal ridge, parallel to the external surface
of the tooth
0.25-0.5mm
Buccal, lingual and gingival proximal clearances of
__ from the adjacent tooth
"S curve"
Angles of exit are 90 º at the buccal and lingual proximal
walls - some preparations require __ to achieve that
truncated
Buccal and Lingual walls are parallel to slightly
__ and are prepared on the long axis of the
crown
rounded
Buccal, lingual and distal walls meet the pulpal floor at
a slightly __ angle
flared
Distal wall is slightly __** why
parallel
Flat pulpal floor __ to occlusal plane
1.5mm
Pulpal floor __ deep at its shallowest point
90 º
In order to have a __ angle of exit on the
buccal and lingual proximal walls, an "S" curve
may be needed to be given on the outline form
when connecting the occlusal and proximal
box preparations.
triangular ridge
The "S" curve helps to conserve the
0.5mm
Axiopulpal bevel using a hatchet or a #330 bur at axio- pulpal line angle, not more than __ wide
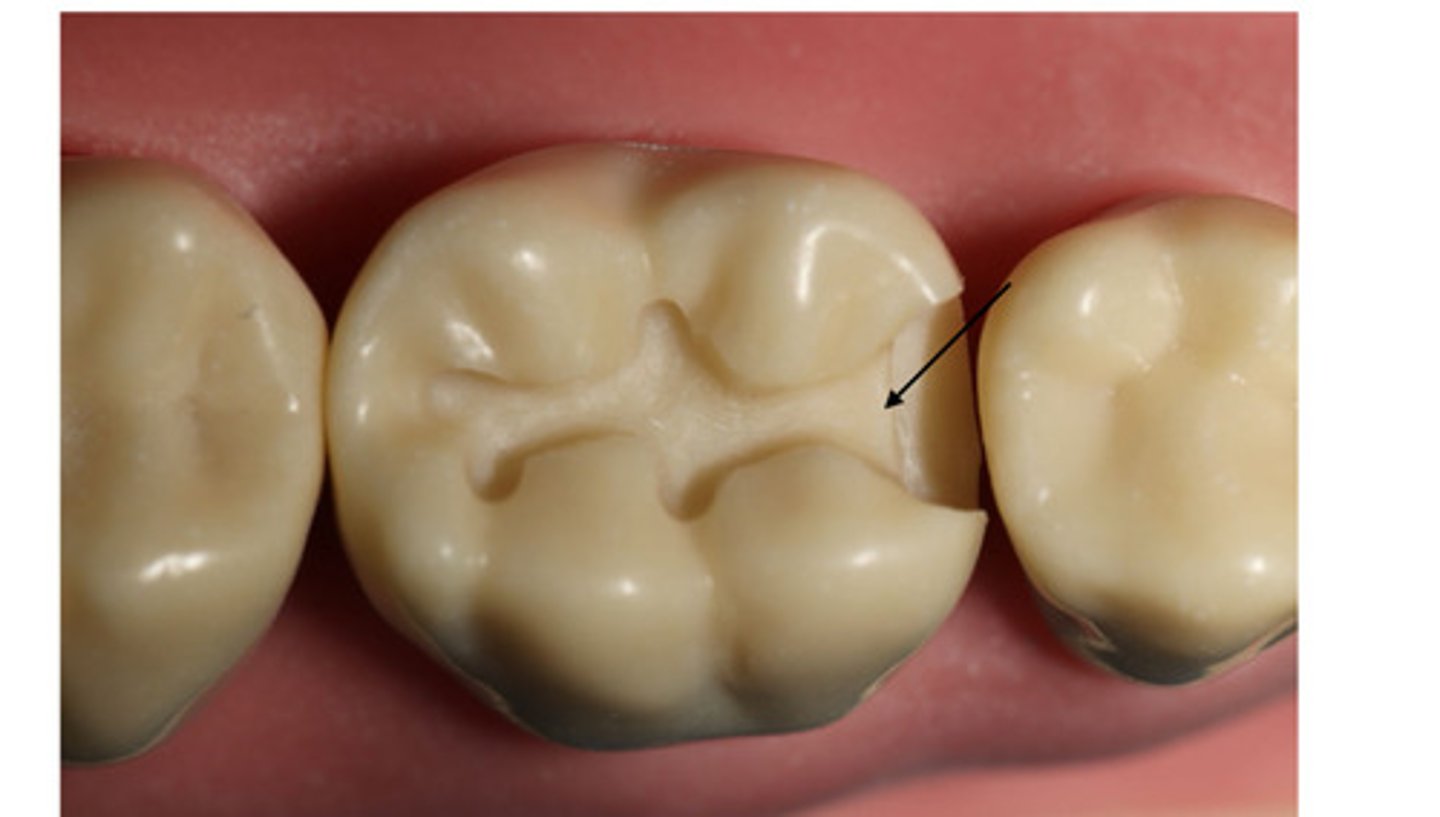
Dentin
You place retention grooves in the ___ and not in the enamel and far away from pulp
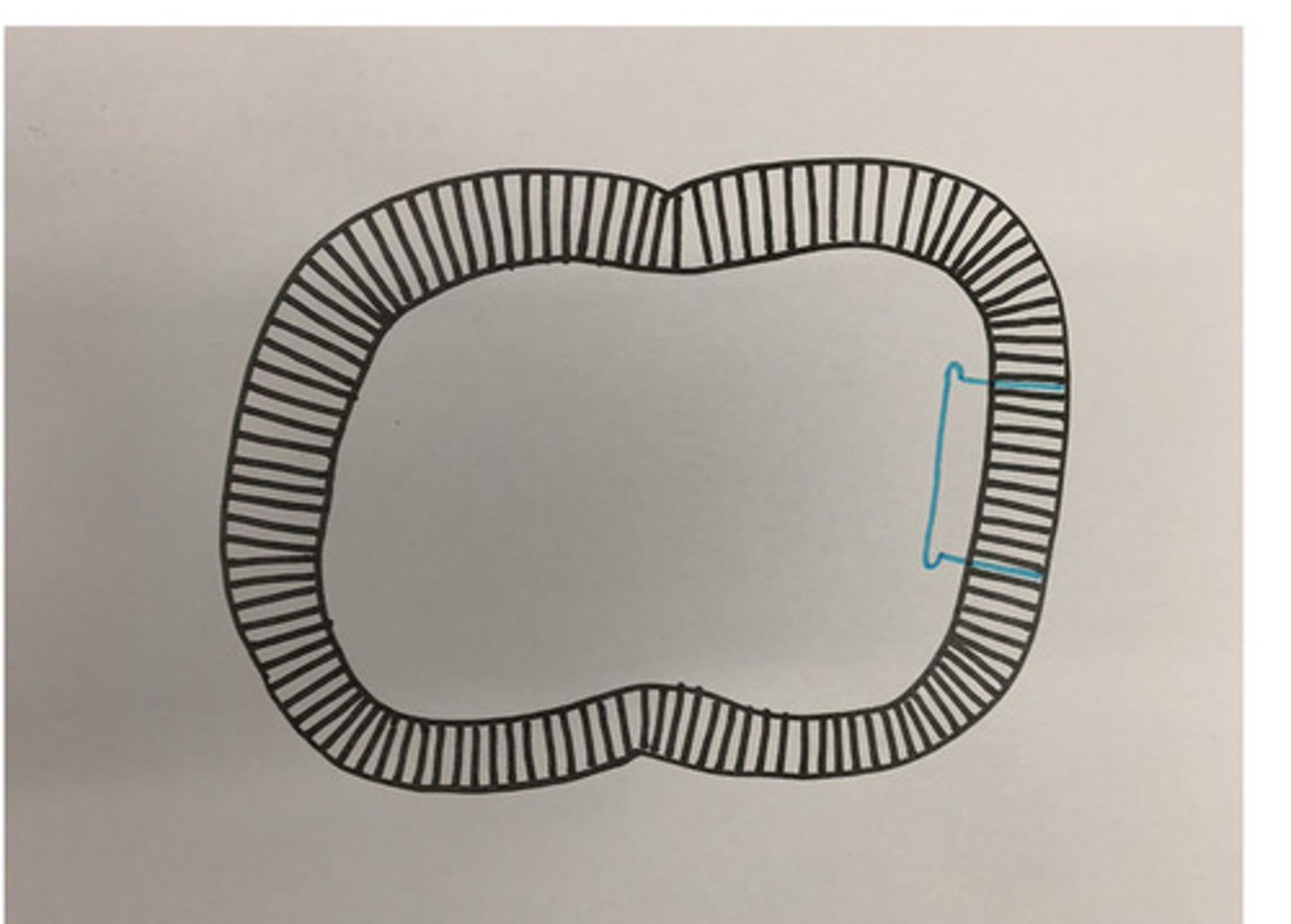
1/4 round bur
Place retention groove with
Retention groove
used to improve retention and resistance with excessive taper, prevents rotational tendencies during cementation, helps guide cast into place, 0.5mm distance from finish line at D axial wall, 1.5mm wide at occlusal and 1.0mm wide at cervical (diverges occlusally) and 1.0mm deep pulpally at cervical base (finish line + groove)
Explorer
Check you retention groove with