Adjustable Pitch Propellers (Jeppesen Powerplant 12-C)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Ground Adjustable Props
Blade angle of the propeller can be changed, but only when engine is not operating
2
New cards
2 Types of Controllable Pitch Props
1. Two Position Props
2. Multiple-Position Props
3
New cards
How does a Multiple-Position Propeller work?
Allows the pilot to select any blade angle between pitch stops;
Still a directly controlled system, lots of pilot input and/or error.
Still a directly controlled system, lots of pilot input and/or error.
4
New cards
What is the Basic operating principle of a Constant-Speed Propeller?
The engine speed is selected, and a governor automatically adjust the prop blade angle to maintain the engine speed.
5
New cards
What are the advantages of a Constant-Speed Propeller?
* Converts a high percentage of the engines power into thrust
* More efficient because it enables the operator to select the most efficient engine speed for a given condition
* More efficient because it enables the operator to select the most efficient engine speed for a given condition
6
New cards
Define Constant-Speed Range as it Relates to Constant-Speed Propellers
The range of blade angles between the high and low pitch stops
* As long as the blade angle is within the constant-speed range, a constant engine speed will be maintained.
* As long as the blade angle is within the constant-speed range, a constant engine speed will be maintained.
7
New cards
On a Constant-Speed Propeller, how is __**engine power**__ output controlled?
By the __**throttle**__, and is indicated by a manifold pressure gauge
8
New cards
On a Constant-Speed Propeller, how is __**blade angle**__ controlled?
By the __**propeller control lever**__
9
New cards
What should an operator do if they observe __**high**__ __**manifold pressure**__?
Adjust prop control to obtain a lower engine speed
OR
Reduce throttle to reduce manifold pressure
OR
Reduce throttle to reduce manifold pressure
10
New cards
What device is responsible for regulating the flow of high-pressure oil to the propeller?
The Governor
11
New cards
What are the 3 functions of a Governor?
1. Boost the pressure of the engine oil it delivers to the prop hub
2. Control the amount of oil that flows to the prop
3. Senses the rotational speed of the engine
12
New cards
Where is a propeller governor typically mounted?
The front of the engine, near the propeller (as near as possible, or on the accessory gearcase)
13
New cards
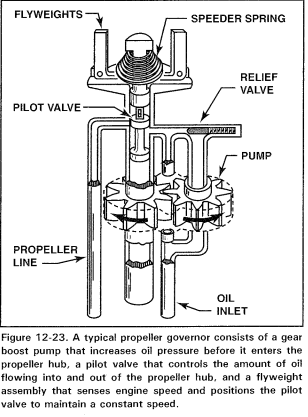
4 Main Parts of a Governor
1. High-Pressure Oil Pump
2. Speeder Spring
3. Flyweights
4. Pilot Valve
14
New cards
Describe the general operation inside of a propeller governor, and what each part does.
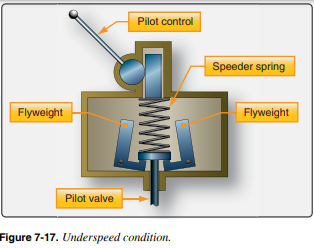
“For a governor to adjust the propeller blade angle to maintain a constant speed, it must be able to sense engine speed. The __**flyweight assembly**__ is the portion of a governor that senses engine speed. A typical flyweight assembly consists of a set of flyweights mounted on a flyweight head that is driven by the same drive shaft as the boost pump. The __**pilot valve**__ is located inside the drive shaft and extends into the flyweight assembly where it rests on the toe of each flyweight. As the flyweights tilt in and out, the pilot valve is moved up or down. To enable an operator to select, or set, a desired blade angle, a control lever adjusts the tension on a __**speeder spring**__ to apply pressure against the flyweights and pilot valve”
\
\-From the Jeppesen text directly
\
\-From the Jeppesen text directly
15
New cards
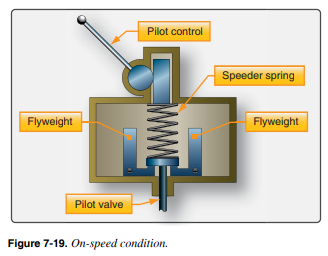
What happens during an __**On-Speed Condition**__?
* __**Flyweight outward pressure = Speeder Spring Pressure**__
* The governor automatically adjusts propeller pitch to maintain a selected speed. Any change in airspeed or load on the propeller results in a change in blade pitch.
* The governor automatically adjusts propeller pitch to maintain a selected speed. Any change in airspeed or load on the propeller results in a change in blade pitch.
16
New cards
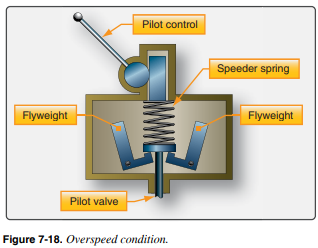
What happens during an __**Overspeed Condition**__?
* __**Flyweight Outward Pressure is greater than Speeder Spring Pressure**__
* As engine speed increases, the centrifugal force acting on the flyweights increases. The flyweights tilt outward, which results in an overspeed condition. As the flyweights move outward, the pilot valve moves up and directs boost pump oil to the propeller hub to increase blade pitch. This increased blade pitch increases load on the prop and slows the engine to an on-speed condition.
* As engine speed increases, the centrifugal force acting on the flyweights increases. The flyweights tilt outward, which results in an overspeed condition. As the flyweights move outward, the pilot valve moves up and directs boost pump oil to the propeller hub to increase blade pitch. This increased blade pitch increases load on the prop and slows the engine to an on-speed condition.
17
New cards
What happens during an __**Underspeed Condition**__?
* __**flyweight outward pressure is less than Speeder spring pressure**__
* This forces the flyweights to tilt inward. When this happens, the governor is said to be in an underspeed condition. The position of the flyweights move the pilot valve downward and oil from the propeller hub is returned to the engine, decreasing blade pitch. This decreased blade pitch decreases load on the prop and speeds up the engine to an on-speed condition.
* This forces the flyweights to tilt inward. When this happens, the governor is said to be in an underspeed condition. The position of the flyweights move the pilot valve downward and oil from the propeller hub is returned to the engine, decreasing blade pitch. This decreased blade pitch decreases load on the prop and speeds up the engine to an on-speed condition.
18
New cards
What would happen if the prop control cable breaks?
the governor would hit the adjustable stop, which limits the minimum blade pitch
19
New cards
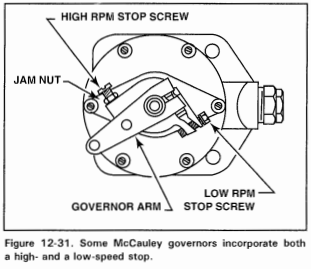
What is the purpose of McCauley governors’ stop screws?
to prevent the engine from underspeeding OR overspeeding (high and low RPM stop screws are used)
20
New cards
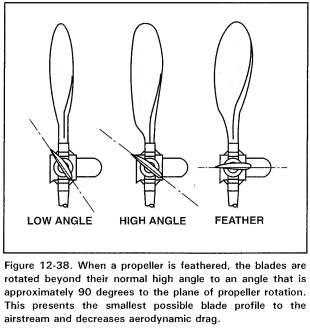
What is Propeller __**Feathering**__? What is its purpose?
1. Propeller Feathering is the rotation of the propeller blades to a 90 degree angle
2. The purpose of propeller feathering is to eliminate the drag of a __**windmilling**__ propeller by presenting the smallest blade profile to the oncoming airstream