newest work in progress
1/688
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
689 Terms
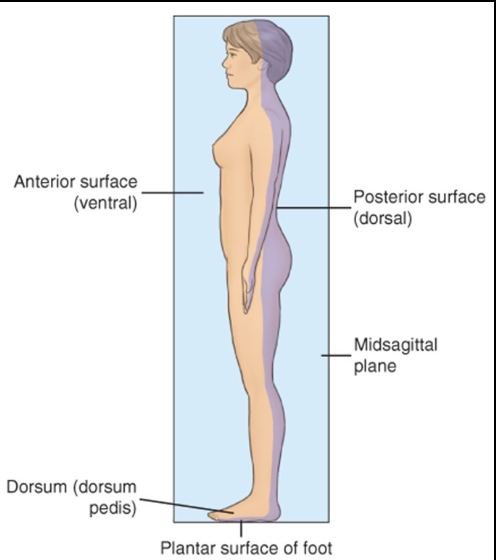
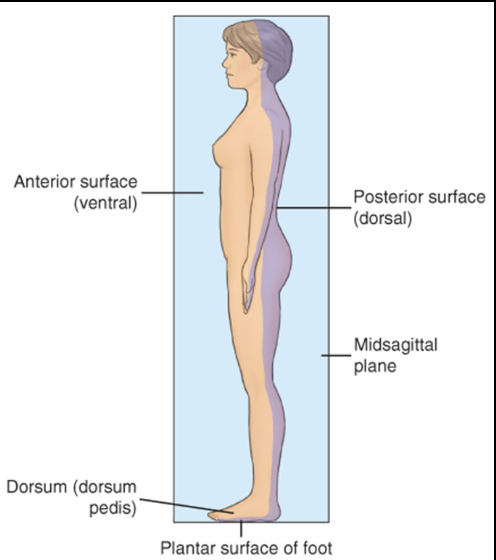
Anterior
Refers to the front surface of the body. Same as ventral
Ventral
Refers to the front surface of the body. Same as anterior
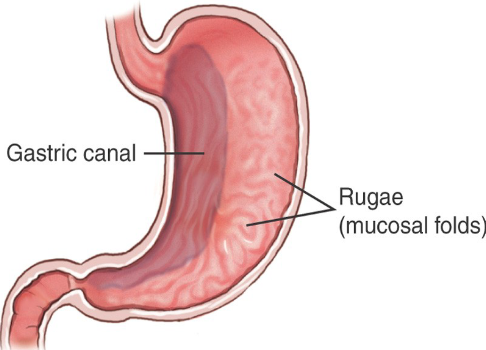
Axial plane
Same as transverse /Horizontal Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into UPPER and LOWER parts.
oblique
body is positioned at different angles/slanting/ not parallel nor at a right angle
Horizontal plane
Same as transverse /axial Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into UPPER and LOWER parts.
Median plane
Same as Midsagittal plane NOT sagital. A vertical plane that divides the body in the middle into equal RIGHT and LEFT halves.
A (n) left anterior oblique_(LAO)____ position the patient as lying recumbent or erect with the left anterior surface against the image receptor, right side elevated. What is the projection?
PA or posterior to anterior
Besides meaning posterior, dorsal also means….
term for the back of the hand
Posterior
Refers to the back surface of the body. Same as dorsal
Dorsal
Refers to the back surface of the body. Same as posterior
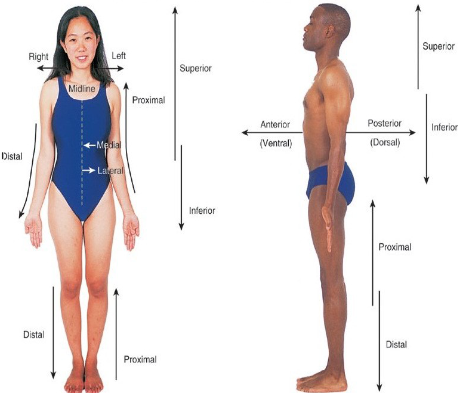
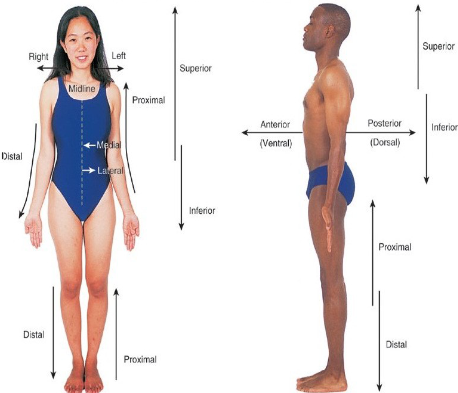
Superior
Refers to a position above or higher than another part of the body. Same as cephalic
Cephalic
Refers to a position above or higher than another part of the body. Same as superior
Inferior
Refers to a position below or lower than another part of the body. Same as caudad
Caudad
Refers to a position below or lower than another part of the body. Same as inferior
Lateral
Near the side of the body
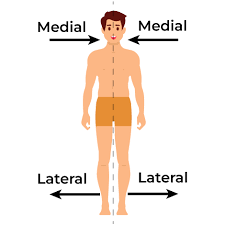
Medial
Lateral refers to the side of the body, while medial refers to the middle or center.
What do each of these mean?: Superficial / Peripheral / Deep
superficial refers to near the surface, peripheral refers to the outer part of the center of the body, and deep refers to further away from the surface.
Proximal
Proximal refers to a position closer to the point of attachment, while distal refers to a position further away.
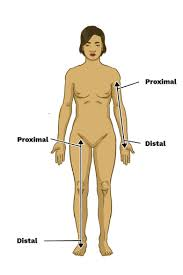
Distal
Proximal refers to a position closer to the point of attachment, while distal refers to a position further away.
Internal / the other term for it is…?
Internal refers to the inside of an organ or structure ie tongue muscles that originate only inside the tongue. Intrinsic
External / the other term for it is…?
External refers to something located outside the organ or structure ie hand muscle that originates from the forearm but goes into the hand. Extrinsic
Visceral
___ refers to the internal organs, while parietal refers to the walls of a cavity.
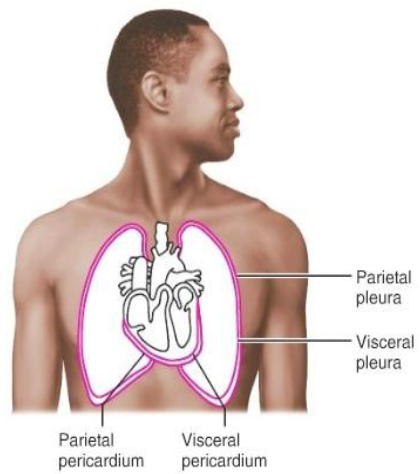
Parietal
Visceral refers to the internal organs, while ___ refers to the walls of a cavity.
True anatomical position
The standard position of the body used as a reference point, standing upright with arms at the sides and palms facing forward.
Erect / Upright
Refers to a position where the body is standing straight up.

Recumbent
Refers to a position where the body is lying down.

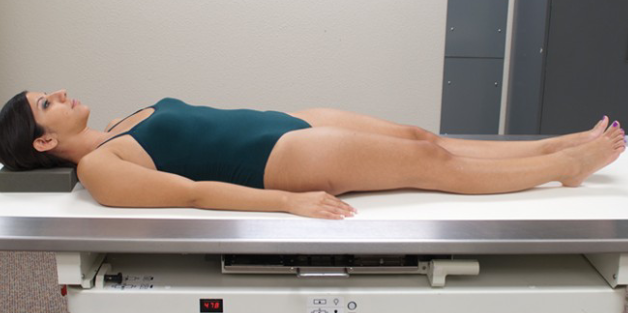
Supine
Refers to a position lying on the back.
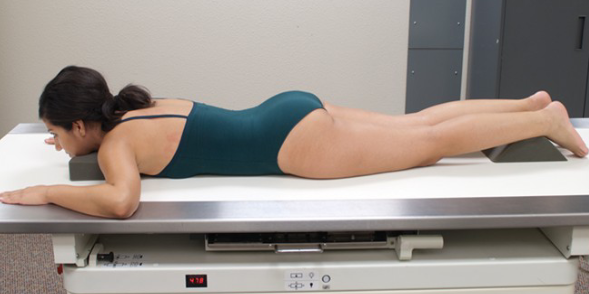
Prone
Refers to a position lying on the stomach.
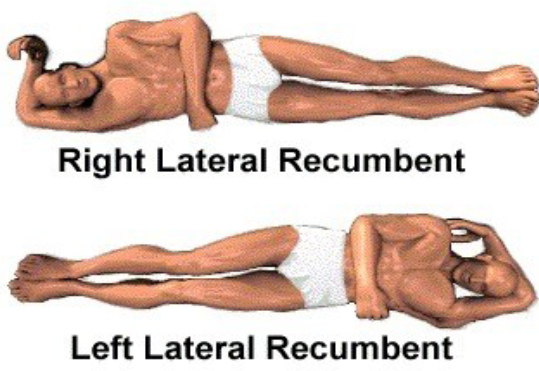
Lateral recumbent
Refers to a position lying on the side.
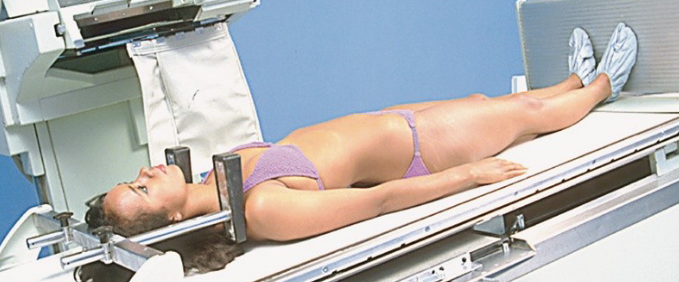
Trendelenburg
A position where the body is laid flat on the back with the legs elevated higher than the head.
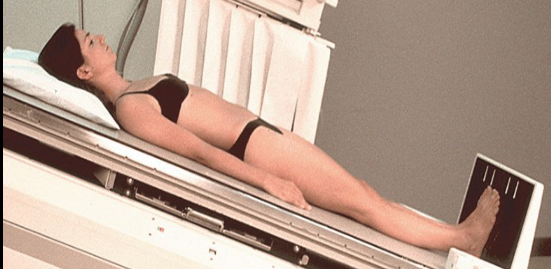
Fowler's
Patients head is elevated above the trunk of the body
Sim's
A position where the patient is lying on their LEFT side their RIGHT knee drawn up.
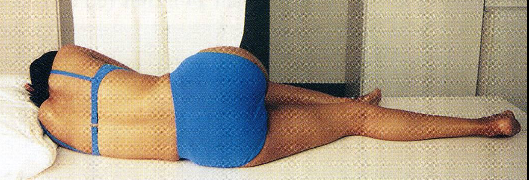
Midsagittal / Median Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body in the middle into equal RIGHT and LEFT halves.
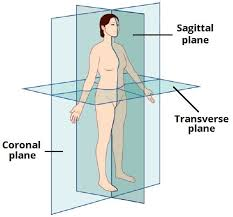
Sagittal plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into RIGHT and LEFT halves and can be placed anywhere to separate the body into these planes. It doesn’t have to be placed in the middle. Median plane is only the same as midsagittal not sagittal.
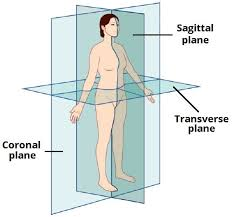
Transverse / Horizontal/axial Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into UPPER and LOWER parts.
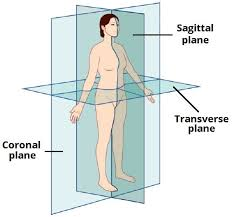
Midcoronal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
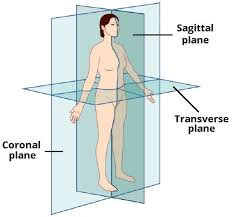
Coronal Plane
A plane that divides the body into front and back sections. Not the same as midcoronal as midcoronal is specifically divided in the middle of the body while coronal can slice and thus divide the anterior and posterior anywhere.
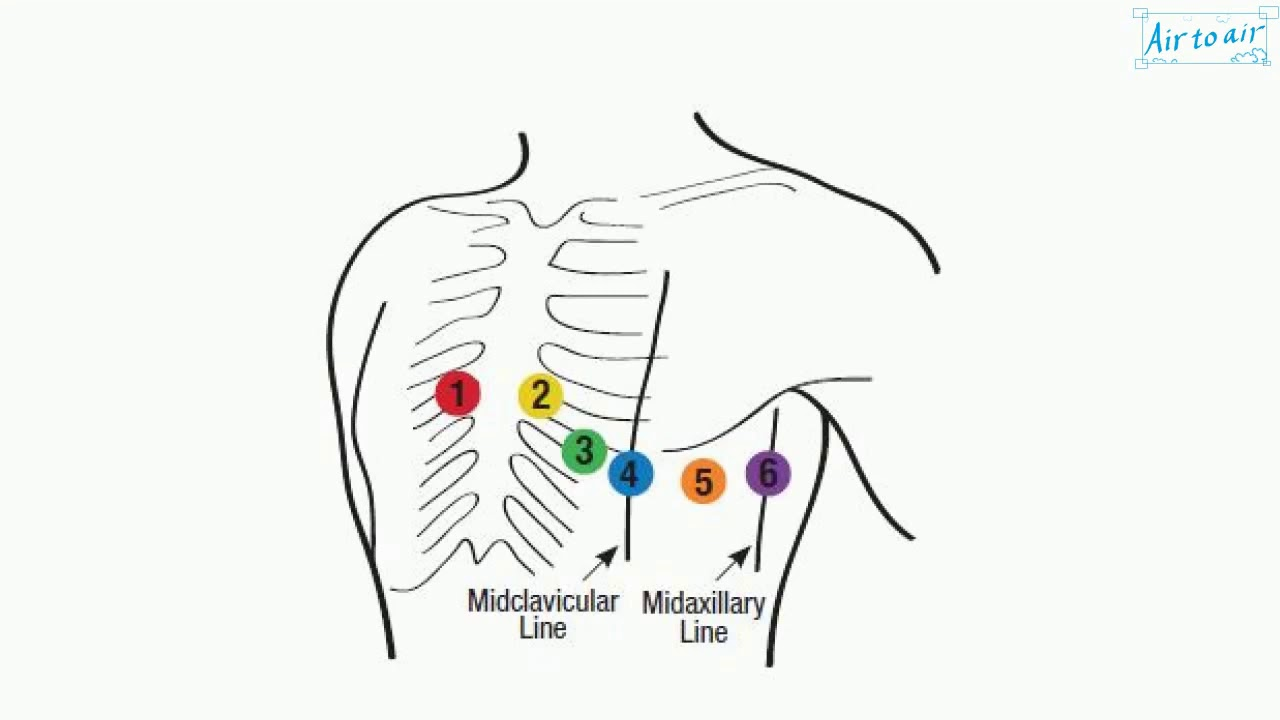
Midaxillary line
a line that extends vertically through the armpit/axilla
Palmar / Volar
___ refers to the palm of the hand, while ___ refers to the palm side of the hand OR sole side of the foot.
Plantar / Dorsum
___ refers to the sole of the foot, while ___ refers to the top of the foot. Note that plantar is apart of the dorsal/posterior.
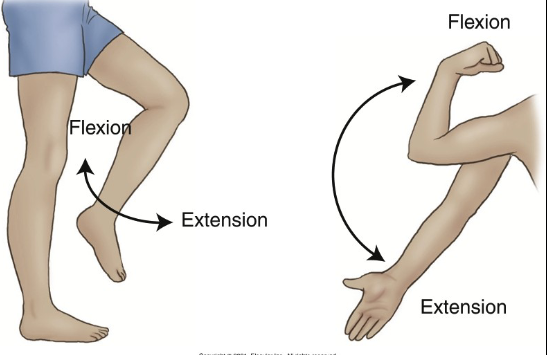
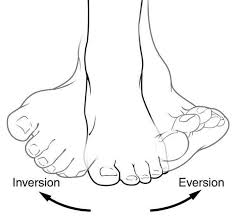
Flexion / Extension
___ refers to bending a joint so its closer to the body, while ___ refers to straightening the joint by flexing it outwards.
Hyperflexion / Hyperextension
___ refers to excessive flexion(stretching a body part inwards), while ___ refers to excessive extension(stretching a body part outwards)
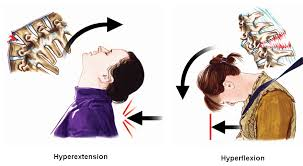
Radial Deviation/Ulnar Deviation
Radial flexion refers to bending towards the radius(flexed toward the thumb), while ulnar flexion refers to bending the wrist towards the ulna(flexed away from the thumb)
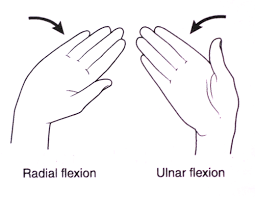
Dorsiflexion / Plantar Flexion
___ refers to raising the foot upwards, while ____ refers to pointing the foot downwards.
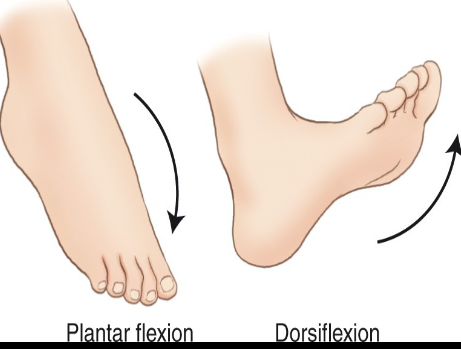
Inversion/Eversion
___ refers to turning it inward, while ___ refers to turning the sole of the foot outward
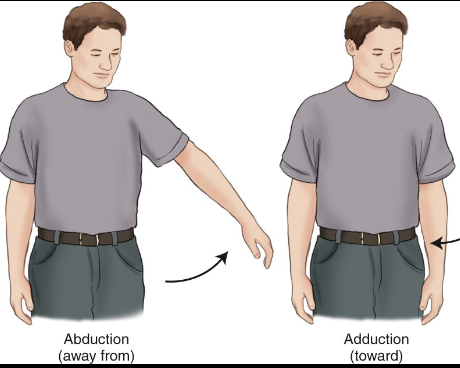
Abduction/Adduction
___ refers to moving it away, while ___ refers to moving a body part towards the midline
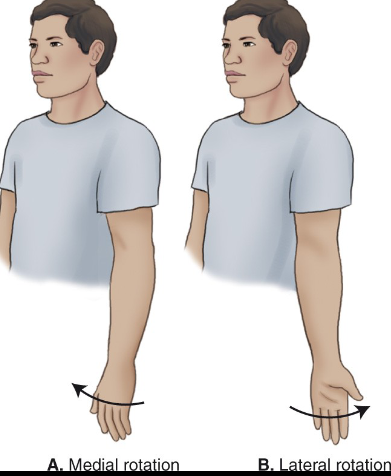
Medial Rotation / Lateral Rotation
___ refers to turning a body part towards the midline, while ___ refers to turning it away.
Supinate
___ refers to turning the palm up, while pronate refers to turning the palm down.
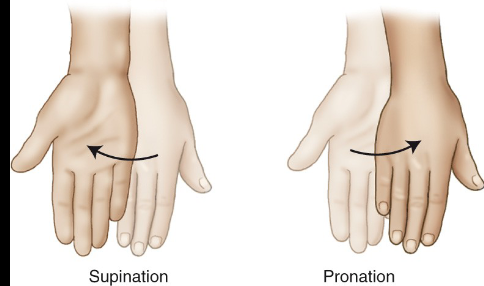
Pronate
Supinate refers to turning the palm up, while ___ refers to turning the palm down.
Circumduction
A circular movement of a body part.
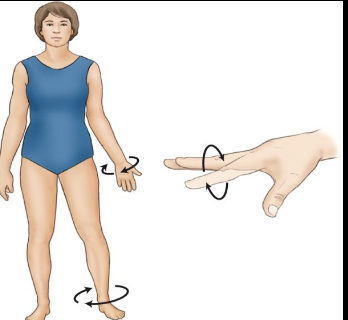
Elevate
___ refers to lifting a body part, while depress refers to lowering it.
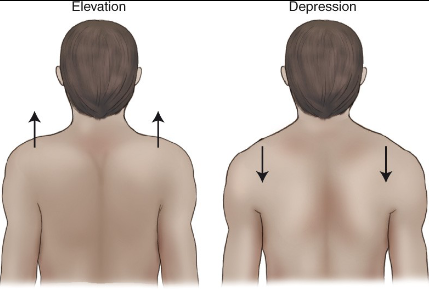
Depress
Elevate refers to lifting a body part, while ___ refers to lowering it.
Ipsilateral / Contralateral
___ refers to the same side of the body, while ___ refers to the opposite side.
Tilt
To incline or slant a body part.
Radiograph
An image produced on a sensitive surface by radiation.
X-ray film
A film that captures the image produced by X-rays.
Radiographic Image
An image created through the process of radiography.
Radiographic Position
The specific orientation of the patient during a radiographic procedure.
Radiographic Projection
The path of the X-ray beam as it passes through the body.
Radiographic View
The perspective from which the radiographic image is taken.
Anteroposterior (AP)
A projection where the X-ray beam passes from the front to the back of the body.

Posteroanterior (PA)
A projection where the X-ray beam passes from the back to the front of the body.
Lateral
A projection taken from the side of the body.

Axial
A projection taken along the axis of a structure aka taken from above or below.
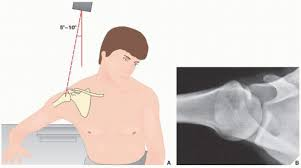
Tangential
A projection that skims the surface of a body and doesnt pass through it.
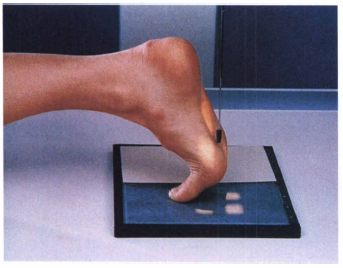
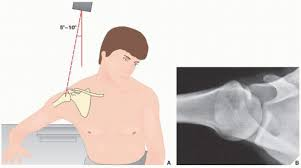
Inferosuperior
A projection where the X-ray beam enters from below and exits above.
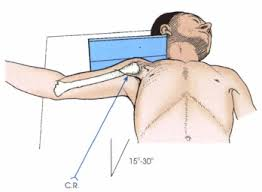
Superoinferior
A projection where the X-ray beam enters from above and exits below.
Right Posterior Oblique (RPO)
A position where the right side of the body is against an imaging screen and leaning back at an angle
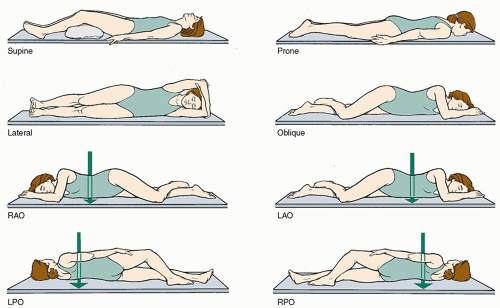
Left Posterior Oblique (LPO)
A position where the left side of the body is against an imaging screen and leaning back at an angle
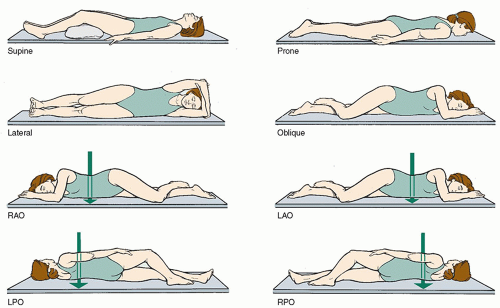
Right Anterior Oblique (RAO)
A position where the right side of the body is against an imaging screen and leaning forward at an angle
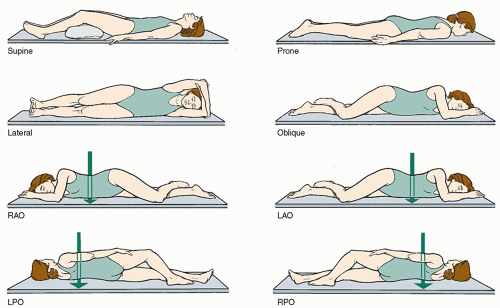
Left Anterior Oblique (LAO)
A position where the left side of the body is against an imaging screen and leaning forward at an angle
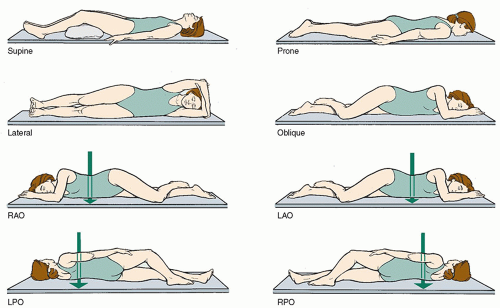
Left Lateral Decubitus
A position where the patient is lying down on their left side and getting a horizontal scan. (bc left, ___=side against imaging screen and not at an angle, ___=LAYONG DOWN getting a horizontal scan)
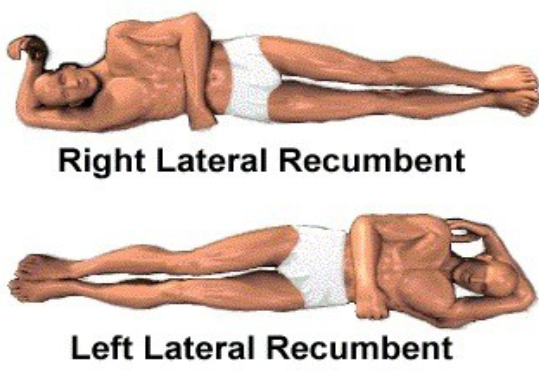
Right Lateral Decubitus
A position where the patient is lying on their right side getting a horizontal scan (bc right, ___ =side against imaging screen and not at an angle, ___ =lying down while getting a horizontal scan)
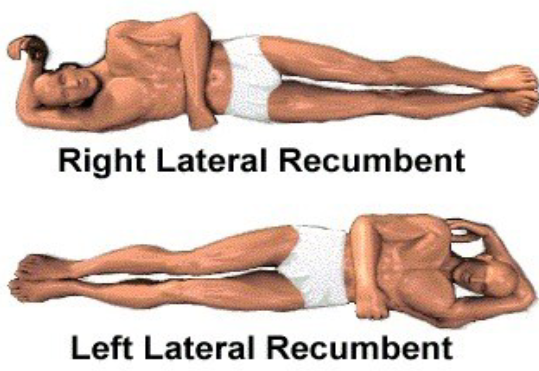
Dorsal Decubitus
A position where the patient is lying on their back and getting a horizontal scan (bc ___=back, ___=getting a horizontal scan while laying down)
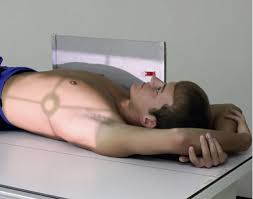
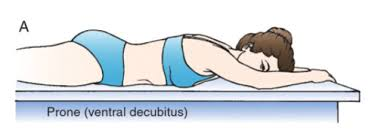
Ventral Decubitus
A position where the patient is lying on their stomach and getting a horizontal scan(bc ___=front, ___=lying down while getting a horizontal scan)
Vertical / Longitudinal
Refers to an orientation that is upright or vertical or y-axiz
Horizontal
Refers to an orientation that is level or flat or x-axis
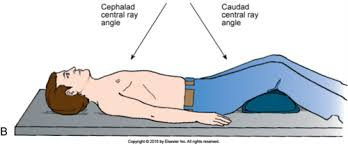
Cephalad angle
An angle directed towards the head.
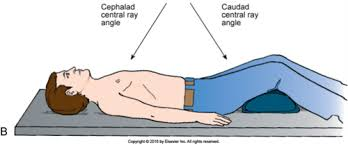
Caudad angle
An angle directed towards the feet.
Cassette with analog film
Film is placed in the cassette, photo is taken, then film is processed in black light room. ___ film cant be used again.
Cassette with phosphor plate aka computed radiograph
Film/___ is placed in the cassette then once the image is captures a barcode is scanned which then converts the image to a digital copy. Once this copy is attained the ___ can be recycled and used again.
Fluoroscopic screen
x-ray tube is below patient and the screen is above which once hit by xray radiation is then converted over to a digital copy creating a video like real time result.
Direct Digital Radiography and what r the 2 types?
Instead of a cassette with film this is a cassette that has a computer in it. Its considered direct if its attached to the table or wall the patient leans on aka the machine/buckeye. After photo is taken it is sent over instantly.
Its considered indirect if the digital cassette can be moved/isnt connected to a machine.
Lengthwise placement
Refers to the placement of the image receptor in the direction of the body's length.
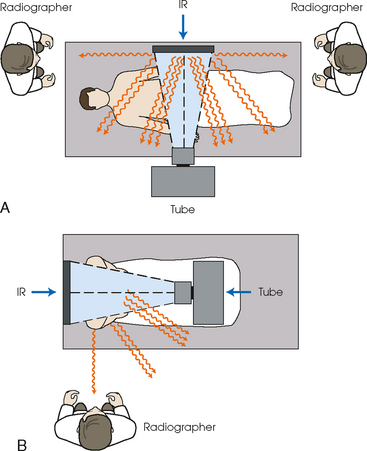
Crosswise placement
Refers to the placement of the image receptor perpendicular to the body's length.
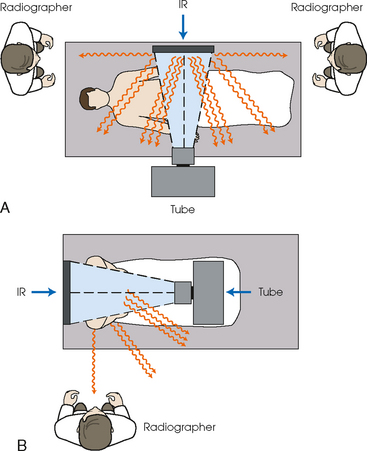
X-rays are emitted from
the ____ in the
shape of a pyramid,
with the center beam
called the ___
X-ray rube
Central ray
WHy is it important to use focus the central ray on a body part?
To reduce radiation & increase image quality (it helps avoid scatter radiation aka radiation bouncing off hard surfaces which can blur images.)
LECTURE 2
What is a requisition form for?
List the information included on a radiology requisition form: (all 7)
Also make sure to list the difference in information for inpatient vs outpatient
provides information about the X- ray procedure to be performed and how to proceed with the examination
1)Patient Name
2)Medical Record Number
3)Birthdate / DOB
4)Nursing Station or Floor (inpatient) / Department or Clinic (outpatient)
5)Clinical Data
6)Handling / Transportation Mode
7)Miscellaneous Information
Clinical Data
info about physical signs or symptoms – it is the reason(s) the X-ray procedure is being ordered
Miscellaneous Information
other info that might be helpful to the radiographer Example: Special projections to be performed
how is X-Ray Tube Position prepared prior to a radiographic examination?
depends on the X-ray examination to be performed:
Vertical: For Table Top (Extremity aka only the limb is laying down) or recumbent (full body laying down) positions
Horizontal: Parallel to the horizon directed at the Upright Image Receptor(aka its on the wall/not laying down) for erect or decubitus positions
how is SID / FFD prepared prior to a radiographic examination?
SID is
Prior to performing the X-ray examination, the technologist will set the SID or distance between the X-ray tube and Image Receptor
determine how much magnification of the body part there is and the amount of radiation required to get through the patient. Magnification will cause distortion on the image. Larger the SID, the less magnification and the more radiation exposure.
40 inches for table and extremity work
◦ 72 inches (6 feet) for CXR’s and Lateral Projections of the Cervical Spine
distortion
misrepresentation of an object size or shape
how is X-Ray Tube Angulation prepared prior to a radiographic examination?
Depending on the body part, the X-ray tube may be angled caudad or cephalad for specific anatomical structures
Range of angulation for a X-Ray Tube Angulation
0 degrees if the tube is vertical
90 degrees if tube is horizontal
between 5- 45 degrees for Axial Projections
To elongate a structure that is curved on itself -30-45 degrees
To open up a joint space – 5 to 10 degrees
Purpose of angling for a X-Ray Tube Angulation
To avoid superimposition of structures; To elongate a structure that is curved on itself; To open up a joint space
how is Bucky prepared prior to a radiographic examination? ie where is it?
X-ray tube must be centered to the Bucky b4 hand
is a tray beneath the X-ray tabletop where the Image Receptor is placed
how is Grid prepared prior to a radiographic examination? ie where is it? when is it used? what does it do?
X-ray tube must be centered to the Bucky b4 hand
Above the Bucky tray/Image Receptor and below the table/wall
is used on body parts over 10cm
absorbs the scatter radiation.
Describe a Bucky / Grid
a tray beneath the X-ray tabletop where the Image Receptor is placed
Above the Bucky tray is a device called a grid, which is a flat thin wafer device