CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 6: Plant Nutrition
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Photosynthesis
the process by which plants manufacture carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light
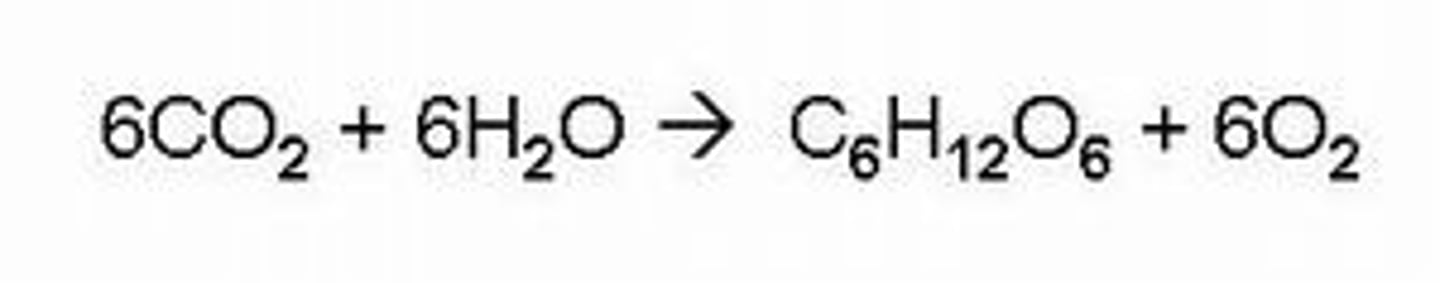
Function of chlorophyll
transfers light energy into chemical energy in molecules, for the synthesis of carbohydrates
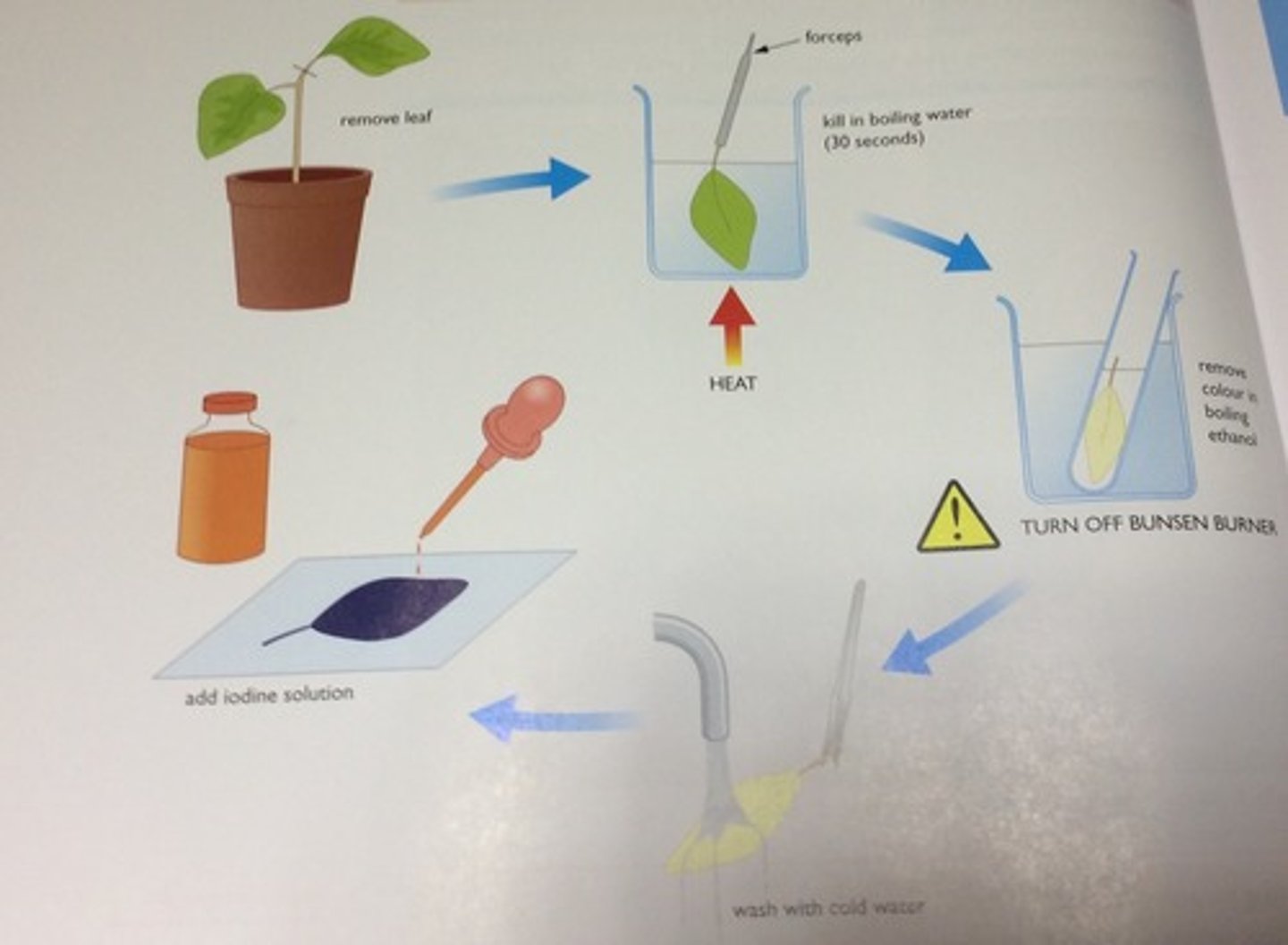
Testing Leaf for Starch
1. Submerge leaf in boiling water to destroy membrane
2. Put the leaf into test tube of ethanol to dissolve chlorophyll
3. Wash leaf in cold water to rehydrate
4. Put drops of iodine solution on leaf
Results: Iodine solution turns blue-black when starch is present
De-starching
To remove starch in plants by leaving plant in the dark for 48 hours
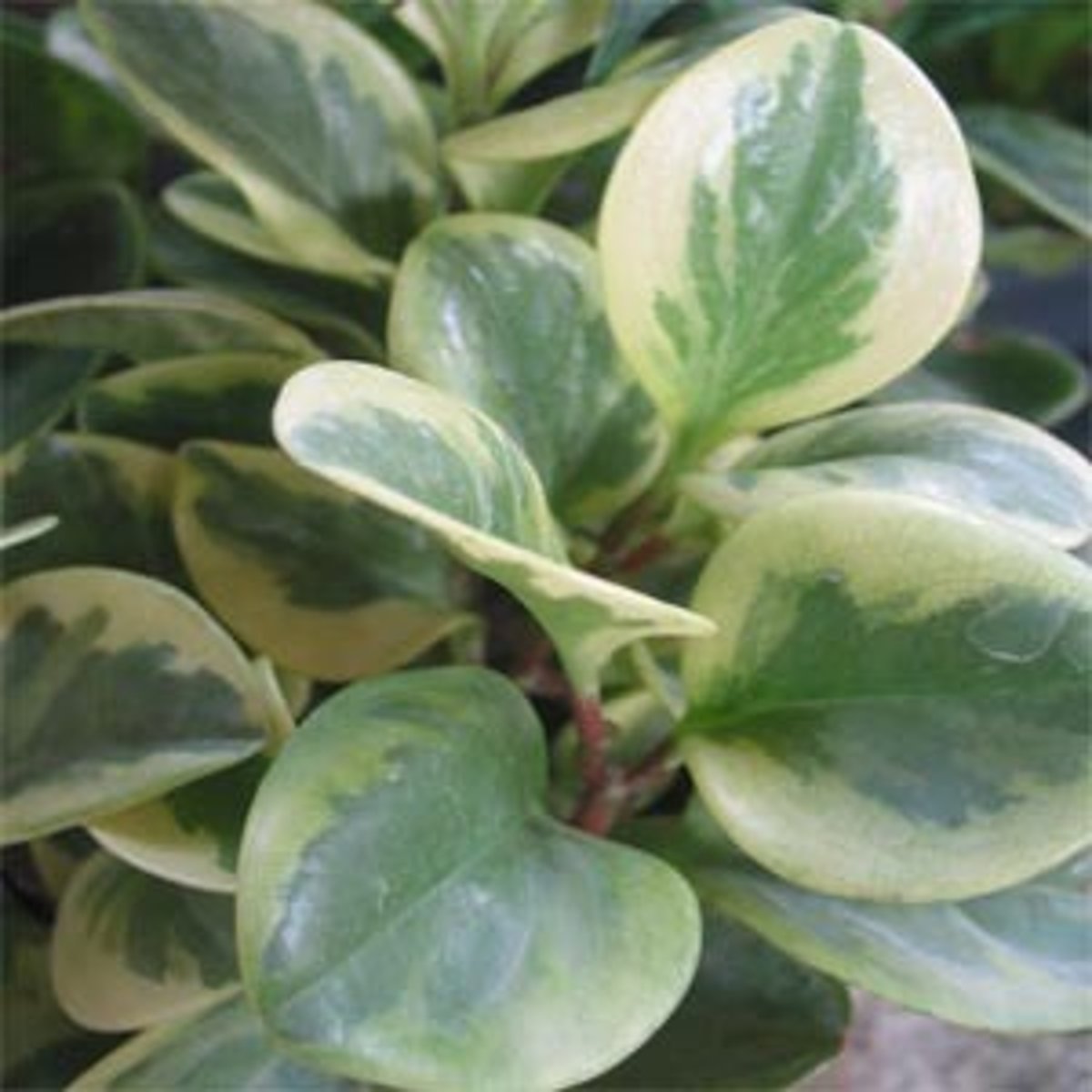
Test for chlorophyll needed for photosynthesis
1. Take a de-starched, variegated plant (some part of leaf does not have chlorophyll)
2. Leave plant under sunlight for 6 hours
3. Test leaf with iodine solution
4. Part that turn blue black contain chlorophyll as starch is produced
5. The white parts contain no chlorophyll, so no photosynthesis occurs there thus no starch is produced

Test for carbon dioxide needed for photosynthesis
1.Take a de-starched plant and cover it with a plastic bag
2.Add soda lime to absorb carbon dioxide
3.Leave plant under sunlight for 6 hours
4.Take leaf from plant and test for starch
5.Results should turn up negative as there is no carbon dioxide for photosynthesis to occur
6.Control should be set up without soda lime
Test for light needed for photosynthesis
1.Take a de-starched plant and cover a part of the leaf with aluminium foil
2.Leave the plant under sunlight for 6 hours
3.Test leaf for starch using iodine solution
4.Test for iodine should be negative on covered part as there is no light for photosynthesis to occur
Function of glucose in plants
-glucose is used for respiration in the leaf
-some glucose is changed into starch to be stored for future use
-used to make cellulose that is required to make cell walls
-converted into sucrose and transported through the phloem
-glucose and nitrate are used to form amino acids for growth
Limiting factor
something present in the environment in such short supply that it restricts life processes
Limiting factor of photosynthesis
light intensity, temperature, carbon dioxide concentration
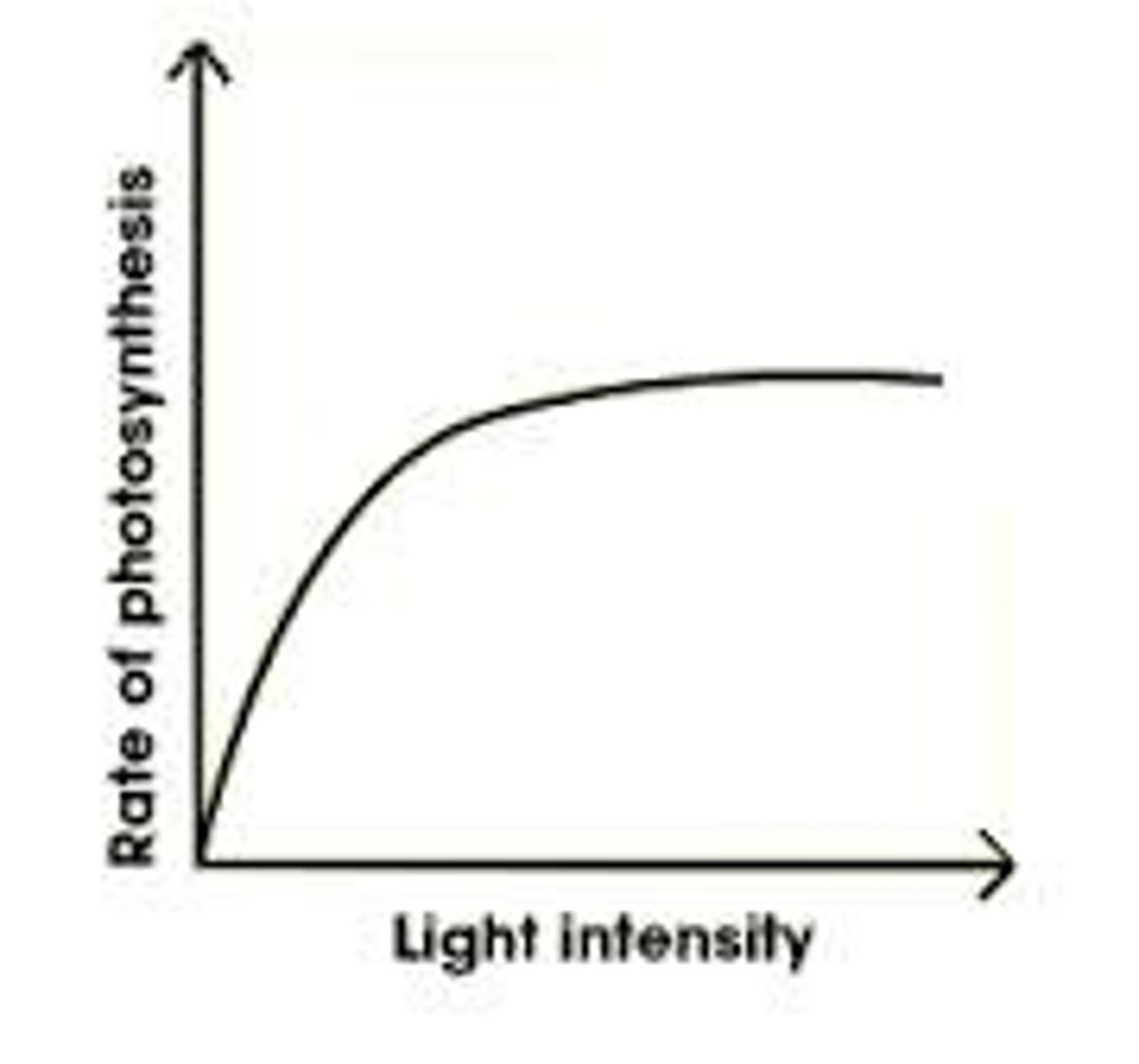
Rate of photosynthesis and light intensity
as light intensity increases, rate of photosynthesis increases until another factor becomes the limiting factor
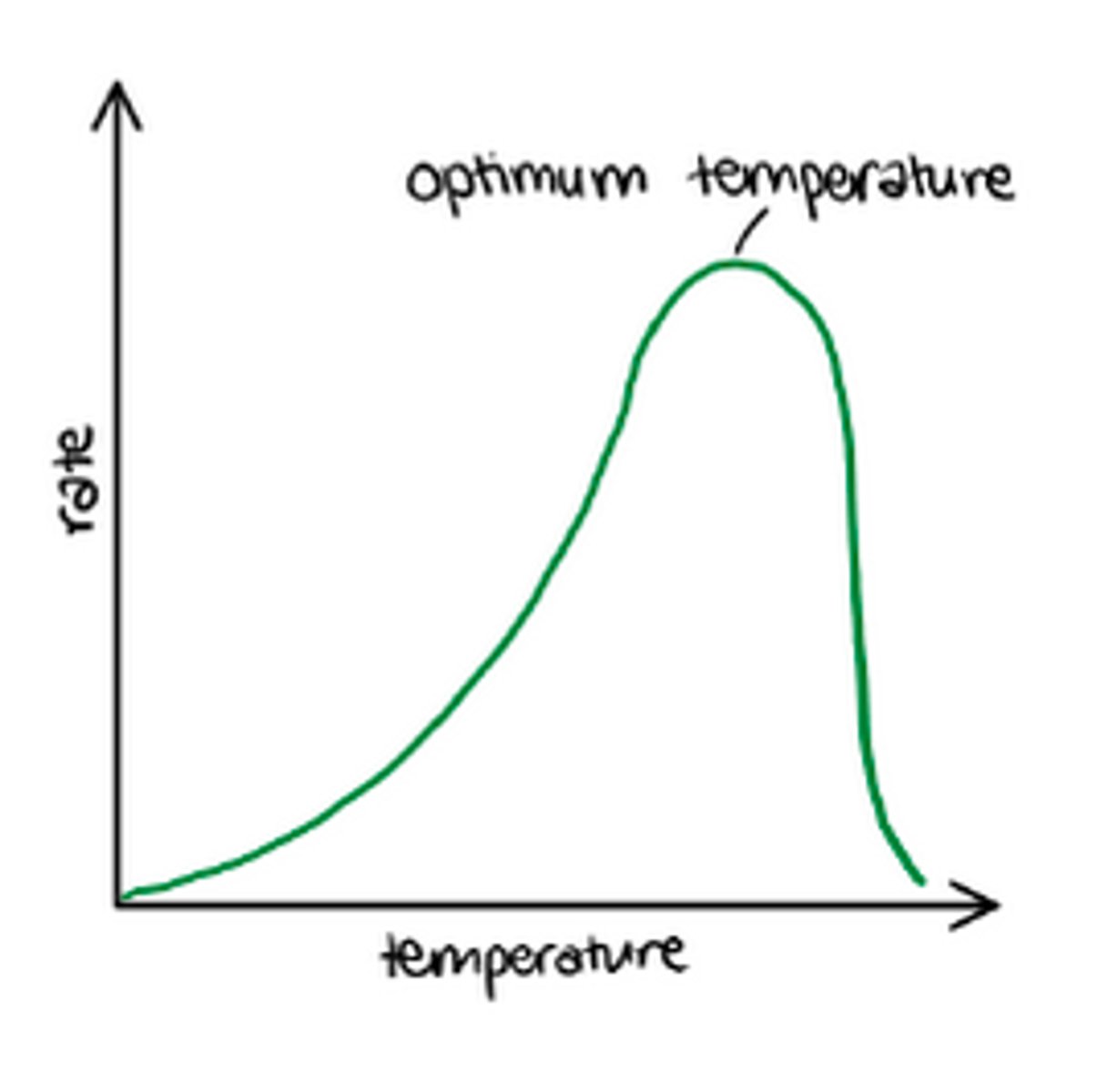
Rate of photosynthesis and temperature
Chemical reactions catalysed by enzymes increase with temperature, as enzymes reach optimum temperature the rate of photosynthesis peaks, after this peak the rate of photosynthesis decreases as the temperature rises because enzymes denature
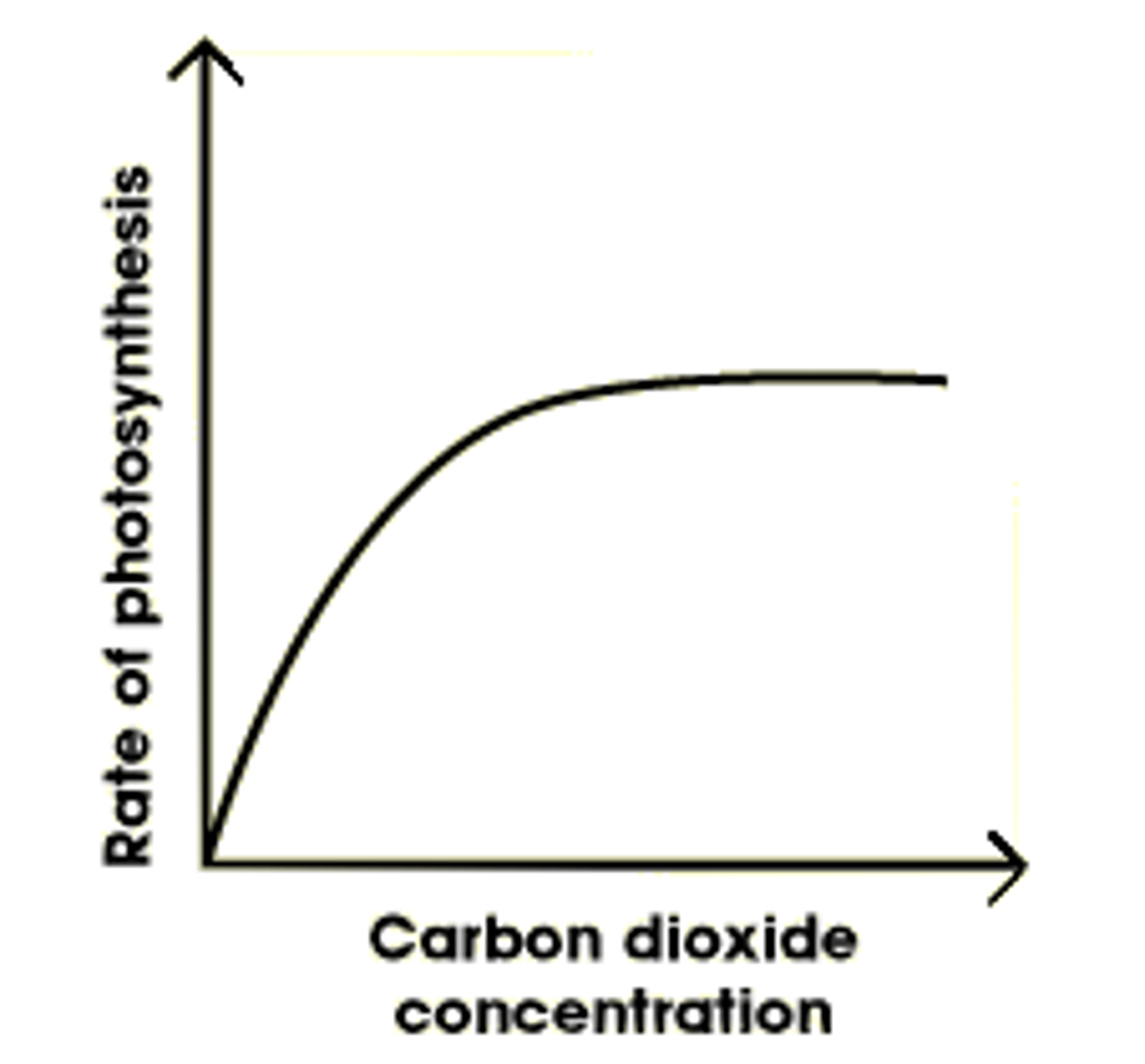
Rate of photosynthesis and carbon dioxide concentration
as carbon dioxide concentration increase, rate of photosynthesis increases until other factors become the limiting factor
Glasshouse production
To improve yield of crops by giving crops best conditions for photosynthesis to occur
-allow plants to grow earlier in the year
-allow plants to grow in places where they do not grow well

Carbon dioxide in Glasshouse production
Pump in carbon dioxide or burn butane to provide carbon dioxide and also raise temperature during cold weather
Temperature in Glasshouse production
Sunlight heats up inside of glasshouse, glass stop heat from escaping
-Electric heaters are used to raise temperature during cold weather
-Ventilator flaps are opened to lower temperature during hot weather
Light in Glasshouse production
Glass lets in sunlight. Artificial lights can be used when light intensity is too low, and blinds to keep out strong sunlight
Leaf structure
-cuticle: waxy waterproof layer that reduces water loss by evaporation
-upper epidermis: single layer of cells with no chloroplasts. Light goes straight through
-palisade mesophyll: contains highest concentration of chloroplasts.Most photosynthesis occurs here
-spongy mesophyll: rounded cells with air spaces
-lower epidermis: contains holes (stomata) to allow diffusion of gasses to occur
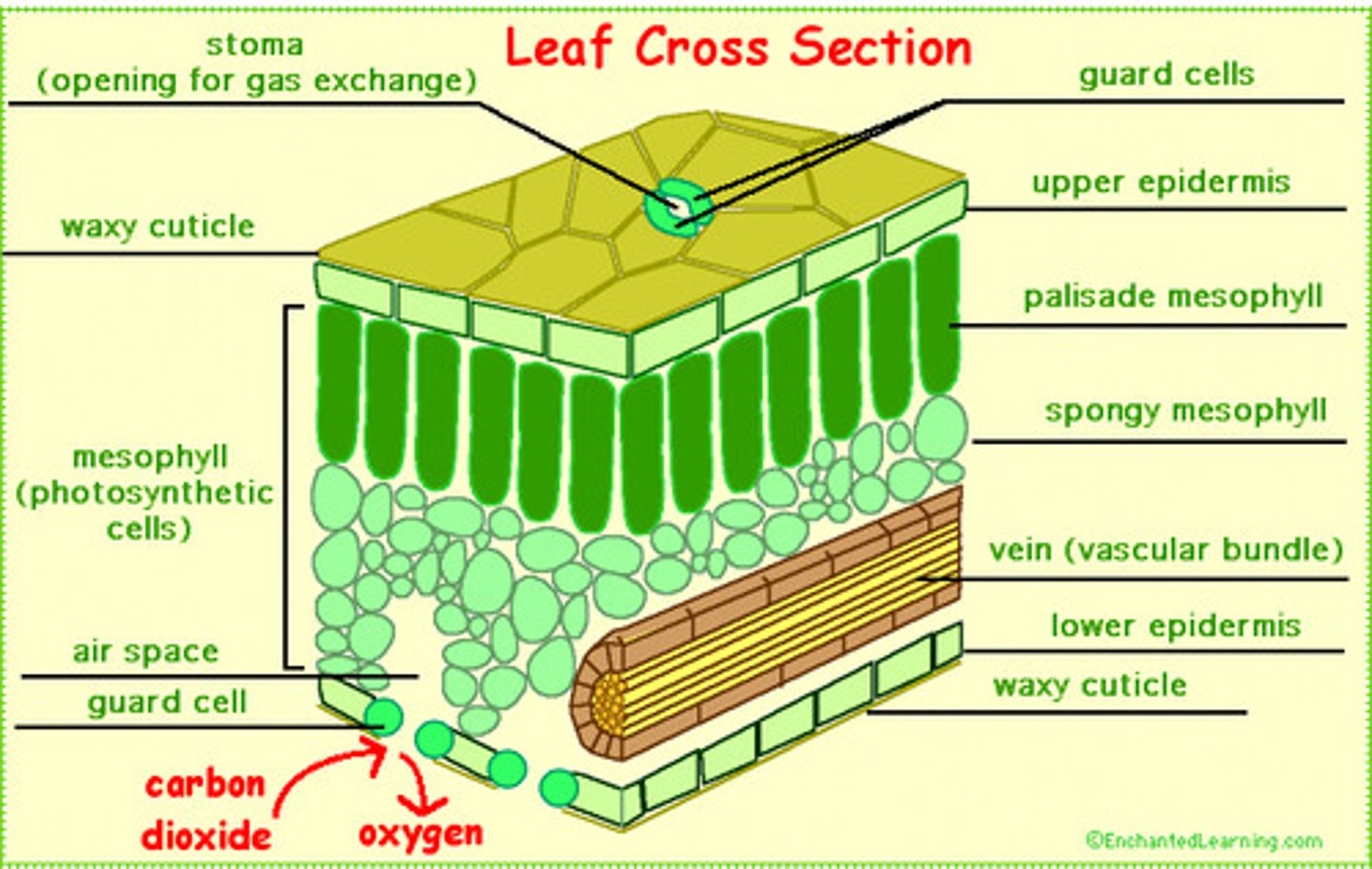
How internal structure of a leaf is adapted for photosynthesis
-a large surface area: to absorb light
-thin shape: allow gas exchange to occur easily
-many chloroplasts: to absorb light for photosynthesis
-veins: support leaf surface and to carry water and ions to leaf cells, transport sucrose and amino acids to other parts of plant
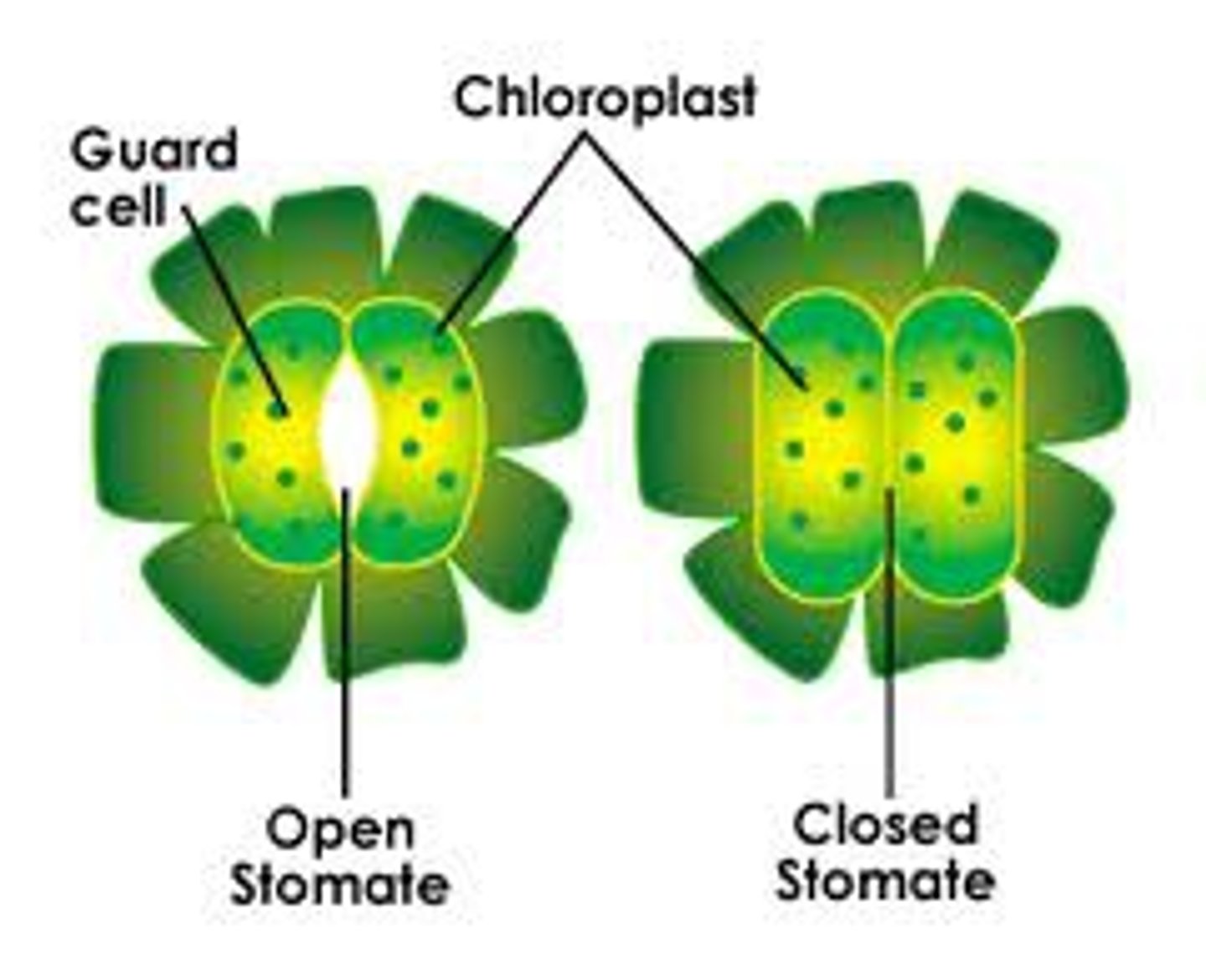
Stomata
area where gas such as carbon dioxide diffuse in and oxygen diffuse out, transpiration also occurs at stomata
Nitrate ions in plant
making amino acids
Magnesium ions in plant
making chlorophyll
Gas exchange in plants
Gas (carbon dioxide) diffuse in through stomata for photosynthesis to occur and oxygen diffuse out as a by product
Hydrogen carbonate test for gas exchange
Hydrogen carbonate is used to test concentration of carbon dioxide in solution
High: yellow
Atmospheric level: red
Low: purple
Leaf can be placed in test tube with hydrogen carbonate to find gas exchange occuring in leaf