IB Bio: Topic 6 (Human Physiology --> 6.4, 6.5, 6.6)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/28
Last updated 1:54 AM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
Inhaling
* Diaphragm contracts
* Chest (rib) muscles contract
* Volume of chest cavity increases
* Air pressure decreases
* Causes air to fill lungs
* Chest (rib) muscles contract
* Volume of chest cavity increases
* Air pressure decreases
* Causes air to fill lungs
2
New cards
Exhaling
* Diaphragm relaxes
* Chest (rib) muscles relax
* Volume of chest cavity decreases
* Air pressure increases
* Forces air out of lungs.
* Chest (rib) muscles relax
* Volume of chest cavity decreases
* Air pressure increases
* Forces air out of lungs.
3
New cards
Muscles at inspiration
* Core muscles:
* External intercostals contract to elevate ribs
* Internal intercostals relax.
* Diaphragm contracts to expand thoracic cavity
\
* External intercostals contract to elevate ribs
* Internal intercostals relax.
* Diaphragm contracts to expand thoracic cavity
\
4
New cards
Muscles at expiration
* Core muscles:
* External intercostals relax
* Internal intercostals contract to pull ribs down
* Diaphragm relaxes to reduce thoracic cavity.
* External intercostals relax
* Internal intercostals contract to pull ribs down
* Diaphragm relaxes to reduce thoracic cavity.
5
New cards
Gas exchange
* Absorbing one type of gas from environment and releasing another type of gas.
* Animals: Cellular respiration (Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide)
* Plants: Photosynthesis (Carbon Dioxide → Oxygen)
* Proceeds due to diffusion
* Movement from high concentration to low concentration.
* Animals: Cellular respiration (Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide)
* Plants: Photosynthesis (Carbon Dioxide → Oxygen)
* Proceeds due to diffusion
* Movement from high concentration to low concentration.
6
New cards
Pneumocytes
* Alveoli cells
* Type 1
* Extremely thin cells of alveoli walls
* allows increased rates of gas exchange via diffusion.
* Type 2
* Secretes fluid surfactant
* helps with gas exchange
* stops walls of alveoli from sticking
* Stops lungs from collapsing.
* Type 1
* Extremely thin cells of alveoli walls
* allows increased rates of gas exchange via diffusion.
* Type 2
* Secretes fluid surfactant
* helps with gas exchange
* stops walls of alveoli from sticking
* Stops lungs from collapsing.
7
New cards
Emphysema
* Chronic respiratory disease
* irreversible damage to alveoli
* less surface area
* smaller number of alveoli
* thicker alveoli walls or destroyed walls
* Inefficient gas exchange
* Low oxygen levels
* high carbon dioxide levels
* Symptoms: shortness of breath and Fatigue
* irreversible damage to alveoli
* less surface area
* smaller number of alveoli
* thicker alveoli walls or destroyed walls
* Inefficient gas exchange
* Low oxygen levels
* high carbon dioxide levels
* Symptoms: shortness of breath and Fatigue
8
New cards
Lung Cancer
* Caused by smoking and air pollution.
* Symptoms:
* Breathing difficulties
* Coughing
* Chest pain
* Loss of appetite
* Weight loss
* General fatigue
* Symptoms:
* Breathing difficulties
* Coughing
* Chest pain
* Loss of appetite
* Weight loss
* General fatigue
9
New cards
Neurons
* Nerve cells
* Allows communication throughout the body with a wide neural network
* Allows communication throughout the body with a wide neural network
10
New cards
Neural Structure
Neurons consist of the cell body, dendrites, axon, Schwann cells, Myelin sheath, and nodes of Ranvier.
11
New cards
Cell body (neurons)
Contains cell nucleus and other normal cell structures.
12
New cards
Dendrites (neurons)
Where signal is received.
13
New cards
Axon (neurons)
long tube-like structure where signal is sent out.
14
New cards
Schwann cells (neurons)
Create Myelin sheath
15
New cards
Myelin Sheath
* the protective layer that surrounds and insulates the axon of a neuron.
* The myelin sheath helps to speed up the transmission of electrical impulses along the axon.
* The myelin acts as an insulator, preventing the electrical charge from leaking out and allowing the impulse to travel faster and more efficiently.
* The myelin sheath helps to speed up the transmission of electrical impulses along the axon.
* The myelin acts as an insulator, preventing the electrical charge from leaking out and allowing the impulse to travel faster and more efficiently.
16
New cards
Nodes of Ranvier
Axon parts with no Myelin sheath
17
New cards
3 types of neurons
Sensory neurons, Interneurons and motor neurons.
18
New cards
Sensory neurons
* Detect stimuli (5 senses)
* Send information to central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
* Send information to central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
19
New cards
Interneurons
* In brain and spinal cord (CNS)
* Processes information
* Thinking or automatic reflexes
* Connects sensory neurons to motor neurons
* Does NOT have Myelin sheaths.
* Processes information
* Thinking or automatic reflexes
* Connects sensory neurons to motor neurons
* Does NOT have Myelin sheaths.
20
New cards
Motor neuron
* Receive information from CNS to muscles for movement.
21
New cards
Action Potential
* Electrical signal transferred along a neuron.
22
New cards
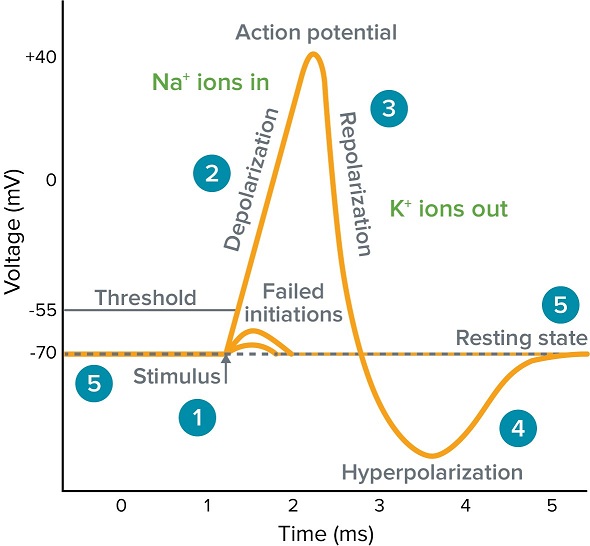
Action Potential steps
1) Resting state
2) Depolarization (rising phase)
3) Repolarization (falling phase)
4) Hyperpolarization (undershoot / refractory period)
2) Depolarization (rising phase)
3) Repolarization (falling phase)
4) Hyperpolarization (undershoot / refractory period)
23
New cards
Resting State (Action Potential)
* Outside of cell: Positive (Na+ on the outside)
* Inside cell: Negative (K+ and proteins inside)
* Salty Banana
* Ion gates are closed (diffusion still occurs)
* Cell is polarized
* Charge difference between inside and outside the cell.
* Resting potential: -70mV
\
* Inside cell: Negative (K+ and proteins inside)
* Salty Banana
* Ion gates are closed (diffusion still occurs)
* Cell is polarized
* Charge difference between inside and outside the cell.
* Resting potential: -70mV
\
24
New cards
Membrane permeability during Resting rate (action potential)
* Ions diffuse through membrane to reach equilibrium
* K+ diffuses more easily than Na+
* and so more K+ moves out
* More positive charges are outside
* More negative charges are inside
* K+ diffuses more easily than Na+
* and so more K+ moves out
* More positive charges are outside
* More negative charges are inside
25
New cards
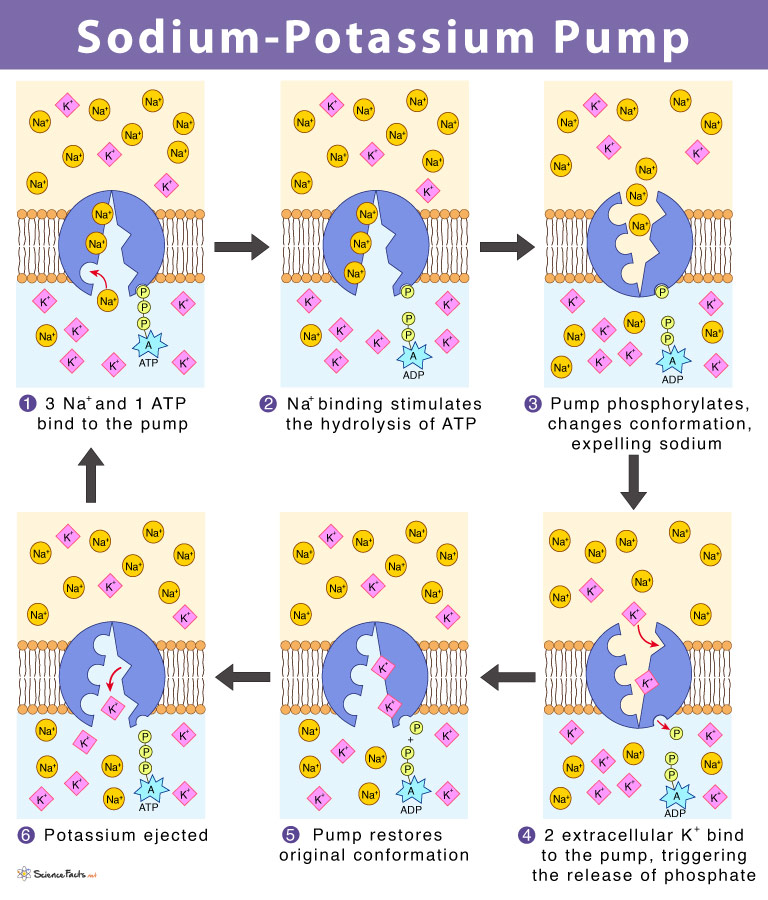
Sodium-Potassium Pump
* Prevents equilibrium
* Maintains resting potential @ -70mV
* Keeps Na+ outside and K+ inside
* Uses ATP for active transport of ions.
* Maintains resting potential @ -70mV
* Keeps Na+ outside and K+ inside
* Uses ATP for active transport of ions.
26
New cards
Sodium-Potassium Mechanism
1. 3 Na+ ions bind to pump and ATP is signaled
2. ATP binds to pump, ATP loses phosphate, and energy is released.
3. Pump changes shape and Na+ ions are released outside the cell.
4. 2 K+ ions bind to pump
5. Phosphate unbinds from pump
6. Pump returns to original shape and K+ ions are released into cell.
27
New cards
Depolarization
* Sensory neurons receive stimulation.
* Threshold level is -55mV
* Action potential will only be transmitted if stimulation is strong enough. (>-55mV)
* Threshold level is -55mV
* Action potential will only be transmitted if stimulation is strong enough. (>-55mV)
28
New cards
Steps in Depolarization
* K+ gates closed
29
New cards