Ch.2 anatomy
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
The single most abundant protein in the body is ________.
Glucose
Increasing the concentration of an enzyme substrate would _____ the reaction
Speed up
An enzyme’s ______ is the molecule upon which an ezyme acts.
Substrate
The organic compounds that function in building tissues and acting as enzymes are the ____
Proteins
Two or more polypeptides chains combine to form a complex structure called a ____
Quanternary Structure
Amino Acids are linked together by _____ Bonds
Peptidebond
The most important eicosanoids are prostaglandins
Prosta
The most important steroid is
Cholestorol
What is room temperature fat ?
Saturated
What is liquid temperature fat ?
Unsaturated
The 4 major subclasses of lipids include triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, and ___
Eicosanoids
Whats the most abundant protein in your body ?
Collagen
What does fiborous protein do ?
Structural
What does Globular protein do ?
Functional
Which statement best describes fiborous proteins ?
Most often appear in body structure
The building blocks of proteins are
Amino Acids
What kind of bonds holds proteins together ?
Peptide bonds
What do Hydrogen bonds hold ?
DNA and Protein
Which lipid is formed of four interlocking carbon rings ?
Cholesterol
Shape and function determines what ?
Function
The building blocks of a triglyceride are
Three fatty acid chains and one glycerol molecule
The part of a phospolipid that associates with water is
The Phosphate head
Whats the most important eicosanoids ?
Prostaglandins
What does cholesterol do ?
The structural basis for manufacture of all body steroids. A component of cell membranes
What does ICF stand for ?
Inside Cellular Fluid
What does ECF stand for ?
Extra Cellular Fluid
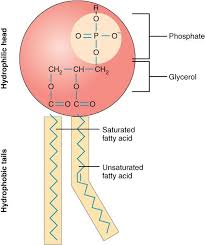
What does this image represent ?
Lipids
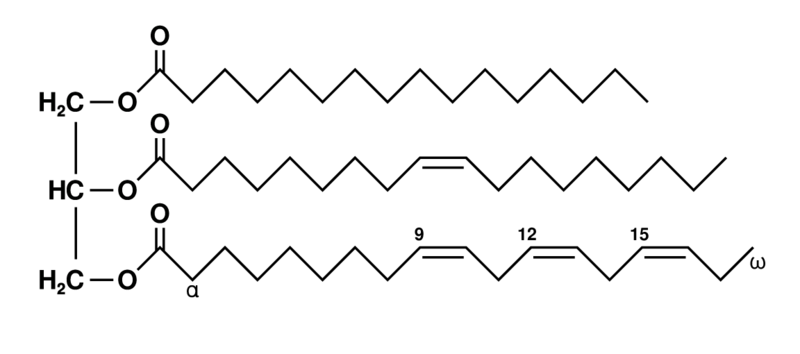
What does this image represent ?
Lipids
What are the main functions for Lipids ?
Energy, insulation, protection, organ structure
What are the 4 main types of lipids ?
Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Steroids, Eicosanoids
What are triglycerides ?
Body fat
What are Phospolipids do ?
Membrane
What are Steroids do ?
Powerfull Chemicals
What are Eicosanoids ?
Positive feedback
Which carbohydrate is also known as blood sugar ?
Glucose
In order to break a disacchride down into simple sugars units,____
Water molecules must be added to each bond
Glycogen and starch are examples of a specifc category of carbohydrates called _____
Polysaccharides
Where is Glycogen stored ?
In the Muscle and Liver
What are Monosaccharides ?
Simple sugars
What are Disaccharides ?
Double sugars, too large to pass through cell membrane
What are the building blocks of carbohydrates ?
Monosaccharides
What are Polysaccharides ?
Many sugars
Blood pH falls in a narrow range between ?
7.35 to 7.45
The pH scale is based on a number of _____ in a solution.
Electrons
An acid is a molecule that releases ____.
Protons
Nerve impulses involve the flow of an electrical current, a type of energy known as ____ energy.
Electrical
What is a polymer ?
Chains of similar units called monomers
Dehydration
Removing water to make smaller
Hydrolysis
Adding water to make bigger
What is the most important buffer system ?
Carbonic Acid
What are the important basses ?
Bicarbonate and Ammonia