Chapter 15: Understanding Infectious Diseases and Pathogen Mechanisms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Pathology
Study of disease
Etiology
Study of the cause of disease
Pathogenesis
Development of disease
Infection
Multiplication of any parasitic organisms
Disease
Disturbance in the state of health wherein the body can't carry out all of its normal functions
Signs of Disease
Objective and measurable; directly observed by a clinician
Symptoms of Disease
Subjective; felt or experienced by a patient but cannot be confirmed or measured
Syndrome
A specific group of signs and symptoms
Infectious disease
Caused by infectious agents
Noninfectious disease
Caused by some other factor - for example a poison
Communicable diseases
Can be spread from host to host - examples include measles and hepatitis
Non-communicable disease
Cannot be spread from host to host - examples include food poisoning and tetanus
Iatrogenic disease
Contracted as the result of a medical procedure
Nosocomial disease
Acquired in hospital settings
Zoonotic disease
Transmitted from animals to humans
Subclinical disease
No noticeable signs or symptoms (inapparent infection)
Acute disease
Symptoms develop rapidly
Chronic disease
Disease develops slowly
Subacute disease
Symptoms between acute and chronic
Latent disease
Disease with a period of no symptoms when the causative agent is inactive
Koch's Postulates
A set of criteria to establish a causative relationship between a microbe and a disease
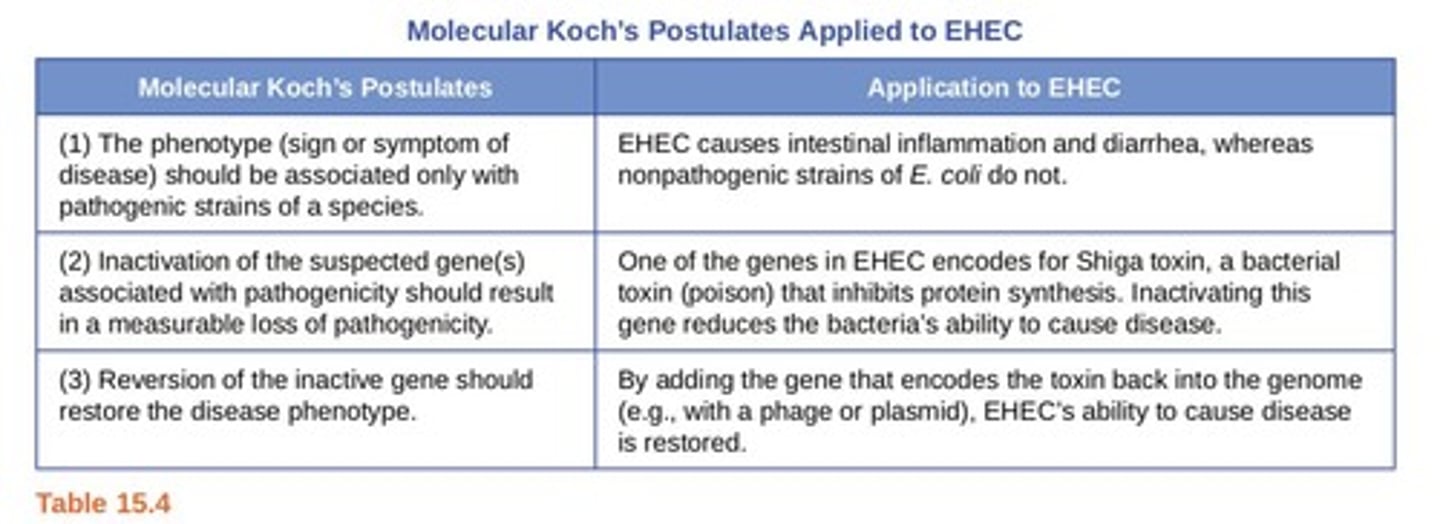
Molecular Koch's Postulates
Premise is to identify a gene that may cause the organism to be pathogenic
Pathogenicity
Capacity to produce disease
Virulence
Intensity of the disease produced by the pathogen
Attenuation
Weakening of the disease-producing ability of the pathogen
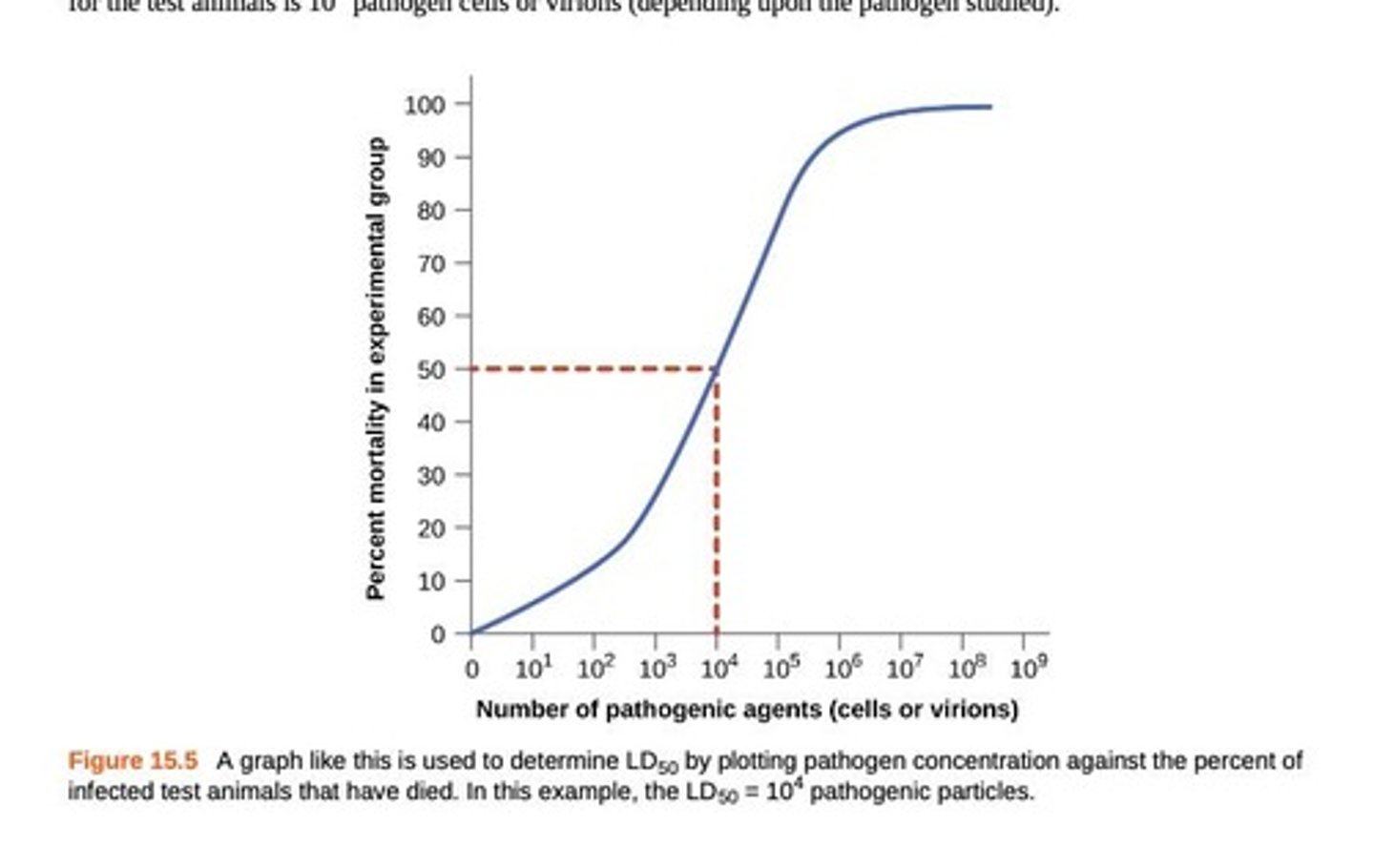
ID50
Infectious dose for 50% of the test population
LD50
Lethal dose for 50% of the test population
Primary pathogen
Always causes disease
Opportunistic pathogen
Can only cause disease when the host's defenses are compromised
Virulence Factors
Molecules that enable pathogens to attach to host cells and cause disease
Adhesins
Molecules that bind to receptors on host cells
Biofilms
Communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces
Invasion
The dissemination of a pathogen throughout local tissues or the body.
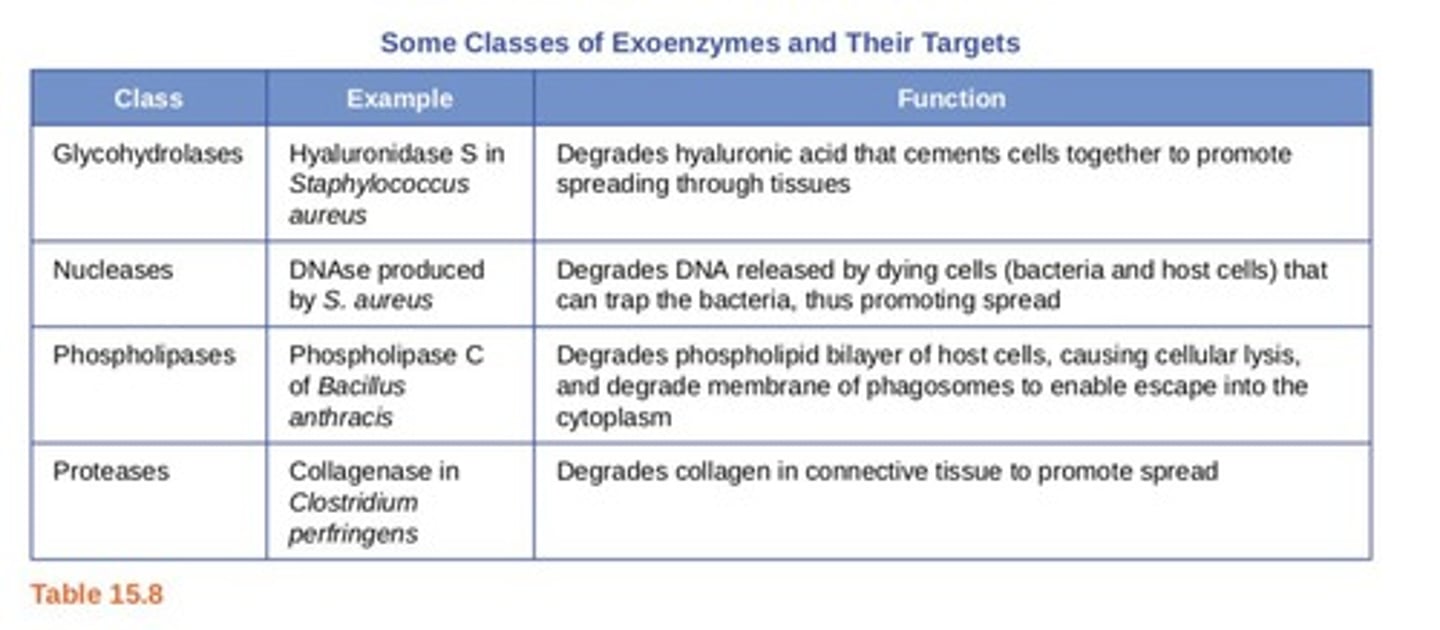
Exoenzymes
Enzymatic virulence factors help bacteria invade tissue and evade host defenses.
Toxin
Substance that contributes to pathogenicity.
Toxigenicity
Ability to produce a toxin.
Toxemia
Presence of toxin in the host's blood.
Toxoid
Inactivated toxin used in a vaccine.
Antitoxin
Antibodies against a specific toxin.
Exotoxins
Proteins produced inside pathogenic bacteria, most commonly gram-positive bacteria, as part of their growth and metabolism.
Endotoxins
Lipid portions of lipopolysaccharides (LPS) that are part of the outer membrane of the cell wall of gram-negative bacteria.
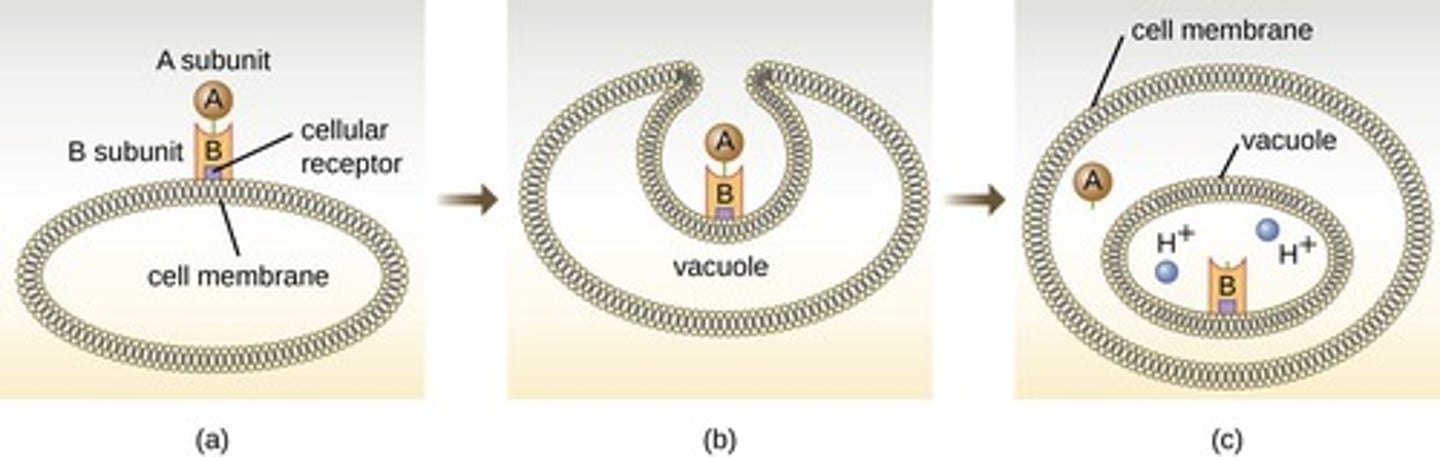
Two-Subunit AB Toxins
A subunit is toxic. B subunit binds host cell receptors.
Primary infection
Acute infection that causes the initial illness.
Secondary infection
Opportunistic infection after a primary (predisposing) infection.
Local infection
Pathogens are limited to a small area of the body.
Systemic infection
An infection throughout the body.
Focal infection
Systemic infection that began as a local infection.
Sepsis
Toxic inflammatory condition arising from the spread of microbes, especially bacteria or their toxins, from a focus of infection.
Bacteremia
Bacteria in the blood.
Septicemia
Growth of bacteria in the blood.
Viremia
Viruses in the blood.
Antigenic variation
100 known serotypes of rhinovirus; each virus has a unique capsid protein.
Antigenic shift
Two strains of influenza virus infect the same cell and the genomes get mixed.
Antigenic drift
Random mutations can occur within the cell that a virus infects creating small changes in virus proteins.
Latent Herpes Virus
Herpes virus goes into latency and incorporates its genome into the host cell.
Antigenic Masking
Some protozoans coat themselves in host antigens to avoid detection by the immune system.
Intracellular Location
Some protozoans have found ways to live inside the host cell to prevent detection.
Immunosuppression
Some protozoans induce the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines to reduce the innate immune response.