16 - Fatty Acid B-Oxidation
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the function of B-oxidation?
The function of beta oxidation is to break down fatty acids to generate ATP during low carbohydrate and insulin concentrations - stimulated by increased epinephrine (binds to B-3 adrenergic receptors and activates cAMP protein kinases)
Describe the process of fatty acids entering the mitochondria.
Fatty acids are activated in the cytosol. Acyl CoA Synthetase (cytosol): Fatty acid + ATP + CoASH → Acyl-CoA (activated) + AMP + PPI. Acyl CoA is then transferred into the mitochondria. Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase (CPT-1): Acyl CoA + Carnitine → Acyl-Carnitine + CoASH. Acyl-Carnitine is then transported with antiport of carnitine into the microchondria. TWO ATP are required to activate one fatty acid to a thioester (high energy C-S bond).
Where does acyl CoA react with carnitine?
Acyl CoA reacts with the BETA-HYDROXY group of the carnitine to form acyl-carnitine.
Describe reaction one of B-oxidation.

Describe reaction two of B-oxidation.
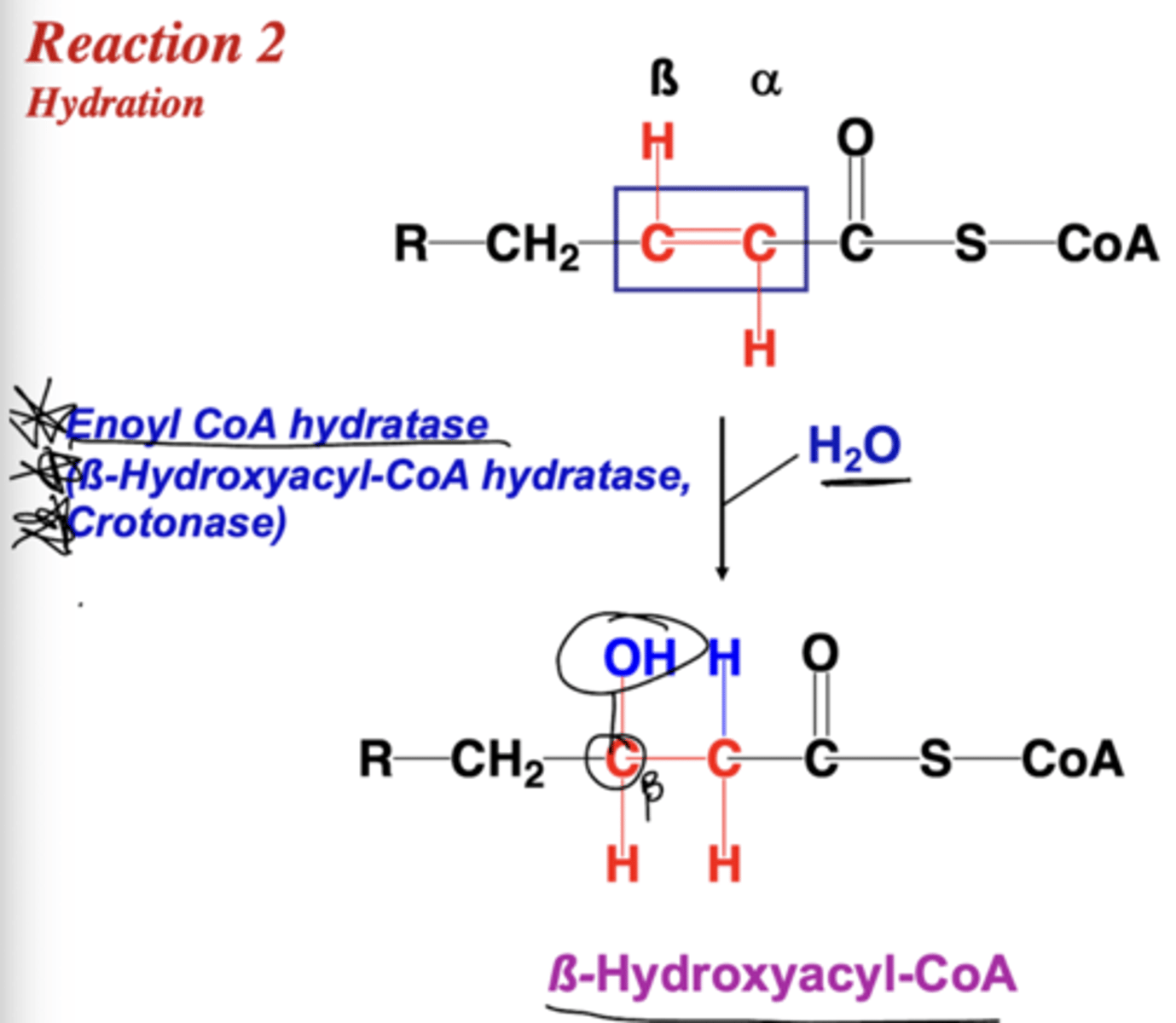
What are the alternative names for enoyl CoA hydratase?
B-hydroxyacyl-CoA hydratase and crotonase
Describe reaction three of B-oxidation.
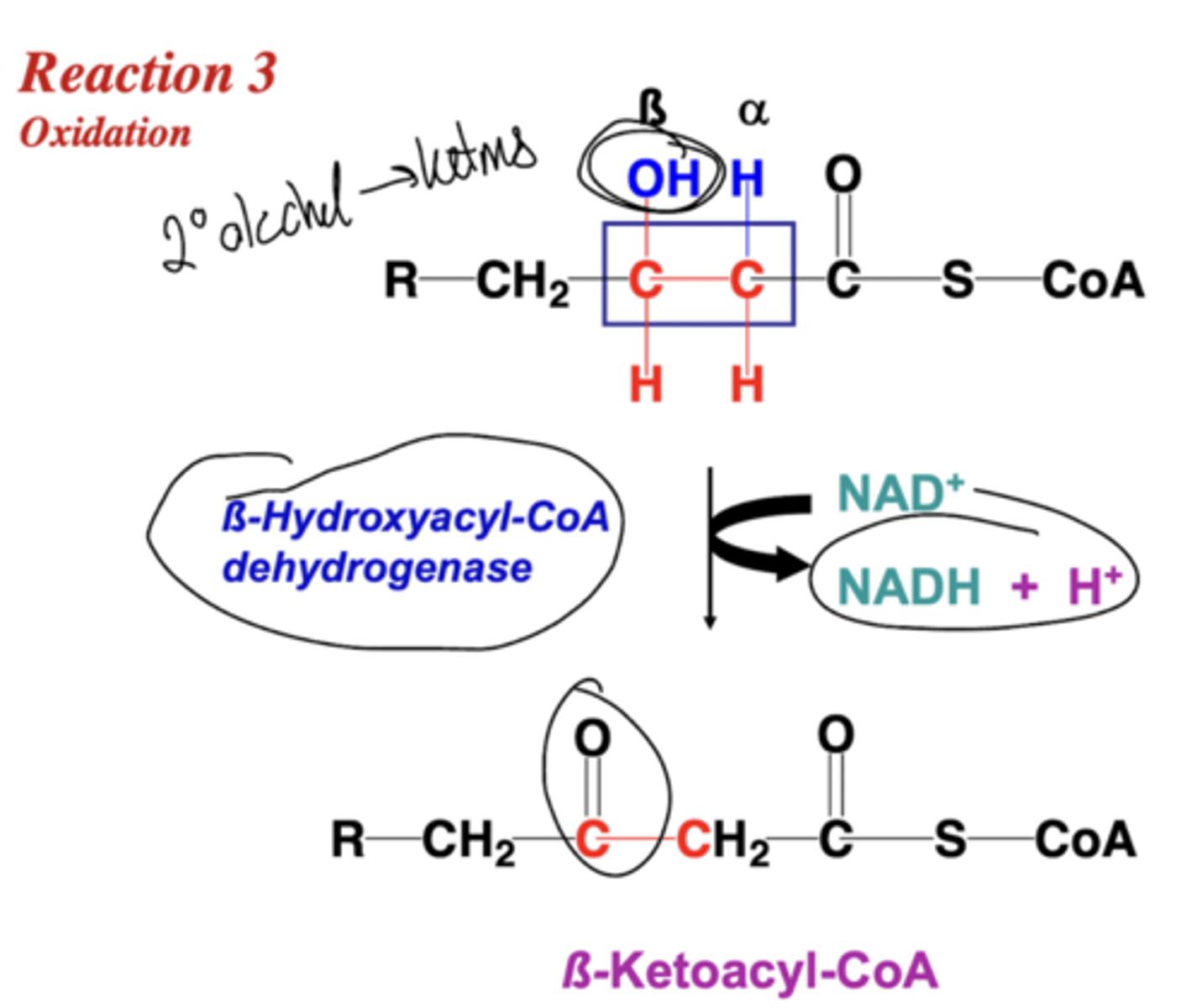
Describe reaction four of B-oxidation.
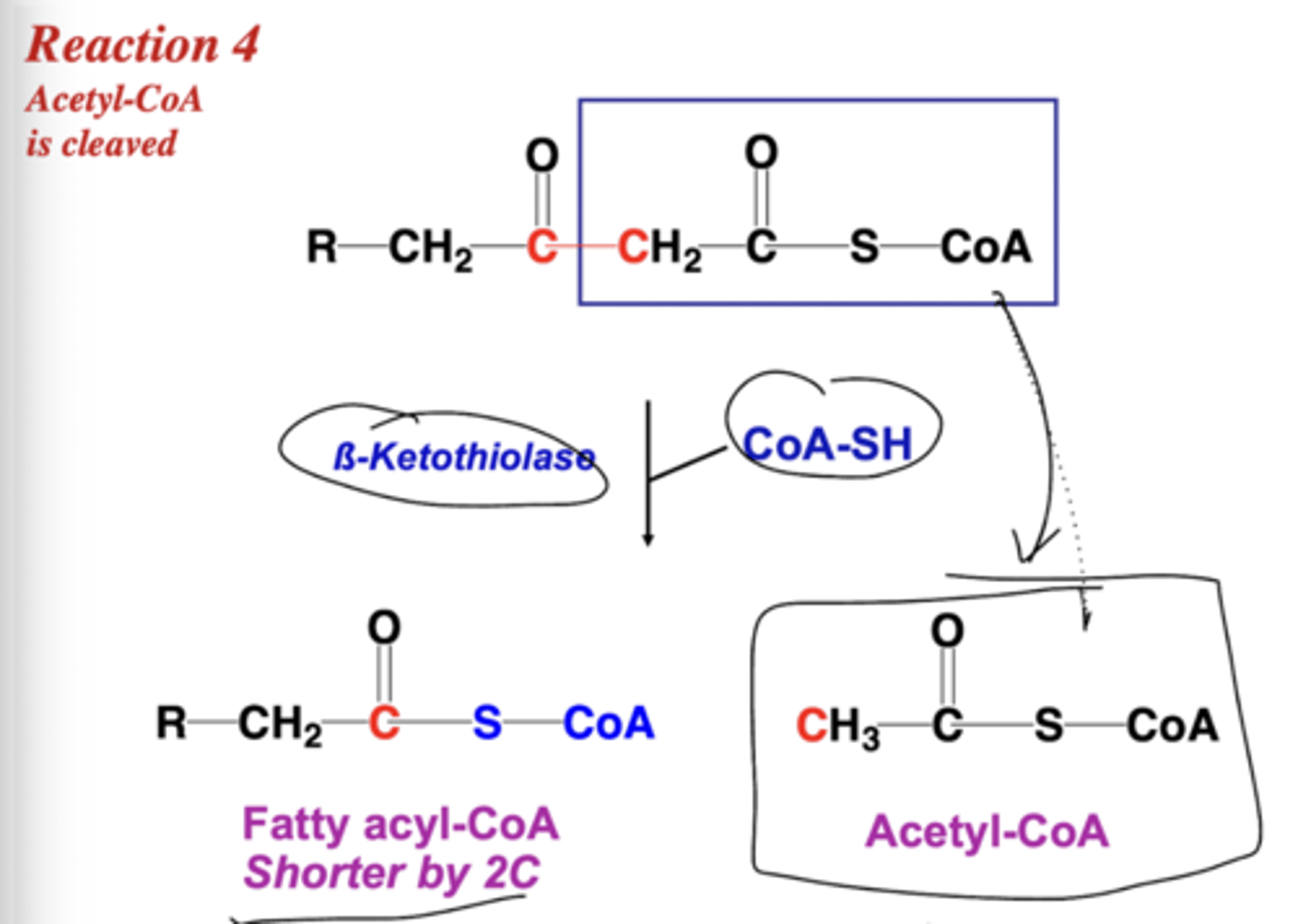
How do you determine the number of B-oxidation cycles for a X-long fatty acid?
Divide the fatty acid carbons by 2 and subtract one to get the amount of cycles. Dividing by two gets the acetyl CoA released.
What are the three ketone bodies?
B-hyroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, acetone. Released during fasting/starvation from acetyl CoA conversion
Briefly describe the first half (up to HMG CoA) of ketone synthesis.
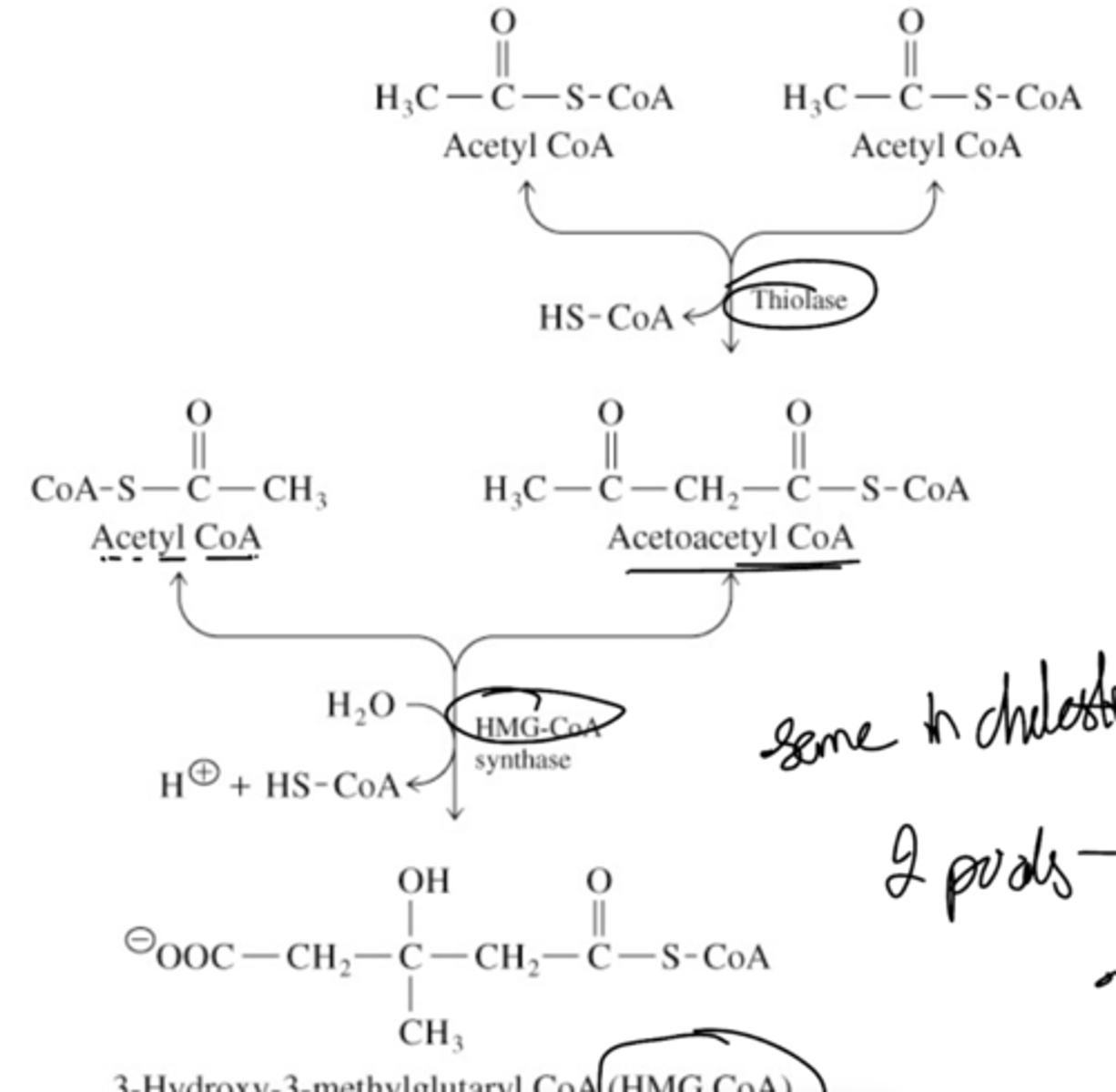
Briefly describe the second half (from HMG CoA) of ketone synthesis.
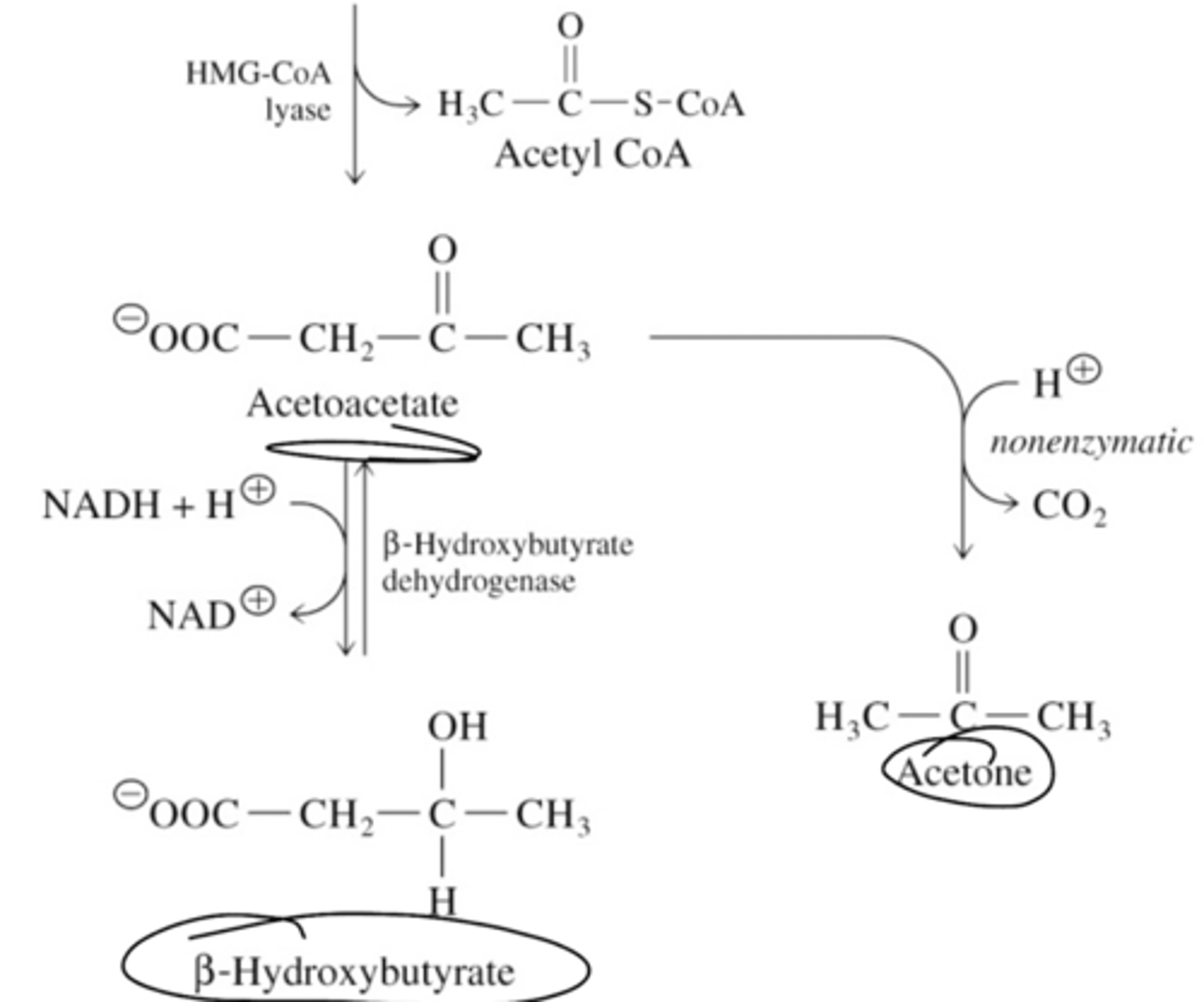
What is ketosis?
accumulation of ketone bodies that happens when acidic ketone lower bloods pH below
7.4
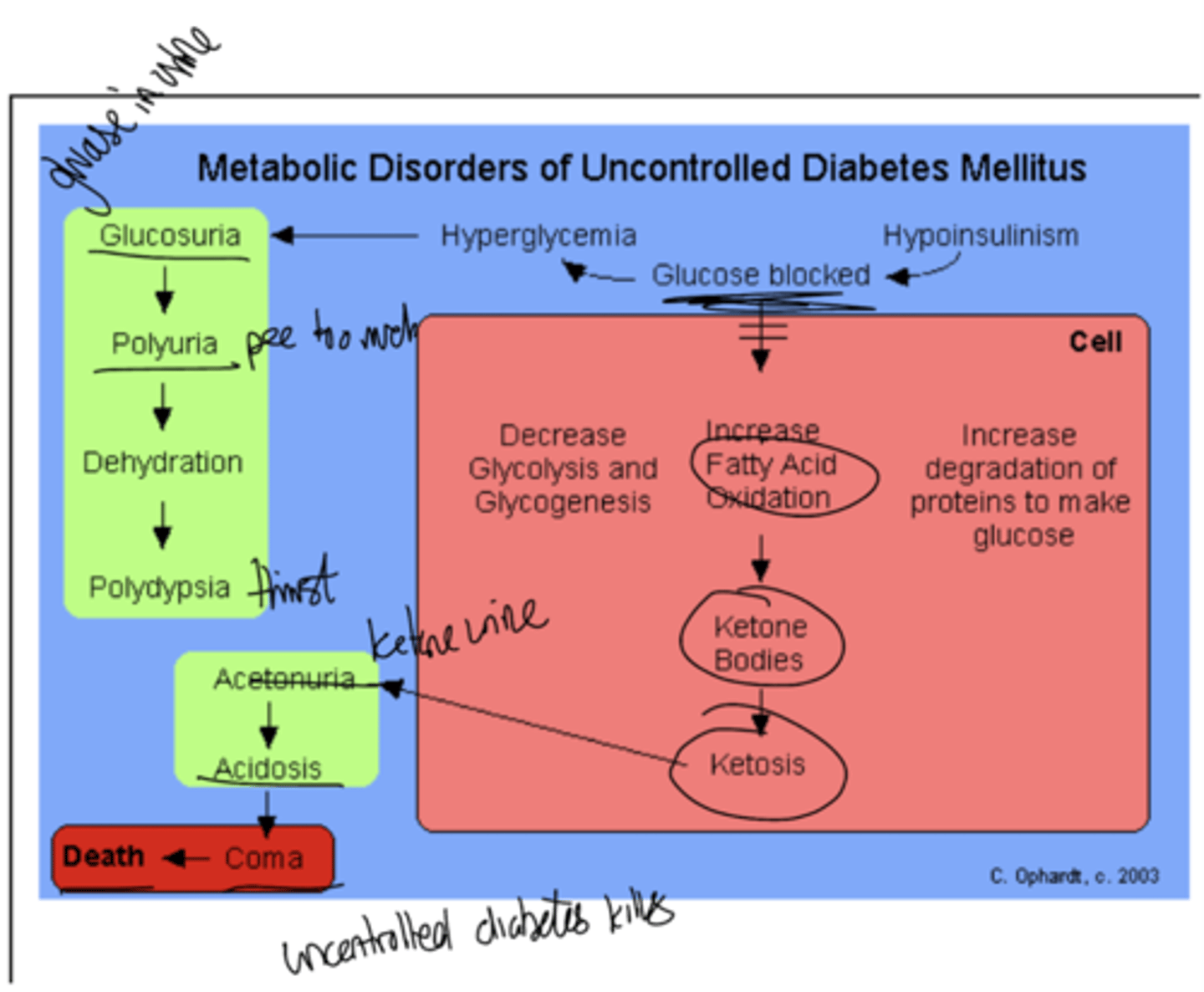
How does uncontrolled diabetes mellitus lead to death?
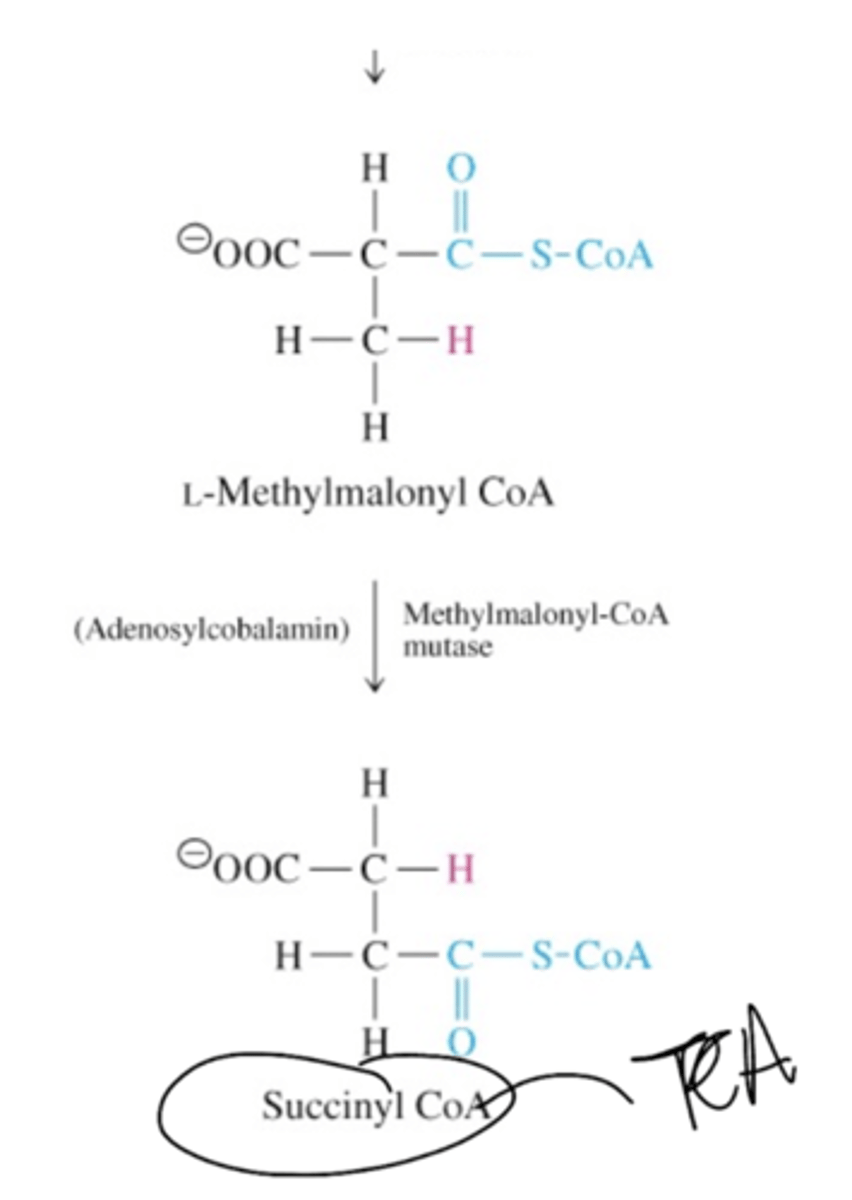
Describe the conversion of propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA (the half up to D-methylmalonyl CoA)

Describe the conversion of propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA (the half down from D-methylmalonyl CoA)
What are the two enzymes required in the B-oxidation of unsaturated FA?
enoyl -CoA isomerase
2,4 dienoyl CoA reductase
Provide the equation for beta-oxidation.
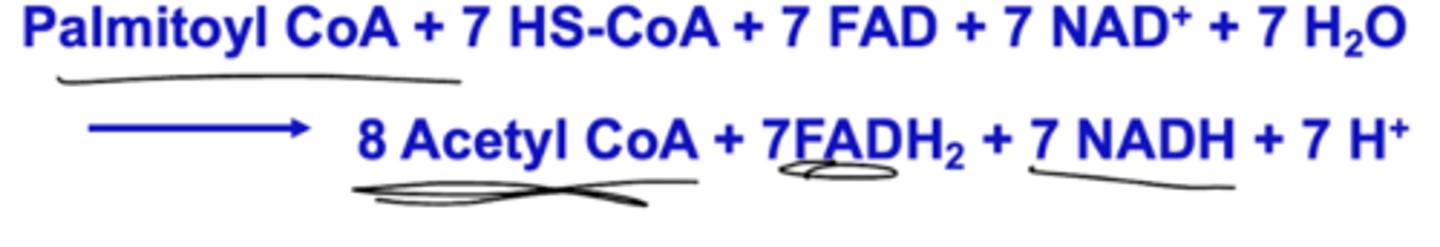
What is the gross and net yield of ATP of B-oxidation?
108 - 2 (to activate fatty acid) = 106 ATP
Where is CPT-1 located? What regulates it?
CPT-1 is on the mitochondrial outer membrane. It is inhibited by malonyl CoA from fatty acid synthesis.
How does T1DM affect CPT-1?
T1DM affects CPT-1: not enough malonyl CoA, leading to rampant beta oxidation with no inhibition
High acetyl CoA, leading to exhaustion of OAA, leading the rest of the acetyl CoA going to ketone synthesis (ketonuria and ketones in breath as acetone)
Where is CPT-2 located? What does it do?
CPT-2 is located on the inner leaflet of the inner mitochondrial membrane - not inhibited by malonyl CoA
Turns acylcarnitine back into acyl-CoA for beta oxidation
What are some characteristics of monoaminoxidase?
target for drugs and is a receptor for norepinephrine - directly regulated by insulin
How is fasting similar to diabetes?
Malonyl CoA is low, CPT-1 activity is high , leading to translocation of FA into the mitochondria, leading to high Beta Oxidation (Ketone synthesis up)
What are the isoforms of CPT-1?
Liver isoform (CPT1A/L): found throughout body on mitochondria of cells EXCEPT SKELETAL MUSCLE AND BROWN FAT
Muscle isoform (CPT1B/M) is highly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle cells and brown fats
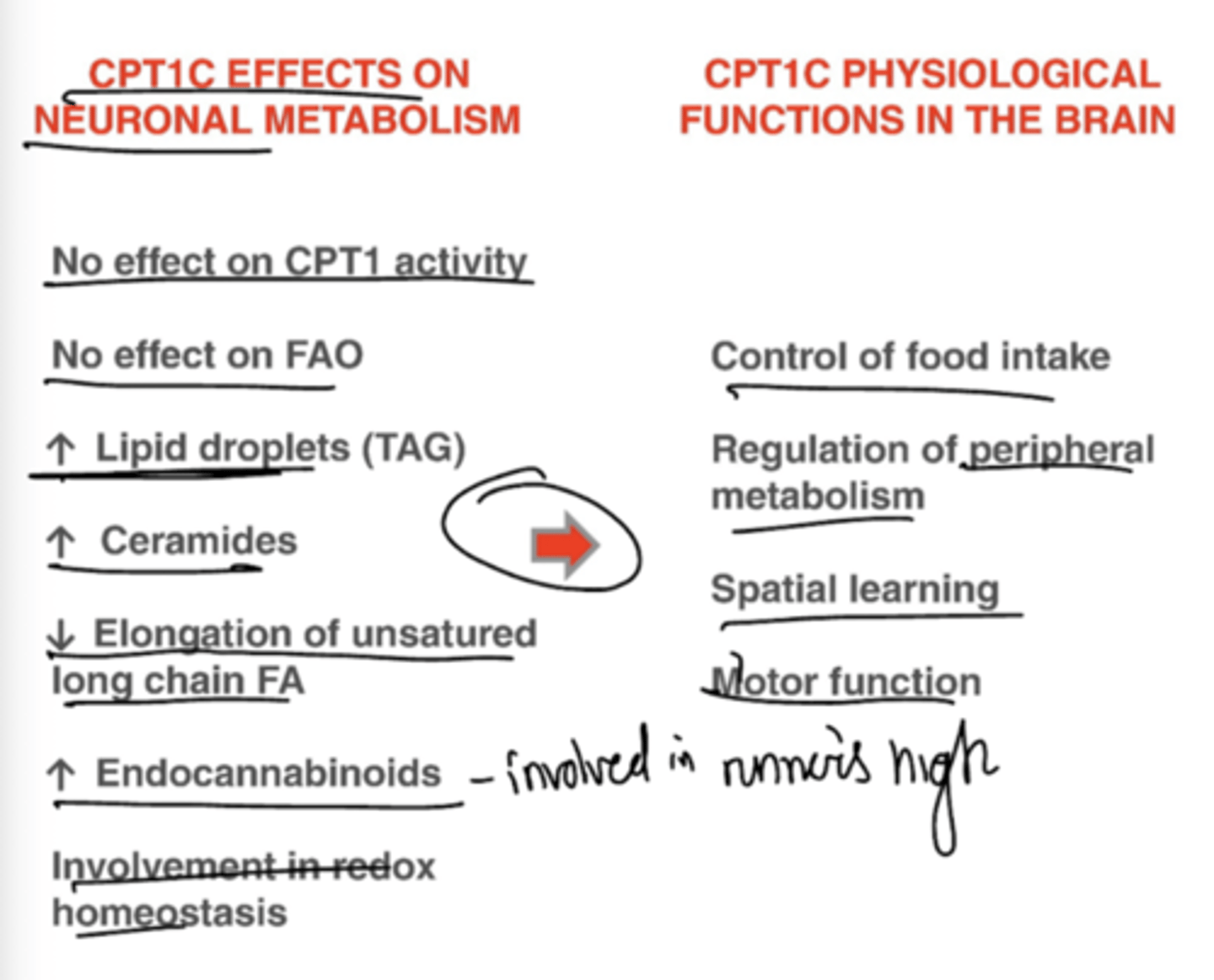
Brain isoform (CPT1C) is expressed in brain and testes
What are CrAT and COT? Where are they found?
CrAT (carnitine acetyltransferase < shorter than 8 strands)
COT (carnitine octanyltransferase < around 8 strands (octa). Found in peroxisomes
Describe CPT1-A deficiency.
CPT1-A deficiency is a rare disorder that confers risk for hepatic encephalopathy, hypoketotic hypoglycemia, seizures, and sudden unexpected death in infancy
Not compatible with life
Describe CPT-II deficiency.
CPT-II deficiency is autosomal recessive
3 types classified on basis of symptomology and age of onset
Neonatal: invariably fatal; onset hours after birth; respiratory failure, low blood sugar, seizures, liver enlargement, liver failure, heart enlargement and cardiac arrest
Infantile: 6-24 months of age presentation; hypoketotic hypoglycemia and loss of consciousness; acute liver failure, liver enlargement, cardiomyopathy; sudden infant death syndrome
Adult: myopathic form and is least severe; rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of muscle release myoglobin) myoglobinuria, recurrent muscle pain, and weakness - mainly muscle weakness and pain in clinical presentation brought about by exercise - 80% male
Describe the effects of CPT-1C on neuronal metabolism and brain function.
What are the products of B-oxidation?
One round of beta-oxidation (4 enzyme steps) produce acetyl CoA from fatty acyl CoA
One molecule of FADH2, NADH, Acetyl CoA, and Fatty acyl CoA (2 shorter)