CHE2C Transition Metals
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Radii pattern on Periodic Table
Decrease then increase across a row (nuclear charge draws d e- inwards = decreasing radius. As d e- increase, e- e- repulsion increases —> increasing radius)
2nd & 3rd row nearly the same (lanthanide contraction, f e- of lanthanides don’t shielf nucleus well, causing contraction
Density pattern on Periodic Table
Increases then decreases (inversely proportional to volume)
3rd row significantly higher densities bc lanthanide contraction (less volume) & higher mass
Where are higher oxidation states more stable?
2nd and 3rd row
What is the common transition metal oxidation state and where are the e- lost?
+2, loss of both s-e-
Which columns of Transition Metals don’t fill as expected? How do they fill?
e- in the 4th (Cr) and 9th (9th) column. Only 1 e- fills the s-orbital
Where are e- removed first for transition metals? (orbitals)
s e- are removed before d e-
Do Transition metals have ionic or covalent character?
both
Which transition metals have color?
any metal with partially filled d-subshells
Which transition metals are colorless or white?
filled and unfilled subshells
What is ferromagnetic?
permanent domains of magnetism
Why are TM great catalysts?
Multiple ox states and coordination numbers possible
ligands can easily bond and multiple bonding sites available
generally coordinatively unsaturated (can accept more ligands)
What kinds of reactions do TM undergo?
Combination
Decomposition
Single Replacement
Double Replacement
What is Metallurgy?
the process of refining metal ore to the pure metal for industrial use and applications
Scandium
ox state: +3 most common
act similar to AL, Y, and lanthanides bc cation has no d e-
diamagnetic so colorless
Titanium
low density, high strength, low corrosion
similar properties to C and Si
ox state: +3, +4
Vanadium
makes strong and tough steels
compounds are toxic
ox state: +5 most common, +2 through +5 exist
Chromium
corrosion resistant
many compounds have intense colors
toxic and carcinogenic
ox states: +2, +3, +6
Manganese
ox state: +2, +7
applications:batteries, catalyst (MnO2)
Iron Family
most common element by mass on Earth, forms inner and outer core
form metal carbonyl bonds (M - CO)
ox states: +2,+3
Cobalt Family
ferromagnetic
used to color glass, changes color a lot
form metal carbonyl bonds (M - CO)
easily takes ligands
ox states: +2, +3
Nickel Family
corrosion-resistant
“double-magic” = extremely stable
form metal carbonyl bonds (M - CO)
ox state: +2
Copper Family (Coinage Metals)
bronze and crass alloy
durability and corrosion-resistant
naturally blue
high conductivity
ox states: +1, +2
Zinc Family
ox state: +2
corrosion-resistant, hard, brittle, diamagnetic, reducing agent
common sacrificial anode
Lanthanides
f e- don’t play a big role in bonding, elements in series have similar chemistry to each other
similar to Sc and Y
highly reactive with halogens and chalcogens
ox state: +3 common, +2, +4
low toxicity
Actinides
all radioactive and paramagnetic
similar properties to lanthanides
toxic due to radioactivity

Linear
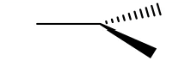
Trigonal planar
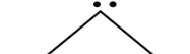
Bent (Trigonal planar)
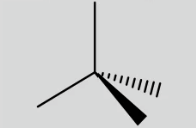
Tetrahedral
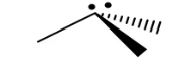
Trigonal pyramidal (tetrahedral)

Bent (tetrahedral)
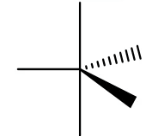
Trigonal Bipyramidal
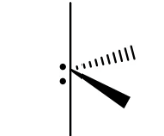
Seesaw (Trigonal Bipyramidal)
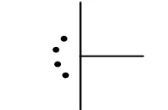
T-shaped (Trigonal Bipyramidal)
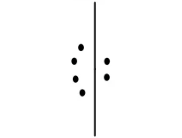
Linear (Trigonal Bipyramidal)
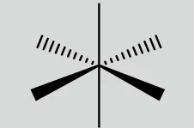
Octahedral
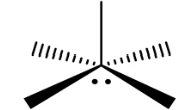
Square pyramidal (Octahedral)
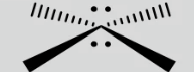
Square planar (octahedral)
Coordination Compound
TM ions, in combination with ligands and counter ions, form these compounds.
General term for neutral compounds that contain TMs
Complex Ions
TM ions in combination with ligands form these compounds
This term is used when the TM species has a nonzero charge
Counter Ions
Anions or cations needed to produce a compound with no net charge
appropriate counter ions added to a complex ion (charged) to make it a coordination compound (neutral)
Ligands
Groups (not including counter ions) that surround the transition metal ions
Coordination Number (CN)
Number of nearest neighbors to the transition metal ion (usually ligands)
count the number of ligands around the TM ion, can vary from 2 to 12
Complex
general term for any species involving ligands connected to a transition metal ion
Ox State
Primary valence of the TM
Ligands will have
lone pair or e- ready to form a bond
Neutral or negative charge
Monodentate
A ligand with one pair of e- to attach to the TM
Polydentate
A ligand with 2 or more pairs of e- to attach (bond) to the TM
H2O
Neutral, Aqua
NH3
Neutral, Ammine
CO
Neutral, Carbonyl
NO
Neutral, Nitrosyl
CH3NH2
Neutral, Methylamine
C5H5N
Neutral, Pyridine
F-
Anions, Fluoro
Cl-
Anion, Chloro
Br-
Anion Bromo
I-
Anion, Iodo
O²-
anion, oxo
OH-
anion, hydroxo
CN-
Anion, Cyano
SO4²-
Anion, Sulfato
S2O3²-
Anion, Thiosulfato
NO2-
Anion Nitrito-N-
ONO-
Anion Nitrito-O-
SCN-
Anion, Thiocyanato-S-
NCS-
Anion, Thiocyanato-N-
en
Bidentate
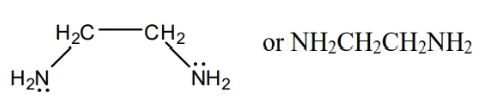
ox²- or C2O4²-
Bidentate
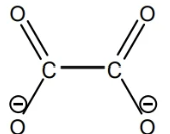
Nomenclature: When considering a complex ion and the counter ion, are cation named first or anions?
cation first
composite ligand
ligands that contain a prefix in its name (ex: en and EDTA^4-), must used composite prefixes
How does the naming of the complex ion work?
Ligands are named in alphabetical order first (not including prefix) and then the metal with ox state is named last
complex ion is anion —> metal must be named in Latin if possible with suffix ate
complex ion is cation, metal is named in English with no additional suffix
Composite Prefix for 2
Bis-
Composite Prefix for 3
Tris-
Composite Prefix for 4
Tetrakis-
Latin Name for Iron
Ferrate
Latin Name for Copper
Cuprate
Latin Name for Tin
Stannate
Latin Name for Silver
Argentate
Latin Name for Lead
Plumbate
Latin Name for Gold
Aurate
IS the TM cationic or anionic?
cationic
How to tell if the complex is positive or negative?
[ ] listed first = cationic
[ ] listed second = anionic
Ionization Isomers
A structural isomer where a ligand and a counter ion switch
coordination isomers
a structural isomer where the transition metals of a bi-metallic (2 metal) species switch ligands
linkage isomers:
A structural isomer where a multi-atom ligand connects to the TM through different atoms
Geometric Isomers:
A stereoisomer where the arrangement of the ligands are either neighboring (cis or fac) or across (trans or mer) from each other
trans
2 identical ligands are bonded across from each other (2ligands same axis)
VSEPR shape: Square Planar or Octahedral
Chiral not possible
cis
2 identical ligands are bonded neighboring each other (2 ligands different axis)
VSEPR shape: square planar or octahedral
chiral possible
fac
3 identical ligands are bonded neighboring each other (3 different axes)
VSEPR shape: Octahedral
chiral possible
mer
3 identical ligands, and 2 of the 3 are bonded on the same axis
VSEPR shape: Octahedral
no chiral
optical isomer/chiral
mirror image is different
When can a tetrahedral be a optical isomer?
Only is all 4 ligands are different
When can a octahedral be a optical isomer?
all 6 ligands are different
etc.
can a complex be both a geometric and an optical isomer at the same time?
yes
Is attraction low energy or high energy? What about repulsion?
attraction is low E, repulsion is high E
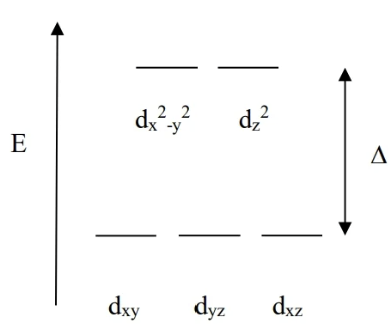
Octahedral CFT
each L is attempting to bond with M on the axis, so dx²-y²and dz² exist at high E

Tetrahedral CFT
each L is attempting to bond with M off the axis, so dx²-y² and dx² are low E
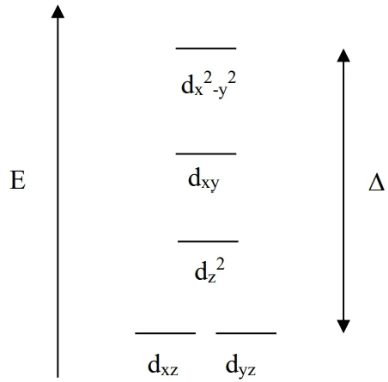
Square Planar CFT
Ligands are on the xy axes
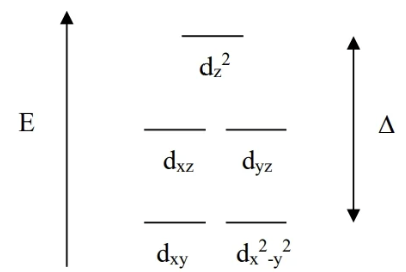
Linear Shape CFT
highest E is the dz² orbital bc it lies right on the z axis