Psyc 3980 - Midterm
1/159
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
Empiricism
Using evidence from the senses or from instruments that assist with sense, as the basis for conclusions
Theory-Data Cycle
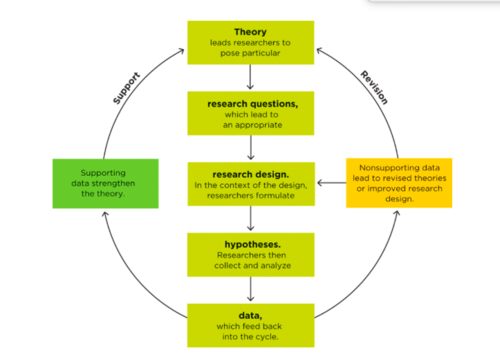
Theory
A set of statements - as simple as possible - that describes general principles about how variables relate to one another
Hypothesis
The specific outcome the researcher will observe in a study if the theory is accurate
Falsifiability
A feature of a scientific theory, in which it is possible to collect data that will indicate that the theory is wrong
Merton’s Scientific Norms
Universalism
Communality
Disinterestedness
Organized skepticism
Universalism
Scientific claims are evaluated according to their merit, independent of the researcher’s credentials or reputation. The same pre-established criteria apply to all scientists and all research
Communality
Scientific knowledge is created by a community and its findings belong to the community
Disinterestedness
Scientists strive to discover the truth, whatever it is; they are not swayed by conviction, idealism, politics, or profit
Organized skepticism
Scientists question everything, including their own theories, widely accepted ideas, and “ancient wisdom”
Applied research
Done with a practical problem in mind and the researchers conduct their work in a local, real-world context
Ex. If a school district’s new method of teaching language arts is working better than the former one. The efficacy of a treatment for depression in a sample of trauma survivors
Basic research
To enhance the general body of knowledge rather than to address a specific, practical problem
Ex. Might want to understand the structure of the visual system, the capacity of human memory, the motivations of a depressed person
Translational research
Use of lessons from basic research to develop and test applications
Ex. Basic research on the biochemistry of cell membranes might be translated into a new drug for schizophrenia. How mindfulness changes people’s patterns of attention might be translated into a study skills intervention
Interrelationship of the three types of research

_________ researchers may not have an applied context in mind.
Basic
_________ researchers may be less familiar with basic theories and principles.
Applied
__________ researchers attempt to translate the findings of basic research into applied areas.
Translational
Journal
A monthly or quarterly periodical containing peer-reviewed articles on a specific academic discipline or subdiscipline, written for a scholarly audience
Journalism
News and commentary published or broadcast in the popular media and produced for a general audience
Identify each activity as an example of either producing or consuming research
Creating and testing a hypothesis on sexuality in teenagers
Producing research
Using research findings to update patients treatment plans
Consuming research
Using previous studies to create a new study that analyzes all of those previous findings
Producing research
Reporting current trends in biology research in a news article
Consuming research
Keyanna is thinking of marketing consulting as a potential future career. Identify each task associated with consulting as either producing research or consuming research.
Collect and analyze data, and present the results to clients
Producing research
Test different marketing strategies to identify the best one
Producing research
Keep up to date on current product trends
Consuming research
Look at analyses conducted by other firms, and inform clients of the findings
Consuming research
Which of the following jobs most likely involves producer-ofresearch skills rather than consumer-of-research skills?
University professor
As a true empiricist, one should:
Base one’s conclusions on direct observations
A statement, or set of statements, that describes general principles about how variables relate to one another is a(n) _________.
Theory
Why is publication an important part of the research process?
Because when a study is published, other scientists can verify or challenge it, making science self-correcting
Which of the following research questions best illustrates an example of basic research?
Can 2-month-old human infants tell the difference between four objects and six objects?
Probabilistic
The findings do not explain all cases all of the time
Confound
A potential alternative explanation for a research finding; a threat to internal validity
Confederate
An actor who is directed by the researcher to play a specific role in a research study
Five ways in which intuition is biased:
Being swayed by a good story
Being persuaded by what comes easily to mind
To think about what we cannot see
Focusing on the evidence we like best
Biased about being biased
Availability heuristic
A bias in intuition, in which people incorrectly estimate the frequency of something, relying predominantly on instances that easily come to mind rather than using all possible evidence in evaluating a conclusion
Present/present bias
A bias in intuition, in which people incorrectly estimate the relationship between an event and its outcome, focusing on times the event and outcome are present, while failing to consider evidence that is absent and harder to notice
Confirmation bias
The tendency to consider only the evidence that supports a hypothesis, including asking only the questions that will lead to the expected answer
Bias blind spot
The tendency for people to think that compared to others, they themselves are less likely to engage in biased reasoning
Sources of information
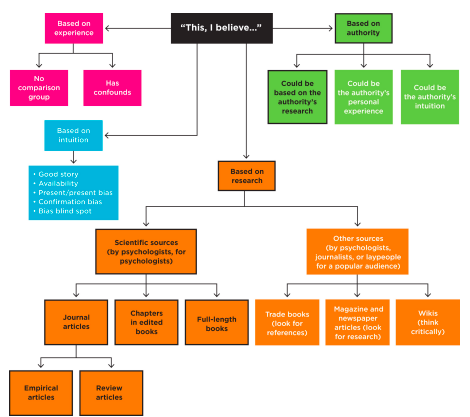
What two guiding questions can help you read any academic research source?
What is the argument?
What is the evidence?
Empirical journal article
A scholarly article that reports for the first time the results of a research study
Review journal article
An article summarizing all the studies that have been published in one research area
Effect size
The magnitude, or strength, of a relationship between two or more variables
Disinformation
A news story, photo, or video deliberately created to be false or misleading
Meta-analysis
A way of mathematically averaging the effect sizes of all the studies that have tested the same variables to see what conclusion that whole body of evidence supports
Destiny concluded that her new white noise machine helped her fall asleep last night. She based this conclusion on personal experience, which might have confounds. In this context, a confound means:
Another thing might have also occurred last night to help Destiny fall asleep
What does it mean to say that research results are probabilistic?
Research conclusions explain a certain proportion of possible cases but may not explain all
After two students from his school commit suicide, Marcelino concludes that the most likely cause of death in teenagers is suicide. In fact, suicide is not the most likely cause of death in teens. What happened?
Marcelino was probably influenced by the availability heuristic; he was too influenced by cases that came easily to mind
When is it a good idea to base conclusions on the advice of authorities?
When authorities base their advice on research that systematically and objectively compares different conditions
Which of the following is the most reliable source for reading the details of a psychological study?
Scientific journals
In reading an empirical journal article, what two questions should you be asking as you read?
What is the argument? What is the evidence to support the argument?
Variable
An attribute that varies, having at least two levels, or values
Level
One of the possible variations, or values, of a varibale
Constant
An attribute that could potentially vary but that has only one level in the study question
Measured variable
A variable in a study whose levels (values) are observed and recorded
Manipulated variable
A variable in an experiment that a researcher controls, such as by assigning participants to its different levels (values)
Construct
A variable of interest, stated at an abstract level, usually defined as part of a formal statement of a psychological theory
Conceptual variable
A variable of interest
Operational definition
The specific way in which a concept of interest is measured or manipulated as a variable in a study
Operational variable
The specific way in which a concept of interest is measured of manipulated as a variable in a study
Operationalize
To turn a conceptual definition of a variable into a specific measured variable or manipulated variable in order to conduct a research study
Frequency claim
A claim that describes a particular rate or degree of a single variable
Association claim
A claim about two variables, in which the value (level) of one variable is said to vary systematically with the value of another variable
Correlate
To occur or vary together systematically, as in the case of two variables
Correlational study
A study that includes two or more variables, in which all of the variables are measured; can support an association claim
Positive association
An association in which high levels of one variable go with high levels of the other variable, and low levels of one variable go with low levels of the other variable
Negative association
An association in which high levels of one variable go with low levels of the other variable, and vice versa
Zero association
A lack of systemic association between two variables
Casual claim
A claim arguing that a specific change in one variable is responsible for influencing the value of another variable
Validity
The appropriateness of a conclusion or decision
Construct validity
An indication of how well a variable was measured or manipulated in a study
Generalizability
The extent to which the subjects in a study represent the populations they are intended to represent; how well the settings in a study represent other settings or contexts
External validity
An indication of how well the results of a study generalize to, or represent, individuals or contexts besides those in the study itself
Statistical validity
The extent to which statistical conclusions derived from a study are accurate and reasonable
Point estimate
A single estimate of some population value
Confidence interval (CI)
A given range indicated by a lower and upper value that is designed to capture the population value for some point estimate
Covariance
The degree to which two variables go together
Temporal precedence
One of three criteria for establishing a casual claim, stating that the proposed casual variable comes first in time, before the proposed outcome variable
Internal validity
One of three criteria for establishing a casual claim; a study’s ability to rule out alternative explanations for a casual relationship between two variables
Experiment
A study in which at least one variable is manipulated and another is measured
Independent variable
A variable that is manipulated
Dependent variable
The variable that is measured
Most important validity in frequency claims?
External validity
Most important validity in association claims?
Construct and statistical validities
Which of the following variables are manipulated, rather than measured? (Could be more than one.)
Amount of aspirin a researcher gives a person to take, either 325 mg or 500 mg.
Type of praise a researcher uses in groups of dogs: verbal praise or a clicking sound paired with treats.
Which of the following headlines is an association claim?
Workaholism is tied to psychiatric disorders
Which of the following headlines is a frequency claim?
Eighty percent of women feel dissatisfied with how their bodies loo
Which of the following headlines is a causal claim?
Taking a deep breath helps minimize high blood pressure, anxiety, and depression
Which validity would you be interrogating by asking: How well did the researchers measure sensitivity to tastes in this study?
Construct validity
Which validity would you be interrogating by asking: How did the researchers get their sample of people for this survey?
External validity
In most experiments, trade-offs are made between validities because it is not possible to achieve all four at once. What is the most common trade- off?
Internal and external validity
Self-report measure
A method of measuring a variable in which people answer questions about themselves in a questionnaire or interview
Observational measure
A method of measuring a variable by recording observable behaviors or physical traces of behaviors
Physiological measure
A method of measuring a variable by recording biological data
Categorical variable
A variable whose levels are categories
Ex. male and female
Quantitative variable
A variable whose values can be recorded as meaningful numbers
Ordinal scale
A quantitative measurement scale whose levels represent a ranked order, and in which distances between levels are not equal
Interval scale
A quantitative measurement scale that has no “true zero”, and in which the numerals represent equal intervals between levels
Ratio scale
A quantitative measurement in which the numerals have equal intervals and the value of zero truly means “none” of the variable being measured
Reliability
The consistency of the results of a measure
Test-retest reliability
The consistency in results every time a measure is used
Interrater reliability
The degree to which two or more coders or observers give consistent rating of a set of targets
Internal reliability
In a measure that contains several items, the consistency in a pattern of answers, no matter how a question is phrases
Correlation coefficient r
A single number, ranging from -1.0 to 1.0, that indicates the strength and direction of an association between two variables