Sociology Midterm 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:41 PM on 3/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
1
New cards
Cultural Relativism
assumes every culture has intrinsic (essential) worth
\
Ex. Multiculturalism
\
Ex. Multiculturalism
2
New cards
Ethnocentrism
assumes “our” culture is superior
\
* On maps, Great Britain is always in the centre on a map
\
* On maps, Great Britain is always in the centre on a map
3
New cards
Rationalization
the action of attempting to explain or justify behavior or an attitude with logical reasons, even if these are not appropriate
\
Ex. The Werkglocken, McDonalidization
\
Ex. The Werkglocken, McDonalidization
4
New cards
Consumerism
the protection or promotion of the interests of consumers
\
Ex. “It’s not the steak we sell, it’s the sizzle”, The Nag Factor
\
Ex. “It’s not the steak we sell, it’s the sizzle”, The Nag Factor
5
New cards
Multiculturalism
provides minorities with rights
\
\-Man wanted to wear a Turban as part of his RCMP uniform - ALL Canadians have rights even the minority
\
\-Man wanted to wear a Turban as part of his RCMP uniform - ALL Canadians have rights even the minority
6
New cards
Globalization
Increased trade, communication, production
7
New cards
Rights Revolution
1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights
\
\-Compensation for past injuries
\
\-Compensation for past injuries
8
New cards
Culture
relationship between individuals and society
\
\-knowledge, language, values, customs and material objects passed to others over time that help us to deal with real-life problems
\
\-culture provides us with more choices and greater freedom
\
\-knowledge, language, values, customs and material objects passed to others over time that help us to deal with real-life problems
\
\-culture provides us with more choices and greater freedom
9
New cards
What are the 2 Types of Culture?
Material Culture, Non-material
10
New cards
Material Culture
tangible artifacts, physical objects
11
New cards
Non-material
Values, Beliefs, Traditions
\
\-Sociology focuses on this
\
\-Sociology focuses on this
12
New cards
6 Features of Culture
1. Culture is learned (values)
2. Culture is shared (symbols, hockey)
3. Culture is transmitted (intergenerational)
4. Culture is cumulative
5. Culture is human
6. Distinguished humans from animals
13
New cards
Postmodernism
An eclectic mixing of elements from different times and places
\
\-The erosion of authority
\
\-A decline of consensus about core values
\
\-The erosion of authority
\
\-A decline of consensus about core values
14
New cards
Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis
\-language is an important symbolic system
\
\-if language is lost, the entire culture is put at risk
\
\-language determines our thought
\
\-if language is lost, the entire culture is put at risk
\
\-language determines our thought
15
New cards
Fruit Machine
Assumed Gay men were irrational - Mental Illness - Security threats to the state - put electrodes on genitalia and present stimulus images of men and women to determine sexuality
16
New cards
Abstraction
The ability to use symbols such as language
17
New cards
Cooperation
The ability to construct norms and laws
18
New cards
Production
Using tools and techniques used to take and create what we want
19
New cards
What are the Building Blocks of Culture?
1. Values - General beliefs of right and wrong
2. Norms - specification of appropriate behavior's
3. Laws - codified norms
4. Sanctions - rewards and punishments
20
New cards
Folkways
customary behavior
\
\- norms governing simple day to day matters.
\
* These are norms you should not violate
\
* They are the least respected and most sanctioned
\
Ex. Walking on the wrong side of the hallway
\
\- norms governing simple day to day matters.
\
* These are norms you should not violate
\
* They are the least respected and most sanctioned
\
Ex. Walking on the wrong side of the hallway
21
New cards
Mores
carry serious moral condemnation
\
* taken more seriously than folkways
\
* You must not violate them
\
* Criminal Code of laws
\
* Even violates of mores that are not laws will be met with shock and severe disapproval
\
* Ex. Booing during the national anthem, cheating
\
* taken more seriously than folkways
\
* You must not violate them
\
* Criminal Code of laws
\
* Even violates of mores that are not laws will be met with shock and severe disapproval
\
* Ex. Booing during the national anthem, cheating
22
New cards
Language and Gender
women use more modifers and tag questions
\
\-women have more variety in their vocabulary for colors, textures, food, clothing, cooking and parenting
\
\-men use imperative form more often than women. Men use expletives more often than do women (direct)
\
\- women are more likely to disclose aspects of their personal lives and feelings. Often, men are not comfortable doing so
\
\-At the beginning of male-female relationship, men talk more than women. This often decreases over time
\
\-women have more variety in their vocabulary for colors, textures, food, clothing, cooking and parenting
\
\-men use imperative form more often than women. Men use expletives more often than do women (direct)
\
\- women are more likely to disclose aspects of their personal lives and feelings. Often, men are not comfortable doing so
\
\-At the beginning of male-female relationship, men talk more than women. This often decreases over time
23
New cards
Subcultures
groups in society with their own distinct values, norms, folkways, and mores
\
* are minority cultures that differ in some way from the dominant culture but don’t directly oppose it
* May be organized around occupations or hobbies and typically exhibit a fairly neutral contrast to the mainstream: there is no significant opposition to the dominant culture
\
Ex. Hutterites, Immigrants
\
* are minority cultures that differ in some way from the dominant culture but don’t directly oppose it
* May be organized around occupations or hobbies and typically exhibit a fairly neutral contrast to the mainstream: there is no significant opposition to the dominant culture
\
Ex. Hutterites, Immigrants
24
New cards
Countercultures
subcultures in opposition to the dominant culture
\
* are minority cultures that feel the power of the dominant culture and exist in opposition to it
* Defined oppositionally
* Groups reject elements of the dominant culture, such as clothing styles or sexual norms
\
Ex. Hippies
\
* are minority cultures that feel the power of the dominant culture and exist in opposition to it
* Defined oppositionally
* Groups reject elements of the dominant culture, such as clothing styles or sexual norms
\
Ex. Hippies
25
New cards
Dominant Culture
* The dominant culture is the one that, through its political and economic power, is able to impose its values, language, and ways of behaving and interpreting behaviour on a given society.
* Canada's dominants are white, English-speaking people of Christian and European stock , Middle Class
* Canada's dominants are white, English-speaking people of Christian and European stock , Middle Class
26
New cards
High Culture
* High culture is the culture of the elite, a distinct minority
* Associated with theatre, opera, classical music, and ballet
* Associated with theatre, opera, classical music, and ballet
27
New cards
Cultural Capital
refer to the knowledge and skills needed to acquire the sophisticated tastes the mark someone as a person of high culture. The more cultural capital you have, the "high" your cultural class.
28
New cards
Popular Culture
is the culture of the majority, particularly of those who do not have power
29
New cards
Cultural Studies
draws on both the social sciences and the humanities to cast light on the significance of, and meanings in, popular culture
30
New cards
Sanctions
* People react to how others follow or do not follow norms
* Positive Sanction = reaction that supports behavior
* Reward for "doing the right thing"
* Range from small gestures like a smile, a high five, or a supportive comment to larger material rewards
* Negative Sanction = reaction designed to tell offenders they have violated a norm
* Positive Sanction = reaction that supports behavior
* Reward for "doing the right thing"
* Range from small gestures like a smile, a high five, or a supportive comment to larger material rewards
* Negative Sanction = reaction designed to tell offenders they have violated a norm
31
New cards
Culture Symbols
* Symbols are cultural items that hold significance
* They can be either tangible material objects or intangible, non-material objects, such as songs or even remembered events
* Cultural symbols are likely to be interpreted differently by people inside and outside of the culture they represent
* They can be either tangible material objects or intangible, non-material objects, such as songs or even remembered events
* Cultural symbols are likely to be interpreted differently by people inside and outside of the culture they represent
32
New cards
Potlatch Act of 1884
* The Potlatch is a traditional ceremony of North-west Coast Indigenous people living in the United States and Canada
* Gift-giving
* Canadian government saw the ceremony as an impediment to assimilation
* In 1884, the Canadian government banned the Potlach, making participation in the ceremony a misdemeanour
* Gift-giving
* Canadian government saw the ceremony as an impediment to assimilation
* In 1884, the Canadian government banned the Potlach, making participation in the ceremony a misdemeanour
33
New cards
Outlawing Peyote
* Spanish explorers arrived in Mexico in the 16th century, they encountered an Indigenous population that practised monotheistic religion they could relate to because of its similarity to their own Christian belief
* The Spaniards did not approve of the hallucinogen peyote
* Eurocentrism = Involves taking a broadly defined "European" position to address others, and assuming that the audience shares that position
* Cultural Globalization = the intensification and expansion of cultural flows across the globe
* The Spaniards did not approve of the hallucinogen peyote
* Eurocentrism = Involves taking a broadly defined "European" position to address others, and assuming that the audience shares that position
* Cultural Globalization = the intensification and expansion of cultural flows across the globe
34
New cards
Social Stratification
society's categorization of its people into rankings based on factors such as wealth, income, education, family background, and power.
35
New cards
What are the 3 Basic Emotional Reactions to Social Class?
resistance, paralysis and even rage
36
New cards
Income
refers to economic gain attained by wages, salaries and income transfers from the government
37
New cards
Wealth
refers to accumulated assets of goods such as buildings, land, farms, houses, factories
38
New cards
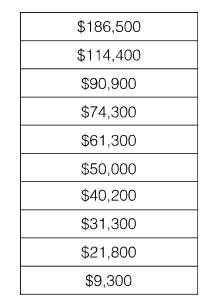
Income inequality
\-Statistics Canada after-tax family income by decile, 2014 (the values that divide that distribution into ten equal parts)
\
uses median incomes (the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount
\
\-means will be lower (data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set)
\
uses median incomes (the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount
\
\-means will be lower (data set is found by adding all numbers in the data set and then dividing by the number of values in the set)
39
New cards
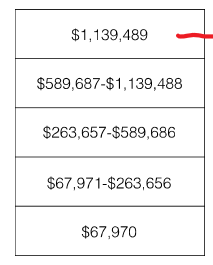
Wealth Inequality
\-Statistics Canada 2013
\
\-The top 20% of Canadians own 67% of all wealth. Using this measure, the bottom own nothing 2015
\
\-The top 2 Canadians have more money than 11 million combined (2017)
\
\-The top 20% of Canadians own 67% of all wealth. Using this measure, the bottom own nothing 2015
\
\-The top 2 Canadians have more money than 11 million combined (2017)
40
New cards
Child Poverty
\-1.2 Million Children living in poverty
\
\-50% of all First Nations children (60% on reserves) and 15% of all other children are considered relatively impoverished in 2016
\
\-50% of all First Nations children (60% on reserves) and 15% of all other children are considered relatively impoverished in 2016
41
New cards
Absolute Poverty
refers to an inability to attain the basic necessities of life
\
where an individual does not have the financial means to obtain commodities to sustain life.
\
\-Basic Needs Measure
\
where an individual does not have the financial means to obtain commodities to sustain life.
\
\-Basic Needs Measure
42
New cards
Relative Poverty
refers to an inability to secure an average standard of living
\
\-they are considered deprived relative to others
\
standard of living compared to economic standards of living within the same surroundings.
\
Ex. LICO
\
\-they are considered deprived relative to others
\
standard of living compared to economic standards of living within the same surroundings.
\
Ex. LICO
43
New cards
Consequences of Relative Poverty
\-Delayed Vocabulary Development
\-Poor health and hygiene
\-Poor nutrition
\-Absenteeism and low scholastic achievement
\-Behavioral and Mental Problems (crime/deviance)
\-Low housing Standards
\-Greater likelihood of being poor in adulthood
\-Poor health and hygiene
\-Poor nutrition
\-Absenteeism and low scholastic achievement
\-Behavioral and Mental Problems (crime/deviance)
\-Low housing Standards
\-Greater likelihood of being poor in adulthood
44
New cards
Factors of Poverty
1. Family Structure
2. Age
3. Sex
4. Race/Ethnicty
5. Persons with Disabilities
45
New cards
What Social Groups are at the most risk of Poverty?
Single Parent Families, Young People, Female, Immigrants chosen by job, language and education perform better then domestic Canadians
46
New cards
Open Social Stratification
work your way into different classes, you get what you put in (Canada)
47
New cards
Closed Social Stratification
\-your classification can not change
\
Ex. Caste system in India
\
Ex. Caste system in India
48
New cards
Meritocracy
a system in which the talented are chosen and moved ahead on the basis of their achievement
49
New cards
Ascribed Status
ascribed status refers to the status that an individual acquires by virtue or birth - Race, Sex
50
New cards
Achieved Status
status you work for
51
New cards
4 Characteristics of Structural Functionalism - Davis and Moore
1. Society is held together by consensus; not based upon conflict
2. Inequality is functional for society
3. Eliminating inequality would be harmful
4. Inequality will continue because it is functional and necessary
\
They believe we live in a meritocracy
52
New cards
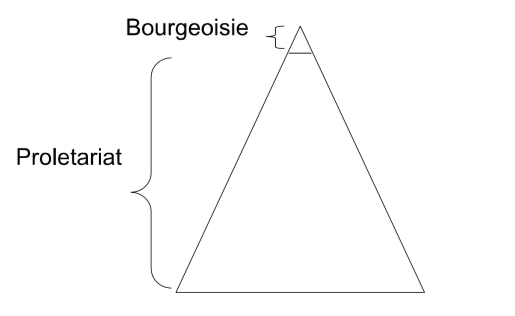
Conflict Theory - Karl Marx
\-There are usually 2 groups found in society: “haves” and “have-nots”
\
\-The social relationships to the means of production refer to people’s position in society (i.e. proletariat or bourgeoise in capitalist societies)
\
\-The proletariat is exploited and experiences alienation
\
* Class as Marx described it, is relational: it reflects the relationship of people to what he called the **means of production** - the resources needed to produce goods
\
* Means of production = capital - money needed to build factories, purchase raw materials, and pay laborers to turn those raw materials into manufactured products
\
* Marx called the owners of capital, **capitalists**; he referred to the members of this class collectively as the **bourgeoisie**. The class of workers, which succeeded the peasant class of the pre-industrial era, made up of the **proletariat**
\
* Petty bourgeoise, made up of small-time owners with little capital (small business class)
\
* Lumpenproletariat, the small time criminals, beggars, and unemployed
\
\-The social relationships to the means of production refer to people’s position in society (i.e. proletariat or bourgeoise in capitalist societies)
\
\-The proletariat is exploited and experiences alienation
\
* Class as Marx described it, is relational: it reflects the relationship of people to what he called the **means of production** - the resources needed to produce goods
\
* Means of production = capital - money needed to build factories, purchase raw materials, and pay laborers to turn those raw materials into manufactured products
\
* Marx called the owners of capital, **capitalists**; he referred to the members of this class collectively as the **bourgeoisie**. The class of workers, which succeeded the peasant class of the pre-industrial era, made up of the **proletariat**
\
* Petty bourgeoise, made up of small-time owners with little capital (small business class)
\
* Lumpenproletariat, the small time criminals, beggars, and unemployed
53
New cards
Laissez-Faire Economics
* Laissez-faire economics - Adam Smith = the idea that governments should not try to manage or interfere in the so-called free market
* Critics believe there is no such thing as "free" market when it is dominated by multinational corporations with near-monopolistic power
* Malthus predicts that dramatic population growth would inevitably lead to a scarcity of food and other resources. He warned that famine, disease, and war would "naturally" limit population growth unless other measures, including birth control and celibacy, were adopted.
* Karl Marx believed inequality was not inevitable
* Inevitable or not, social inequality is a function of many factors like ethnicity, "race", and gender
* Critics believe there is no such thing as "free" market when it is dominated by multinational corporations with near-monopolistic power
* Malthus predicts that dramatic population growth would inevitably lead to a scarcity of food and other resources. He warned that famine, disease, and war would "naturally" limit population growth unless other measures, including birth control and celibacy, were adopted.
* Karl Marx believed inequality was not inevitable
* Inevitable or not, social inequality is a function of many factors like ethnicity, "race", and gender
54
New cards
The Factory Act
* The Factory Act, targeted primarily the booming textile mills of Britain, was considered radical at the time. The mill owning bourgeoise claimed that the act interfered with the "natural course" of business by "severely" limiting the hours that people were allowed to work. They complained that the act would ruin them financially, even drive them out of business
* Limits of the length of the working day and working week for people under 18 were the aspects of the Factory Act that mill owners thought would ruin them
* Limits of the length of the working day and working week for people under 18 were the aspects of the Factory Act that mill owners thought would ruin them
55
New cards
Corporate Identity
there is a shared sense of purpose among members of each class
56
New cards
Class Consciousness
means having an awareness of what is in the best interests of one's class
57
New cards
False Consciousness
* belief that something is in its best interests when it is not
* Marx believed that the proletariat's false consciousness kept them from waging open revolt against a system that was not working in their favour
* Factors include religion, which may be used to argue that poverty and wealth are parts of some divine plan; politics, which are often used to persuade low-income voters that pro-business policies will benefit everyone; and patriotism, which underlies protectionist policies that limit free trade between countries
* Marx believed that the proletariat's false consciousness kept them from waging open revolt against a system that was not working in their favour
* Factors include religion, which may be used to argue that poverty and wealth are parts of some divine plan; politics, which are often used to persuade low-income voters that pro-business policies will benefit everyone; and patriotism, which underlies protectionist policies that limit free trade between countries
58
New cards
“Gig Economy”
* is a trendy term for those who get by performing assorted casual, parttime jobs, typically with hours flexible enough that a person can fit 2 or more kinds of work in around other commitments, such as going to school
* Ex. Uber, Door Dash
* Ex. Uber, Door Dash
59
New cards
3 Classes in a Country
Dominant Capitalist Class, Middle Class, Working Class or Proletariat
60
New cards
Dominant Capitalist Class
composed mainly of those who own or control large-scale production
* Ex. CEOs
* Ex. CEOs
61
New cards
Middle Class
a mixed middle category of small-scale business people, educated profession-technical or administrative personnel, and various salaried employees or wage-earners possessing some certifiable credentials, training or skills
* Ex. Teachers and Nurses
* Ex. Teachers and Nurses
62
New cards
Working Class or Proletariat
made up of people who lack resources or capacities apart from their own labour power
* Ex. Construction, Retail Employees
* Ex. Construction, Retail Employees
63
New cards
*Dominant Ideology*
A dominant ideology is the set of beliefs put forward by, and generally supportive of, society's dominant culture and/or classes
\
* It reflects the class consciousness of the ruling capitalist class and is used to defend or justify the status quo
\
* Ex. Trickle-down theory = term refers to the view that if the wealthy are given the freedom to generate more wealth, others in society will benefit: new jobs will be created, more money will be spent on consumer goods, and a good part of the generated wealth will eventually find its way into the hands of members of the middle and lower classes
\
* It reflects the class consciousness of the ruling capitalist class and is used to defend or justify the status quo
\
* Ex. Trickle-down theory = term refers to the view that if the wealthy are given the freedom to generate more wealth, others in society will benefit: new jobs will be created, more money will be spent on consumer goods, and a good part of the generated wealth will eventually find its way into the hands of members of the middle and lower classes
64
New cards
Neoliberal Ideology
* A dominant ideology that views that individual as a more or less independent player on the sociological scene
* It reflects the belief in a great deal of social mobility (ability to move between classes)
* The American dream = the belief that anyone can "make it" if they are willing to work really hard for it - reflects neoliberal ideology
* Failure to achieve the American dream is likewise placed solely on the individual
* William Ryan refers to this as blaming the victim, assigning individuals responsibility for events or circumstances that have broader social causes, such as the quality of a person's upbringing and education or lack of the resources and social connections that help a person secure a well paying job
* It reflects the belief in a great deal of social mobility (ability to move between classes)
* The American dream = the belief that anyone can "make it" if they are willing to work really hard for it - reflects neoliberal ideology
* Failure to achieve the American dream is likewise placed solely on the individual
* William Ryan refers to this as blaming the victim, assigning individuals responsibility for events or circumstances that have broader social causes, such as the quality of a person's upbringing and education or lack of the resources and social connections that help a person secure a well paying job
65
New cards
Counter-ideology
* An ideology that offers a critique of the dominant ideology, challenging its justice and its universal applicability to society
* Create social change
* Create social change
66
New cards
Hegemony
* Non-coercive methods of maintaining power
* He believed ruling classes relied on something more than their military and police forces to keep society running smoothly while quietly oppressing the masses
* Hegemony is expressed in the reproduction and celebration of the idea that the path to prosperity is available to everyone equally, and that inequality exists because of problems in "the system" but because some people are willing to work harder than others
* He believed ruling classes relied on something more than their military and police forces to keep society running smoothly while quietly oppressing the masses
* Hegemony is expressed in the reproduction and celebration of the idea that the path to prosperity is available to everyone equally, and that inequality exists because of problems in "the system" but because some people are willing to work harder than others
67
New cards
*The "Mincome": A Manitoba Town's Modernist Experiment*
* Manitoba town of Dauphin was home to progressive social experiment around a simple idea: What if every family in the town received a guaranteed, unconditional annual income?
* Families were guaranteed minimum income based on family size
* Fewer work-related injuries, fewer mental-health visits, and an 8.5% drop in hospital visits overall
* Families were guaranteed minimum income based on family size
* Fewer work-related injuries, fewer mental-health visits, and an 8.5% drop in hospital visits overall
68
New cards
Surplus Value
amount appropriated by the bourgeoisie
\
\-profit
\
\-profit
69
New cards
Law of Accumulation
suggests that as the bourgeoise obtains more wealth, the proletariat will eventually have no money to purchase products - the system collapses
\
\-Marx
\
\-Marx
70
New cards
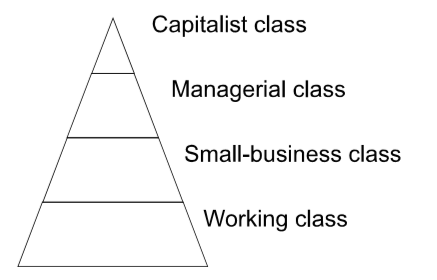
Conflict Theory - Erik Ohlin Wright
\-There are more than 2 classes in contemporary capitalist societies based upon
\
1. Control of the means of production - Capitalist Class
2. Control of the labour of others - Managerial Class
3. Purchase of the labour of others - Small Business Class
4. Sale of one’s labour - Working Class
\
1. Control of the means of production - Capitalist Class
2. Control of the labour of others - Managerial Class
3. Purchase of the labour of others - Small Business Class
4. Sale of one’s labour - Working Class
71
New cards
Conflict Theory -Max Weber
1. One factor cannot explain social stratification
\
2. We should take a multidimensional approach to social stratification, including class, status, and party
\
3. Society will be increasingly controlled by bureaucrats
\
4. Inequality will continue
\
* Weber did not agree with Marx's theory of class relations
\
* Weber viewed society as divided into different economic classes, but he believed that Marx's materialist approach was too simplistic, that there was more to social inequality than just who owned the means of production
\
* Weber stresses 3 elements - Wealth, Prestige, and Power - as contributing to social inequality
\
* Wealth/Material Resources = includes not just factories and other property used to make money but also properties that are highly respected by members of the society in question
\
* Prestige = can be turned into various forms of social power, which is usually defined as the ability of individuals or groups to achieve their goals despite the opposition of others
72
New cards
Race
* The term "race" was first applied to humans during European colonial expansion in the 16th and 17th centuries
* Use of the term has reflected beliefs about biological superiority and inferiority in the context of colonial power
* Russian racism was directed at white Siberian communities speaking languages related to Finnish and Hungarian
* White supremacy involving discrimination against anyone not of western European ethnic background - has been the prevailing pattern since people began discussing humans in terms of different "races"
* Races do not exist as distinct biological entities among humans.
\
* Race is a formal social construct
\
* Hispanic is not a race, according to US census bureau
* Use of the term has reflected beliefs about biological superiority and inferiority in the context of colonial power
* Russian racism was directed at white Siberian communities speaking languages related to Finnish and Hungarian
* White supremacy involving discrimination against anyone not of western European ethnic background - has been the prevailing pattern since people began discussing humans in terms of different "races"
* Races do not exist as distinct biological entities among humans.
\
* Race is a formal social construct
\
* Hispanic is not a race, according to US census bureau
73
New cards
Racialization
social process in which human groups are viewed and judged as essentially different in terms of their intellect, morality, values and innate worth because of perceived differences in physical appearance or cultural heritage
74
New cards
Master Narrative
* Michel Foucault
* A master narrative is the story a nation tells about itself to celebrate its past and present
* The master narrative will often gloss over or omit altogether certain unpleasant events that complicate the national self-identity
* "buried knowledge"
* A master narrative is the story a nation tells about itself to celebrate its past and present
* The master narrative will often gloss over or omit altogether certain unpleasant events that complicate the national self-identity
* "buried knowledge"
75
New cards
Indigenous People in Canada
* Canadian textbooks described the First Nations people co-operated with Europeans how to use canoes and snowshoes, and providing the Europeans with new foods, such as pemmican and corn
* This account overlooked the exploitation and social destruction that occurred when Europeans introduced alcohol into the fur trade, setting off a pattern of ruinous colonial intrusion into the lives and culture of Indigenous people
* Residential Schools and 60s Scoop
* This account overlooked the exploitation and social destruction that occurred when Europeans introduced alcohol into the fur trade, setting off a pattern of ruinous colonial intrusion into the lives and culture of Indigenous people
* Residential Schools and 60s Scoop
76
New cards
Indigenous Status
* Indigenous people are defined by a complex system of legal statuses that separates them from non-Indigenous people, and from each other
* Main designations, as defined in Canadian legislation are:
* Registered Indian
* Bill C-31 Indian
* Band Member
* Reserve Resident
* Treaty Indian
* Metis
* Eskimo
* The legal differences come from the Indian Act, which was administered by the federal department of Indian affairs
* Main designations, as defined in Canadian legislation are:
* Registered Indian
* Bill C-31 Indian
* Band Member
* Reserve Resident
* Treaty Indian
* Metis
* Eskimo
* The legal differences come from the Indian Act, which was administered by the federal department of Indian affairs
77
New cards
Indian Act enshrined a sexist definition of "Indian”
1. Any man of "Indian Blood" reputed to belong to a particular band
2. Any child of such a man
3. Any woman married to such a man
\
* A man kept his status no matter whom he married, but a women, if she married someone not legally an Indian, lost her status, and her children would share that fate.
* A non-Indian woman could gain Indian status by marrying an Indian man
78
New cards
Blacks in Canada
* Black communities have existed in Nova Scotia since the British Proclamation in 1779 offered freedom to slaves who left their American masters to fight on the British side in the American Revolution
* They were offered significantly less land and fewer opportunities than white immigrants were, and they endured incredible hardship and prejudice.
* Nova Scotian blacks are treated as an anomaly when they travel west in Canada
* Tensions have long existed between black and white communities
* They were offered significantly less land and fewer opportunities than white immigrants were, and they endured incredible hardship and prejudice.
* Nova Scotian blacks are treated as an anomaly when they travel west in Canada
* Tensions have long existed between black and white communities
79
New cards
Asian Canadians
* 2/3 of visible-minority Canadians were of Asian ancestry, with South Asians and Chinese Canadians making up the 2 largest visible-minority populations in the country
* They were driven from China by poverty and political upheaval, and drawn to British Columbia by opportunities to work
* Head Tax, no other immigrant group was targeted with an entry fee
* Chances of Chinese men marrying Chinese women was low
* Act to Prevent the Employment of Female Labor in Certain Capacities
* 22,000 Japanese Canadians were placed in internment camps and dispossessed of their property
* Japanese Canadian soldiers volunteered to serve in the Canadian Expeditionary Force in World War 1
* The first South Asians to come to Canada were Sikhs, who had been given special status by the British as soldiers and police serving imperial purposes throughout the world
* They arrived in British Columbia at a time when there was a shortage of laborer willing to work in the sawmills, on the roads, and in the bush cutting wood and clearing land
* They were driven from China by poverty and political upheaval, and drawn to British Columbia by opportunities to work
* Head Tax, no other immigrant group was targeted with an entry fee
* Chances of Chinese men marrying Chinese women was low
* Act to Prevent the Employment of Female Labor in Certain Capacities
* 22,000 Japanese Canadians were placed in internment camps and dispossessed of their property
* Japanese Canadian soldiers volunteered to serve in the Canadian Expeditionary Force in World War 1
* The first South Asians to come to Canada were Sikhs, who had been given special status by the British as soldiers and police serving imperial purposes throughout the world
* They arrived in British Columbia at a time when there was a shortage of laborer willing to work in the sawmills, on the roads, and in the bush cutting wood and clearing land
80
New cards
When Immigrants are Refugees
* Vietnamese people from the south, fearing retaliation and oppression, began to leave their country, many in small boats barely capable of making the dangerous journey across the Pacific
* Refugees were rules as a separate class of immigrant
* In 1979-1980, Canada received some 60,000 refugees from Vietnam and neighboring Cambodia and Laos
* The federal government promised to aid the refugees by matching funds raised by individual citizens, churches, and other private organization
* The striking thing about this episode is the empathy with which Canadians viewed the Vietnamese boat people
* Refugees were rules as a separate class of immigrant
* In 1979-1980, Canada received some 60,000 refugees from Vietnam and neighboring Cambodia and Laos
* The federal government promised to aid the refugees by matching funds raised by individual citizens, churches, and other private organization
* The striking thing about this episode is the empathy with which Canadians viewed the Vietnamese boat people
81
New cards
Ethnicity
* refers to membership in a cultural group that has roots in a particular place in the world and is associated with distinctive cultural practices and behaviours.
* most people identify with just one race but may have many ethnicities
* Ethnicity is something you can opt into
* Your ethnicity is not the same as your nationality
* most people identify with just one race but may have many ethnicities
* Ethnicity is something you can opt into
* Your ethnicity is not the same as your nationality
82
New cards
Essentialism
* Views that every ethnic group is defined by a "laundry list" of traits carried down from the past to the present with little or no change
* Static view of ethnic culture, in which culture does not change without the influence of outside forces
* Static view of ethnic culture, in which culture does not change without the influence of outside forces
83
New cards
Postcolonialism
* Framework that analyzes the deconstructive impact colonialism has both the colonizer and the colonized.
* Franz Fanon and Albert Memmi
* Examined French colonies in North Africa and their fight for independence from France
* Addressed the psychological effects of colonization and have inspired considerable sociological study
* Identifies colonialism as a factor in the conflict between ethnic groups.
* Indirect Rule = a governance policy in which a European nation uses the members of a tribe or ethnic group as its intermediaries in ruling African territory
* Franz Fanon and Albert Memmi
* Examined French colonies in North Africa and their fight for independence from France
* Addressed the psychological effects of colonization and have inspired considerable sociological study
* Identifies colonialism as a factor in the conflict between ethnic groups.
* Indirect Rule = a governance policy in which a European nation uses the members of a tribe or ethnic group as its intermediaries in ruling African territory
84
New cards
*Ethnicity as Epiphenomenal*
* "Epiphenomenal" describes a secondary effect that arises from, but does not casually influence, a separate phenomenon
* Marx believed economic structure was the main casual factor in society, and everything else was epiphenomenal
* Suggests that any ethnic conflict is just a by-product of the struggle between economic classes
* Marx believed economic structure was the main casual factor in society, and everything else was epiphenomenal
* Suggests that any ethnic conflict is just a by-product of the struggle between economic classes
85
New cards
Instrumentalism
* Focuses on emerging ethnicity rather than on long-established ethnic characteristics
* Acknowledges that elites can mobilize others who identify with them ethnically
* Elite members who mobilize ethnicity for personal gain are called ethnic entrepreneurs
* Acknowledges that elites can mobilize others who identify with them ethnically
* Elite members who mobilize ethnicity for personal gain are called ethnic entrepreneurs
86
New cards
Social Constructivism
* View that ethnicity is artificial, constructed by individuals to serve some agenda
* It explains how ethnicity is constructed by the elite. It suffers as a theory of ethnicity by overstating the influence of the elite
* Fails to attribute the non-elite members any agency, any power to act without being manipulated
* It explains how ethnicity is constructed by the elite. It suffers as a theory of ethnicity by overstating the influence of the elite
* Fails to attribute the non-elite members any agency, any power to act without being manipulated
87
New cards
Stereotyping
occurs when we exaggerate oversimplified images of the characteristics of social categories
\
\-thought/thinking
\
\-thought/thinking
88
New cards
Prejudice
unfavorable, generalized and rigid beliefs applies to all members of a group
\
\-feelings/attitude
\
\-feelings/attitude
89
New cards
Discrimination
practices that deny groups equal access to societal rewards
90
New cards
“Toward a Critical Theory of Race” - Lucius Outlaw
1. We need to examine the “career” of the term “race”
2. It is unclear whether the term derives from an Arabic, Latin or a German source
3. First (recorded) use in English by William Dunbar in 1508 in a poem
4. It initially was used to denote a class of persons or things. In the 19th and 20th centuries, however, it came to signify groups that were distinguished biologically
91
New cards
3 Reasons Why Race is an Achieved Status as Much as It Is an Ascribed Status
1. “Racial” classifications are arbitrary
\
2. Genetic differences between groups are small
\
3. Genetic differences are behaviorally insignificant
92
New cards
What are the 7 Types of Racism?
Hate, Polite, Subliminal, Systemic, Systematic, Everyday, Ideological
93
New cards
Darwin
suggested that genetics determined whether or not species were able to endure environmental changes
94
New cards
Gregor Mendel
research revealed that biological traits were not passed on as package deals, but rather, are not shuffled like a pack of playing cards
\
\-not clones of our parents
\
\-not clones of our parents
95
New cards
W.I. Thomas
\-“if people define situations as real, they are real in their consequences”
\
\-This is often referred to as the “Thomas theorem”
\
\-The belief in race gives rise to interpersonal (relating to relationships or communication between people) racism
\
\-This is often referred to as the “Thomas theorem”
\
\-The belief in race gives rise to interpersonal (relating to relationships or communication between people) racism
96
New cards
Institutional Racism
\-Intentional/Explicit
\
Ex. Chinese head taxes (Systematic Institutional Racism)
\
Ex. Chinese head taxes (Systematic Institutional Racism)
97
New cards
Hate Interpersonal Racism
\-deliberate
\
\-worst you can say
\
\-worst you can say
98
New cards
Polite Interpersonal Racism
\-saying something ugly in a nice way
\
\-saying it like its not controversial
\
Ex. We should listen to Indigenous peoples about Environmental Issues because they know more about the land
\
\-saying it like its not controversial
\
Ex. We should listen to Indigenous peoples about Environmental Issues because they know more about the land
99
New cards
Subliminal Interpersonal Racism
\-subconscious
\
\-Look at friends
\
Ex. Living in a diverse neighborhood but only interacting with people like yourself
\
\-Look at friends
\
Ex. Living in a diverse neighborhood but only interacting with people like yourself
100
New cards
Institutional Systemic Racism
\-unintended
\
Ex. requirements for police officers - excluding people unintentionally
\
Ex. requirements for police officers - excluding people unintentionally