Protista
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Which protists all obtain energy by photosynthesis, all have chlorophyll a, and some have accessory pigments?
plant-like
(AKA: algae-like)
How are plant-like protists typically categorized?
1. the form of carbohydrate used to store energy
2. number of flagella
3. cell wall composition
How many flagella do euglenoids have at their apical end?
1-3
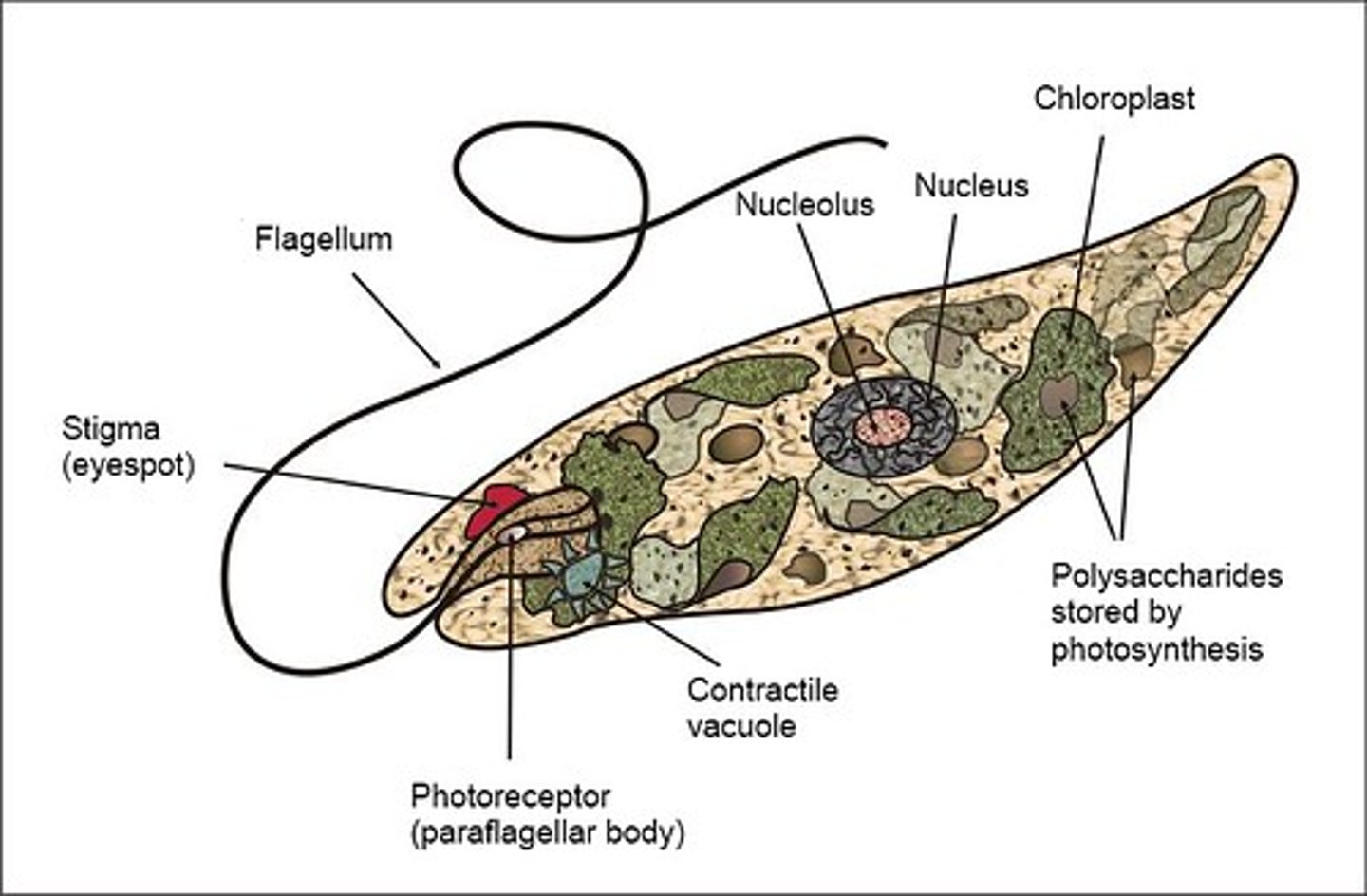
What are the thin, protein strips that wrap over cell membranes of euglenoids?
pellicles
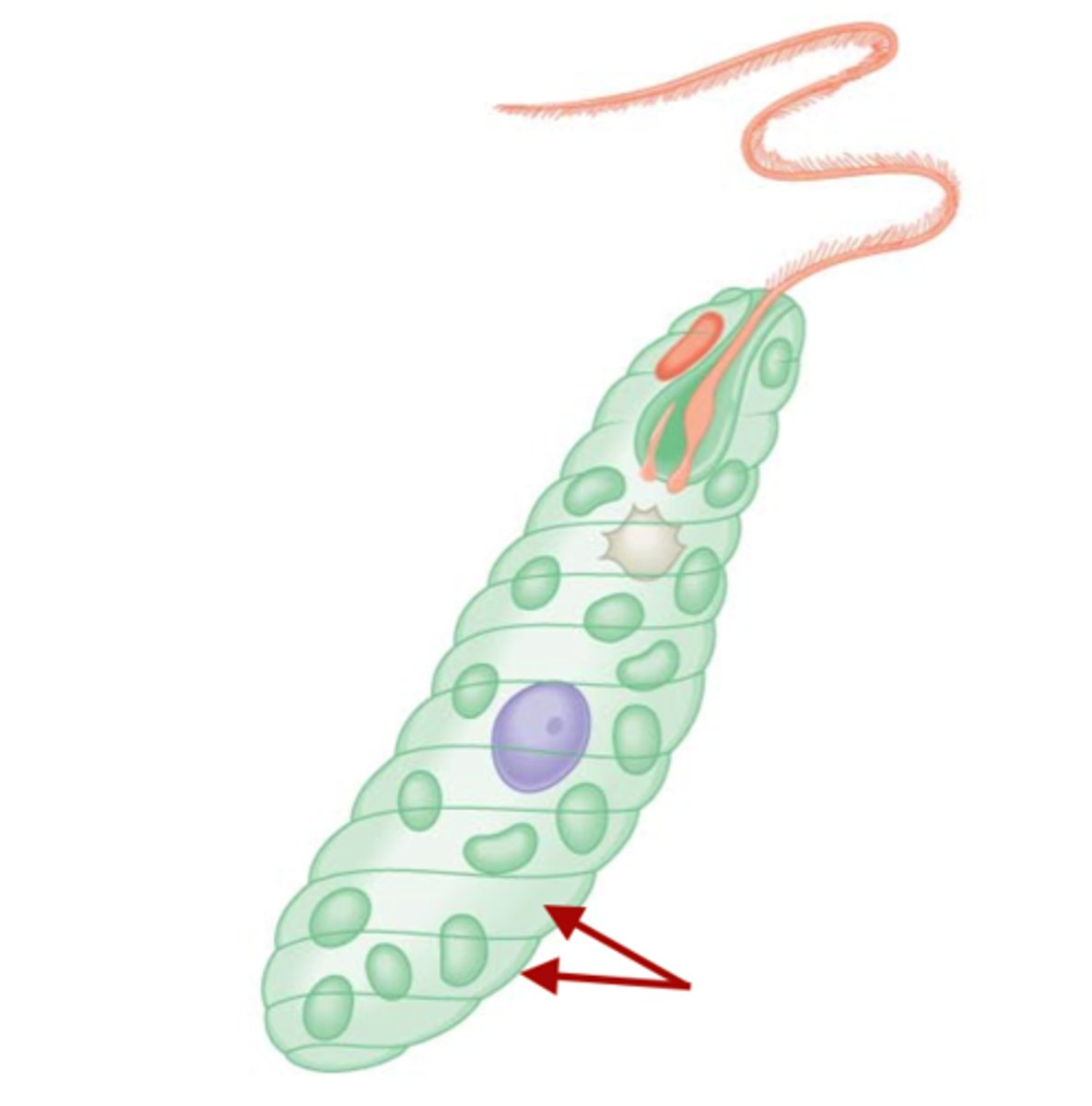
How do euglenoids obtain energy in the absence of light?
heterotrophism
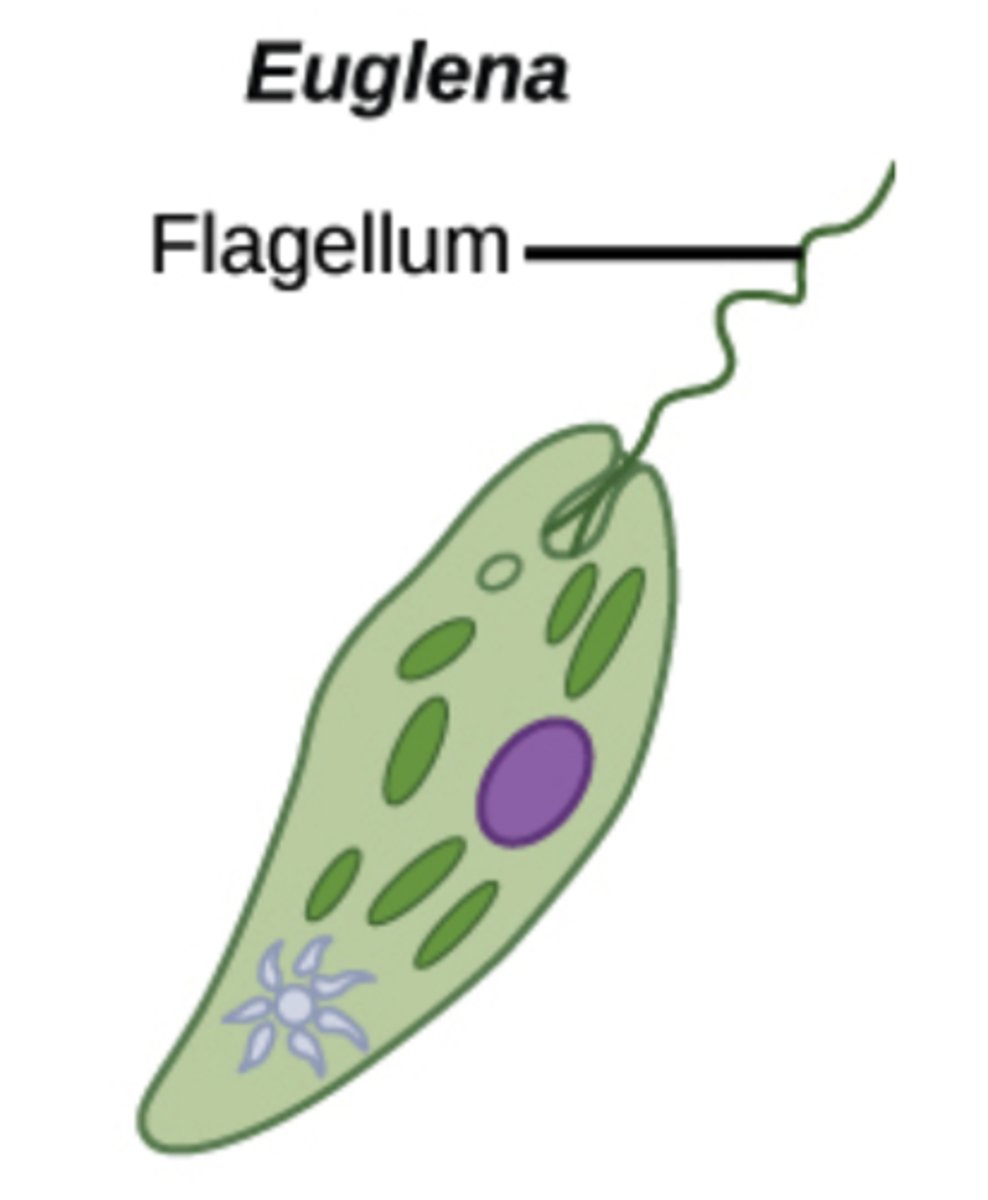
What structure allows euglenoids to perform phototaxis (moving in response to light)?
eyespots
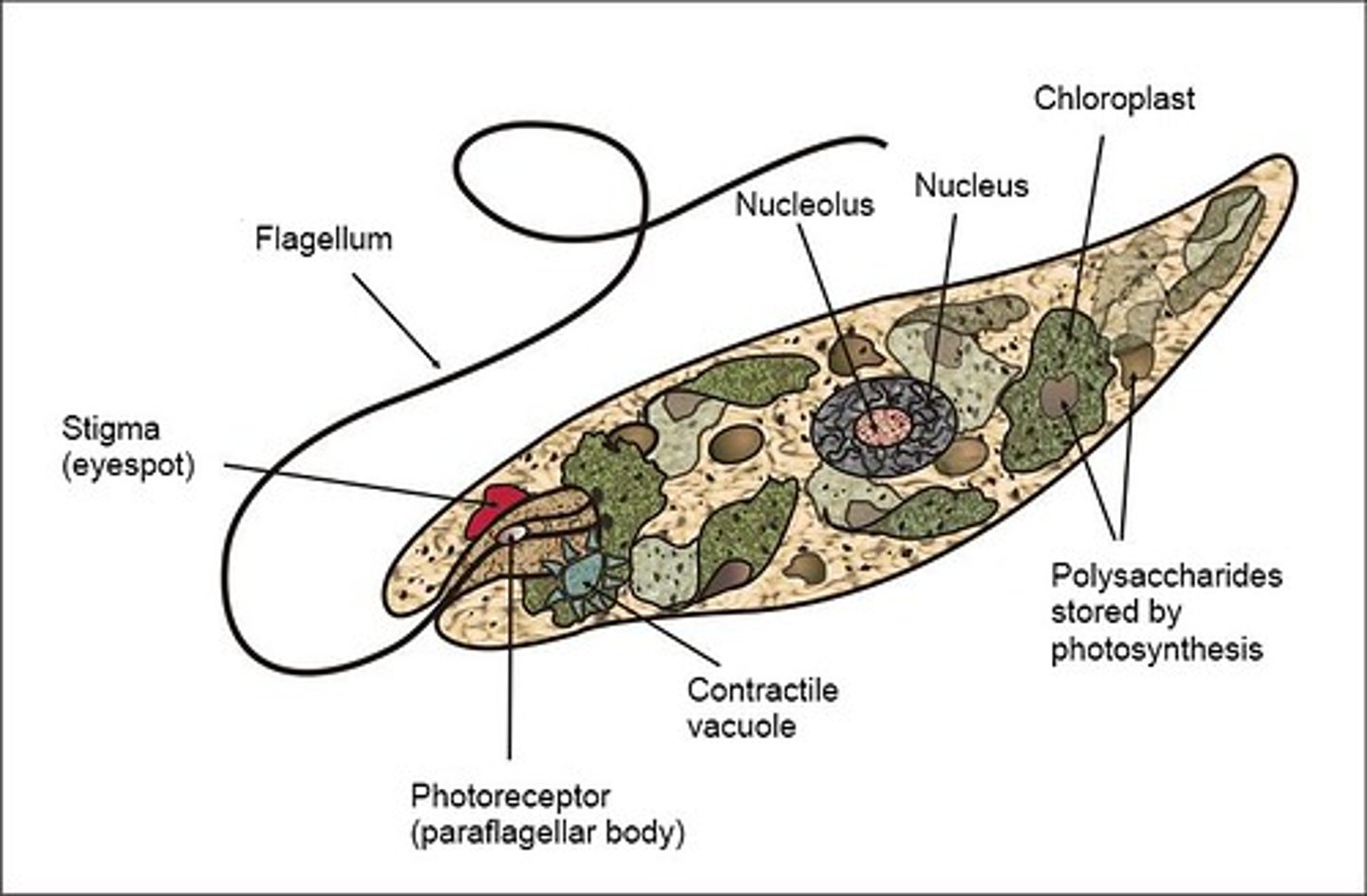
In what type of water do euglenoids live?
fresh water
What describes the motility of euglenoids?
highly motile
Do euglenoids have a cell wall?
no
Which plant-like protists have two flagella - one on their posterior side and one on their transverse side?
dinoflagellates
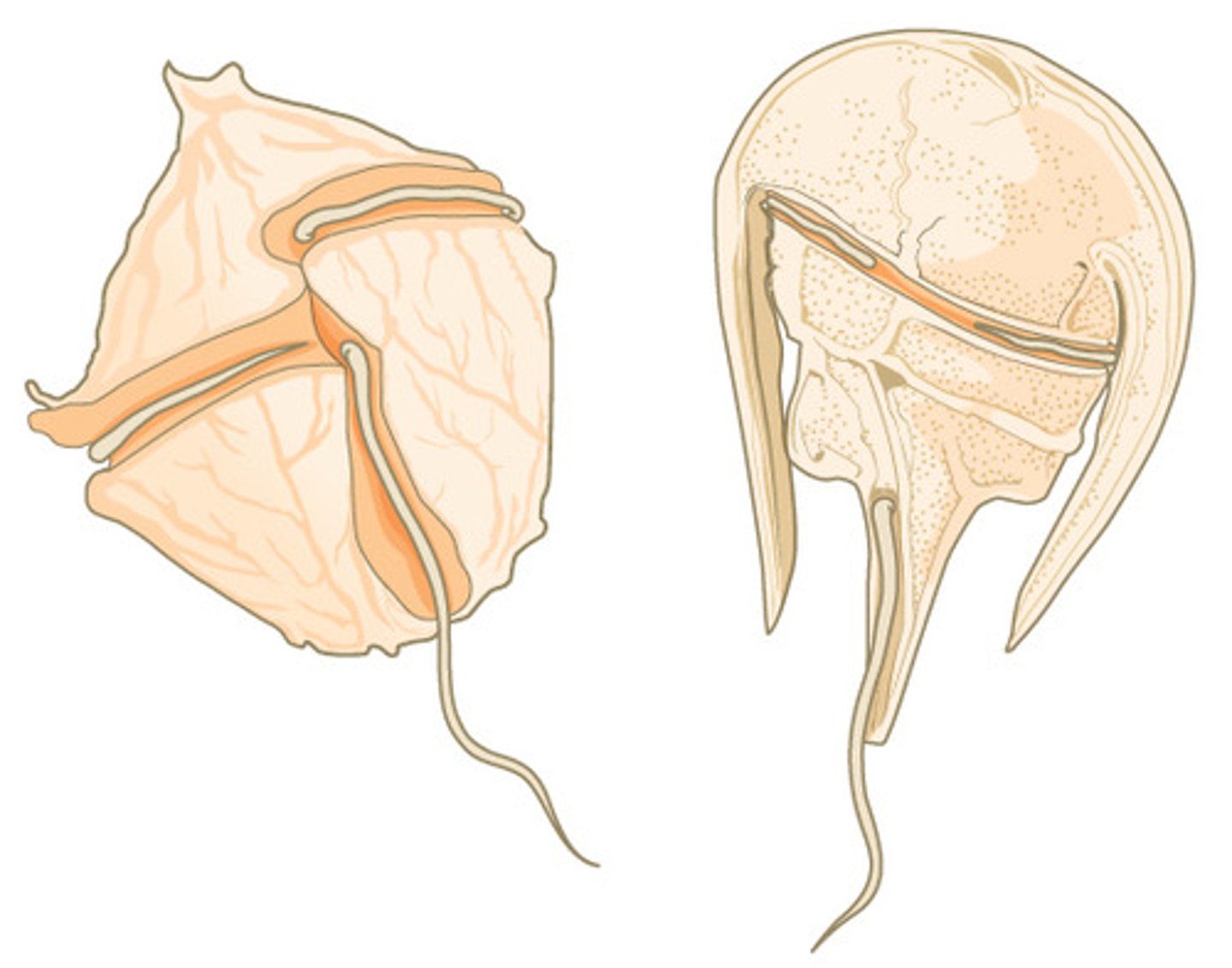
Which flagellum of a dinoflagellate rests, encirculing the mid-groove?
transverse flagellum
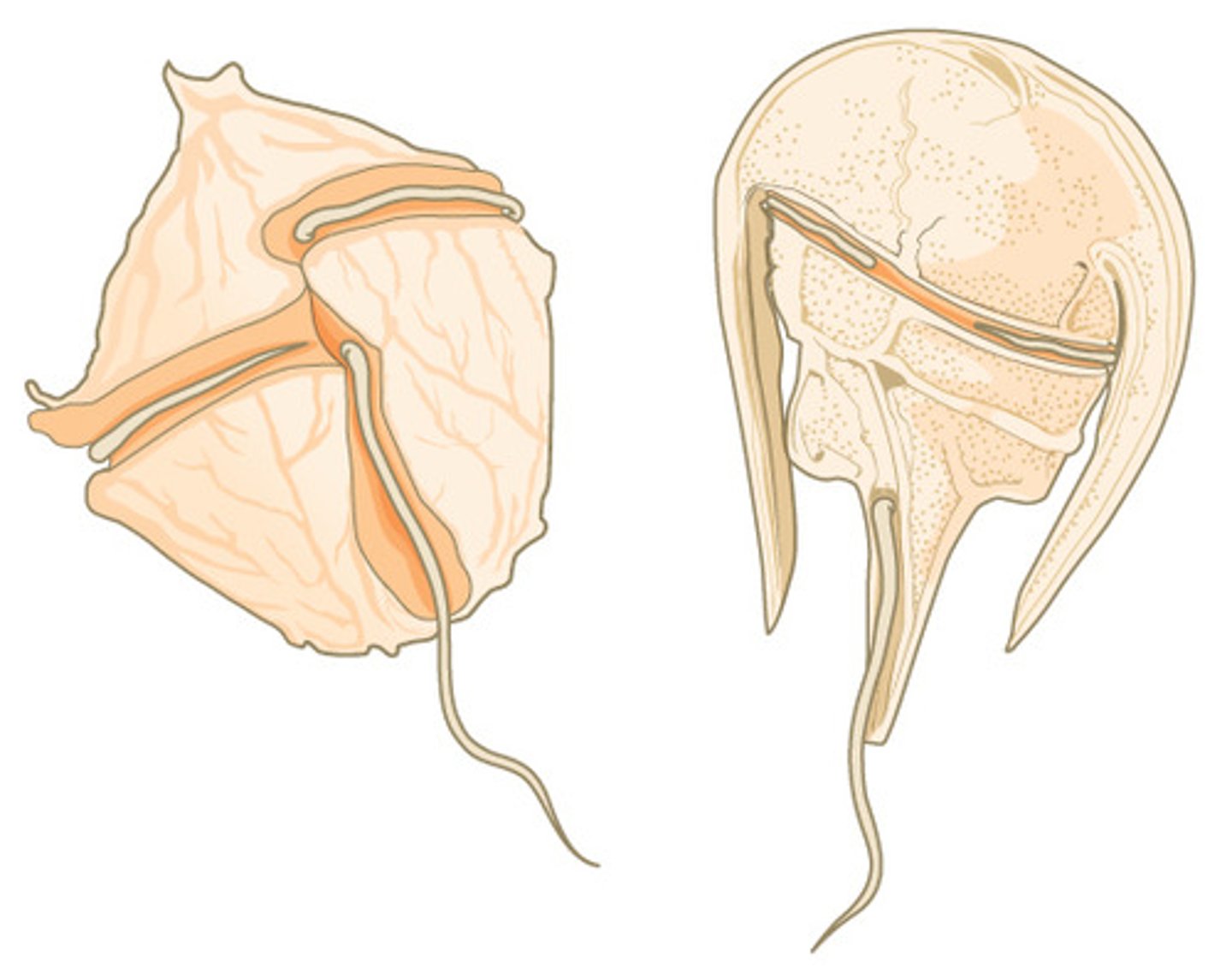
What substance do dinoflagellates produce that concentrates in filter-feeding shellfish?
nerve toxin
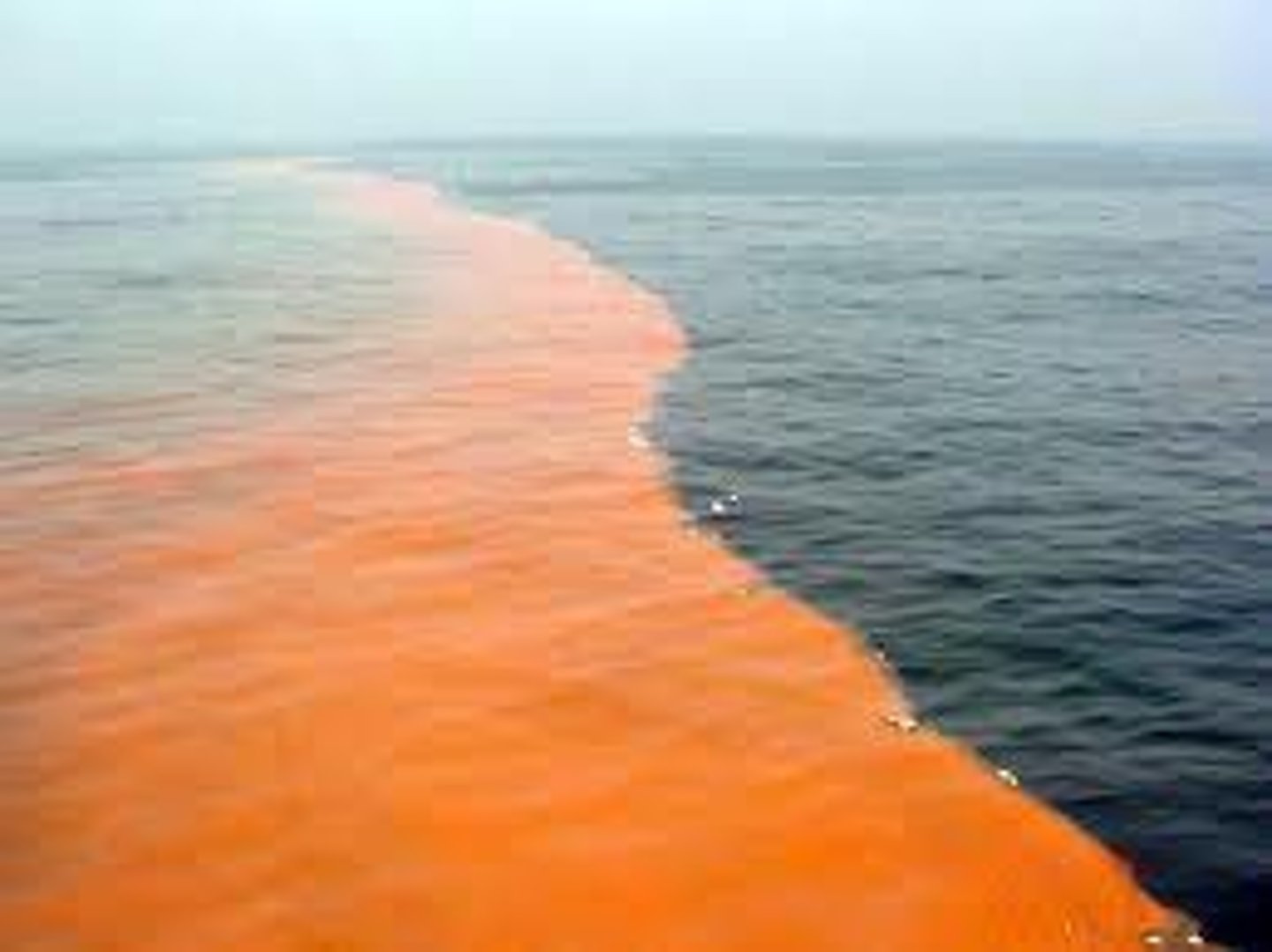
Which plant-like protists cause red tide?
dinoflagellates

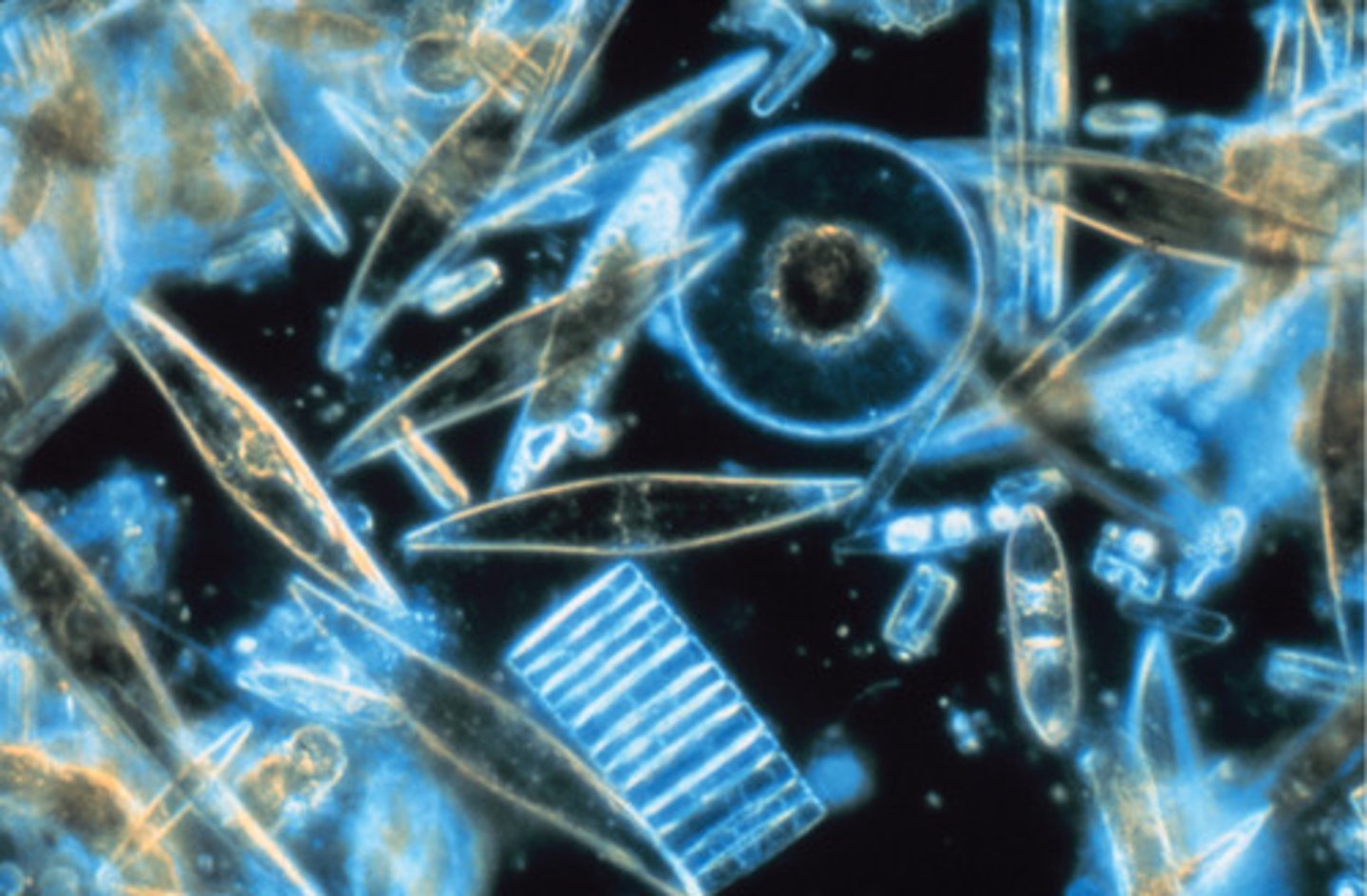
What structure do diatoms possess that fits together like a box with a lid and contains SiO2 (silica)?
tests (shells)
What organisms are multicellular and flagellated sperm cells that look like giant seaweed?
brown algae
(Note: brown algae are technically not protists)
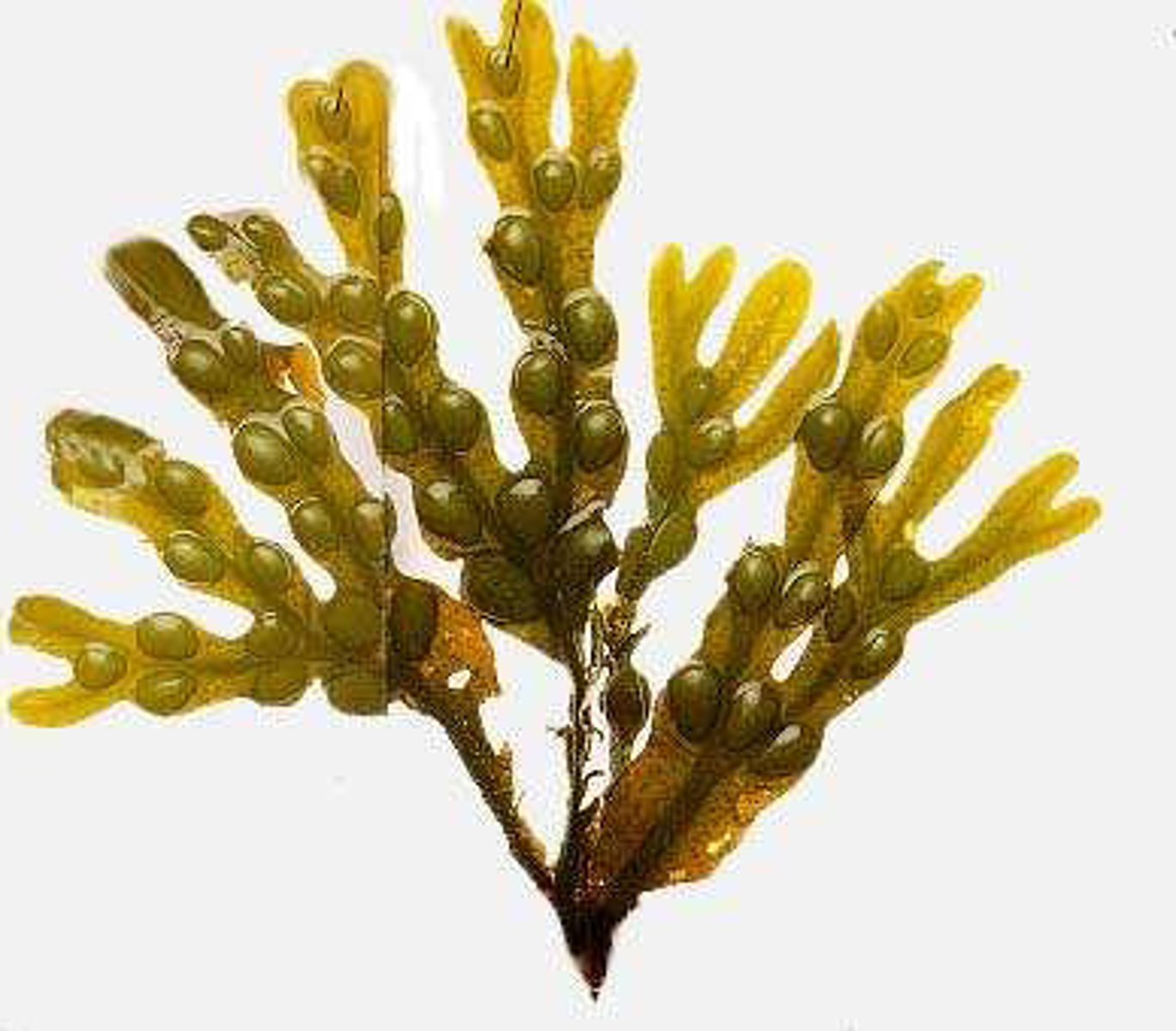

Which plant-like protists are multicellular, red algae that have red accessory pigments called phycobilins?
rhodophytes
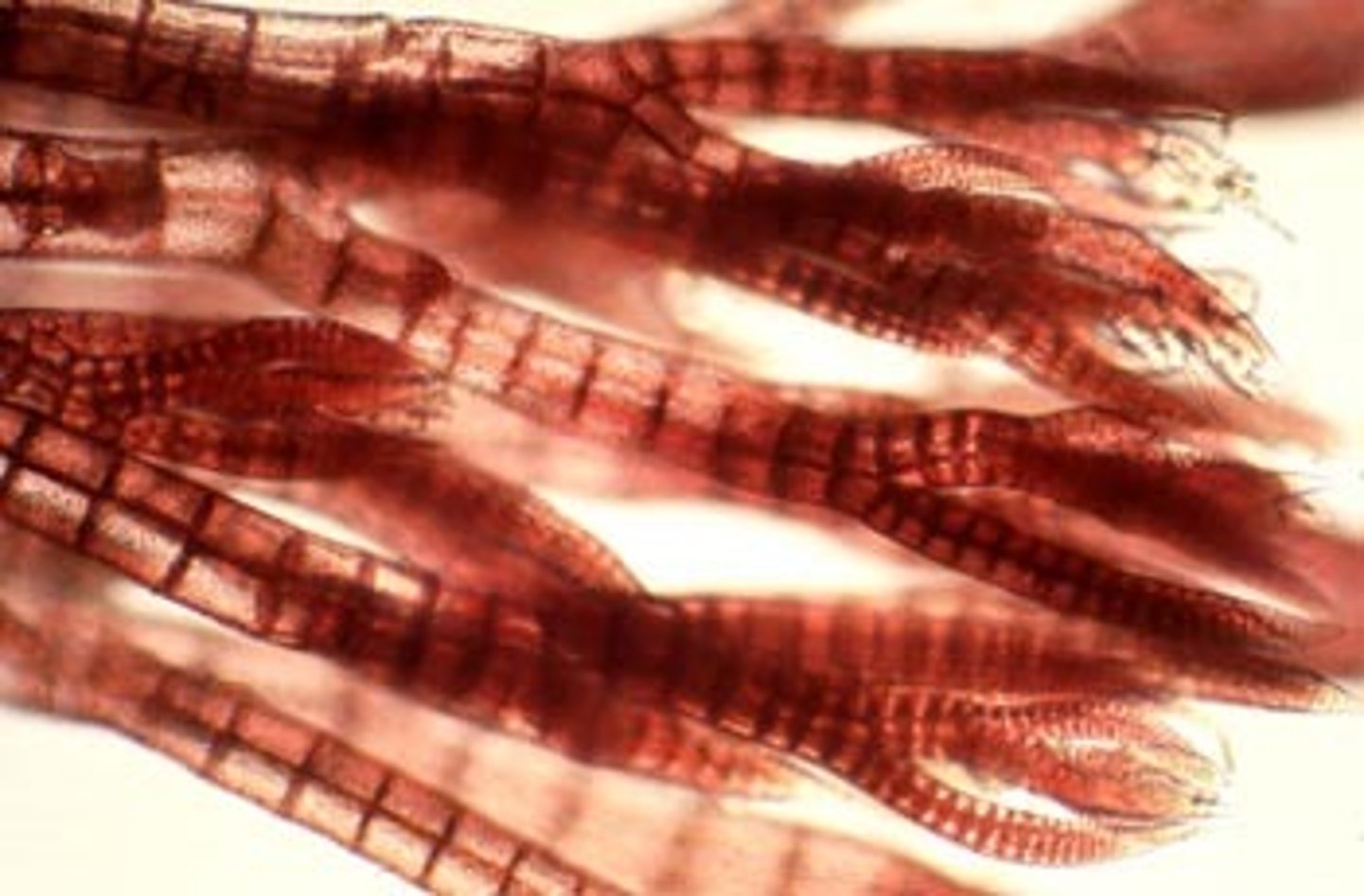
what structure do rhodophyte gametes lack?
flagella
Which plant-like protists are green algae that have both chlorophyll a and b?
chlorophytes
What carbohydrate polymer do chlorophytes have in their cell walls?
cellulose
How do chlorophytes store energy?
starch

What are the types of gametes different chlorophyta can produce?
1. isogamous
2. anisogamous
3. oogamous
Which gamete type has both sperm and egg as equal in size and motile?
isogamous
Which gamete type has the sperm and egg differ in size?
anisogamous
Which gamete type has a large egg cell that remains with the parent and is fertilized by small, motile sperm?
oogamous
What lineage of chlorophytes are believed to be the ancestor of plants?
charophytes
Spirogyras are which type of algae?
green algae
Which protists are heterotrophs, consuming living cells or dead organic matter, and are unicellular eukaryotes?
animal-like protists
(AKA: protozoa)
Which protozoans are amoebas that move by extensions of their cell body called pseudopodia?
rhizopods
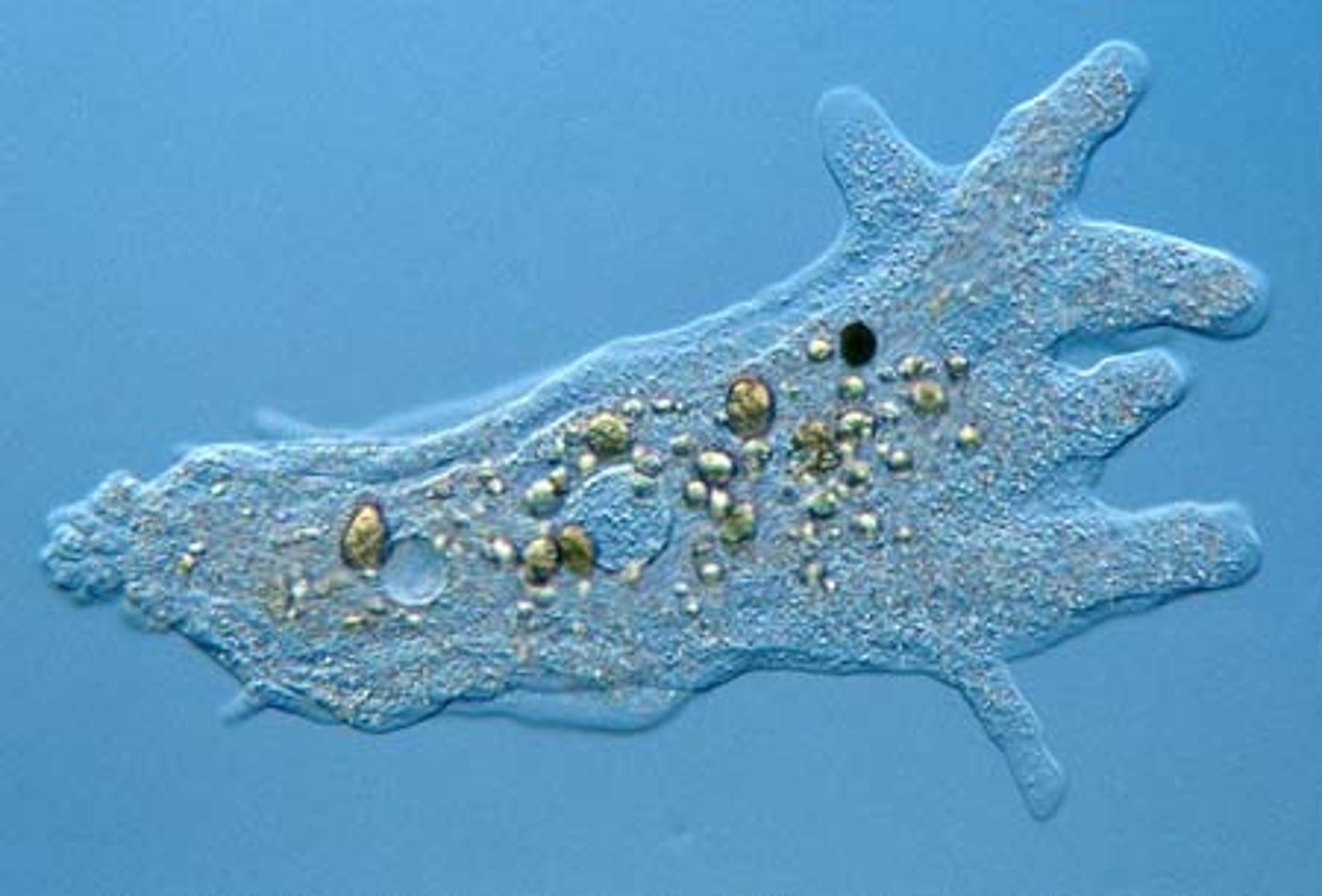
By what mechanism do rhizopods obtain energy?
phagocytosis
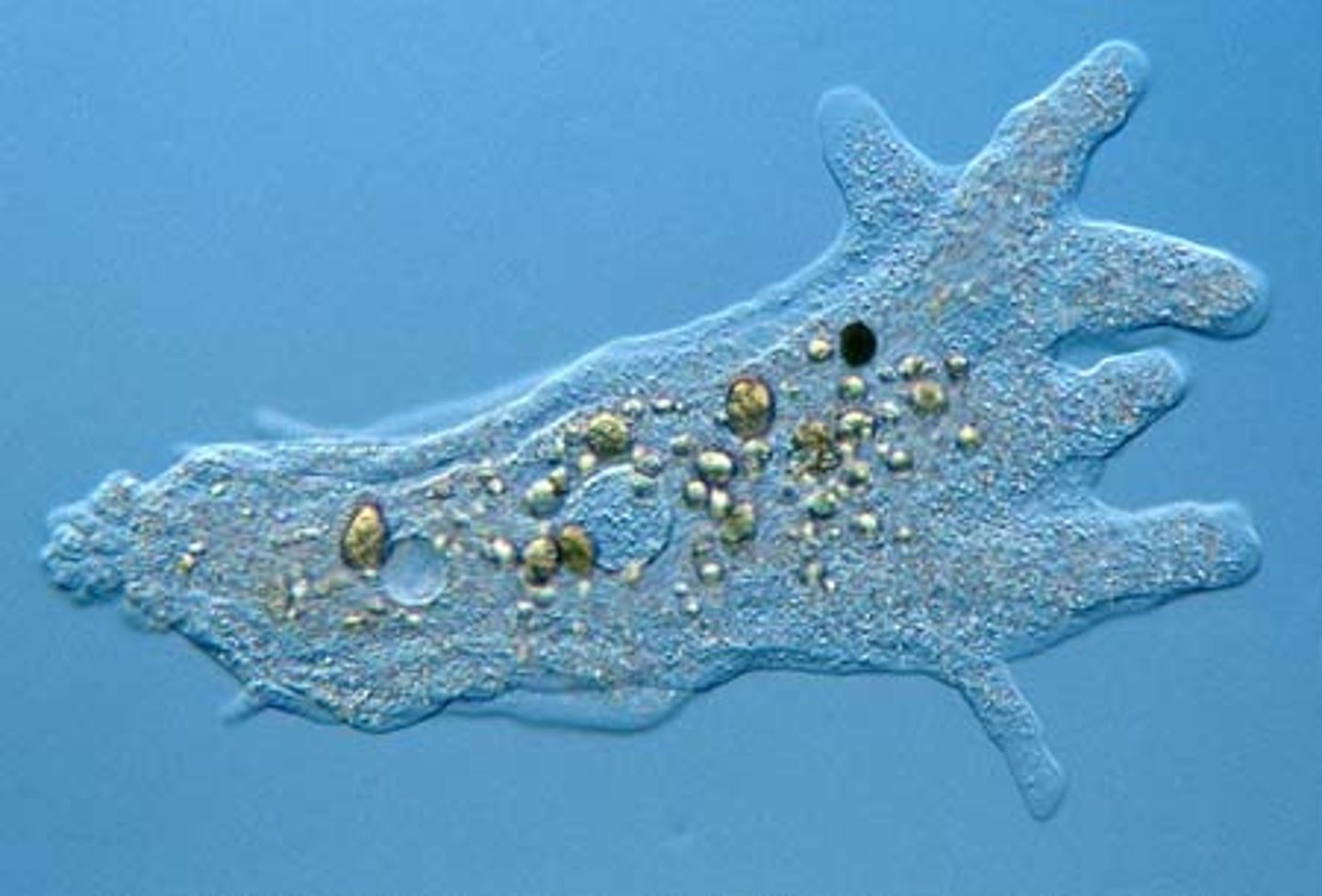
Which protozoans have tests (shells) usually made of calcium carbonate?
forams
(AKA: Foraminafera)
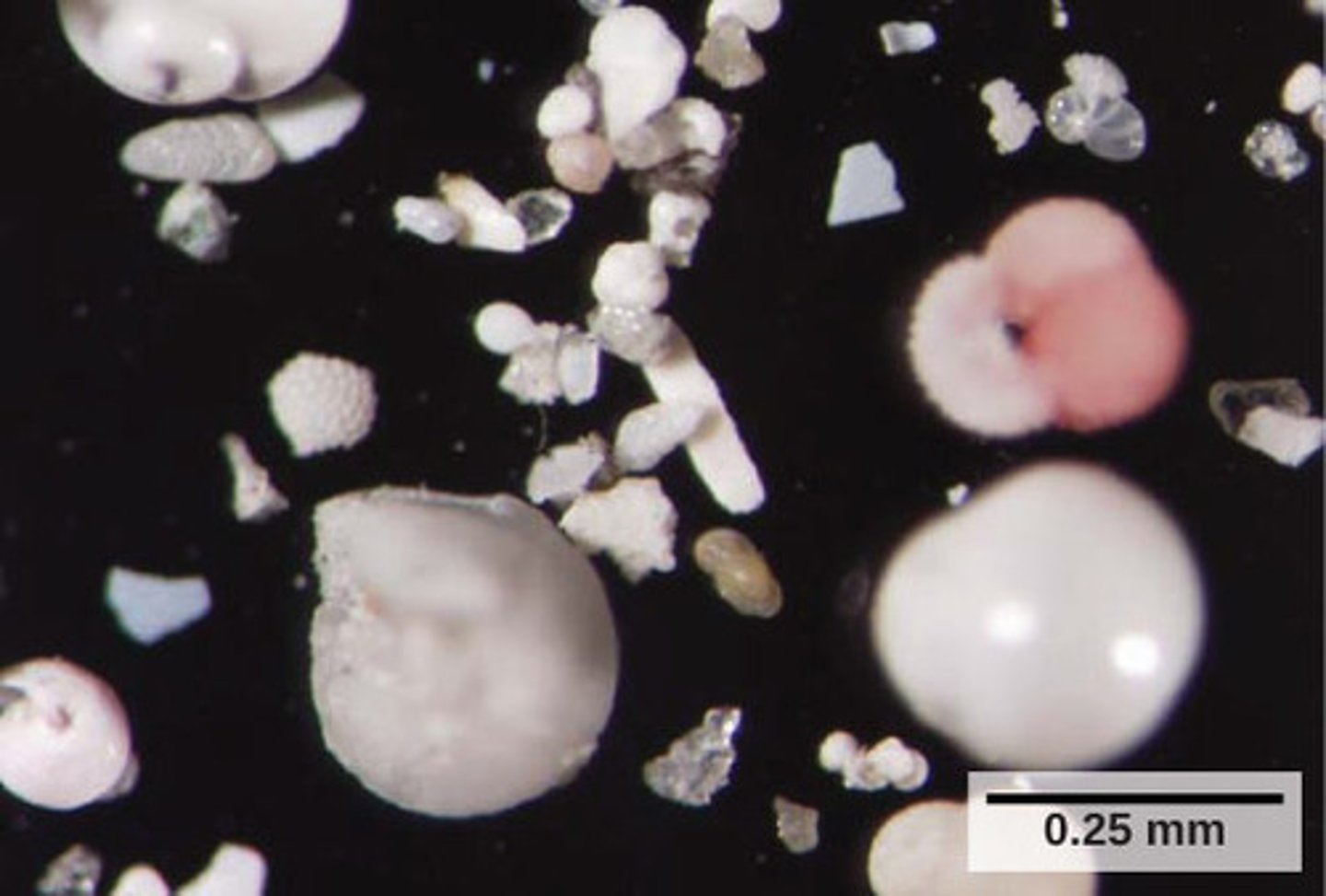

Sediments of forams indicate what about the location?
oil deposits
Which protozoans have an apical complex and are parasites of animals?
apicomplexans
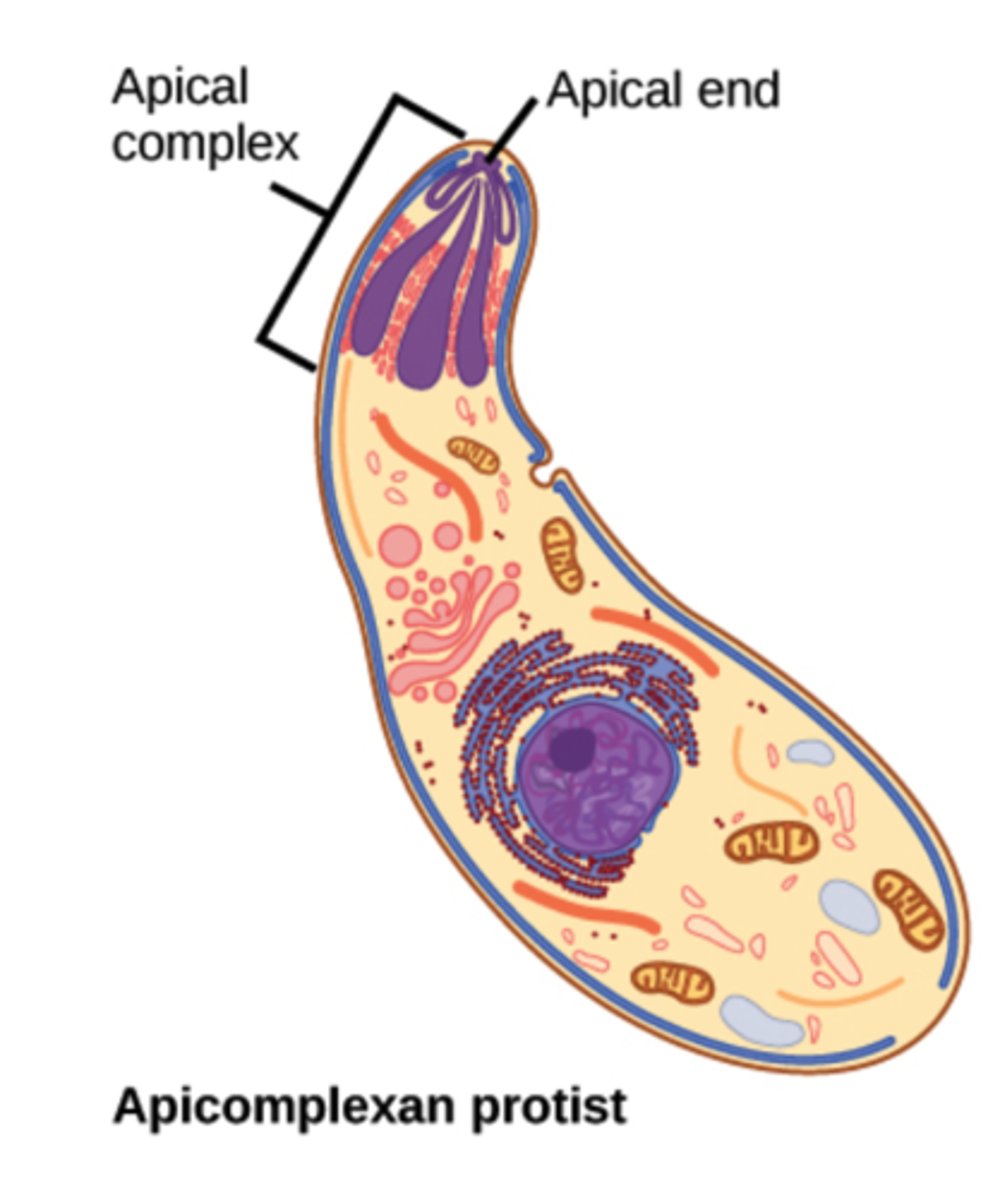
What is the complex of organelles located at an end of the cell within apicomplexans?
apical complex
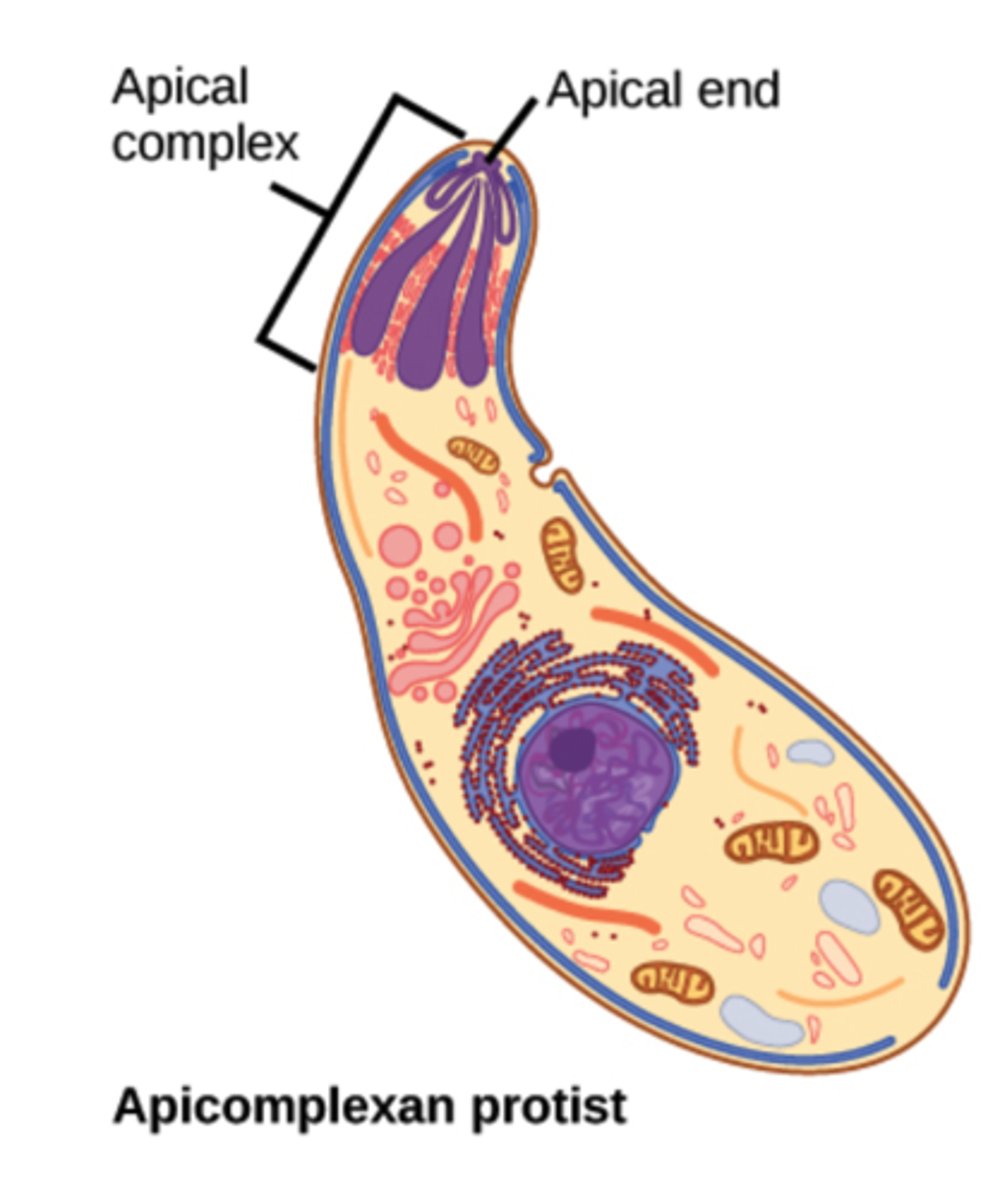
How motile are apicomplexans?
non-motile
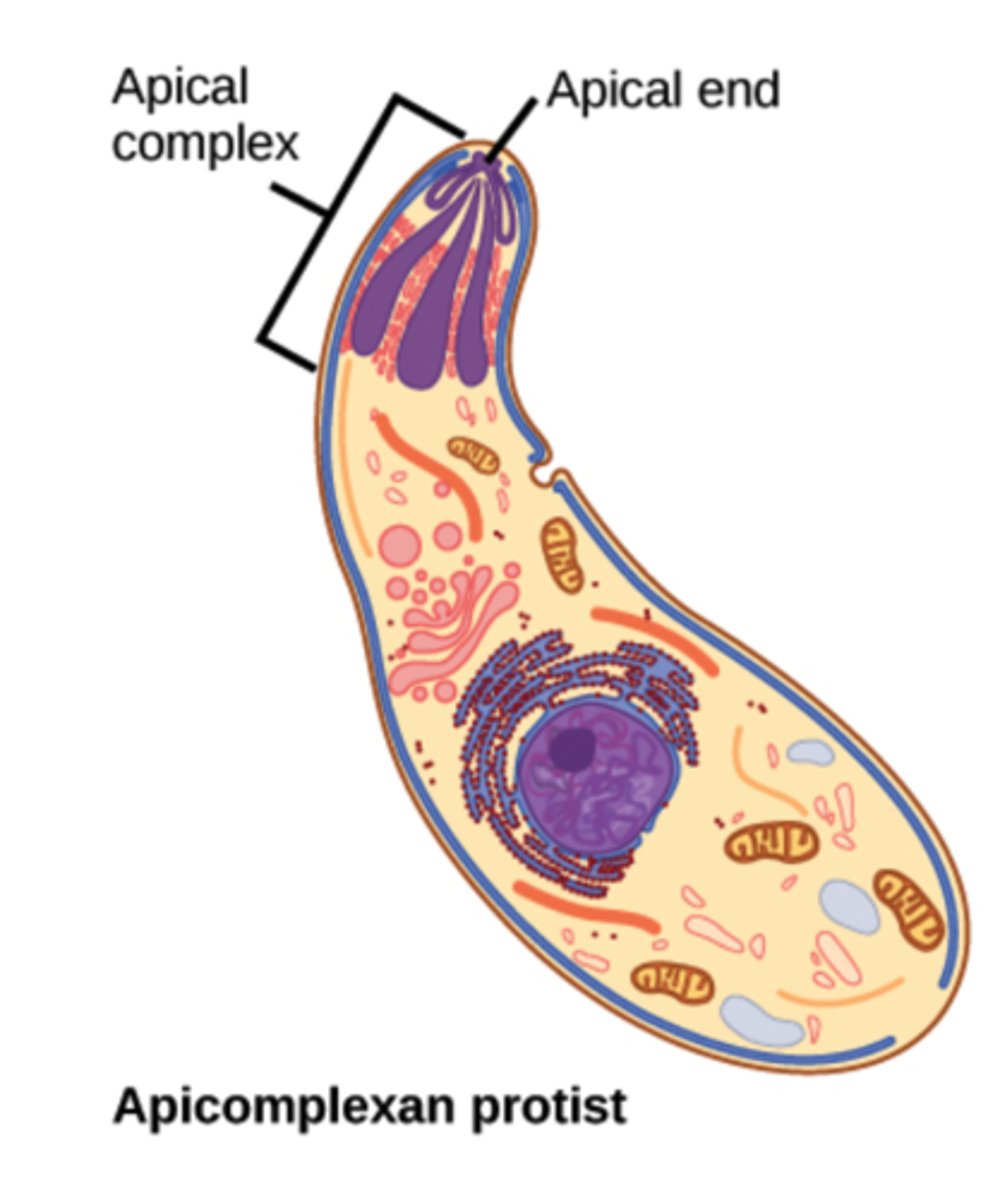
What structures do apicomplexans disperse to complete their life cycle within hosts?
spores
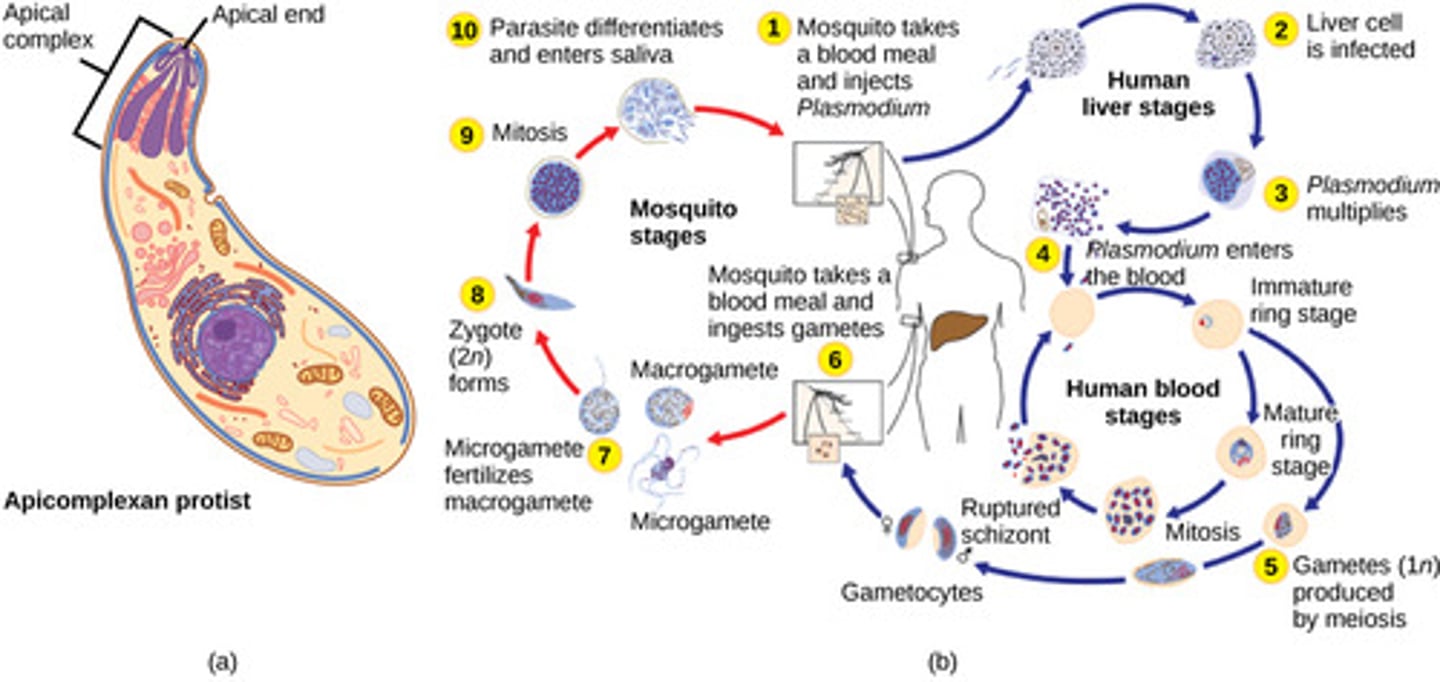
Malaria is caused by what category of protozoans?
apicomplexans
(Note: subphylum sporozoa)
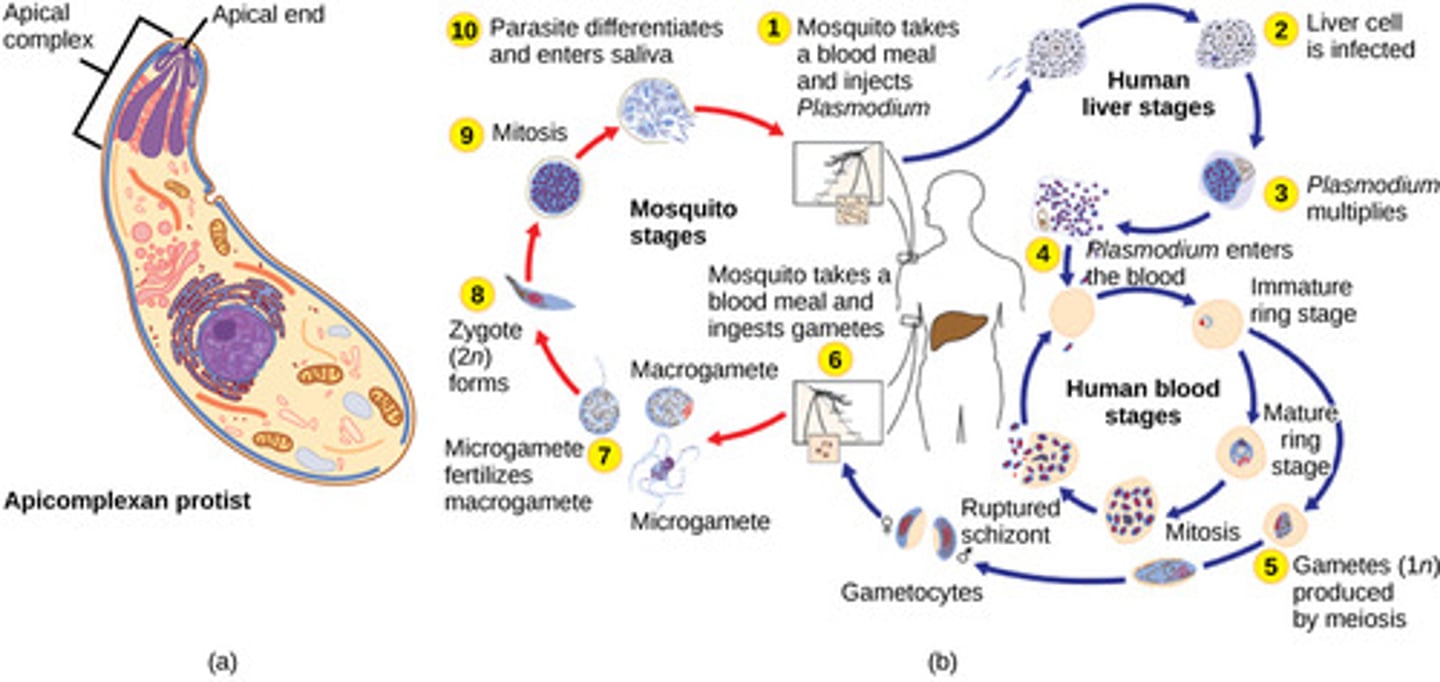
Which protozoans use cilia for moving and other functions?
ciliates
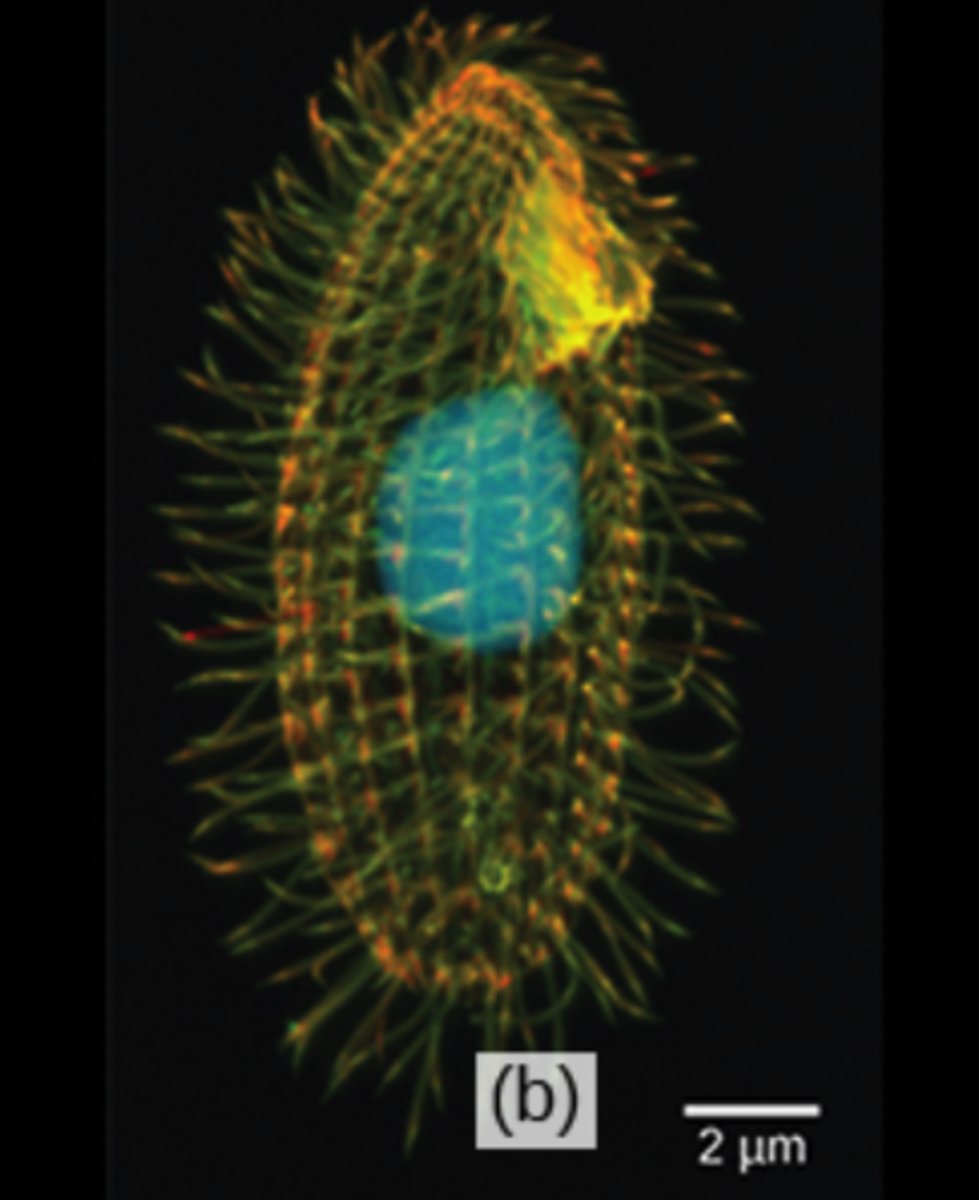
What specialized structure do ciliates possess to ingest food?
mouth pore
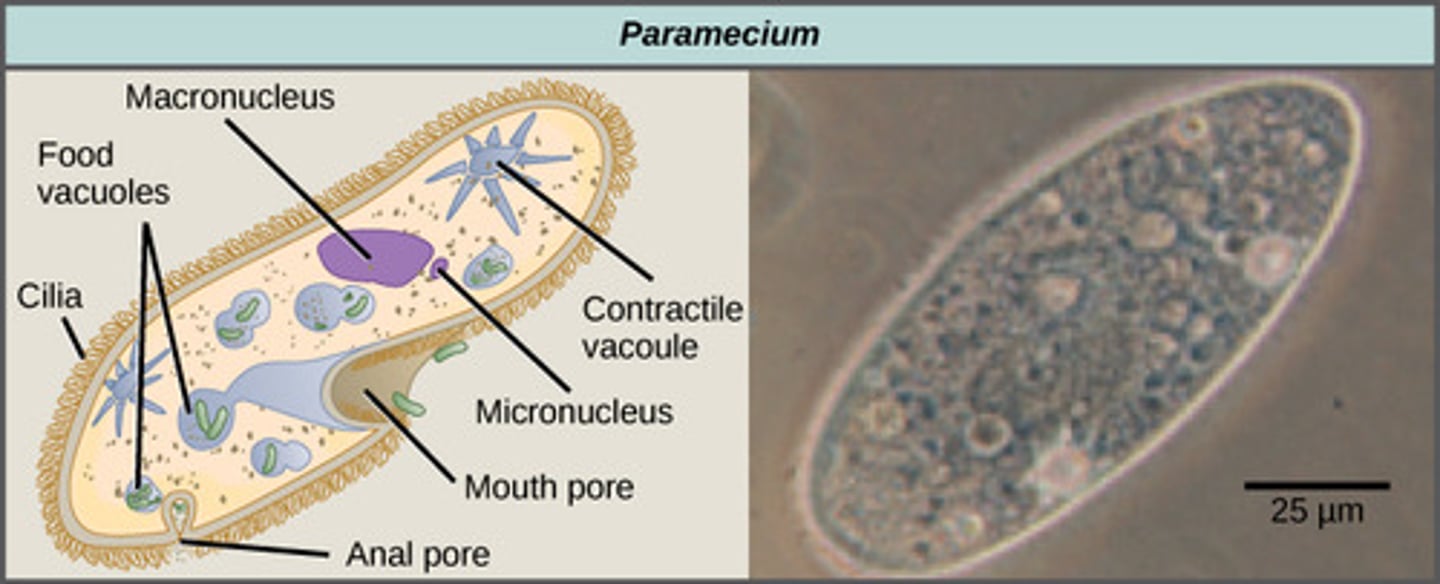
What specialized structure do ciliates possess to balance H20 levels?
contractile vacuole
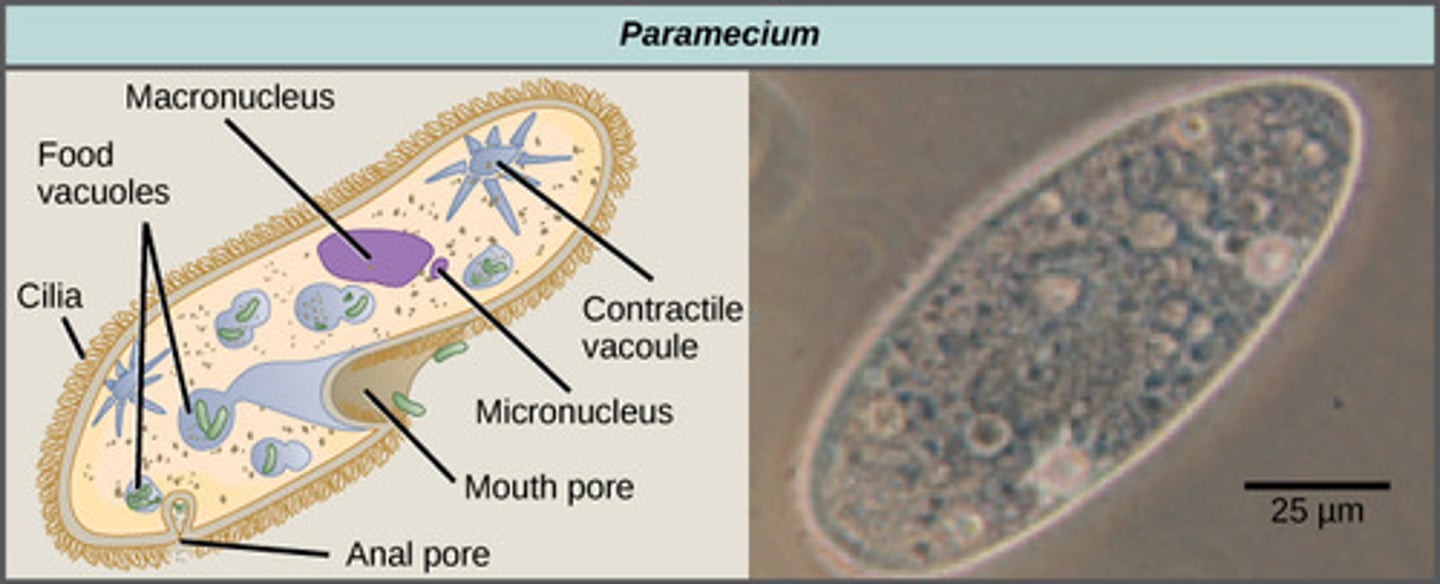
What are the two kinds of nuclei found in ciliates?
1. large macronucleus
2. several small nuclei
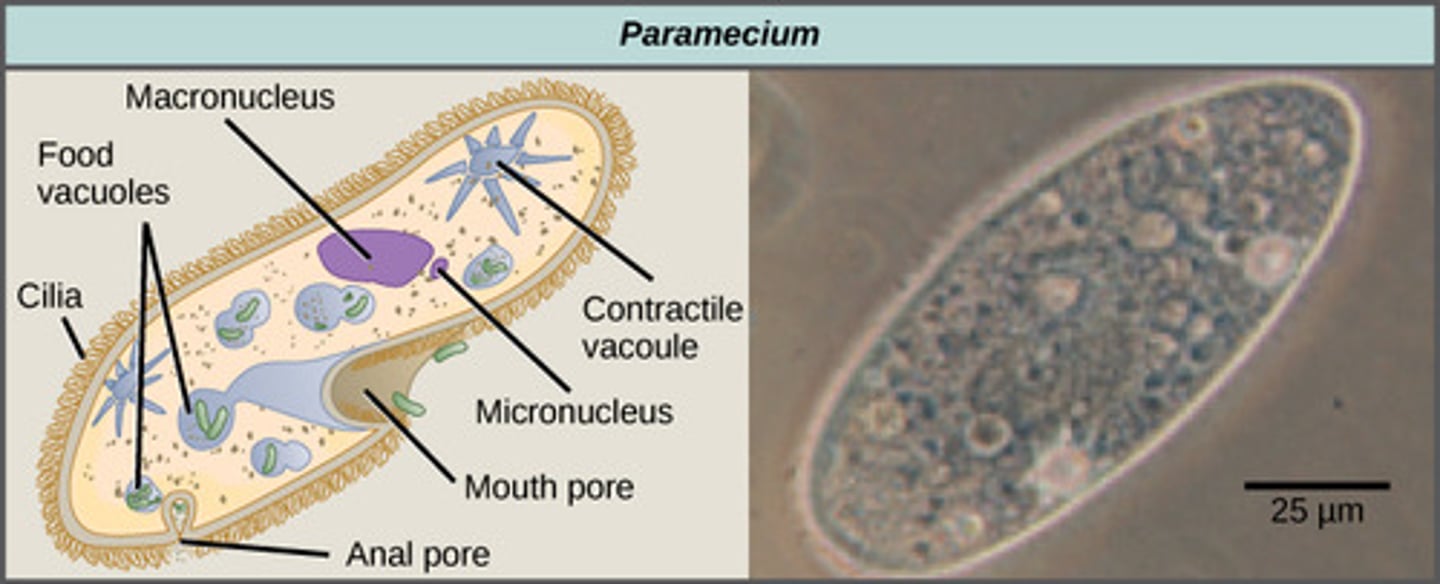
Which animal-like protist group contains paramecium?
ciliates
which animal like protists are a genus of protozoa, and are shapeless and unicellular, moving via pseudopods?
amoebas
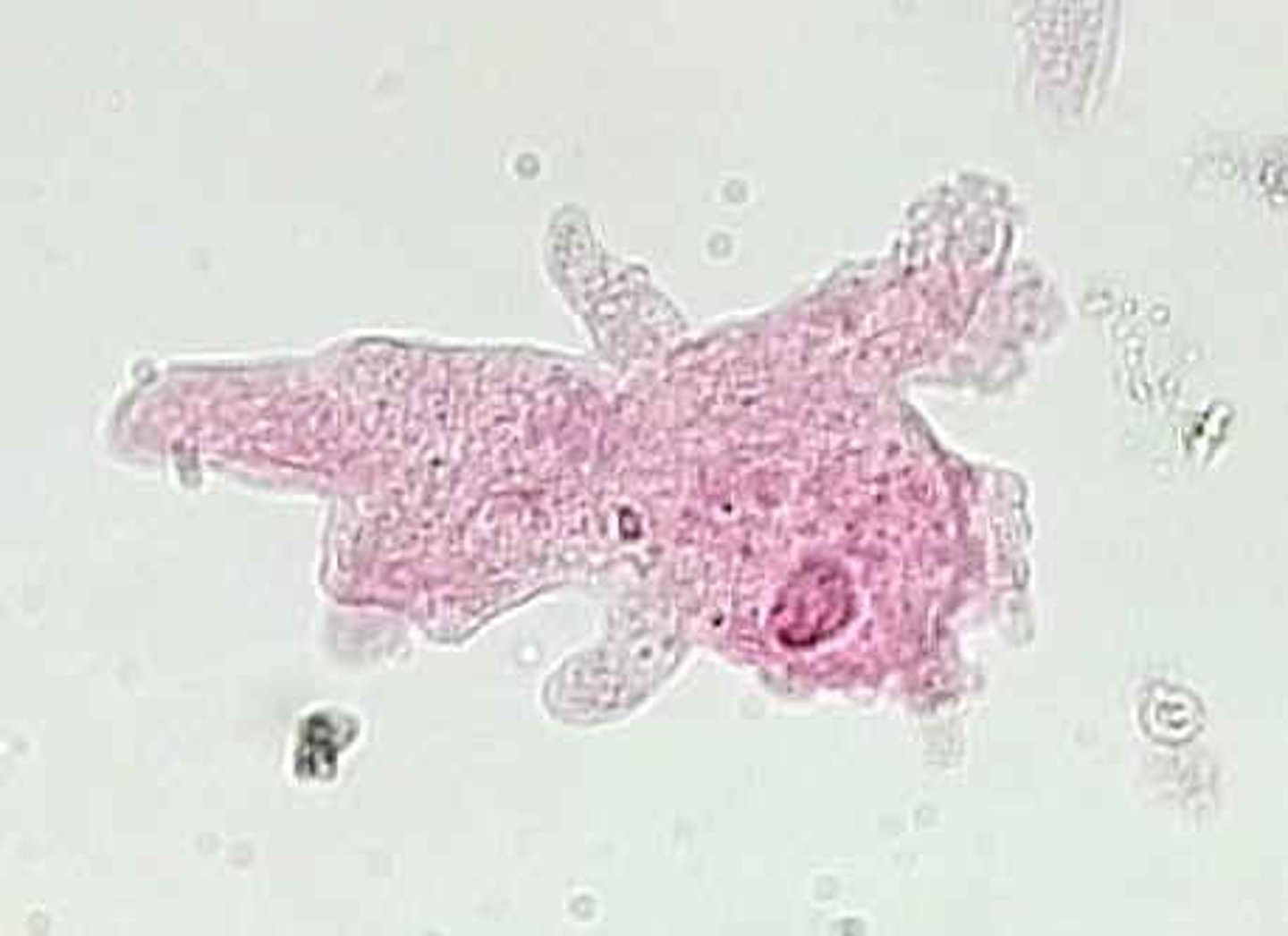
Which group of protists resemble fungi and form filaments/spore-beating bodies as fungi do?
fungus-like protists
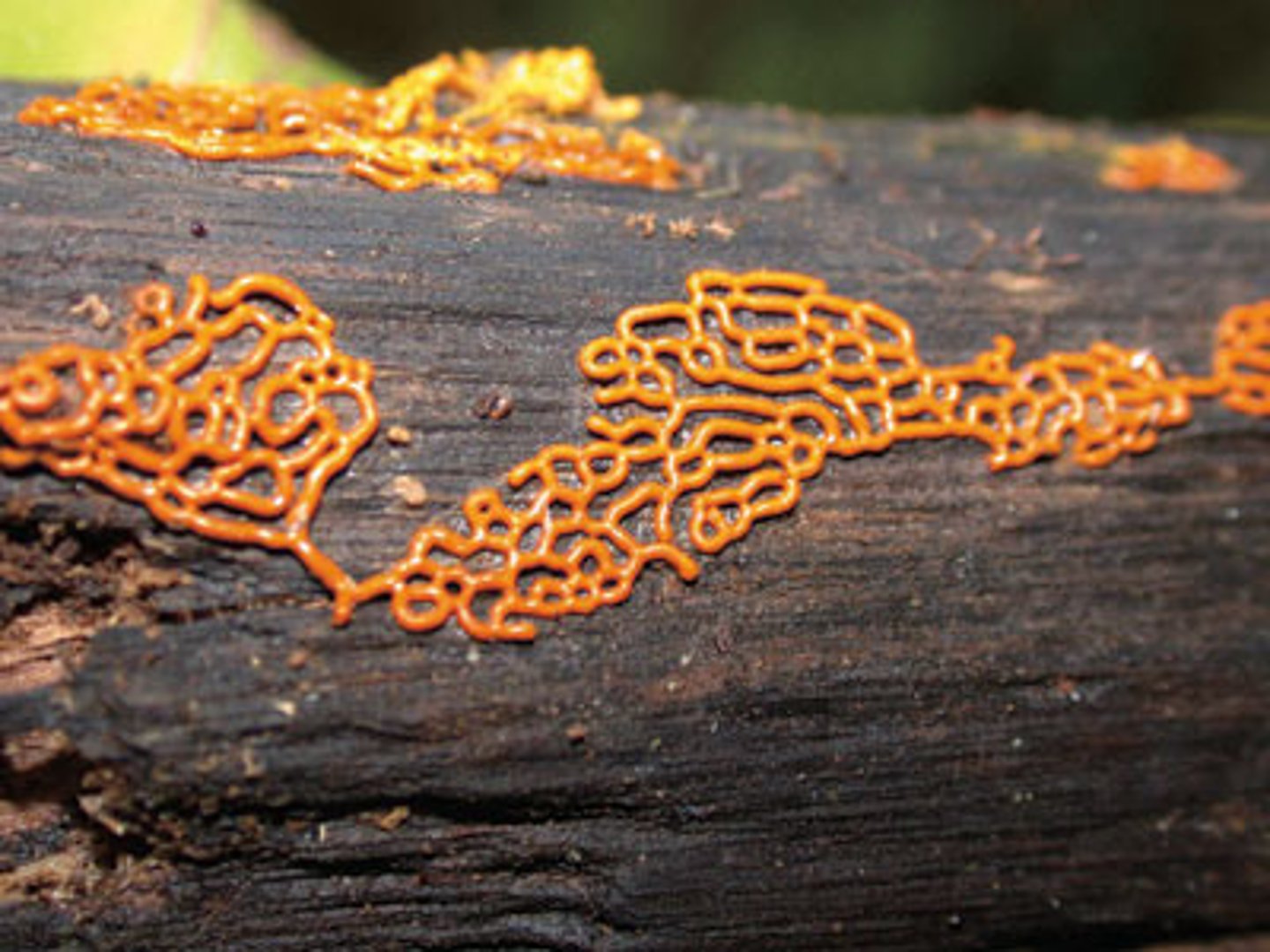

Which fungus-like protists have fungus-like and protozoa-like characteristics?
cellular slime molds
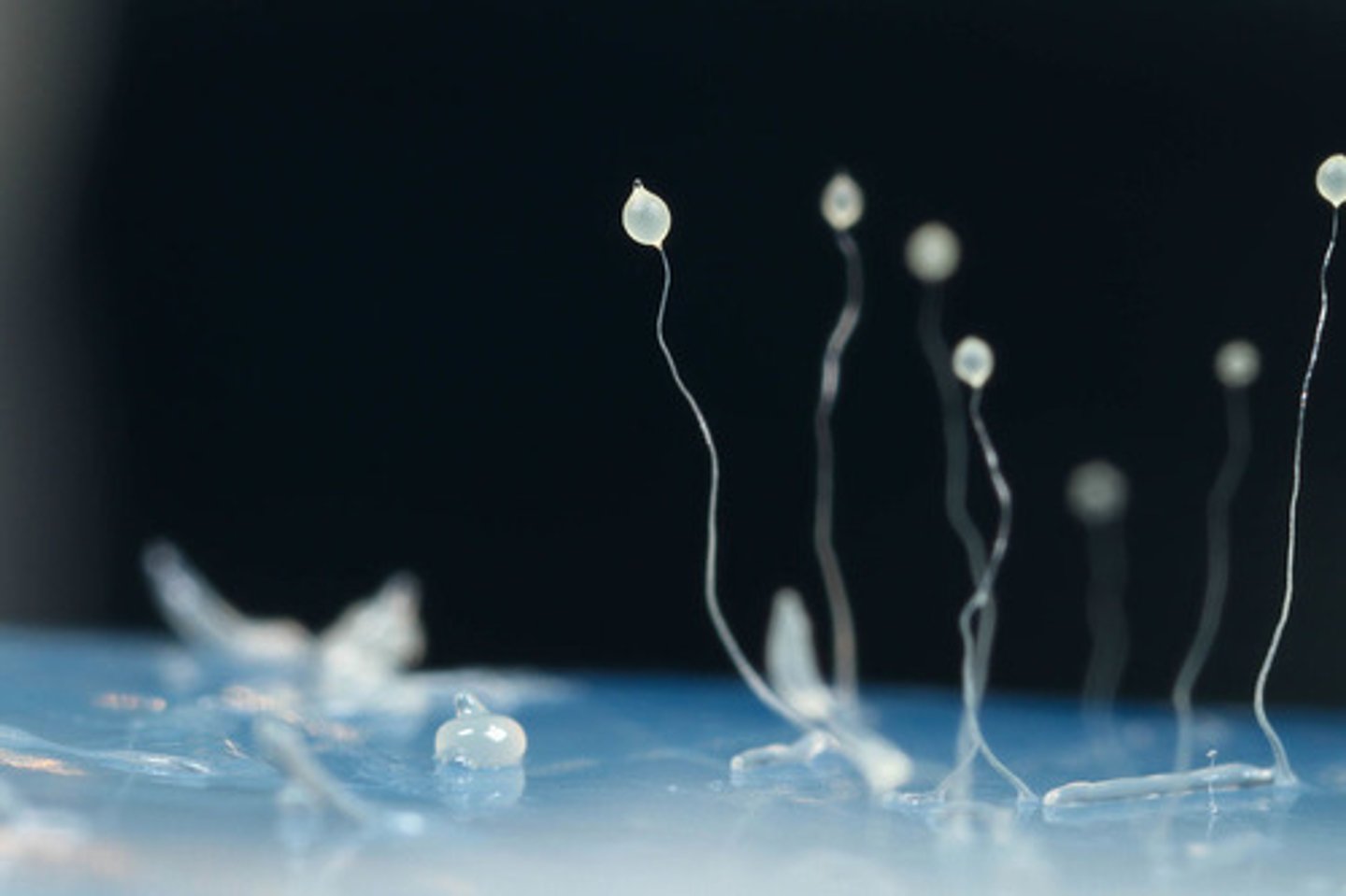
The spores from cellular slime molds germinate into what organisms that feed on bacteria?
amoebas
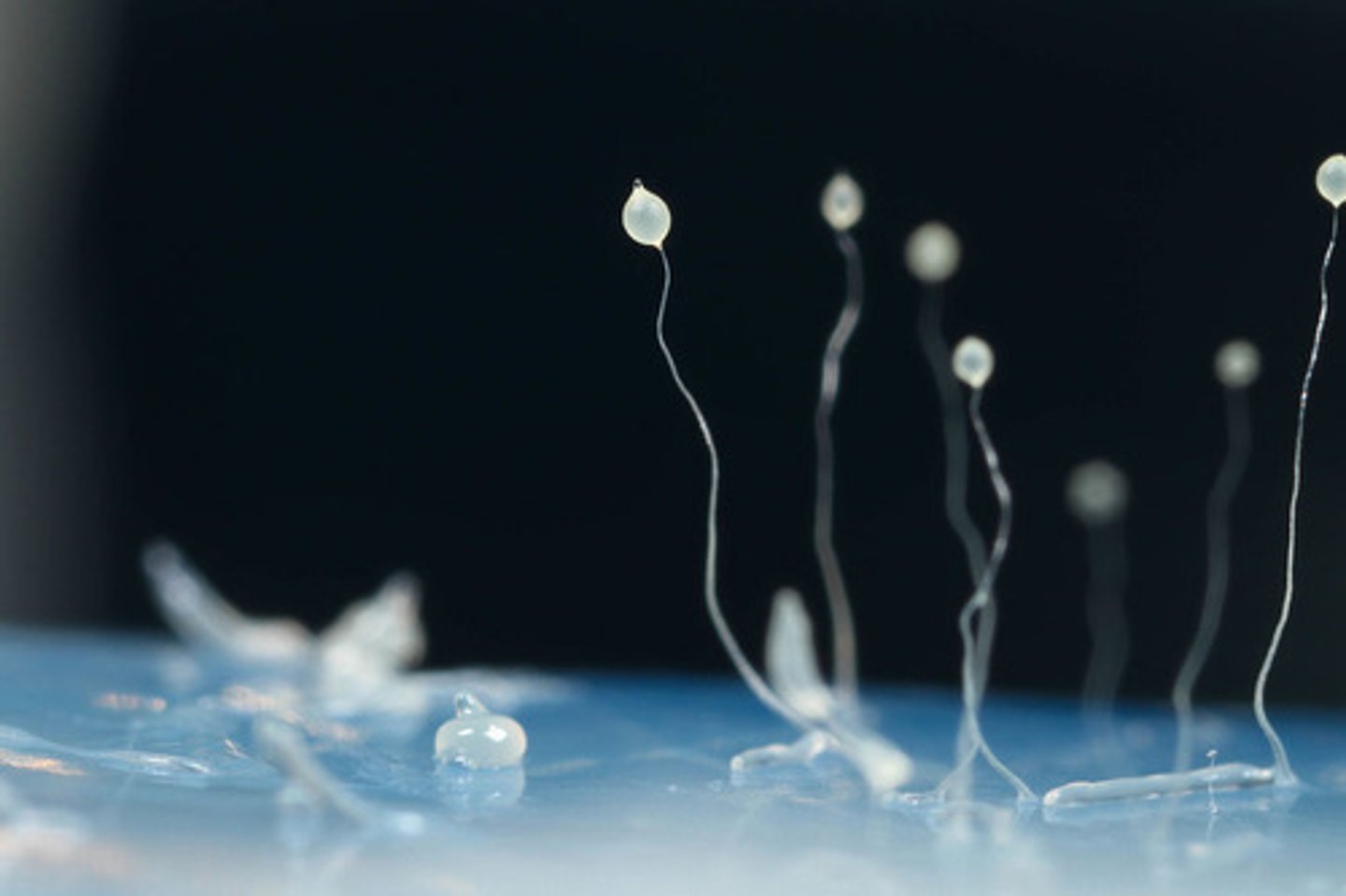
How do the amoebas produced by cellular slime molds multiply?
mitosis
(Note: asexually)
Though amoebas produced by cellular slime molds can reproduce sexually and form a diploid zygote, the zygote undergoes what process?
meiosis
(Note: back to haploid amoeba stage)
When no food is available for cellular slime molds, individual amoebas aggregate into what group?
single-unit slug
(Note: aggregate of haploid cells)
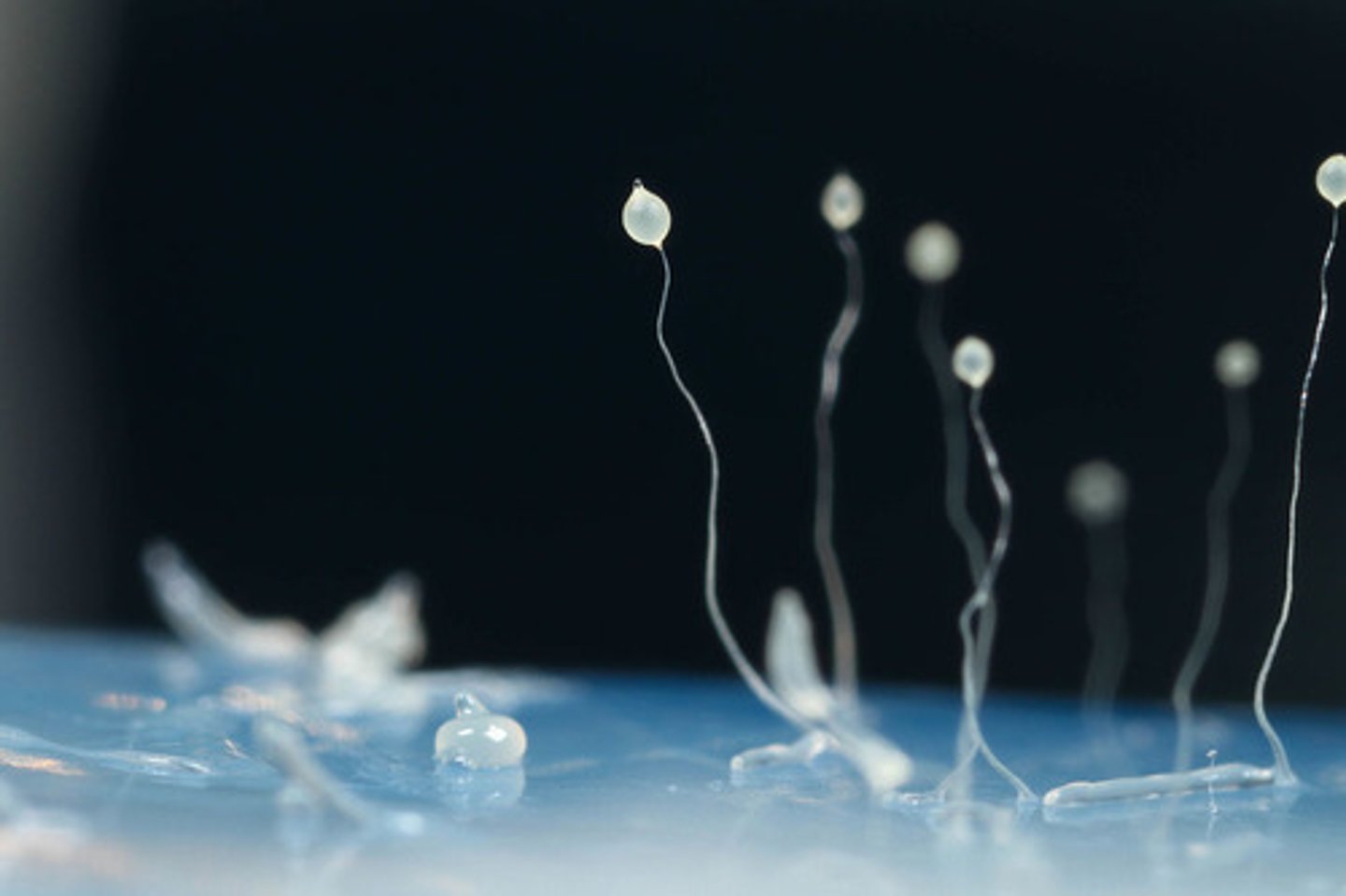
What is the stimulus for cellular slime molds to aggregate?
cAMP secretion by food deprived amoebas
When cellular slime molds aggregate into a slug, the cells mobilize into what structure?
stalk
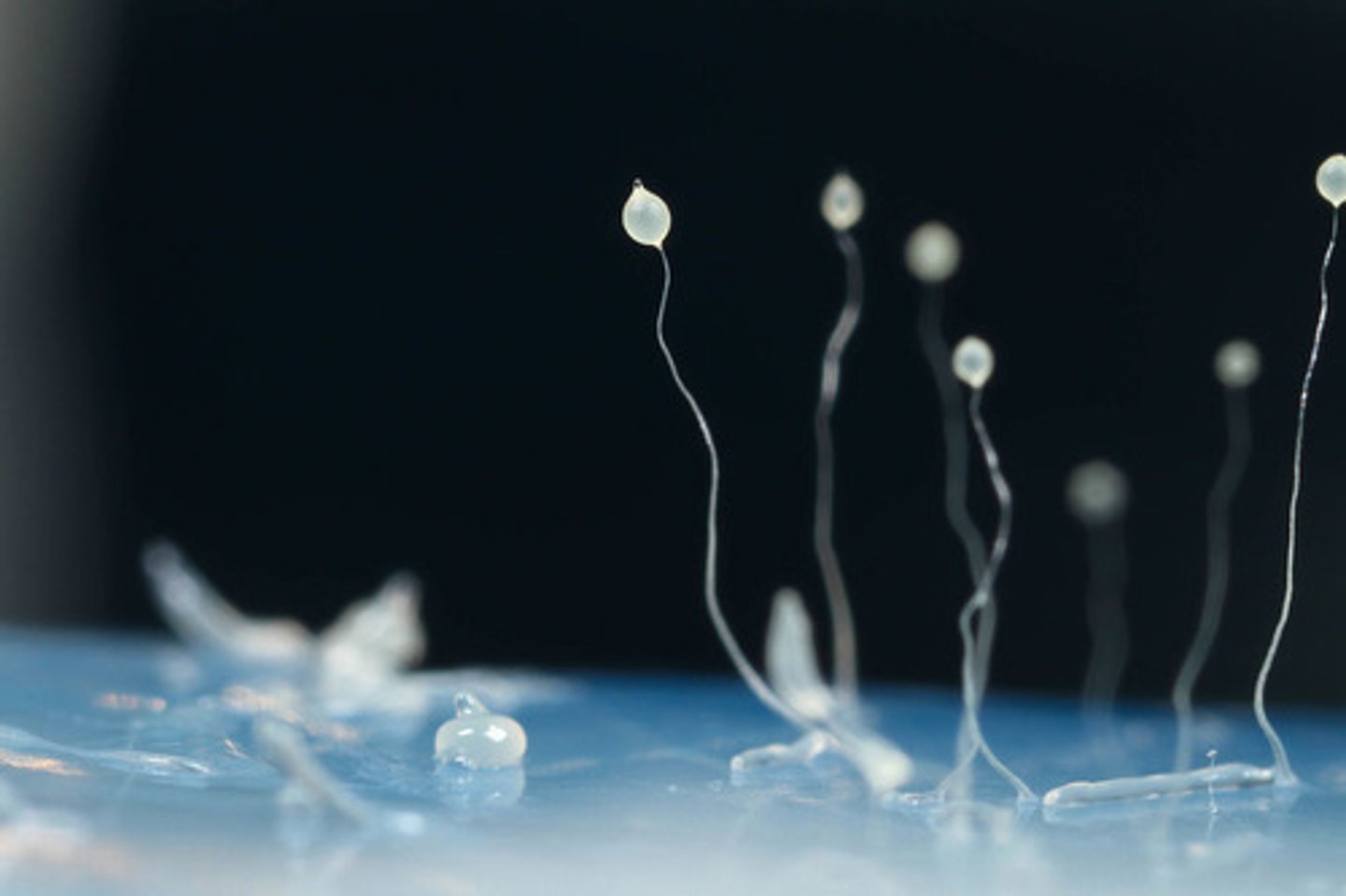
What is the function of a cellular slime mold's stalk?
contain a capsule
that releases haploid
spores which
germinate and repeat
the life cycle
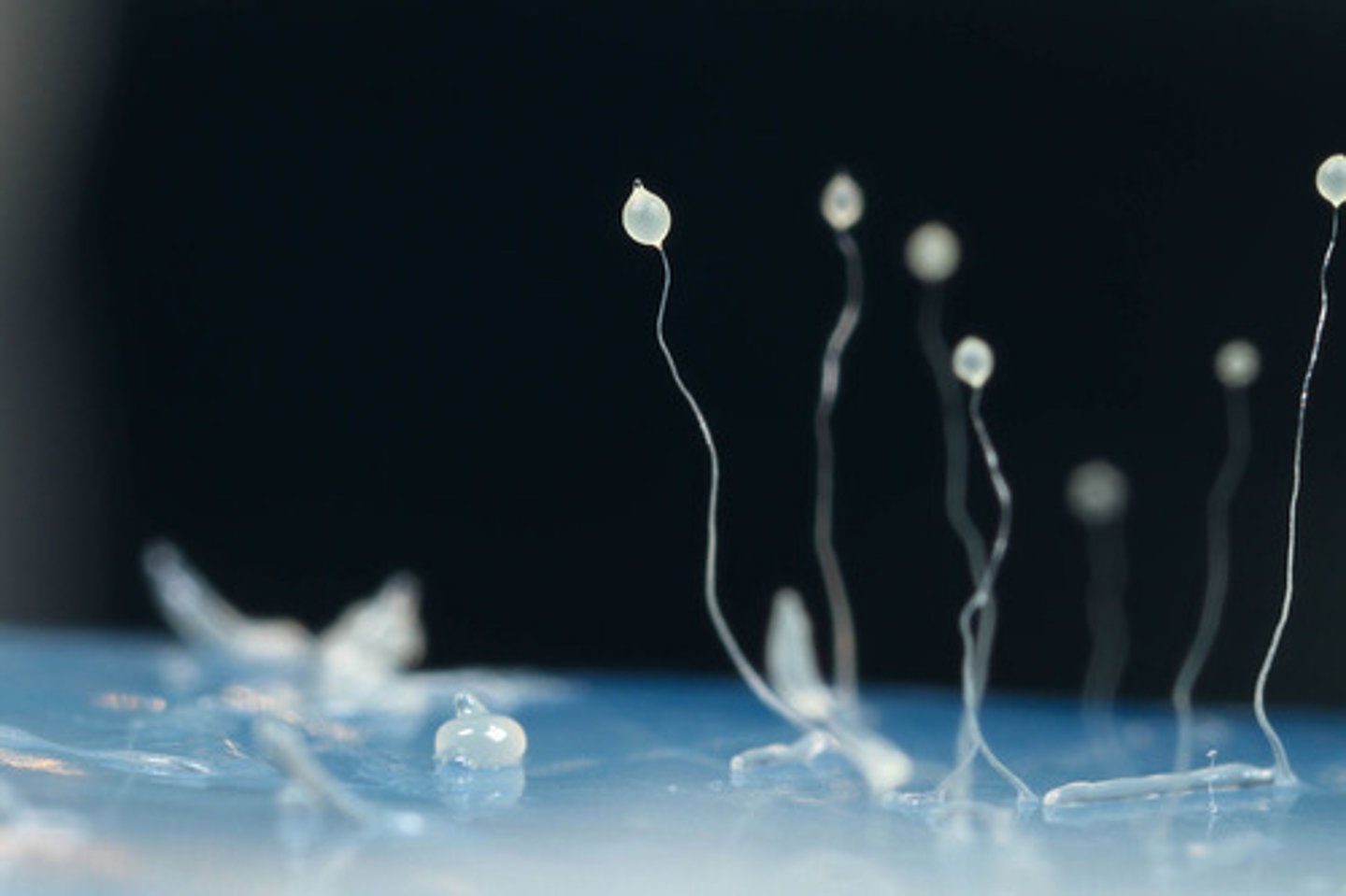
Which fungus-like protists grow as a single, spreading mass (plasmodium) that feeds on decaying vegetation?
plasmodial slime molds
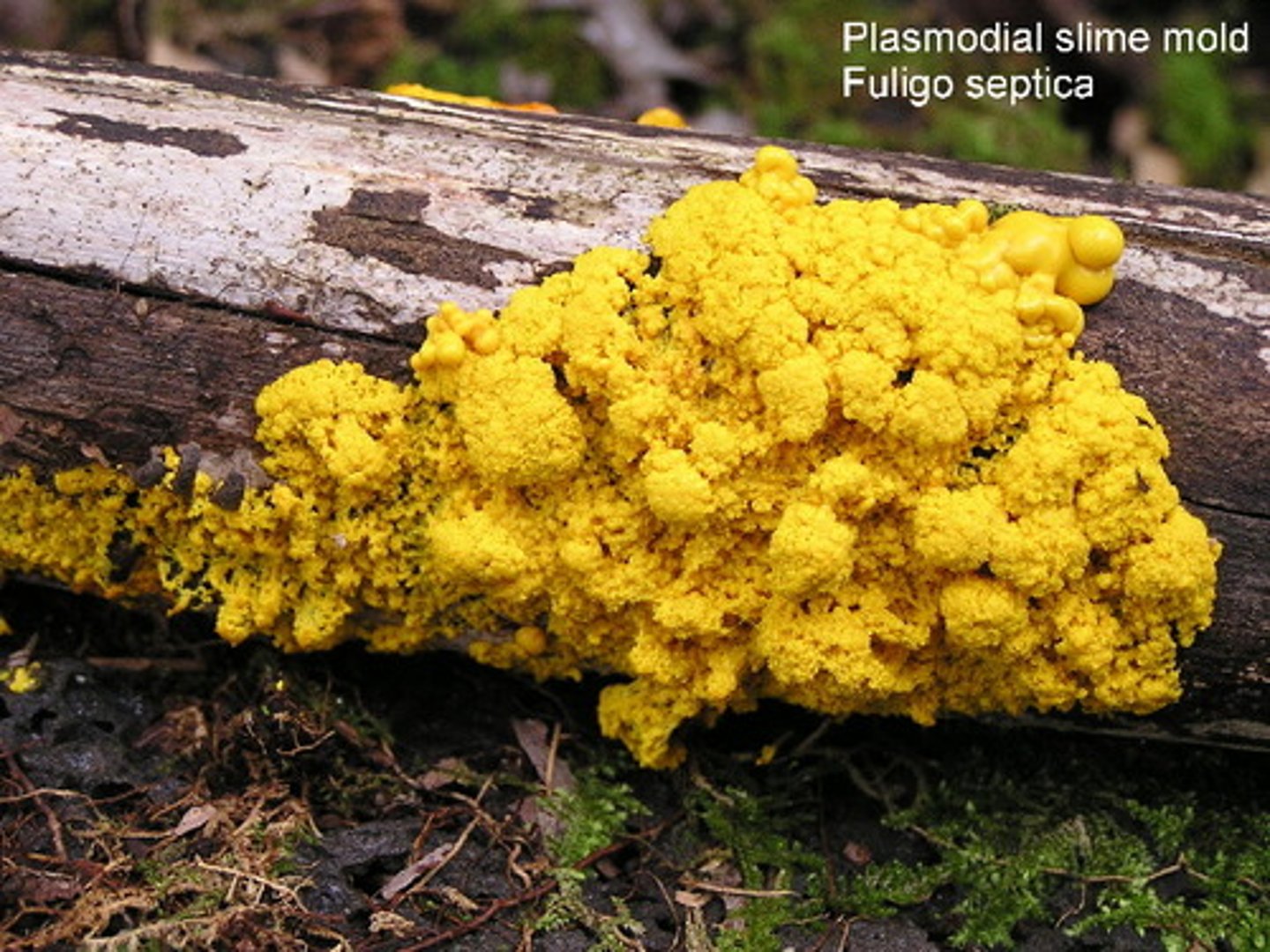

When plasmodial slime molds have no food or water, what structures form to release haploid spores?
stalks bearing fruiting bodies called sporangia
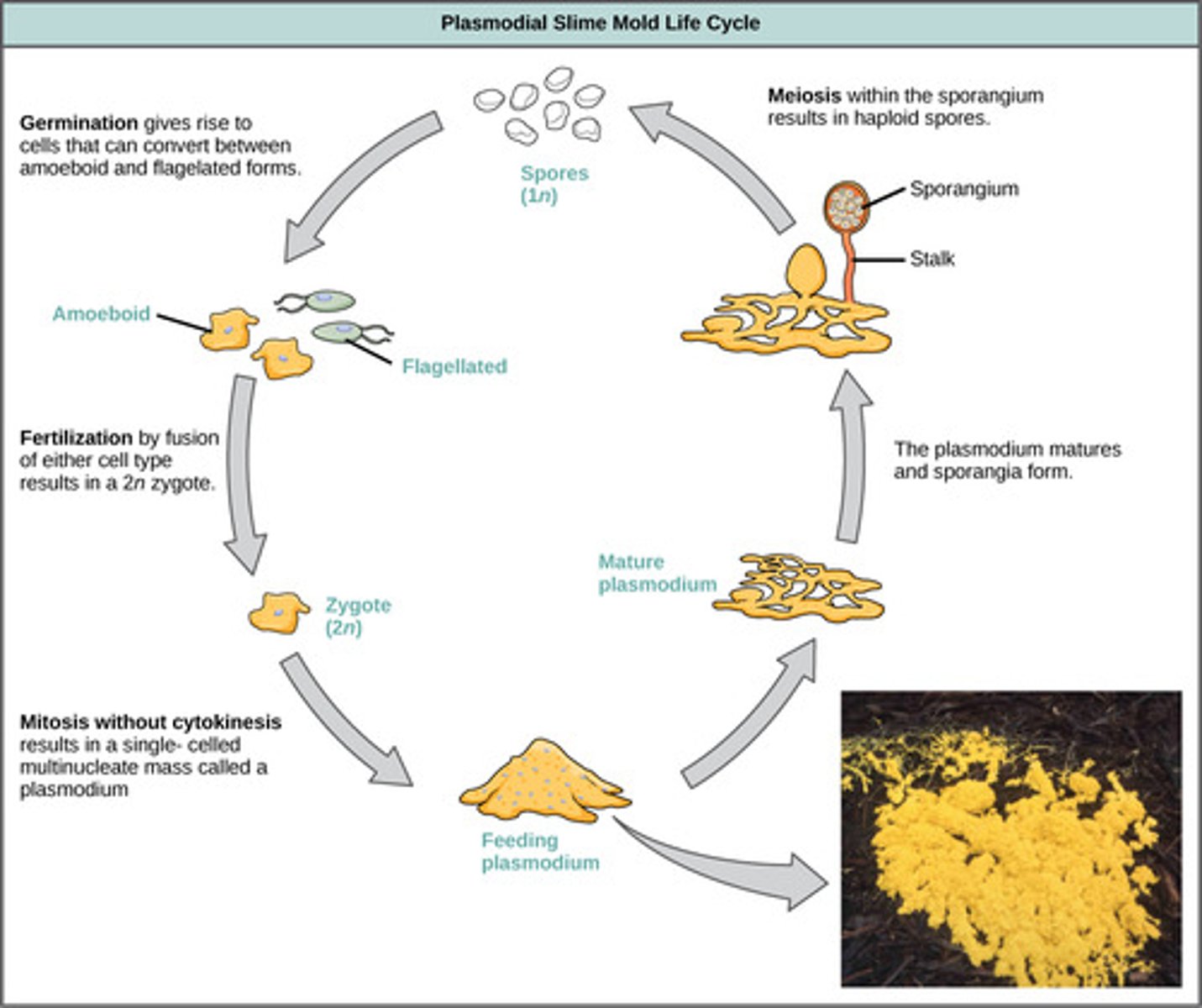
By what process are haploid spores produced within plasmodial slime mold sporangia?
meiosis
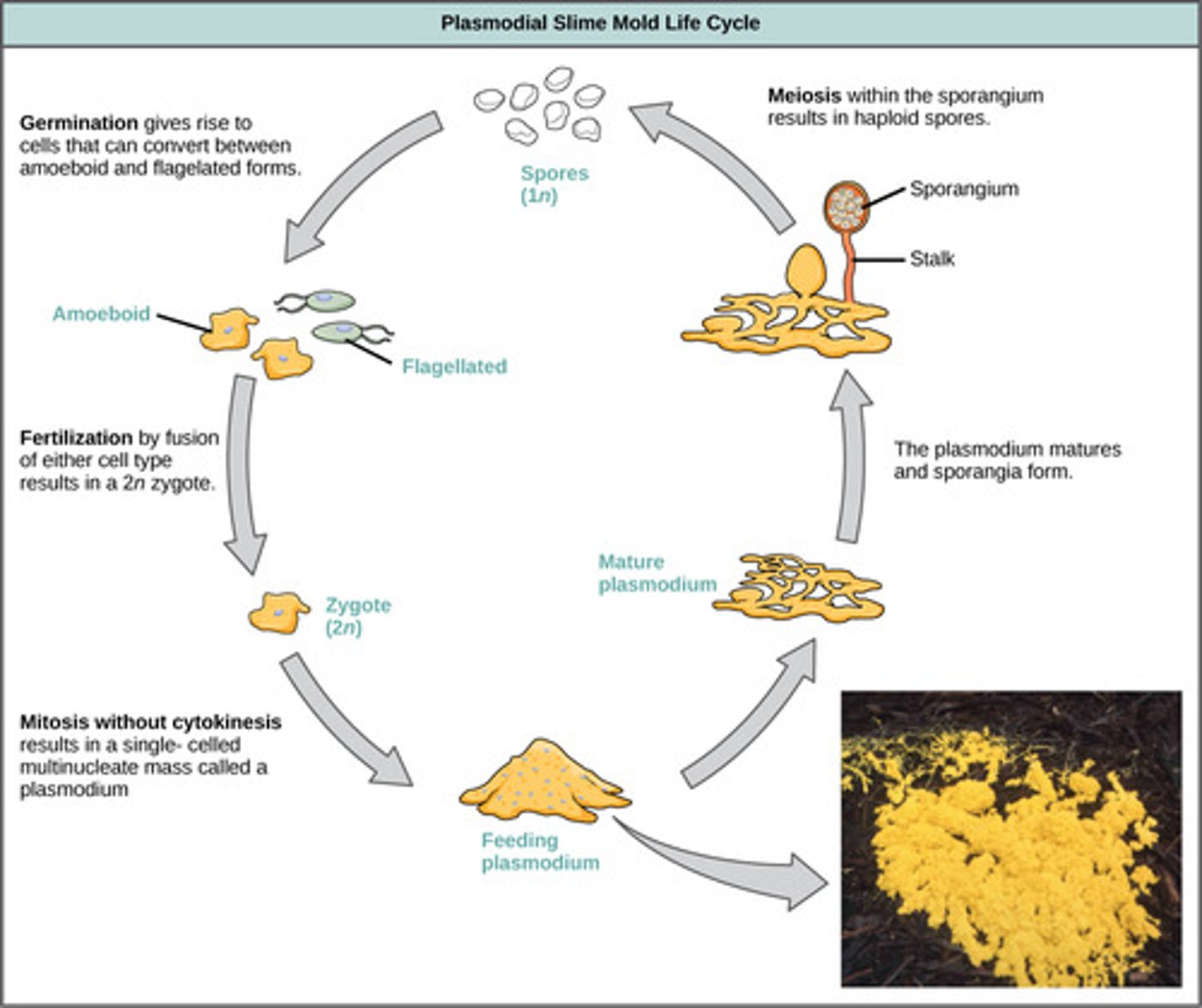
When haploid spores are released from plasmodial slime mold sporangia, what cells germinate?
haploid amoeboid/flagellated cells
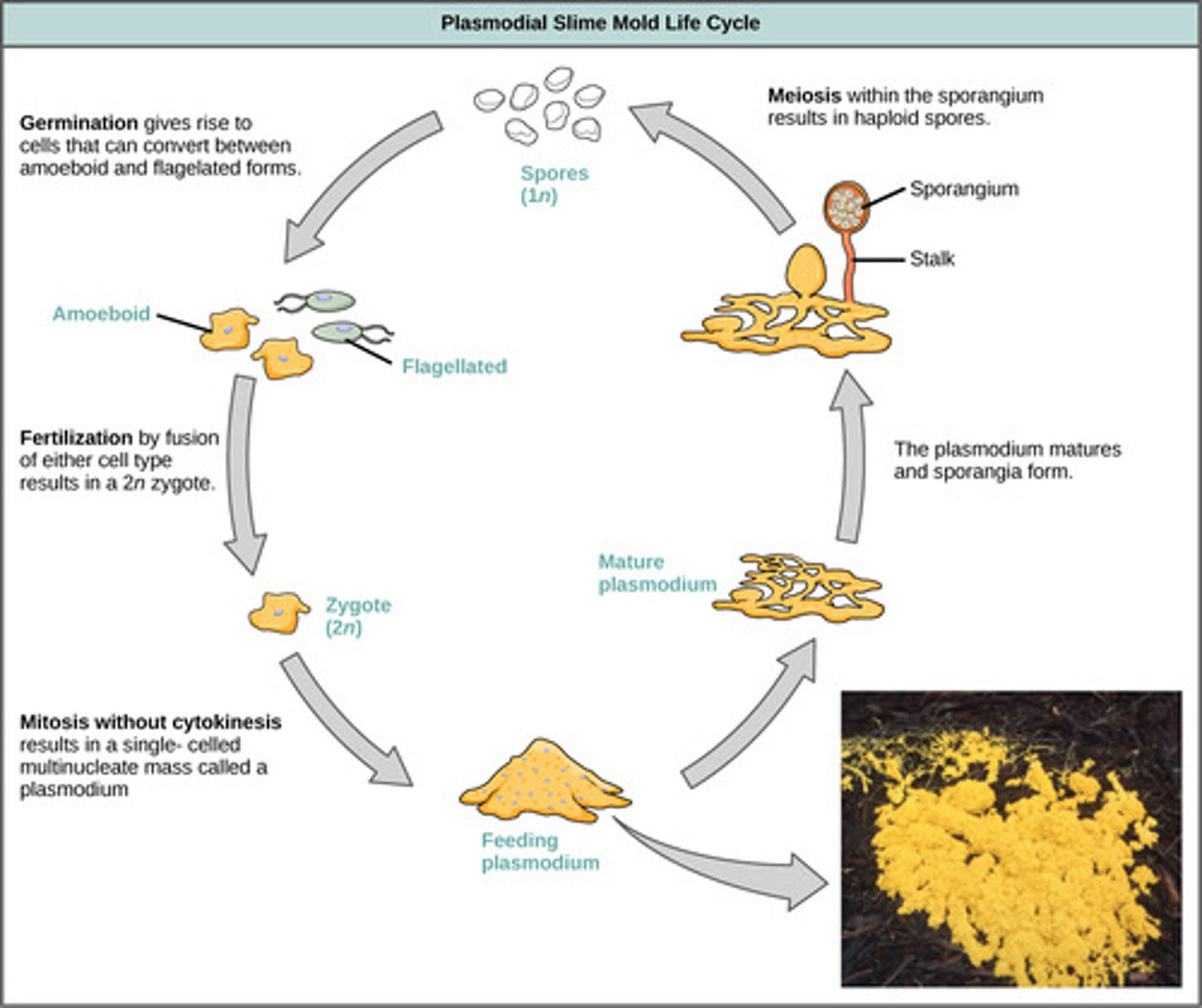
The haploid amoeboid/flagellated cells released by plasmodial slime mold sporangia fuse to form what cells?
diploid cells
(Note: zygote)
The fused diploid cells in plasmodial slime molds perform what action?
the nuclei divide,
giving a large
multinucleate feeding
stage - the plasmodium
(Note: finally back
to the beginning of
the lifecycle!)
Which fungus-like protists are water molds, mildews, and white rusts?
Oomycota
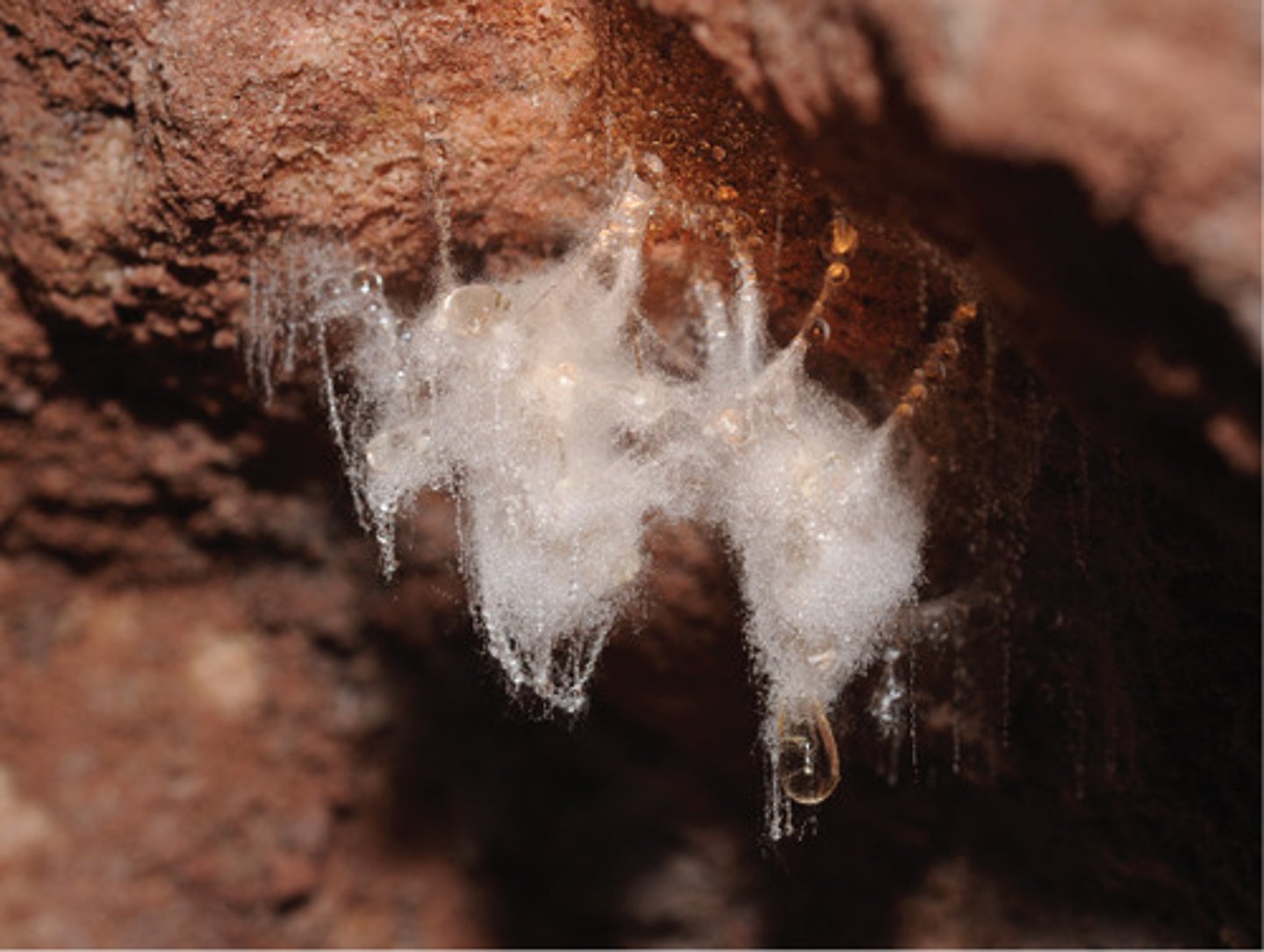

What are the 2 forms within Oomycota?
1. parasites
2. saprobes
Oomycota form filaments called what?
hyphae
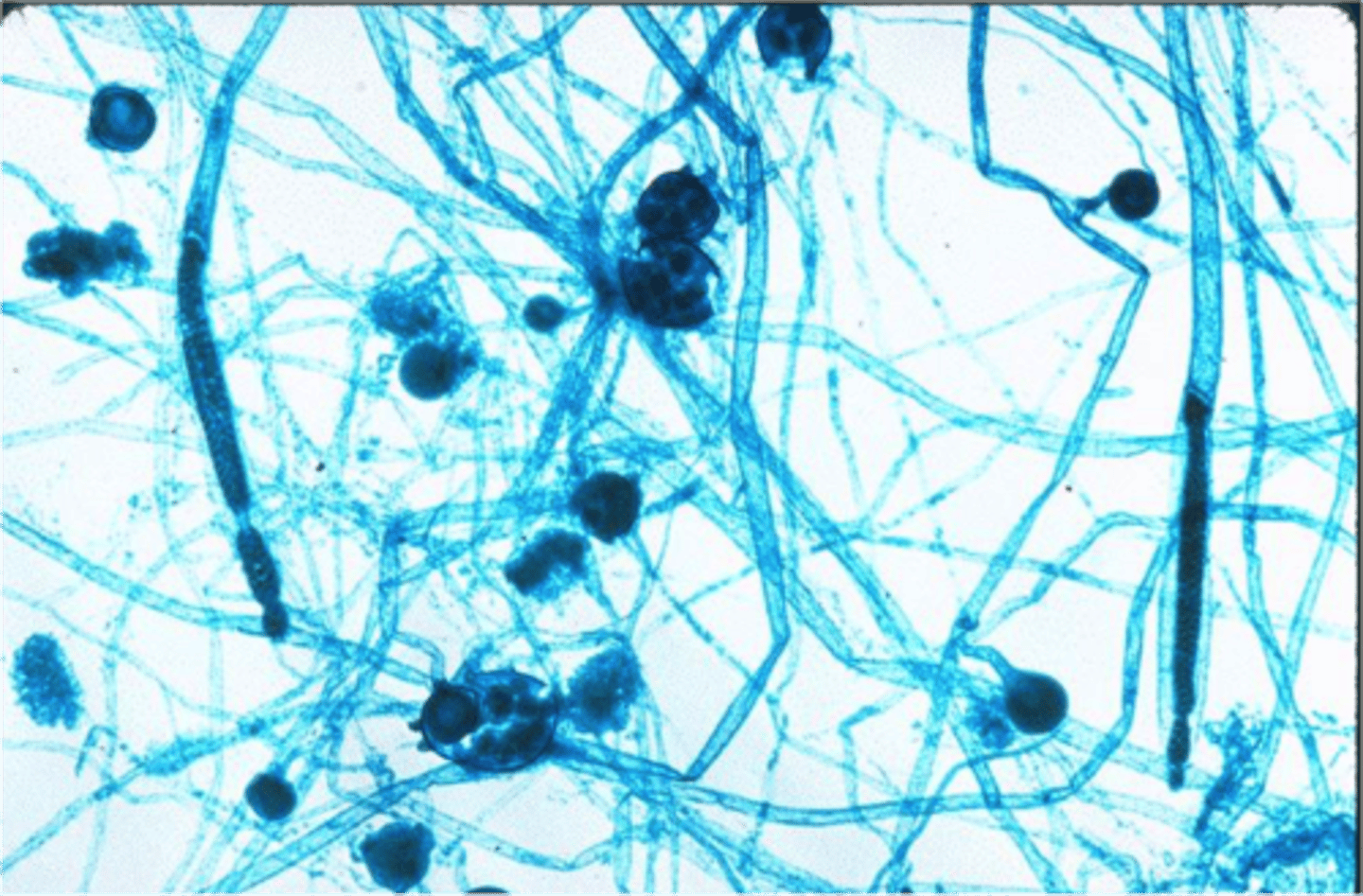
What is the function of hyphae?
secrete enzymes that digest surrounding substances
hyphae lack what structure?
septa
Why are Oomycota classified as coenocytic?
1. lack septa
2. contain many nuclei within a single cell
Cell walls within Oomycota are composed of what material?
cellulose