Cell Divison
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
Cell division
Cell division is the process where a cell divides into two or more daughter cells for growth, repair, or reproduction.
Binary fission (prokaryote)
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction where a single organism divides into two identical offspring. It’s common in prokaryotes like bacteria.
1- cell elongate and DNA is replicated
2- chromosomes segregate and cell wall starts to grow in the middle of the cell
3- Completation of the cell wall formation
4- Seperation of the two daughter cells.
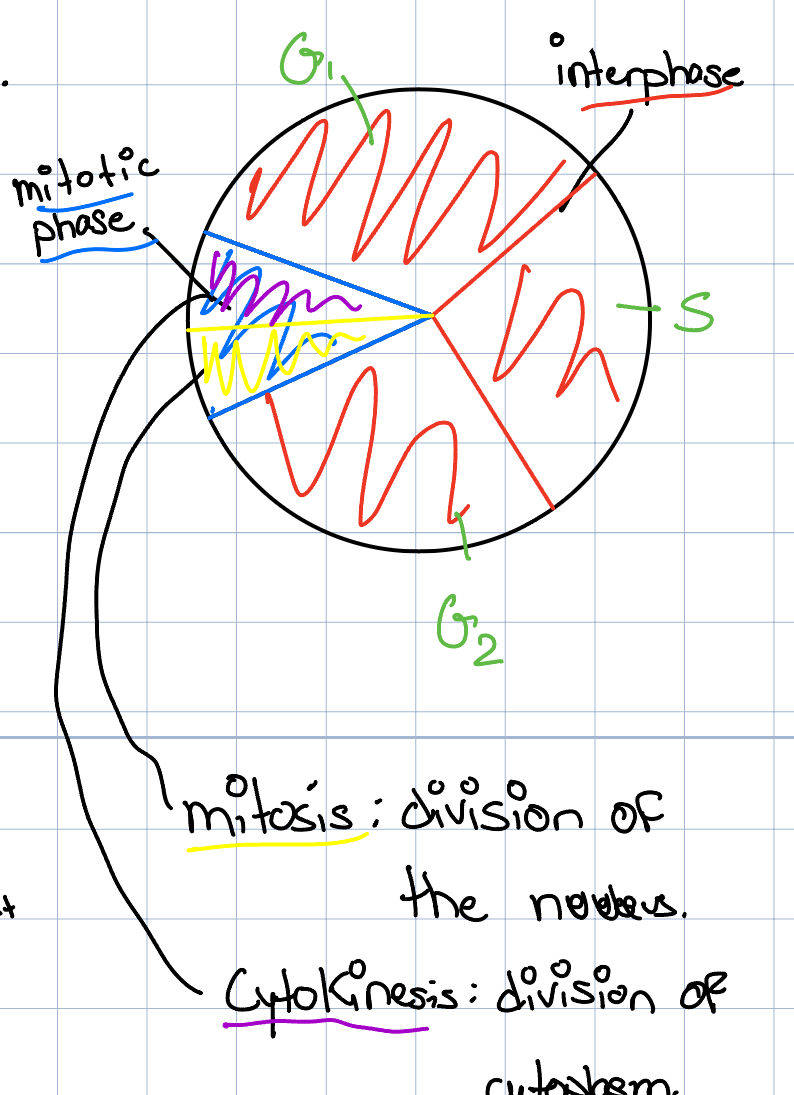
Cell cycle in Eukaryote
last around 20 hours
G0: don’t divide
G1: Productions of protein, production of organelles, increase of the cell size
S: Synthesis of DNA, replication of DNA content.
G2: production of proteins, preparaton for cell division
Mithosis: cell divison
Checkpoints
G1: restriction point, the cell commits to the cell division process
G2: ensure that all chrosomoes have been replicated
G3: ensure DNA integrity or cell size is appropriate.
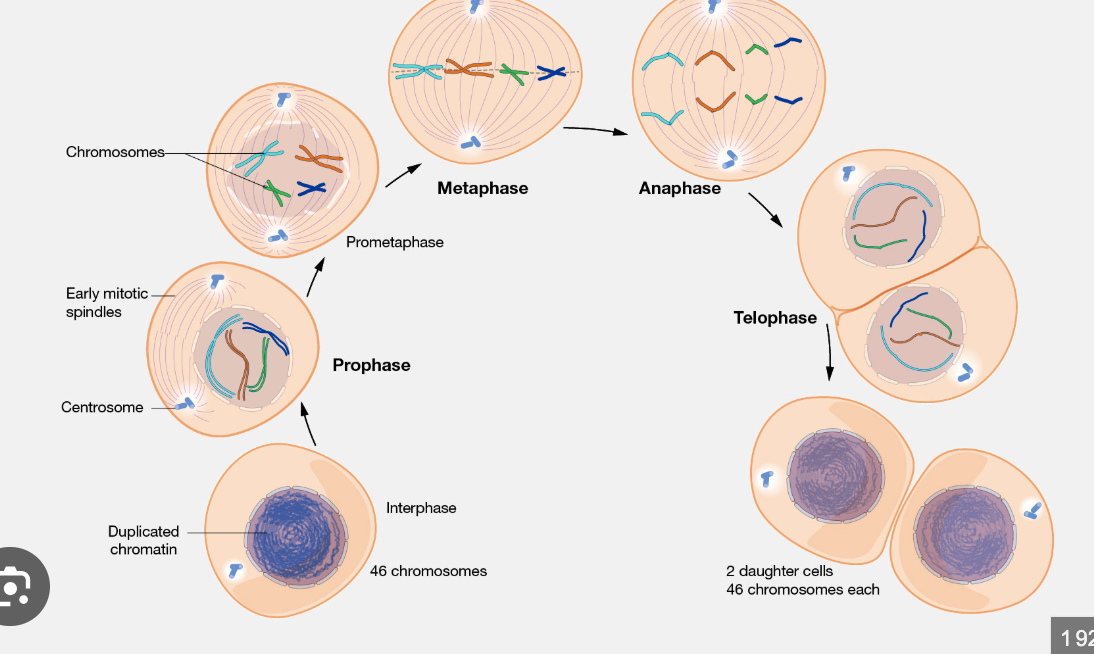
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells. It is used for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Prophase: Chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
Prometaphase: nuclear envelope breaks, spindle attaches to the chromosomes at the centromeres
Metaphase: Chromosomes line up at the cell’s center.
Anaphase: Chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell.
Telophase: New nuclear membranes form around the separated chromosomes.
Cytokinesis: The cell’s cytoplasm divides, creating two daughter cells.
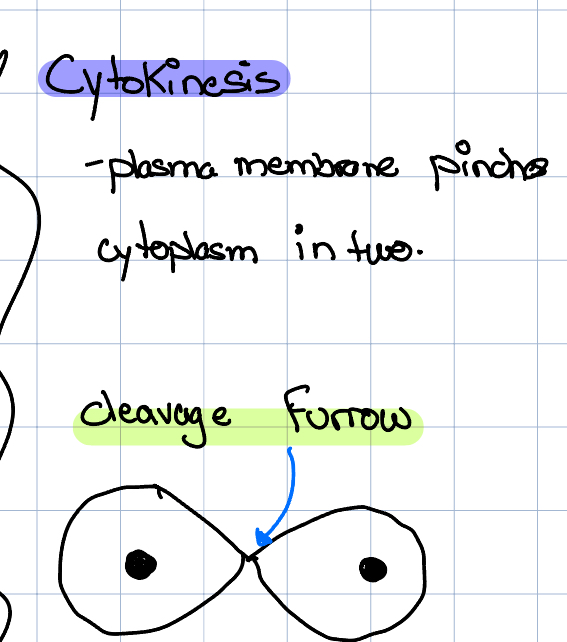
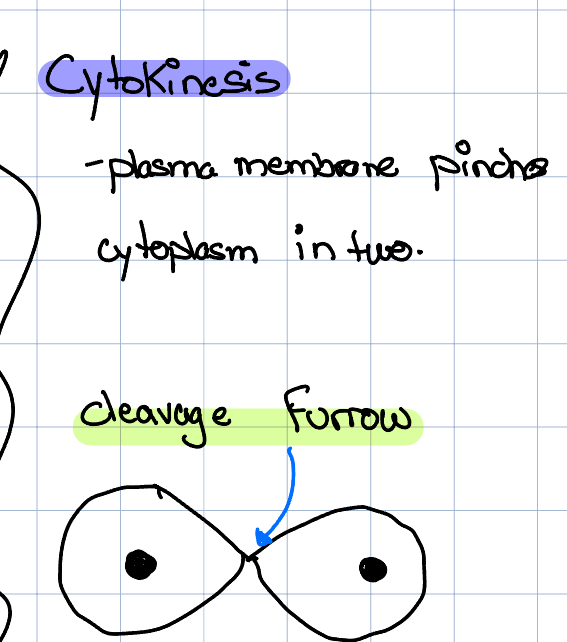
Cytokinesis
Plasma membrane pinches cytoplasm in 2
Difference between mistosis in animals and plants
Cytokinesis:
• Animals → Cleavage furrow
• Plants → Cell plate
Spindle Formation:
• Animals → Centrioles present
• Plants → No centrioles
Cell Shape:
• Animals → Rounds up
• Plants → Stays rigid
Location:
• Animals → Throughout body
• Plants → Meristems only