Human Body Systems: Urinary, Digestive, and Reproductive
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Urine flows
Kidney → Ureter → Urinary Bladder → Urethra
Cortical
mostly in cortex
Juxtamedullary
long loops for concentrating urine
Blood Flow
Renal artery → segmental → interlobar → arcuate → cortical radiate (interlobular) → afferent arteriole → glomerulus → efferent arteriole → peritubular capillaries/vasa recta → venules → renal vein
Filtration
(Glomerulus) - movements of plasma to nephron (no proteins)
Reabsorption
(PCT, loop, DCT) - return of useful solutes to blood
Secretion
(DCT, collecting duct) - active transport into tubule
Concentration
(Loop of Henle, CD) - water reabsorbed to concentrate urine
Urine pathway
Glomerulus → PCT → loop → DCT → collecting duct → papilla → minor calyx → major calyx → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder → urethra
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Normal ~125 mL/min
↑GFR
high pressure, possibly damage
↓GFR
poor perfusion/kidney failure
RAAS system
↓BP → Renin from JGA, Renin converts angiotensinogen → angiotensin I ACE converts → angiotensin II → vasoconstriction + aldosterone
Aldosterone
↑Na⁺ and H₂O reabsorption
ADH
(posterior pituitary): water retention
ANP
blocks aldosterone/ADH
High Glucose
Diabetes
High Protein
Kidney damage
High Leukocytes
Infection
High Blood
Trauma, kidney stones
High/Low pH
Diet, infection
High Specific Gravity
Dehydration
Dark color
Dehydration, blood, diet
Alimentary canal
mouth → anus
Accessory
salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder
Pathway of Food
Mouth → Pharynx → Esophagus → Stomach → Small Intestine → Large Intestine → Rectum → Anus
Carbs
(Amylase) - Simple sugars
Protein
(Pepsin, Trypsin) - Amino acids
Lipids
(Lipase + Bile) - Fatty acids/glycerol
Nucleic acids
(Nucleases) - Nucleotides
Bile
(liver/gallbladder): emulsifies fat
Gastrin
stimulates acid production
Bicarbonate
neutralizes acid (pancreas)
Stratified Squamous
Oral cavity, esophagus, anus (Protection)
Simple Columnar
Stomach to rectum (Absorption/secretion)
Goblet cells
Mucus
Chief cells
Pepsinogen
Parietal cells
HCI + intrinsic factor
G cells
Gastrin
Acinar cells
Pancreatic enzymes
Gametogenesis
Formation of gametes (egg/sperm)
Spermatogenesis
Sperm production in testes
Oogenesis
Egg formation in ovaries
Gametes
Haploid sex cells (n = 23)
Diploid/Haploid
2n = 46 / n = 23
Sperm Pathway
Testes → Epididymis → Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra (prostatic → membranous → penile)
Egg Pathway
Ovary → Fimbriae → Fallopian tube (infundibulum → ampulla → isthmus) → Uterus
FSH
Stimulates gamete production
LH
Triggers ovulation & testosterone
Estrogen
Growth of endometrium
Progesterone
Maintains endometrium
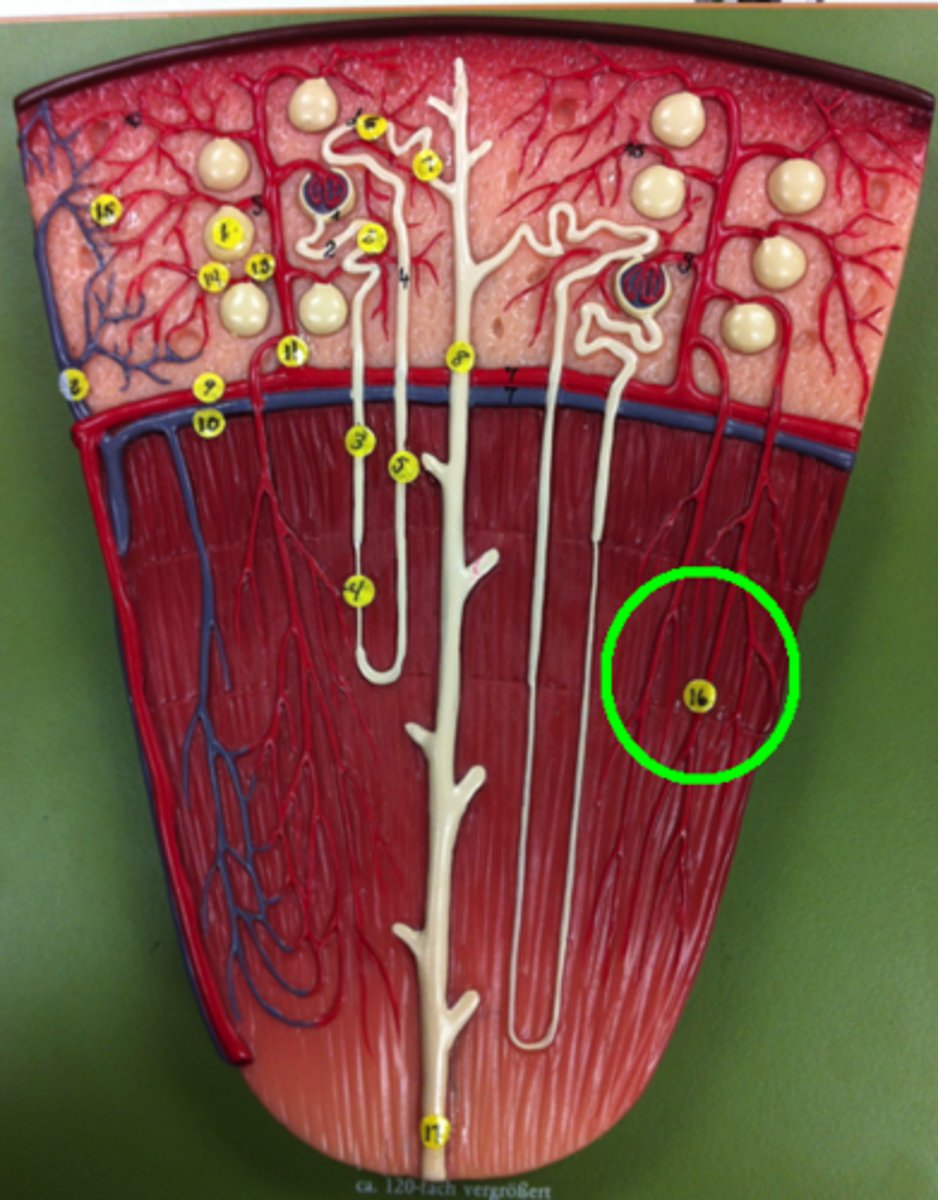
renal capsule
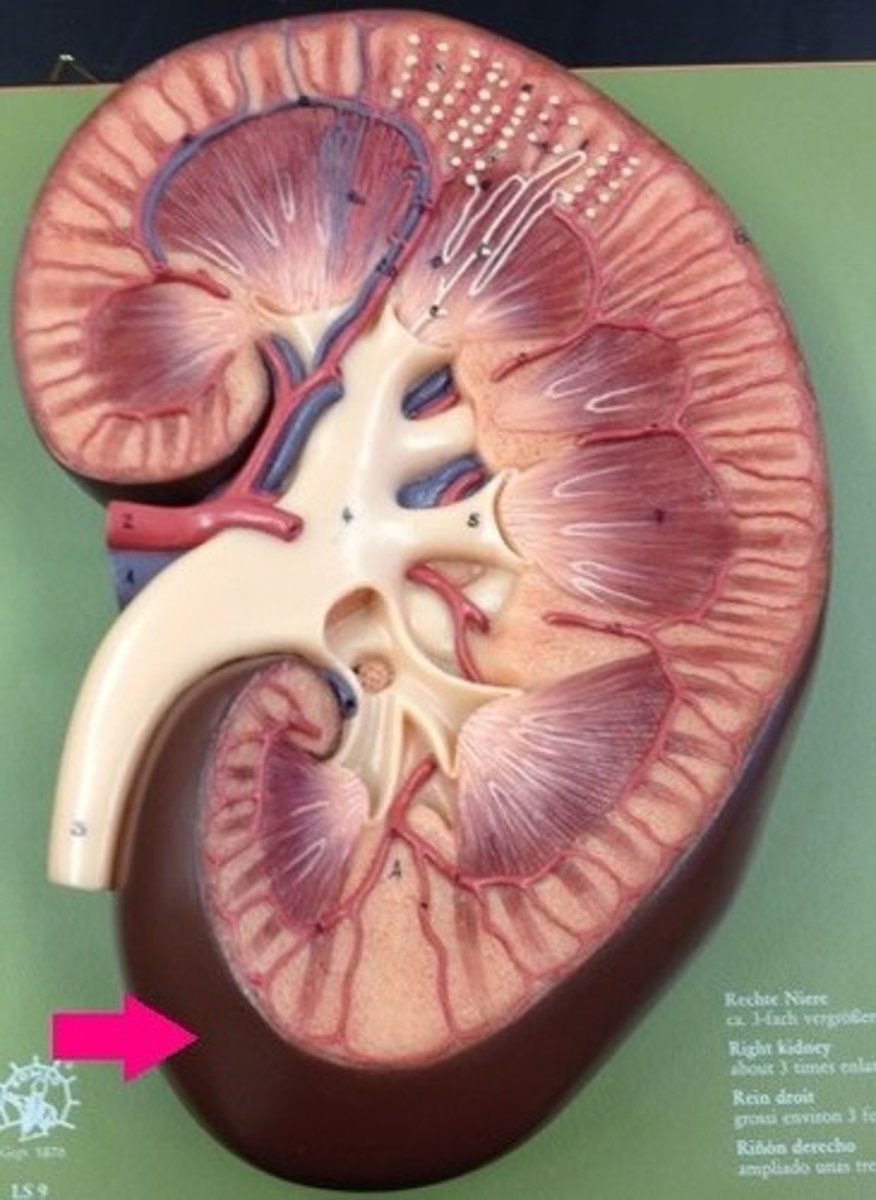
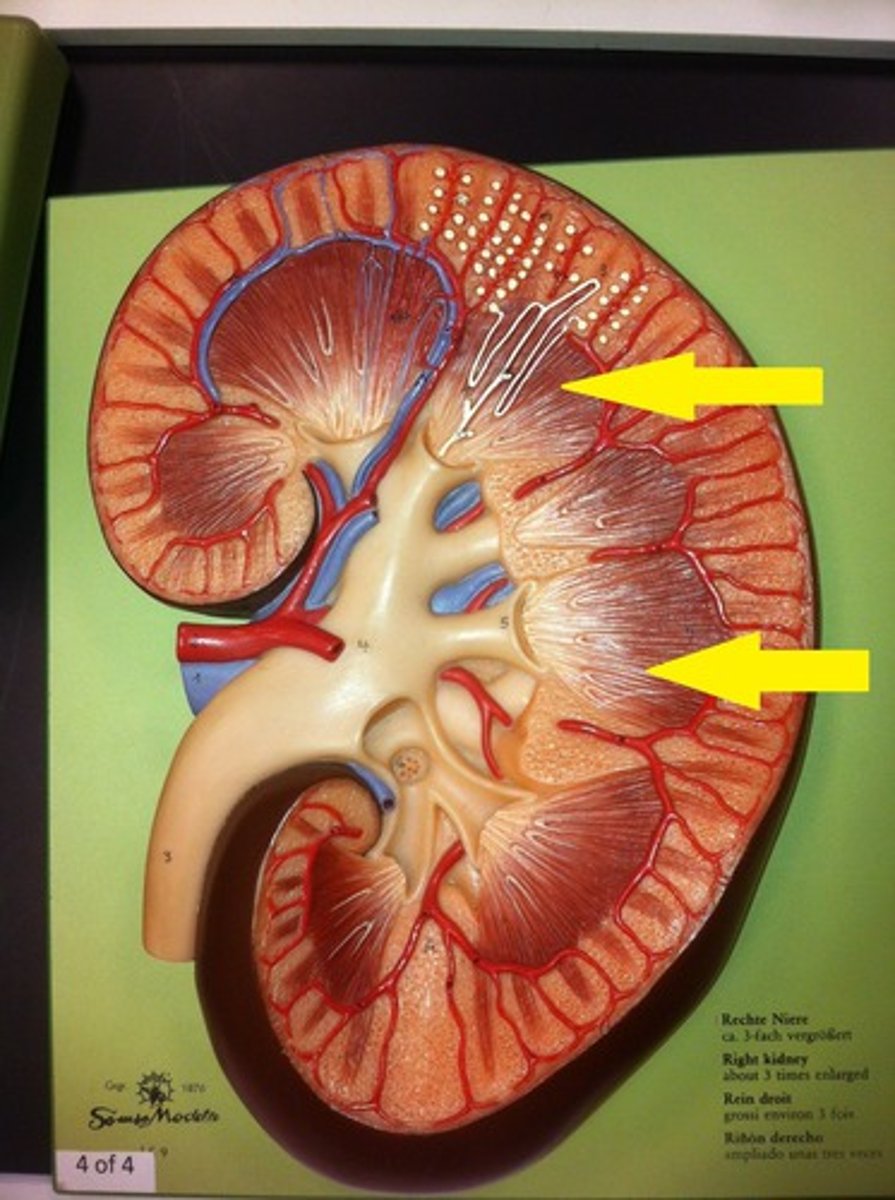
renal cortex
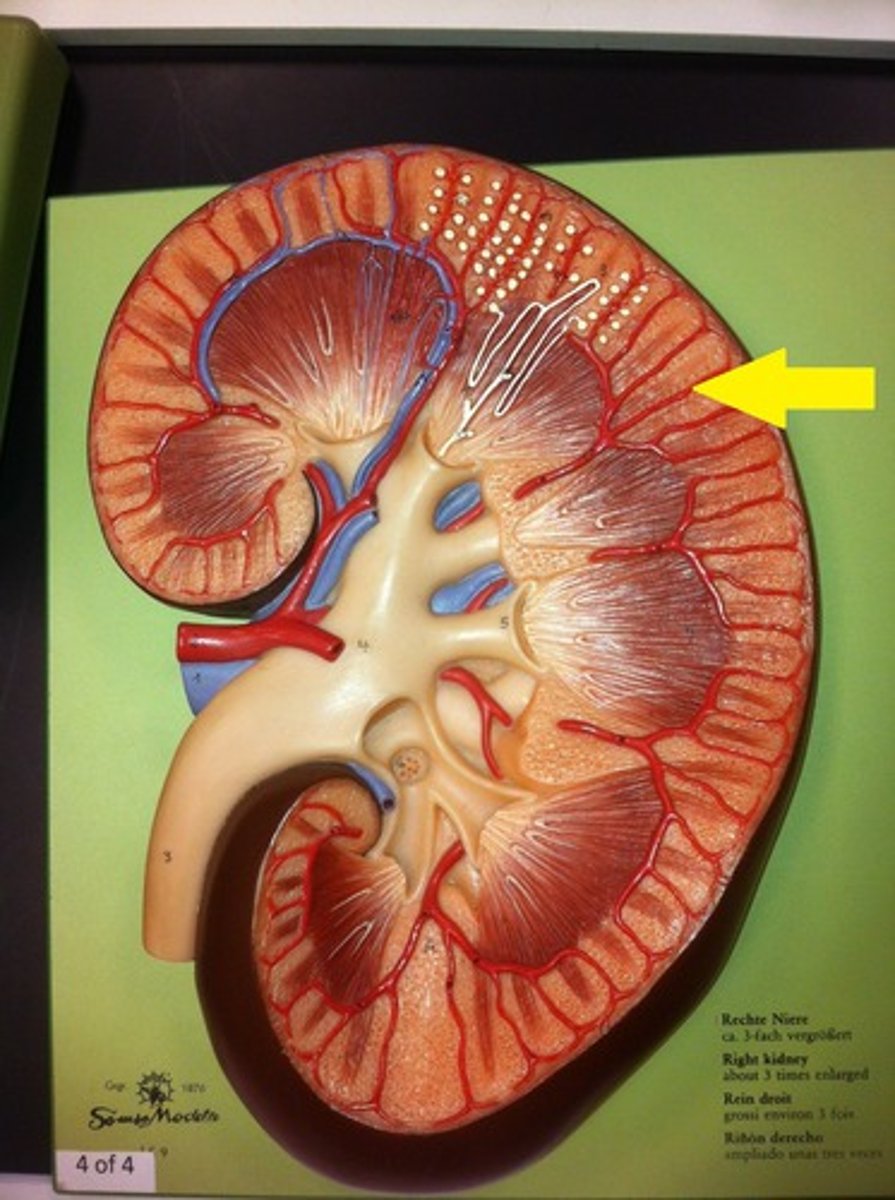
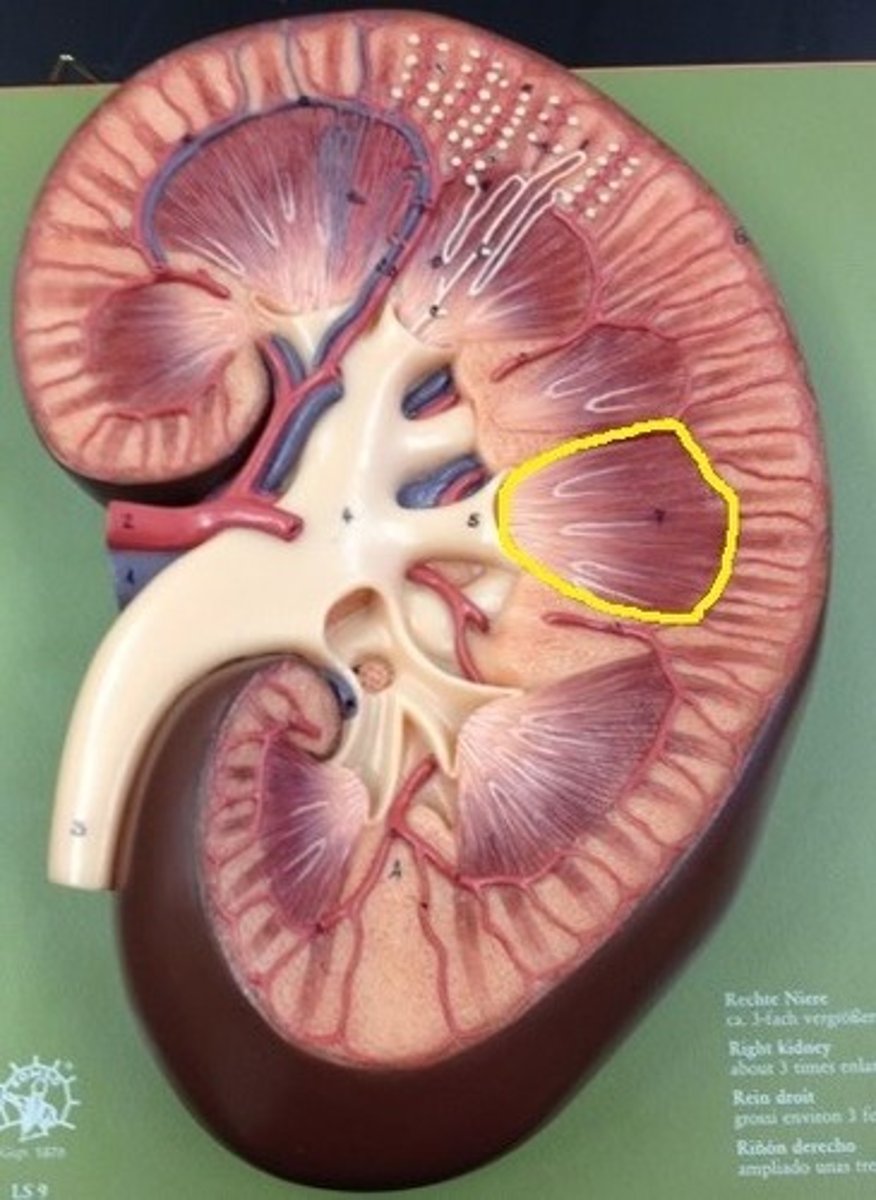
renal pyramids
renal medulla
minor calyx
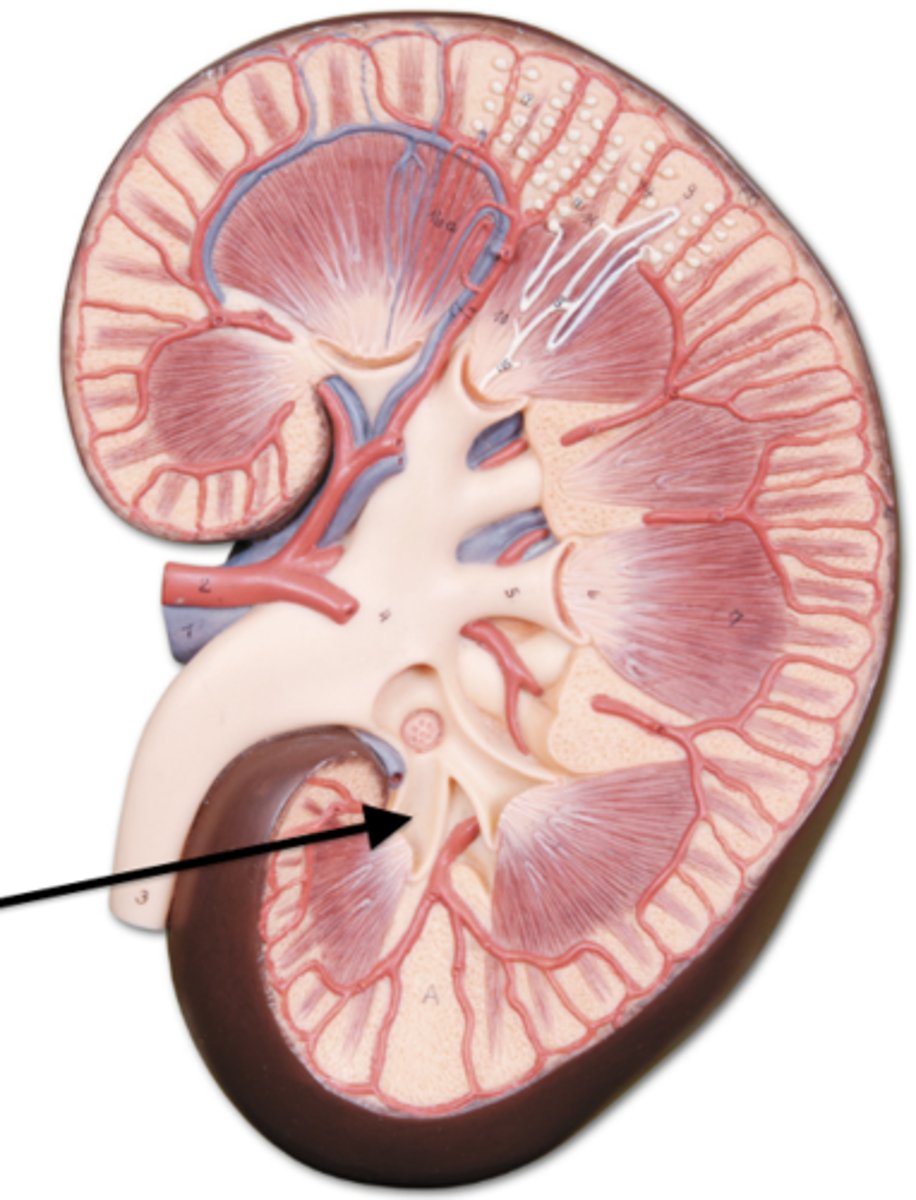
major calyx
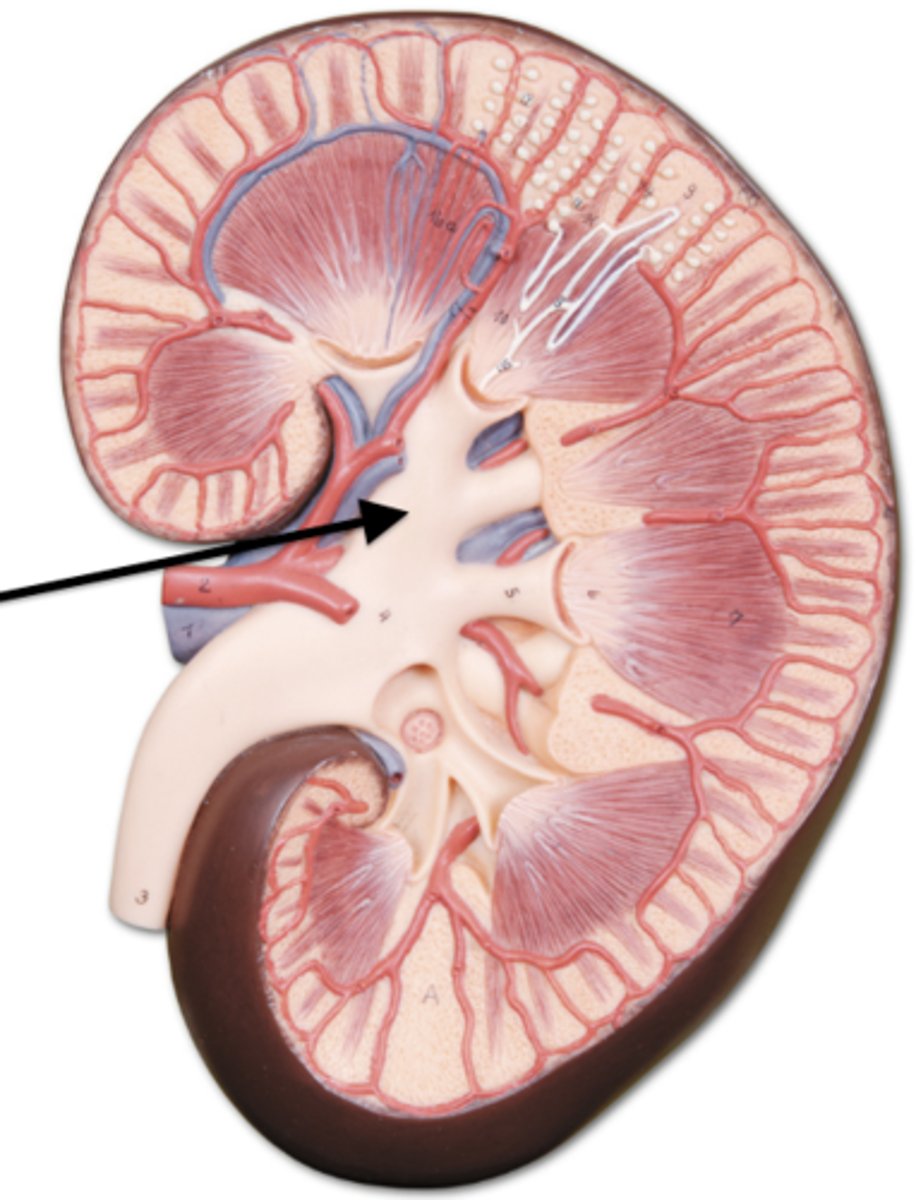
renal pelvis
glomerulus
blood enters afferent and leaves efferent
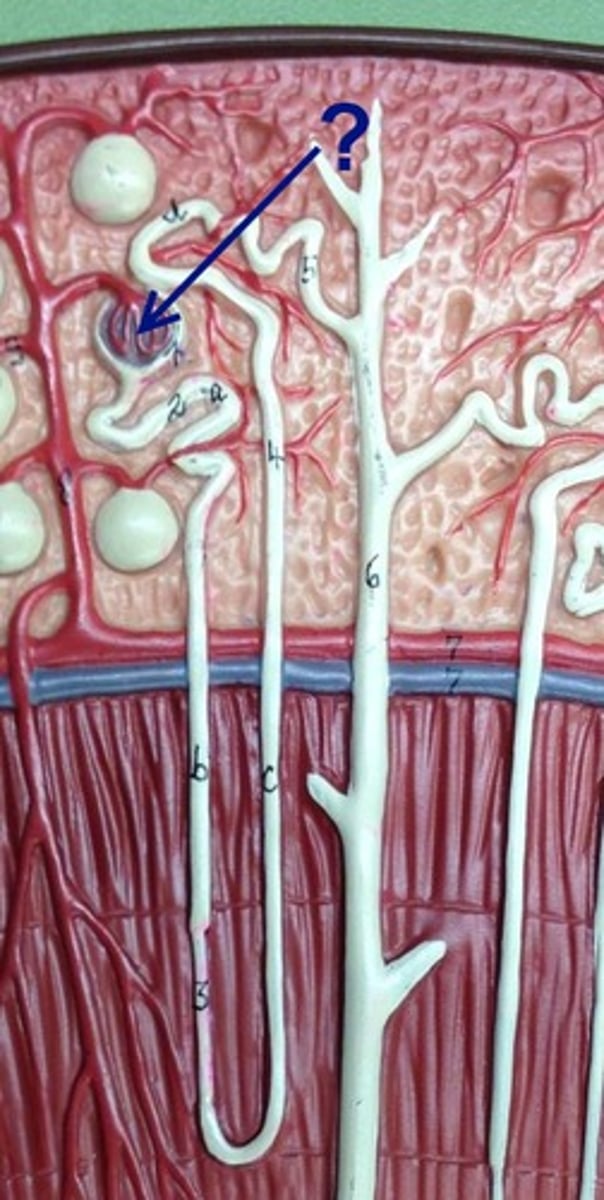
Bowman's capsule
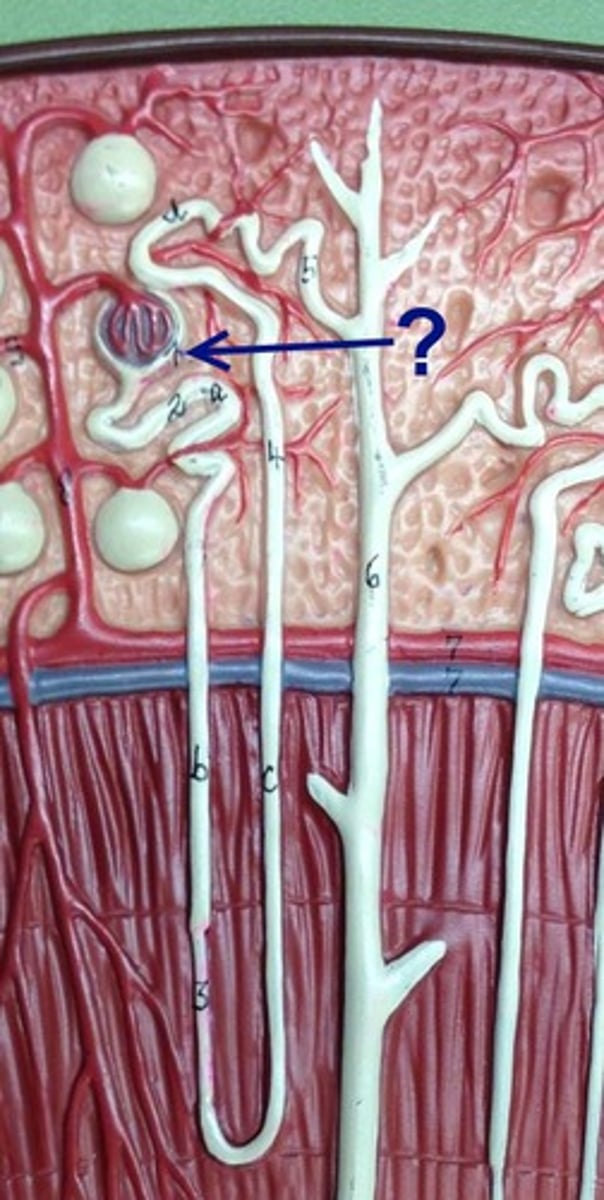
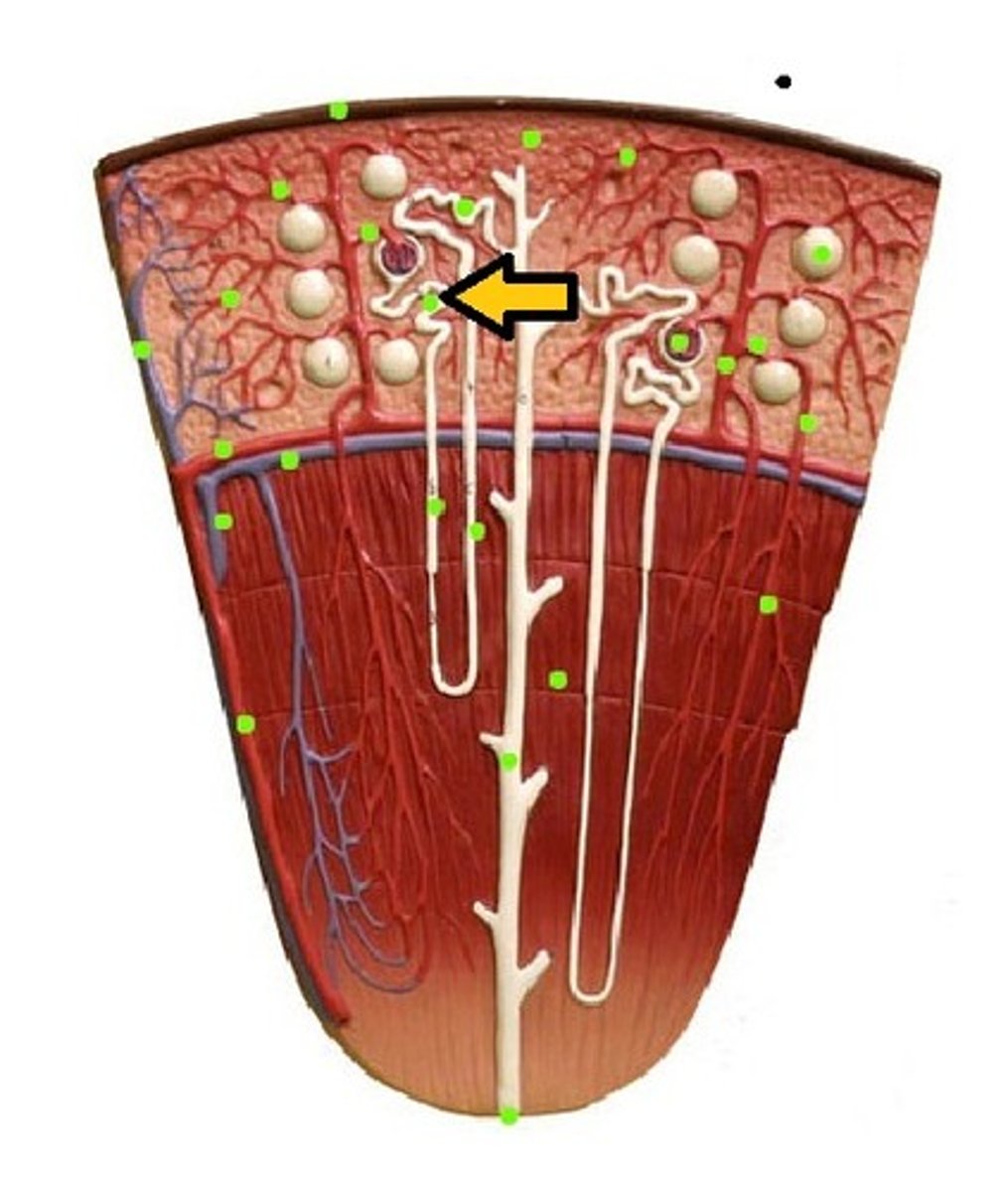
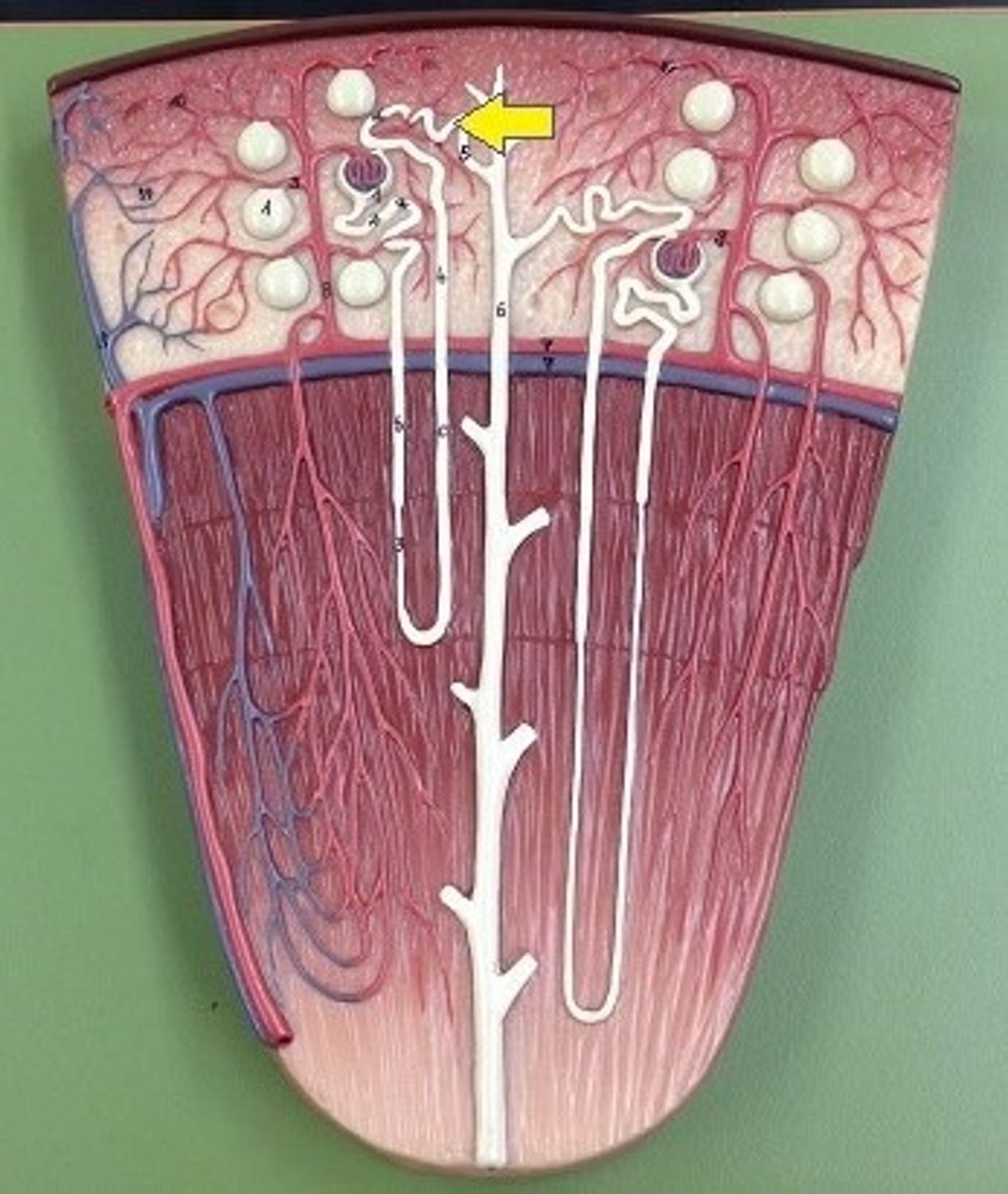
proximal convuluted tubule (PCT)
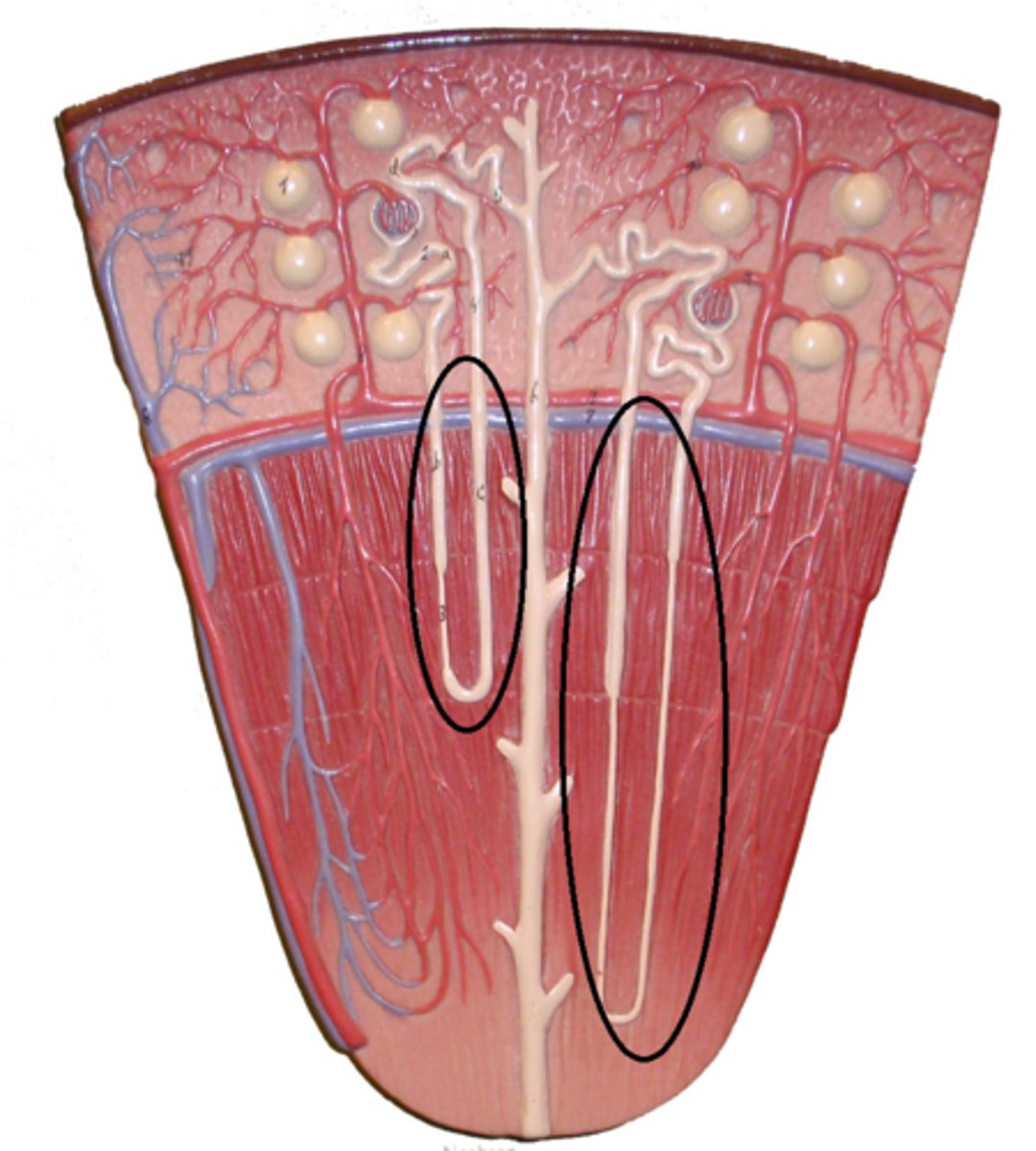
Loop of Henle (nephron loop)
distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
collecting duct
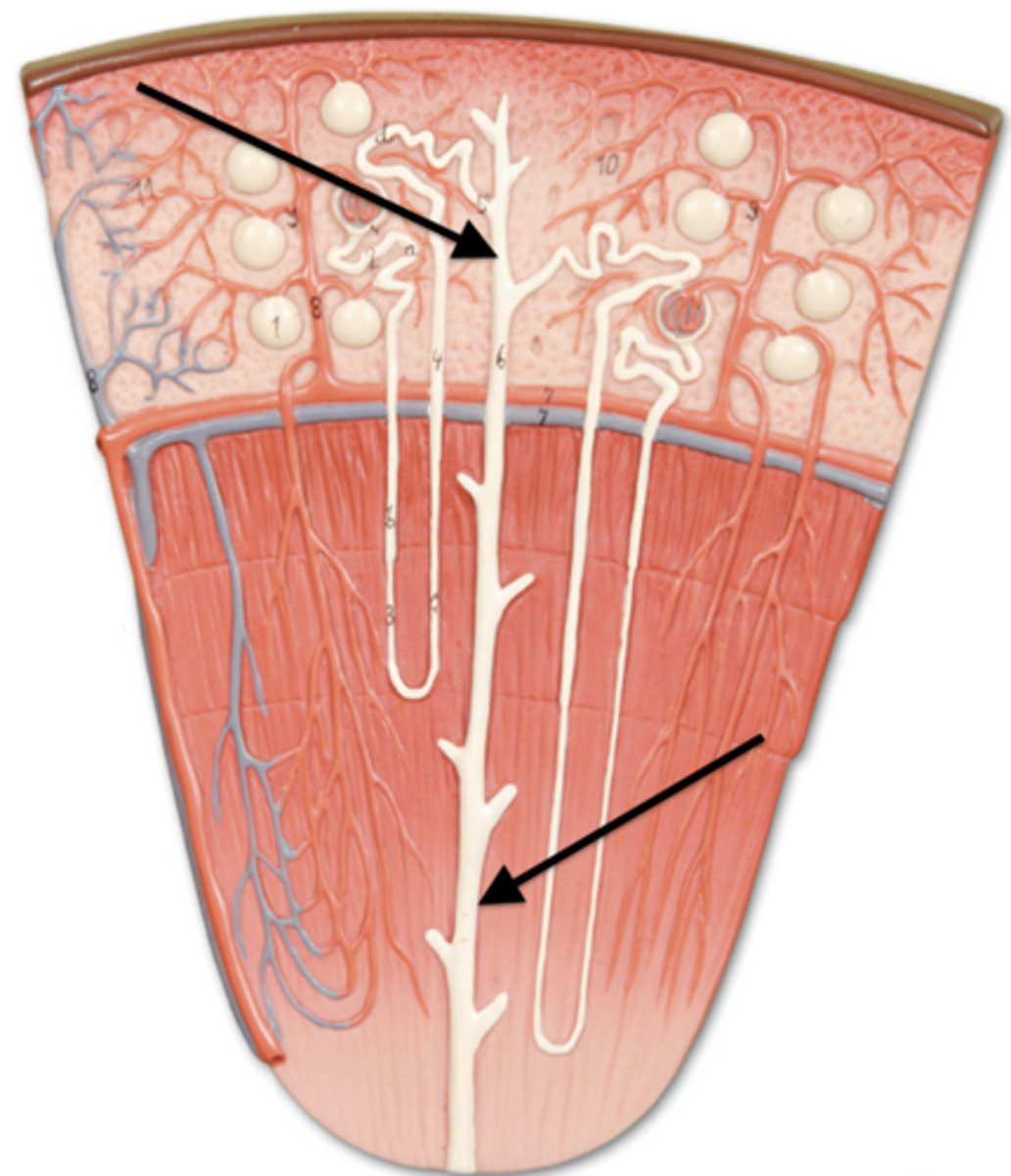
afferent arteriole
enters
efferent arteriole
leaves
peritubular capillaries
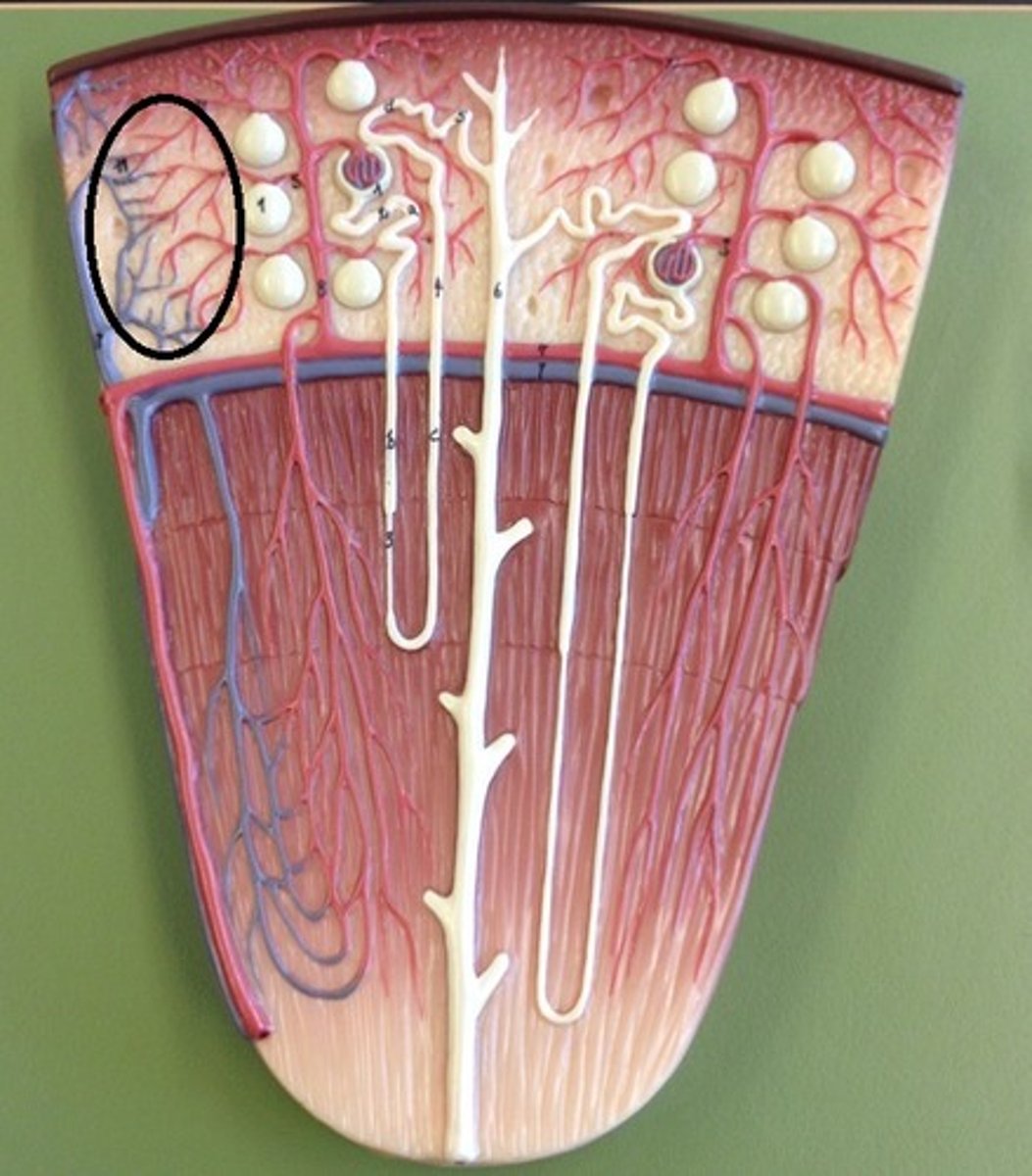
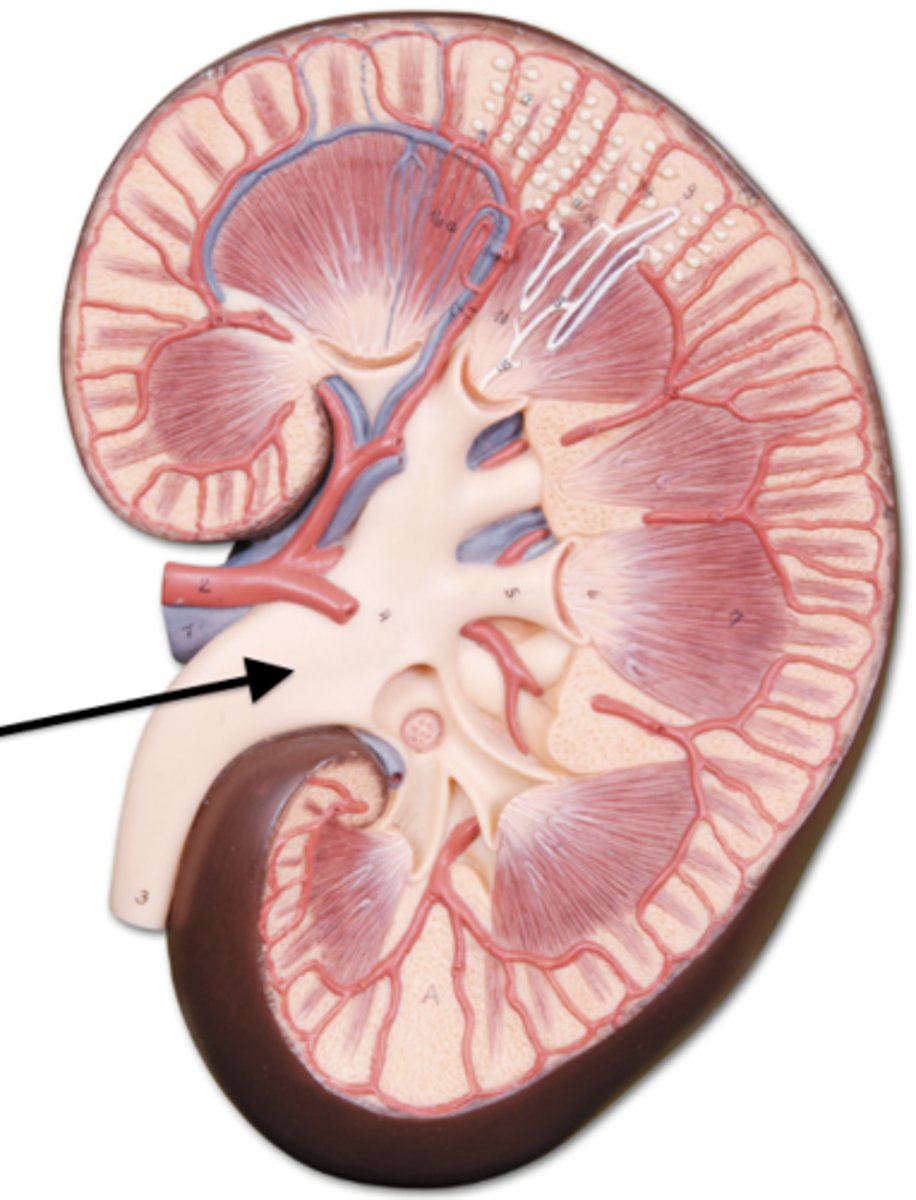
renal hilum
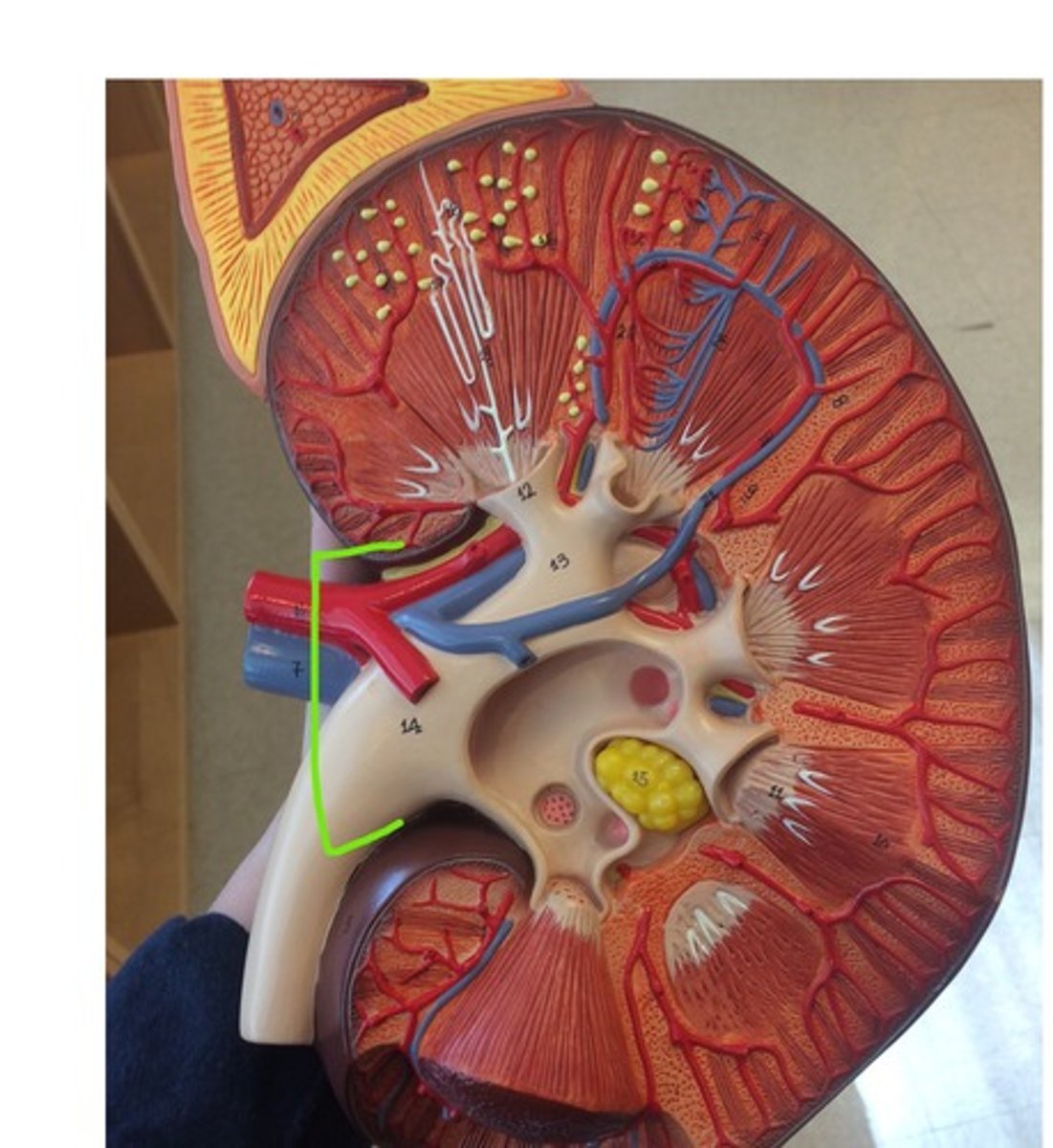
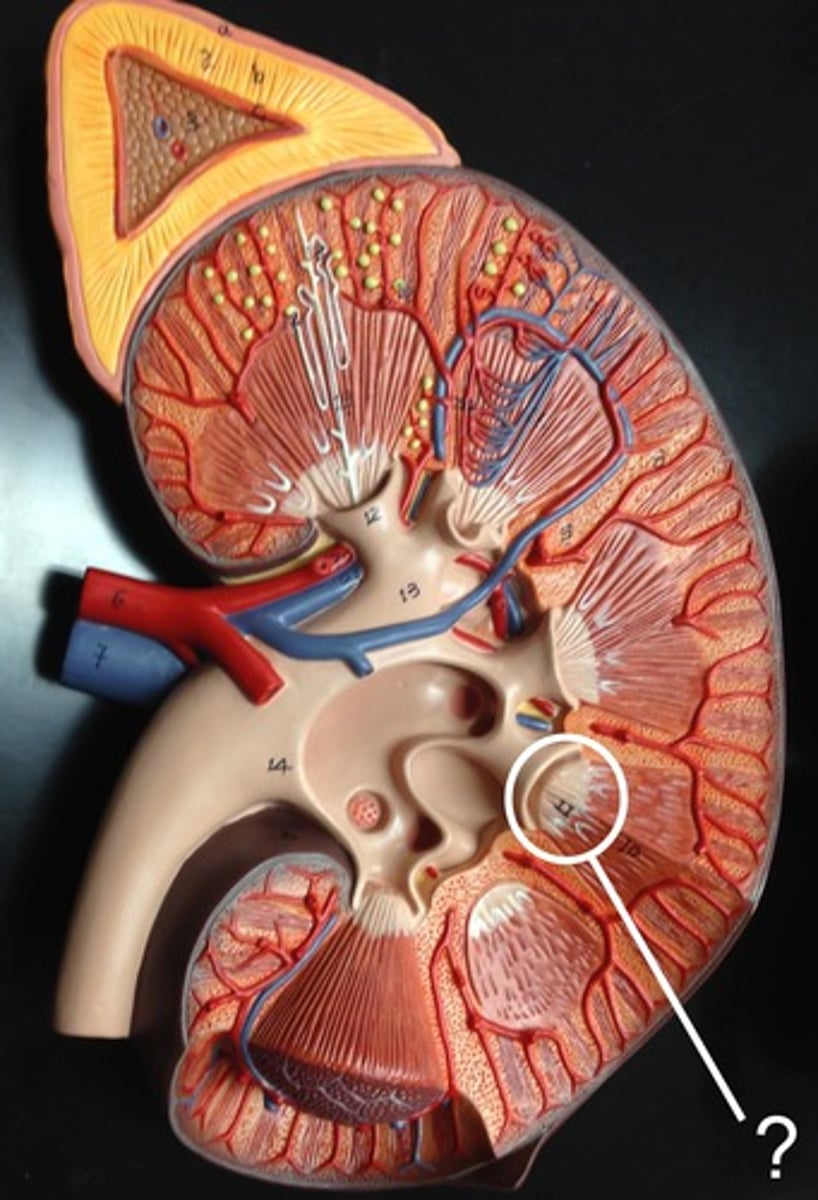
renal papilla
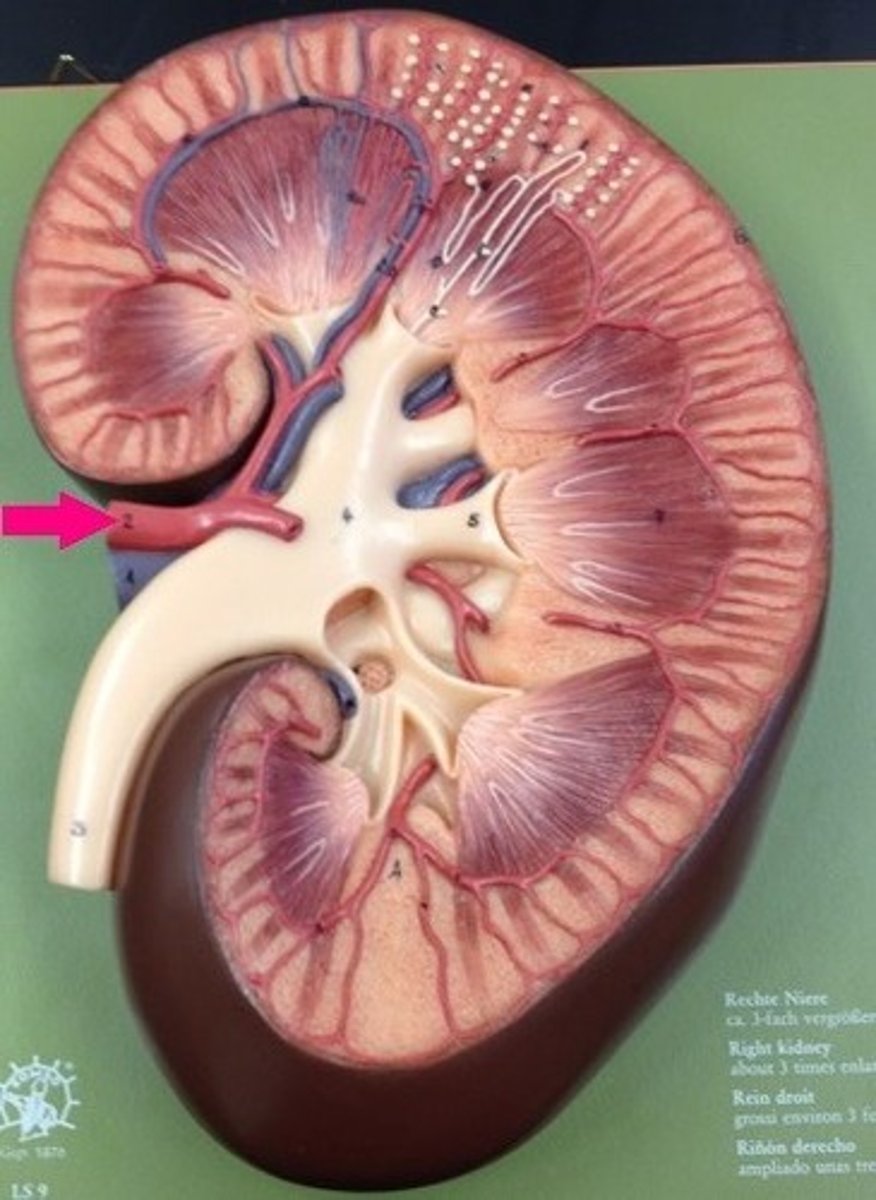
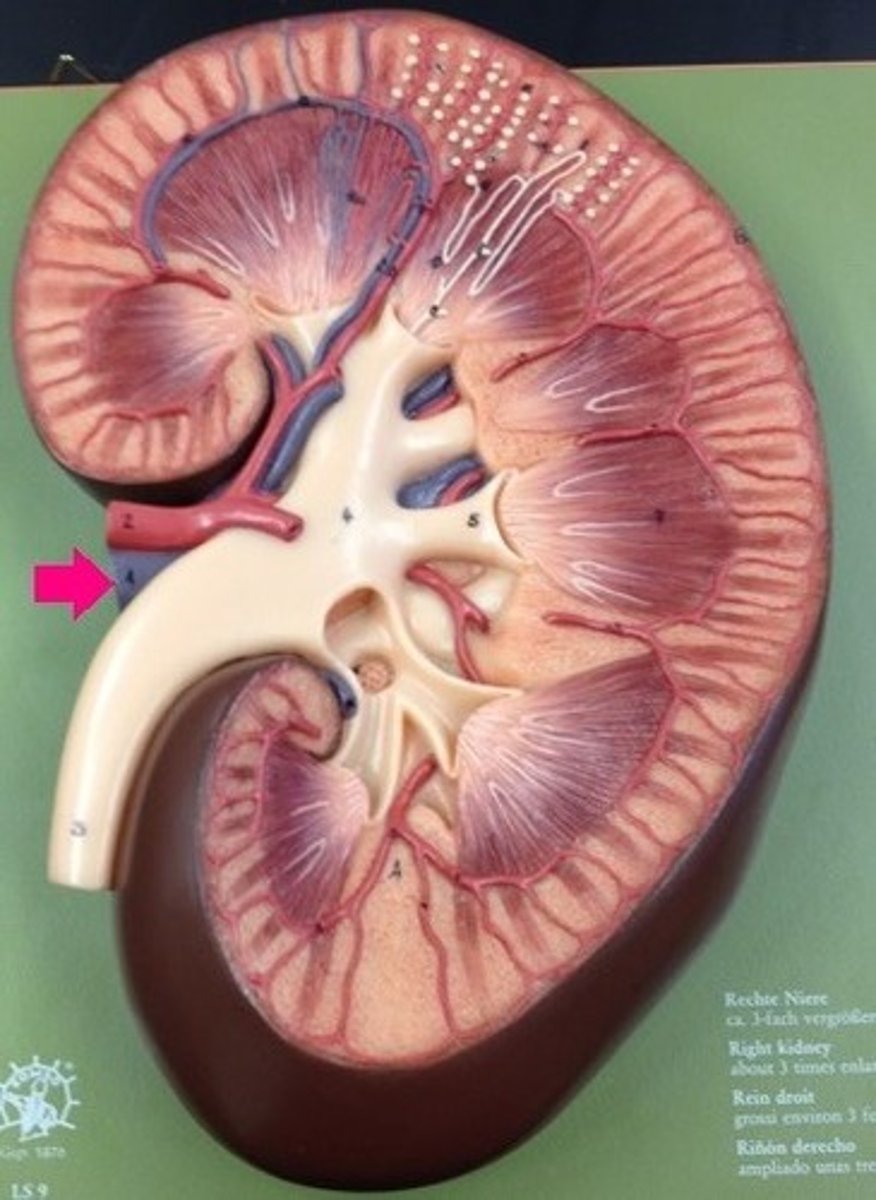
renal artery
renal vein
vasa recta
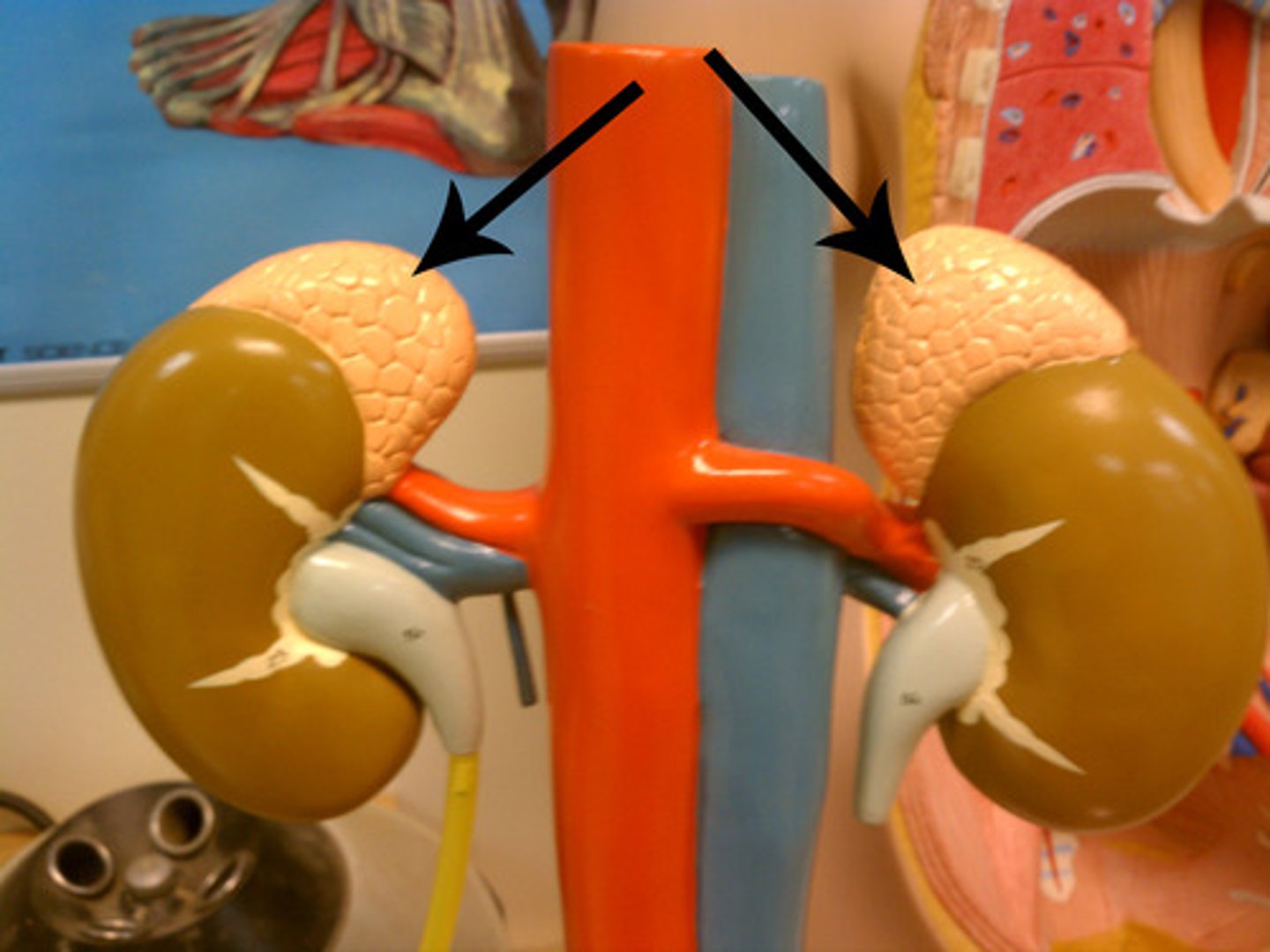
adrenal gland
kidneys (cat)
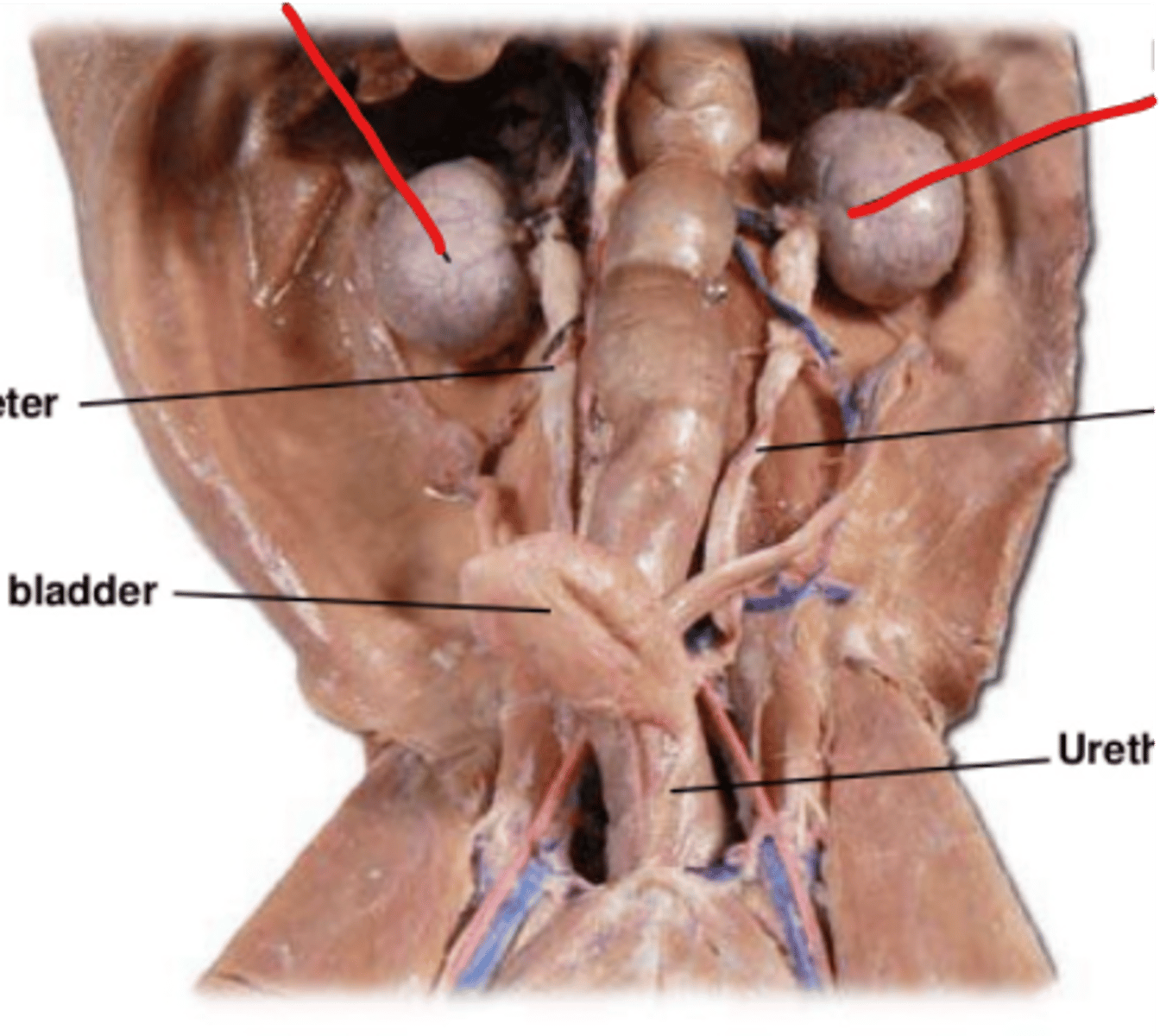
ureters (cat)
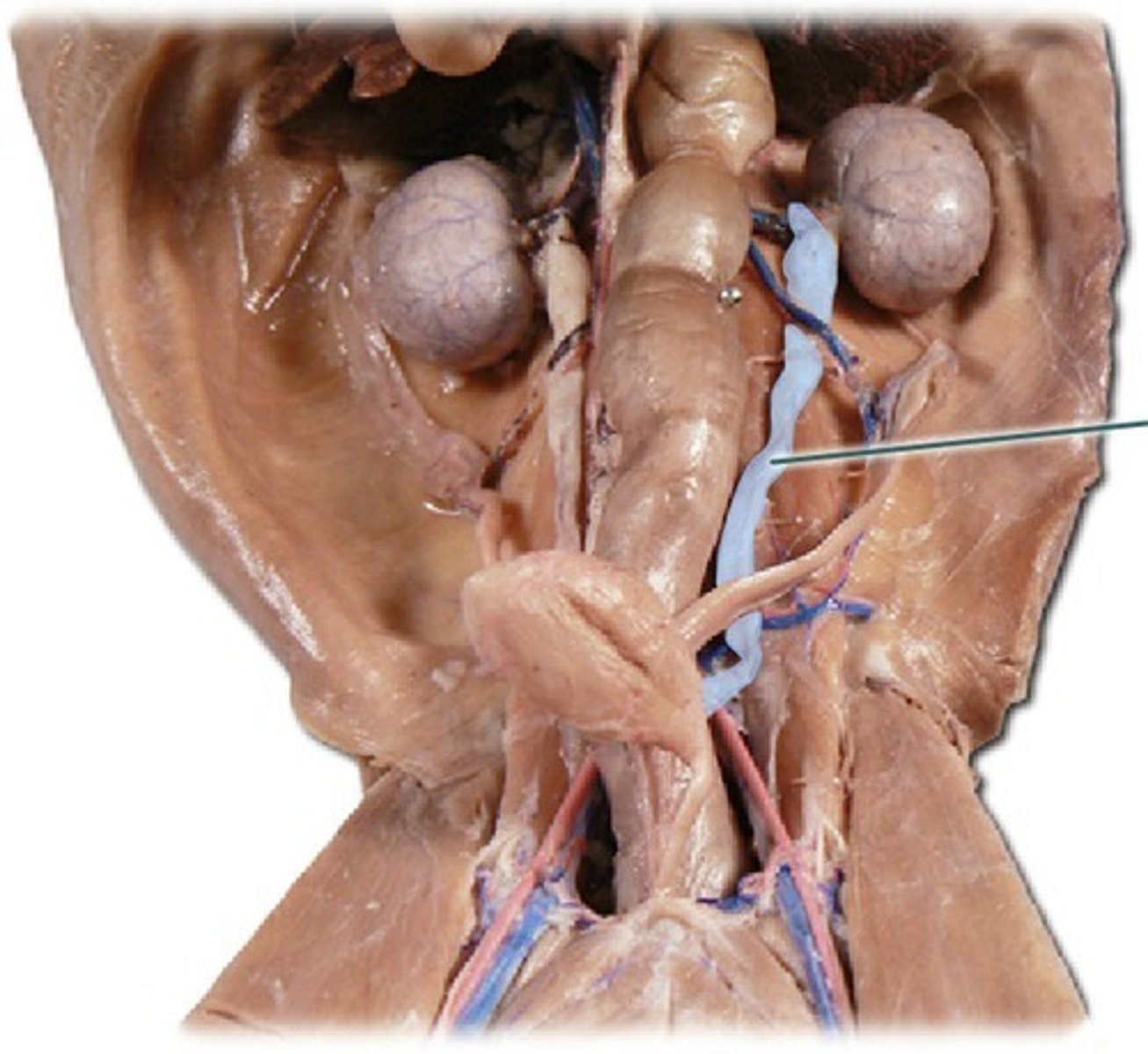
bladder (cat)
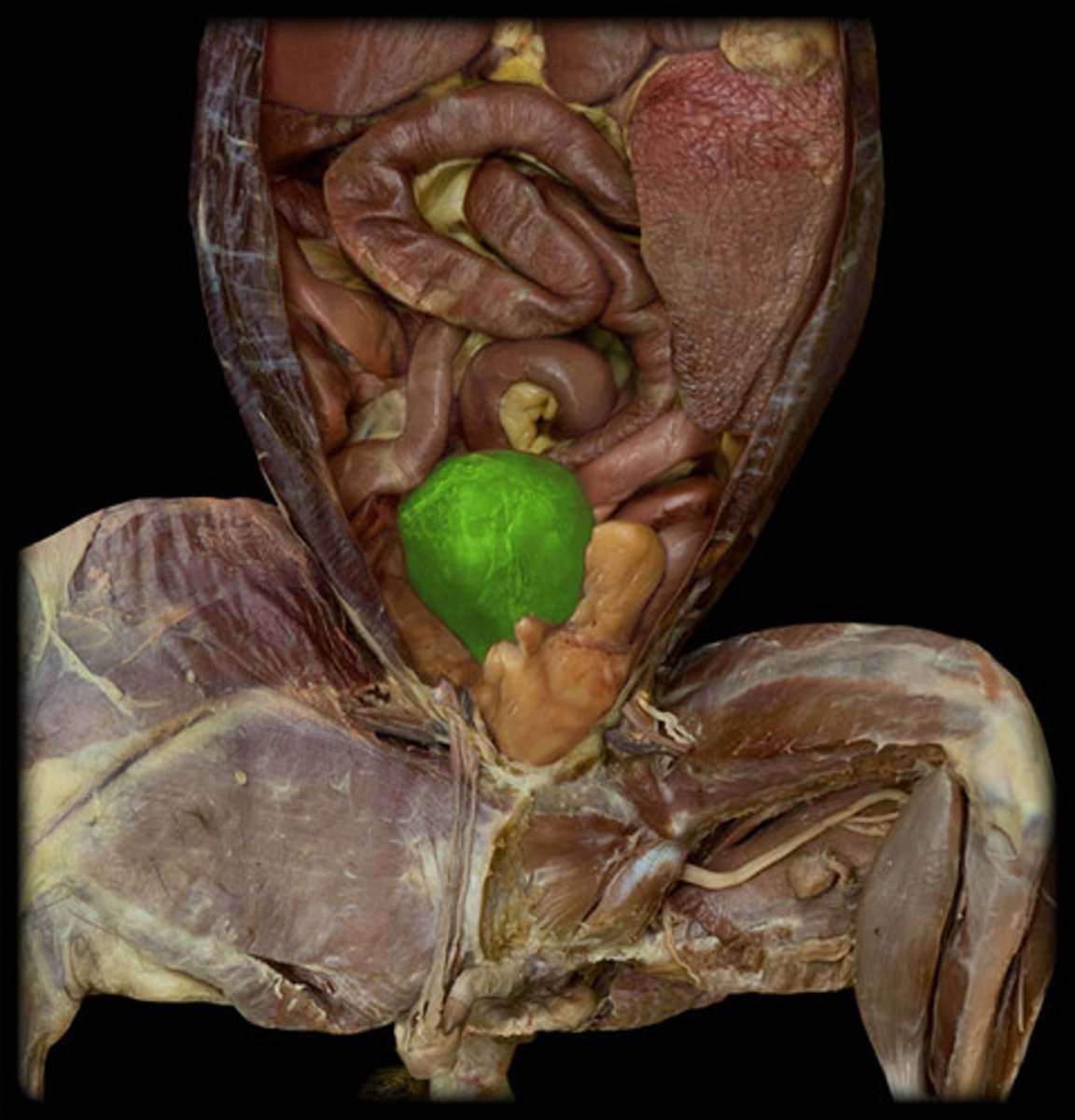
Urethra (cat)
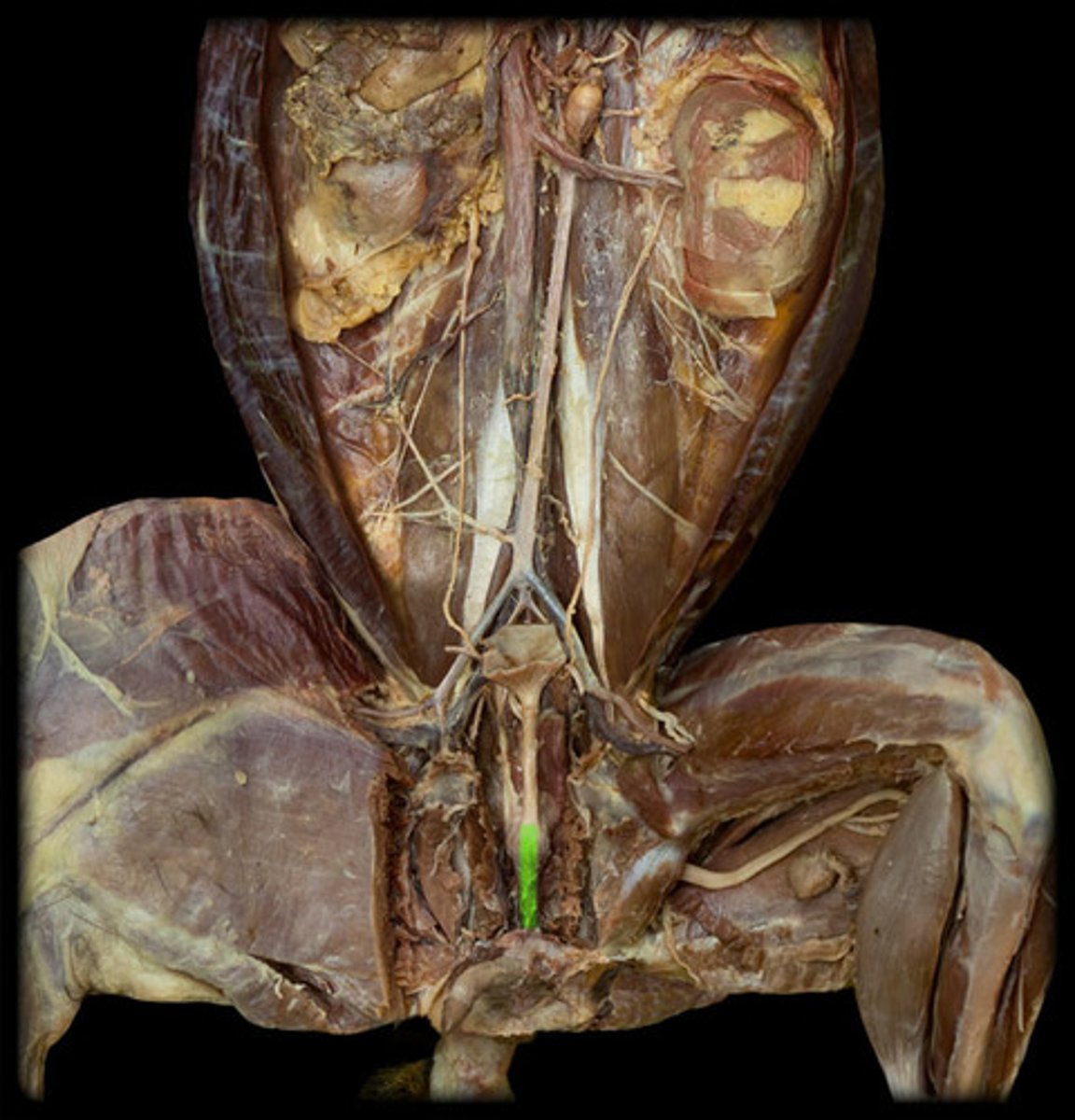
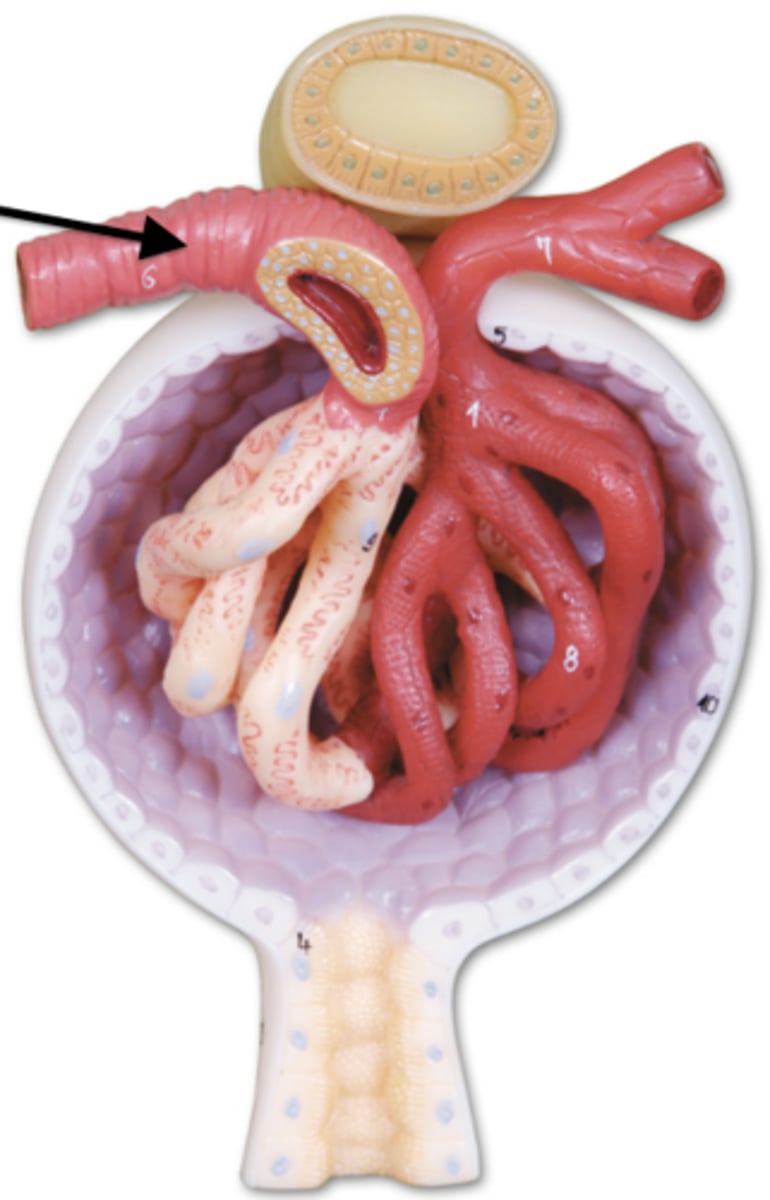
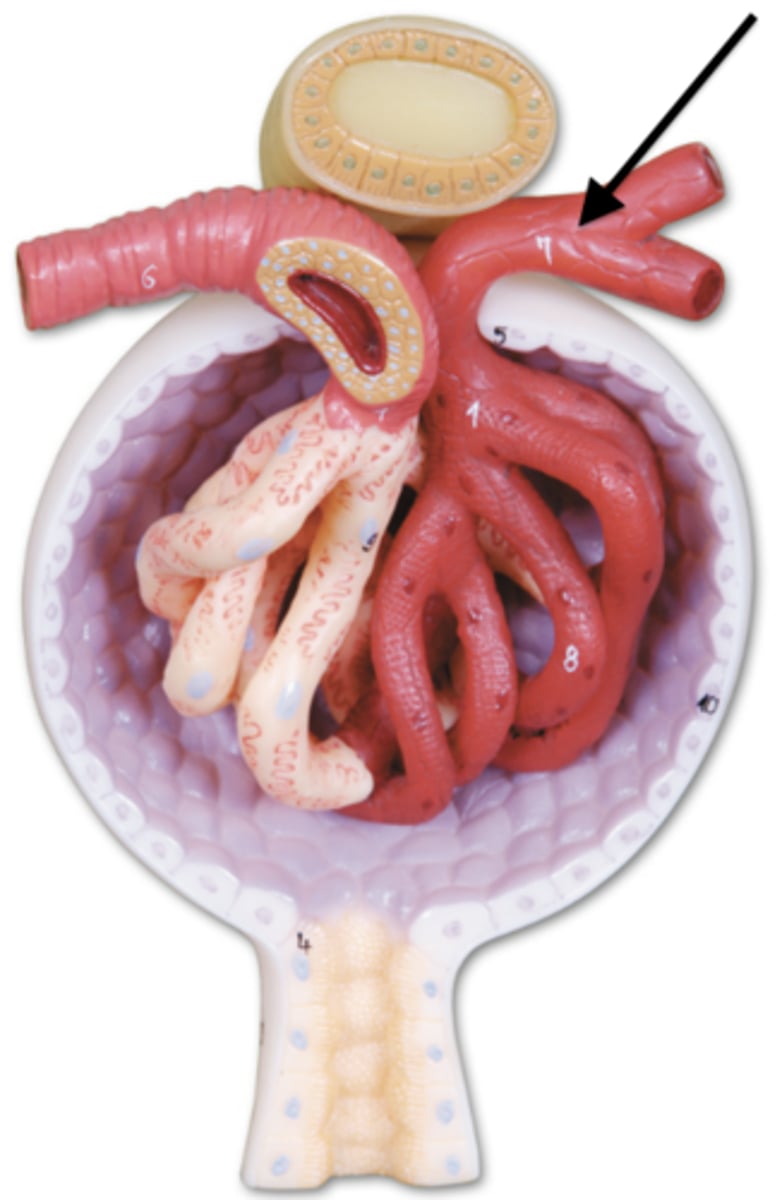
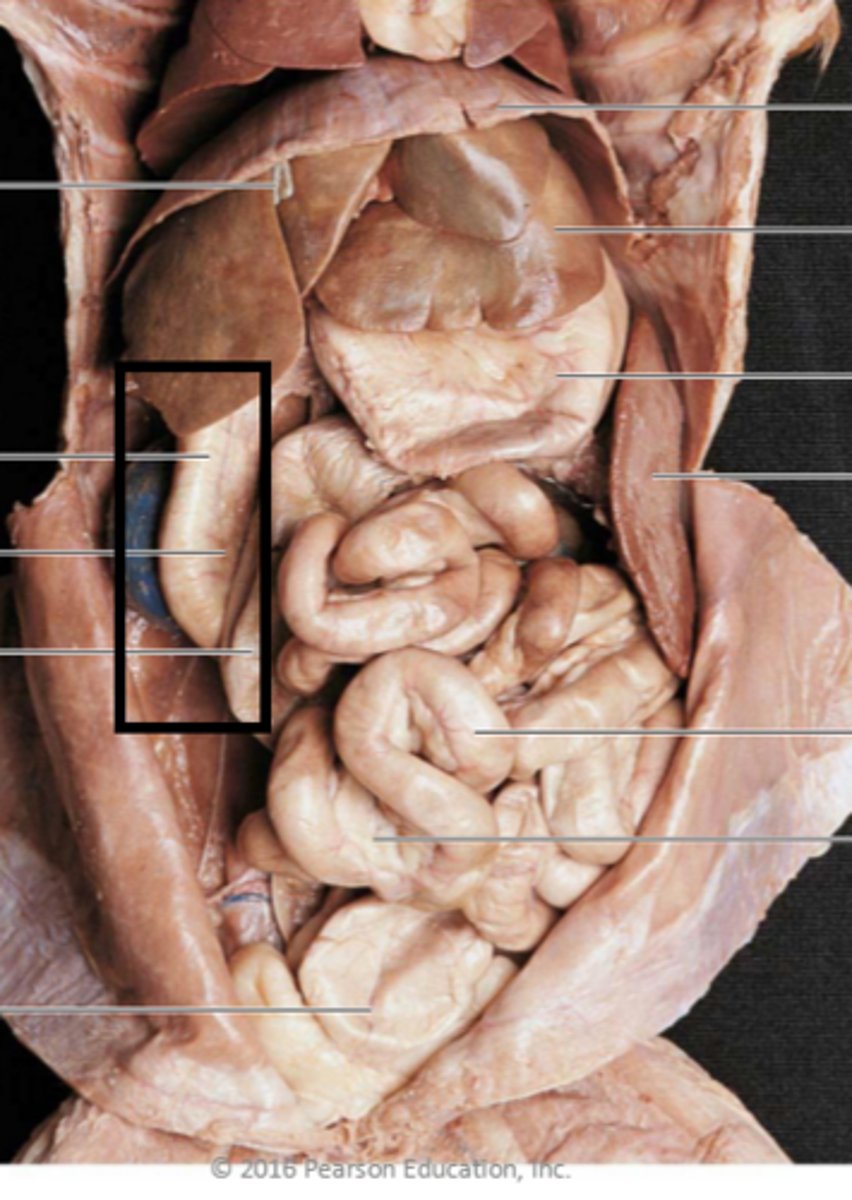
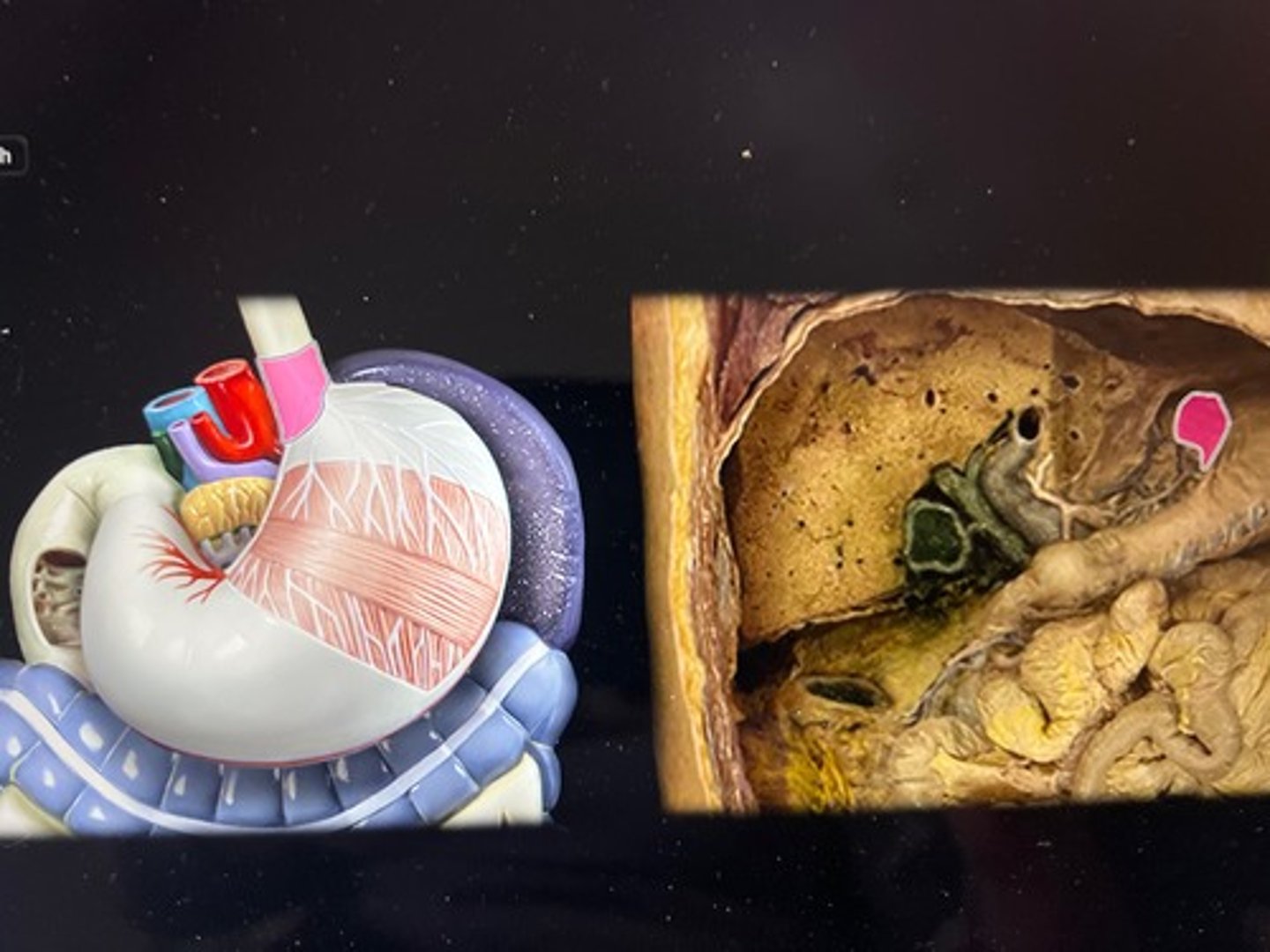
esophagus (cat)
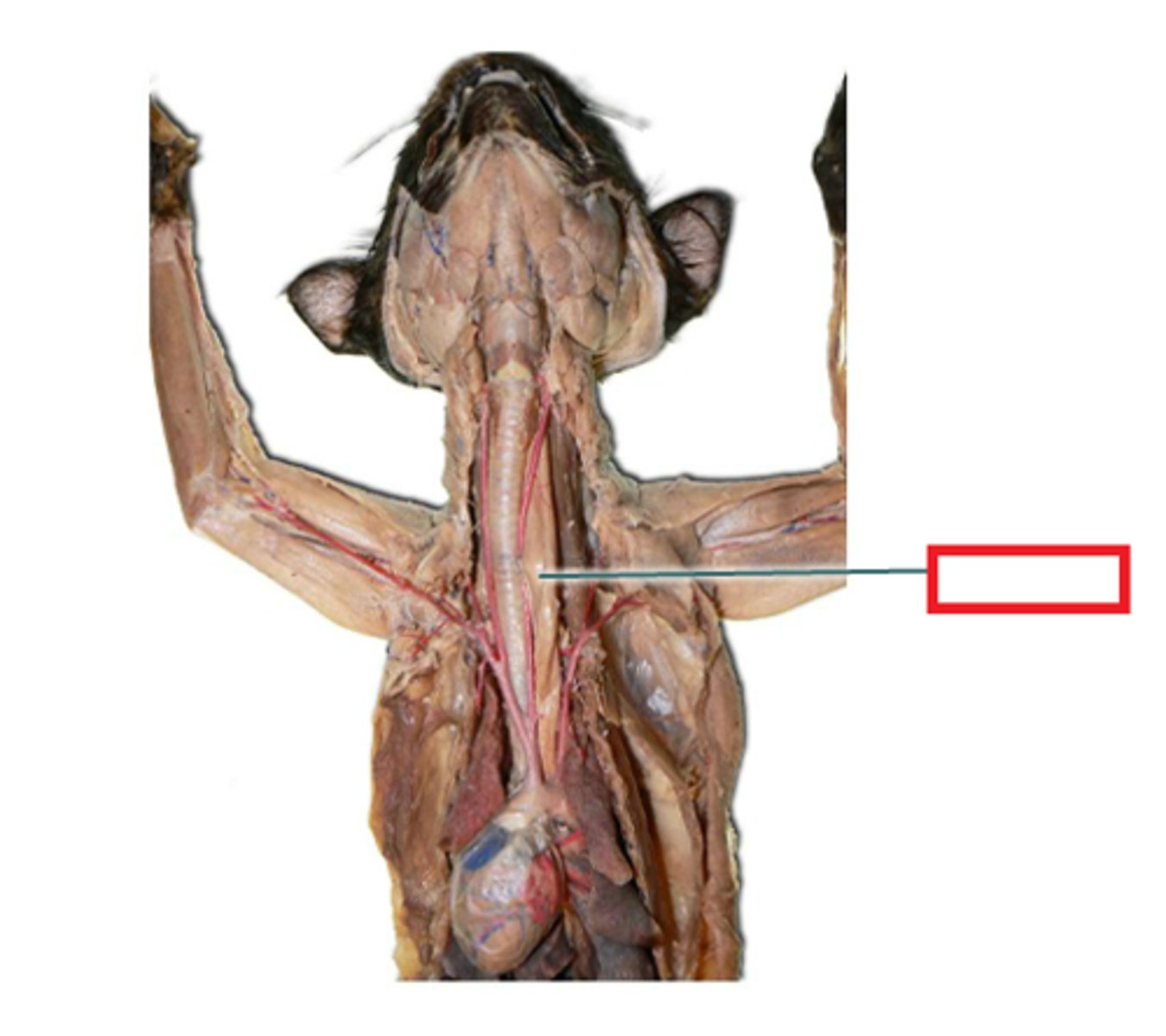
liver (cat)
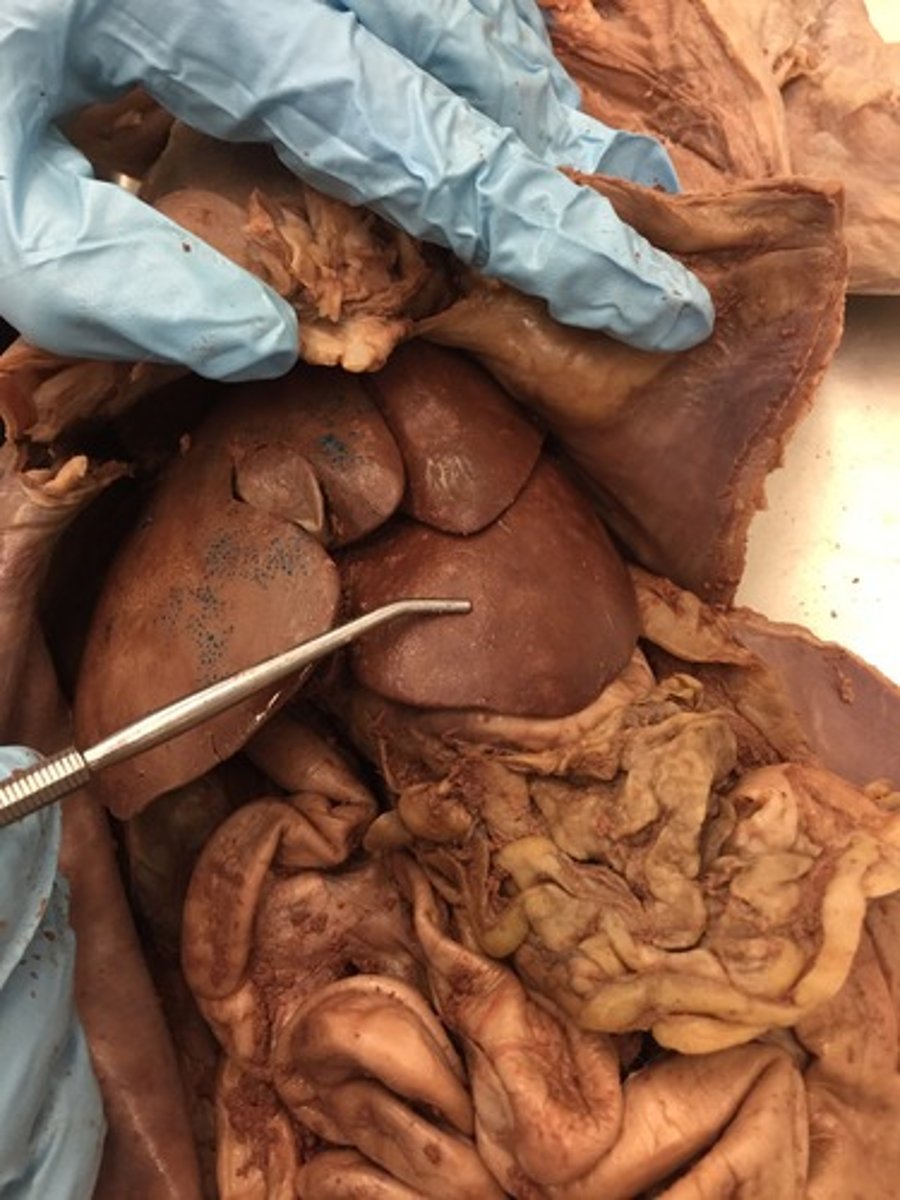
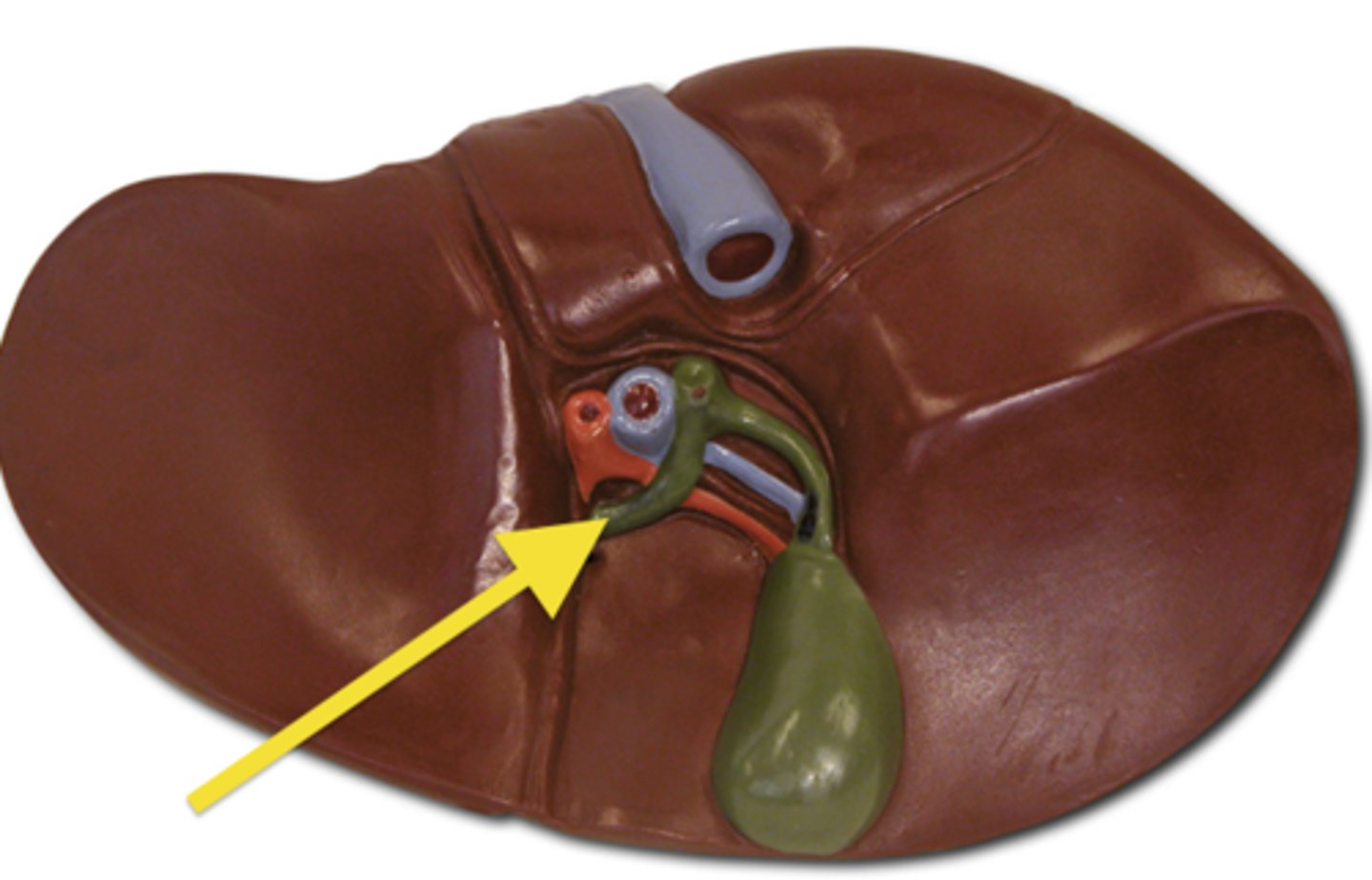
gallbladder cat
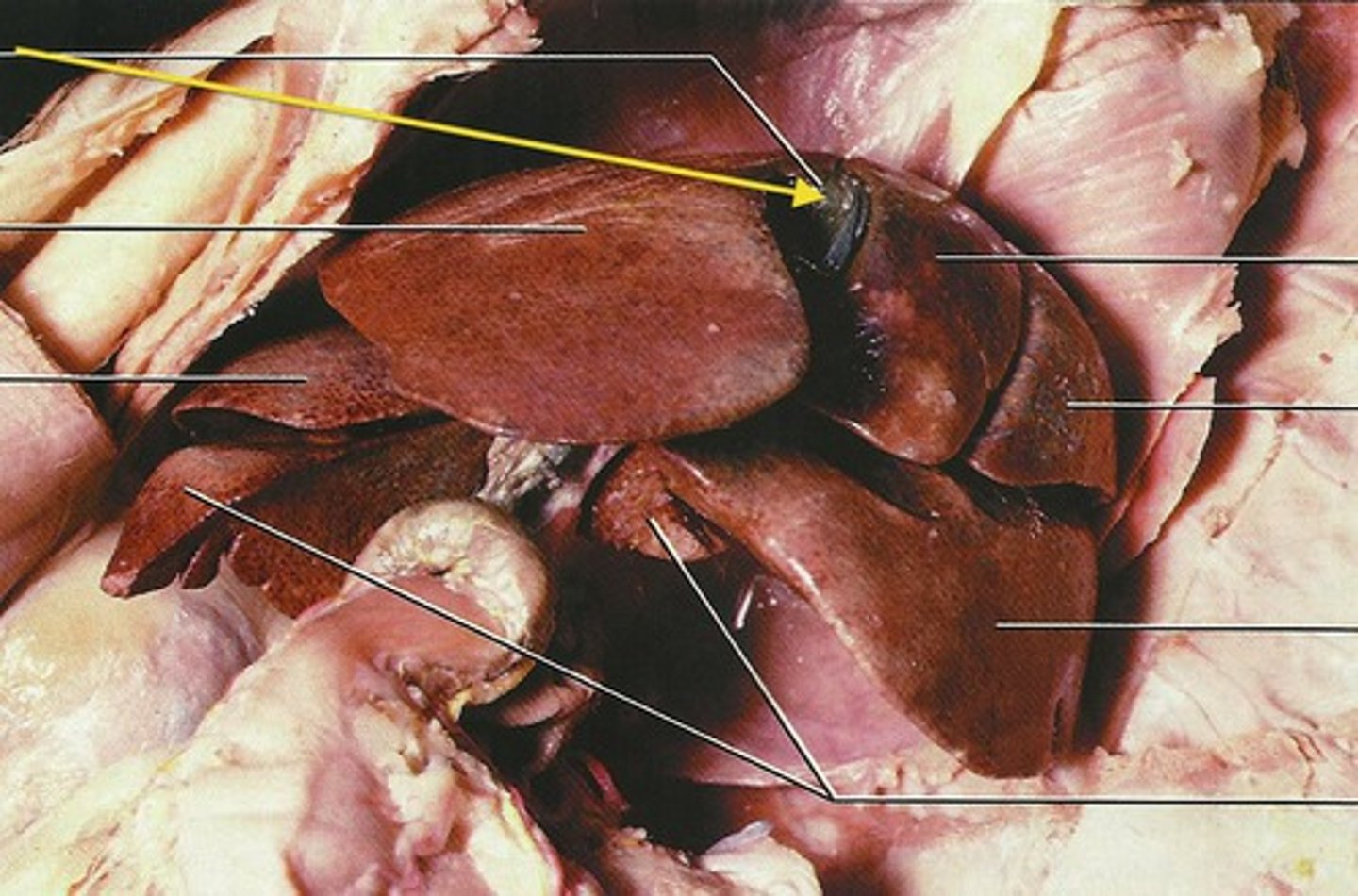
stomach cat
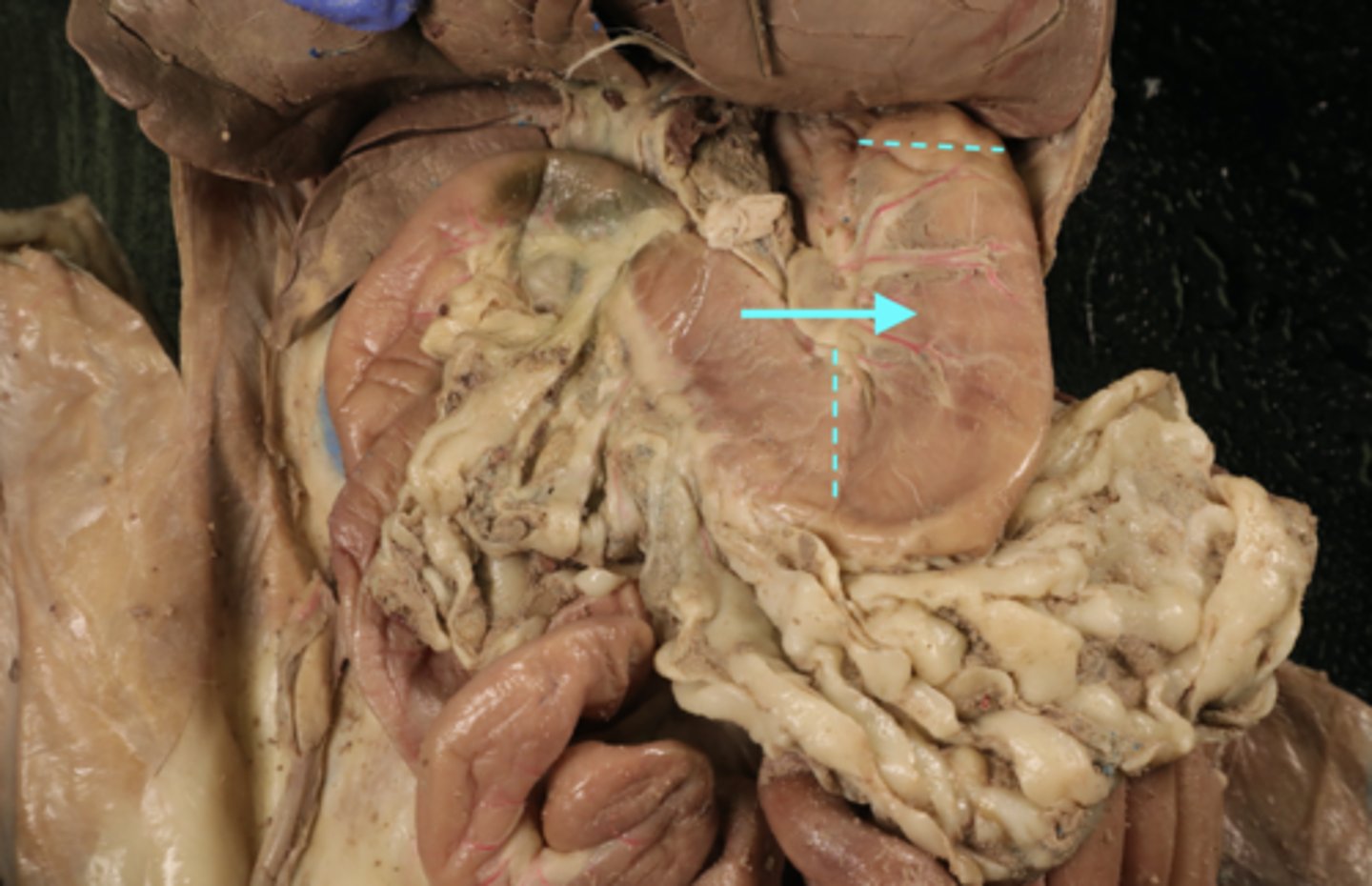
small intestine cat
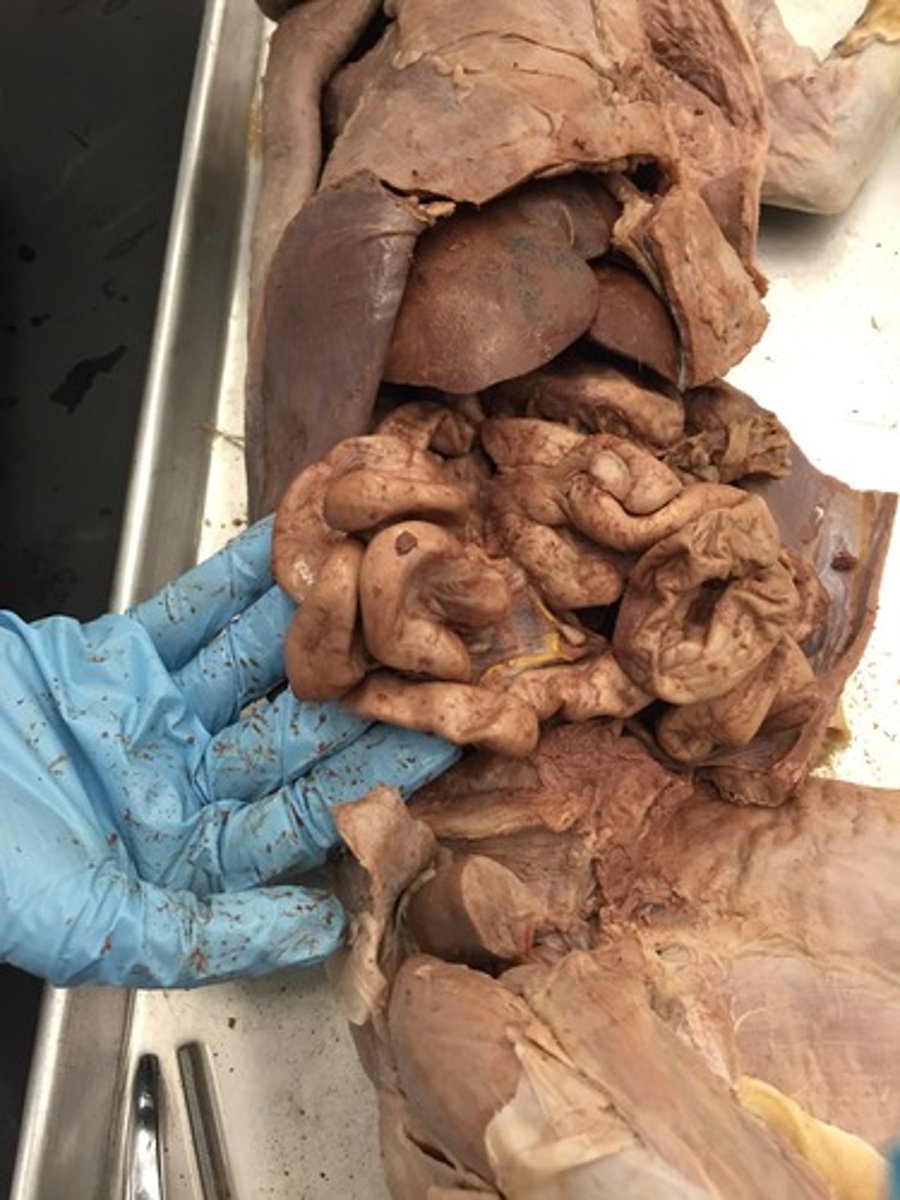
large intestine cat
pancreas (cat)
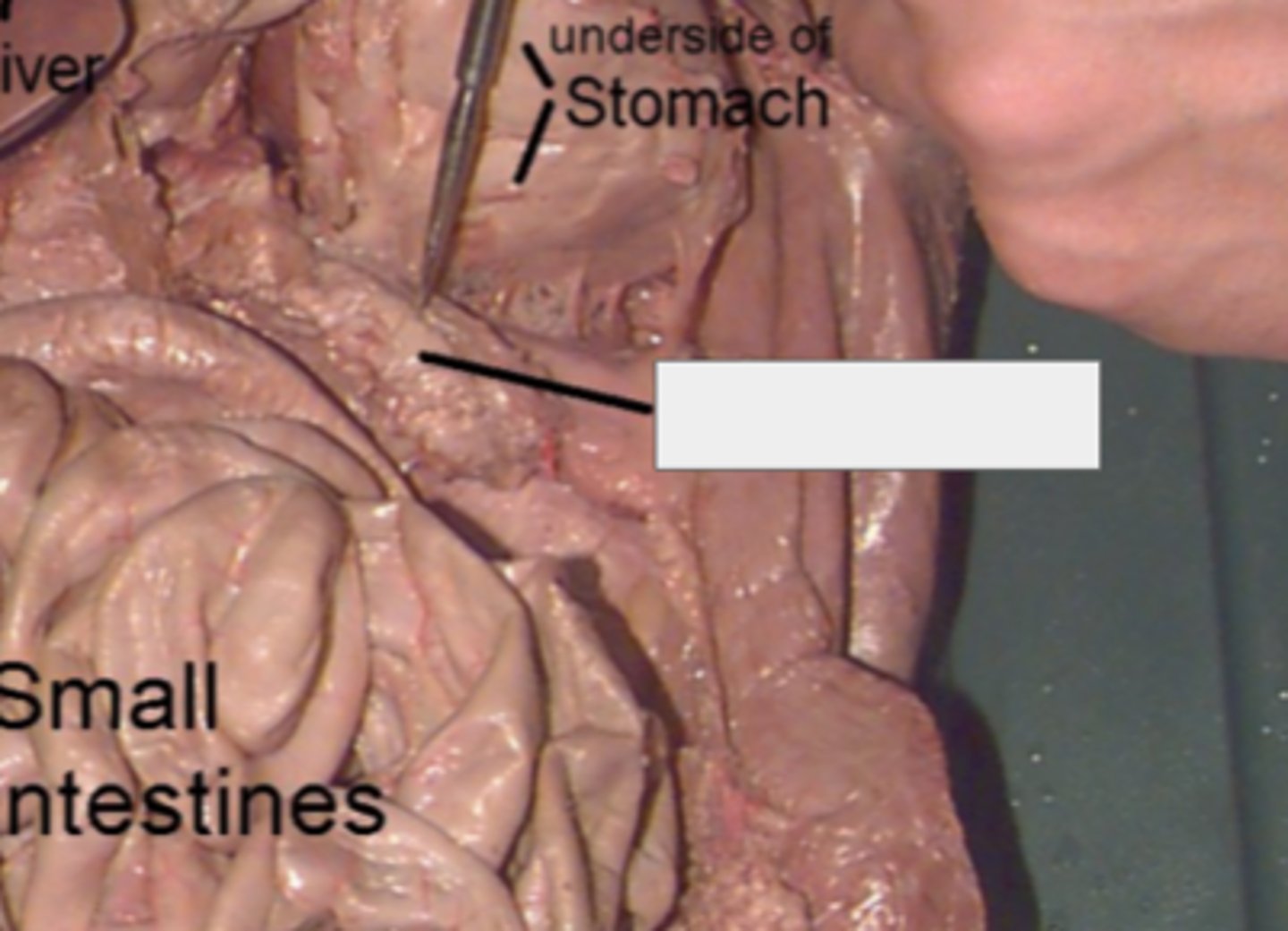
ovaries (cat)
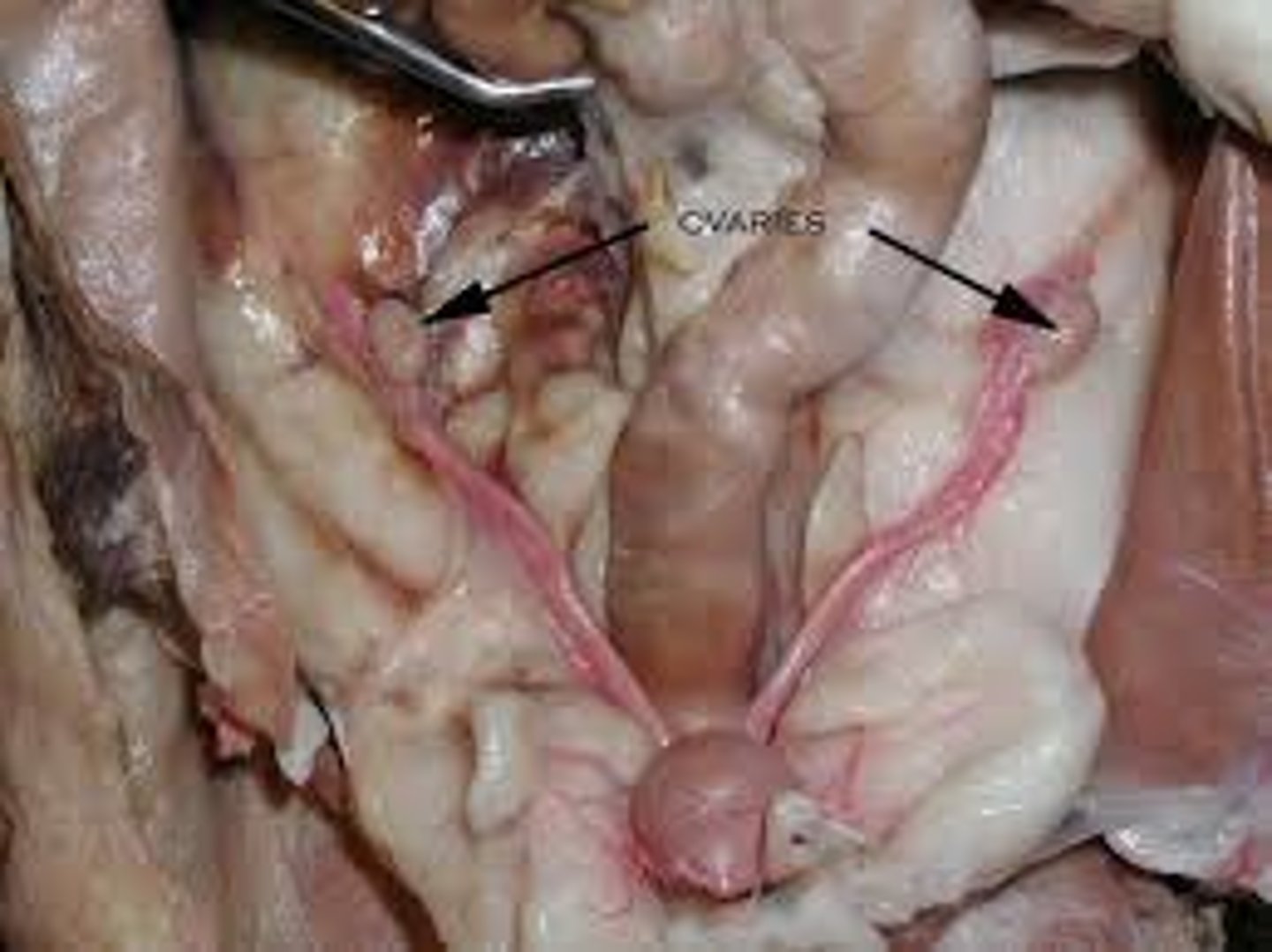
Uterine Horns (cat)
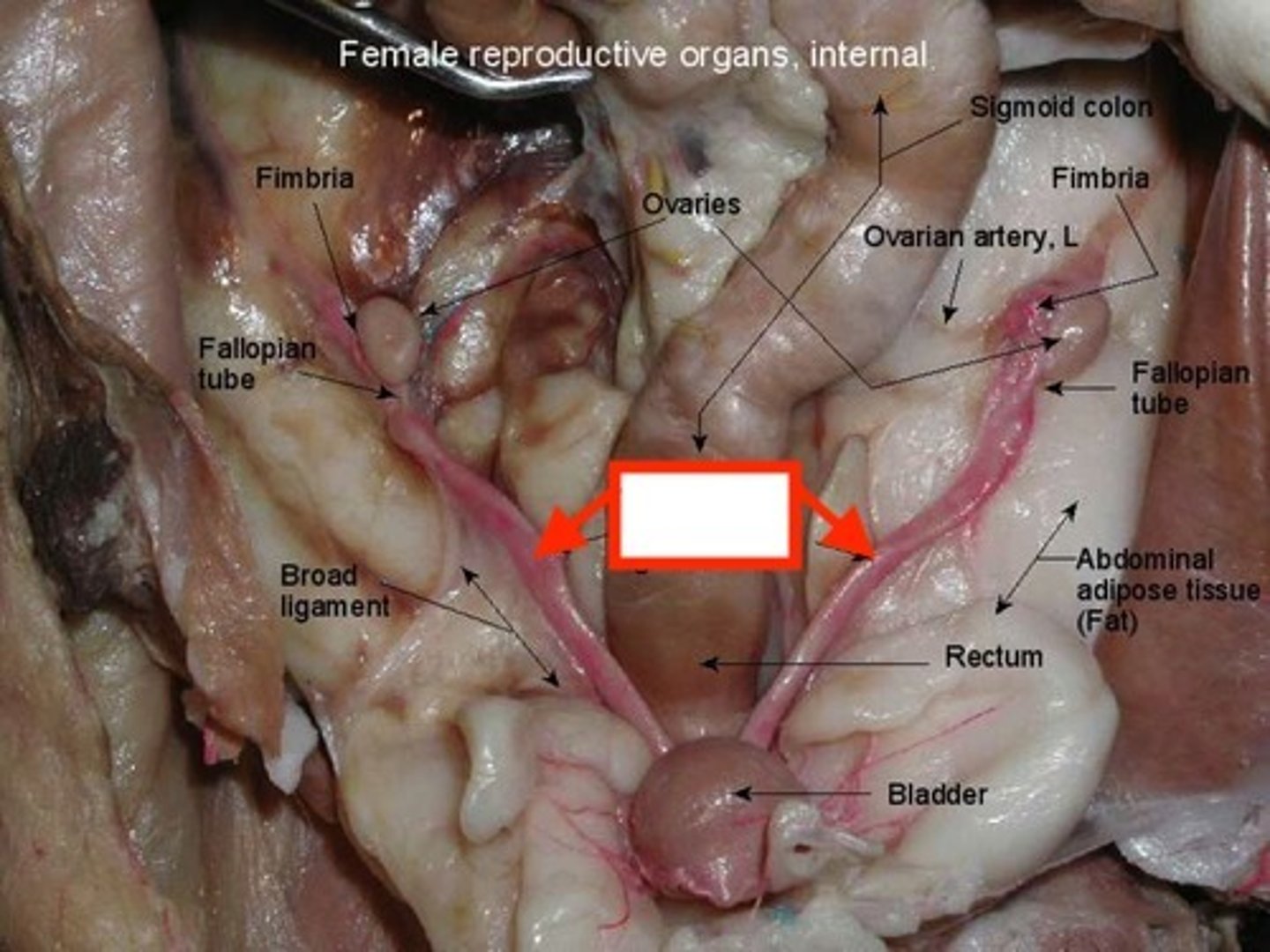
uterus (cat)
tongue
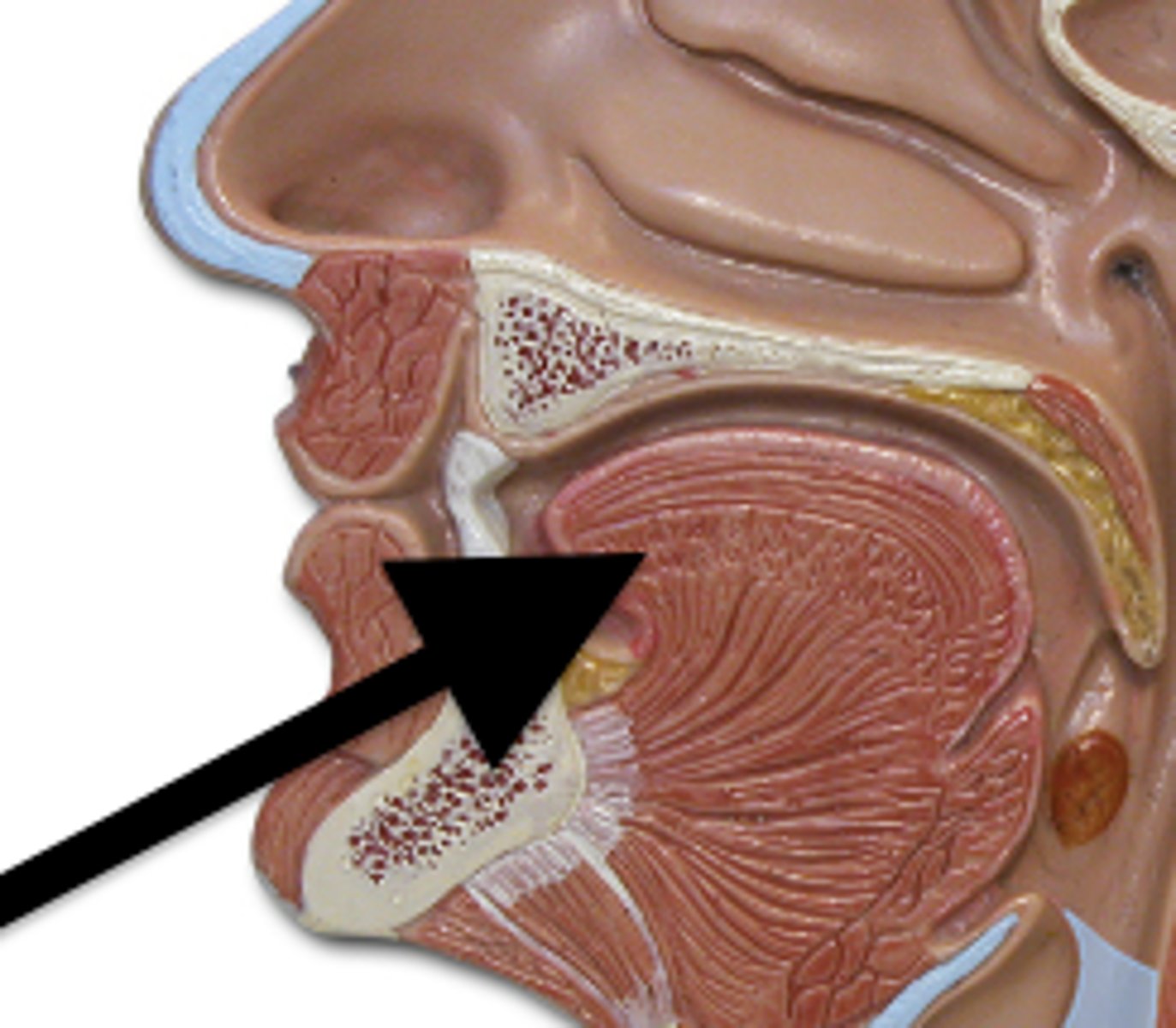
hard palate
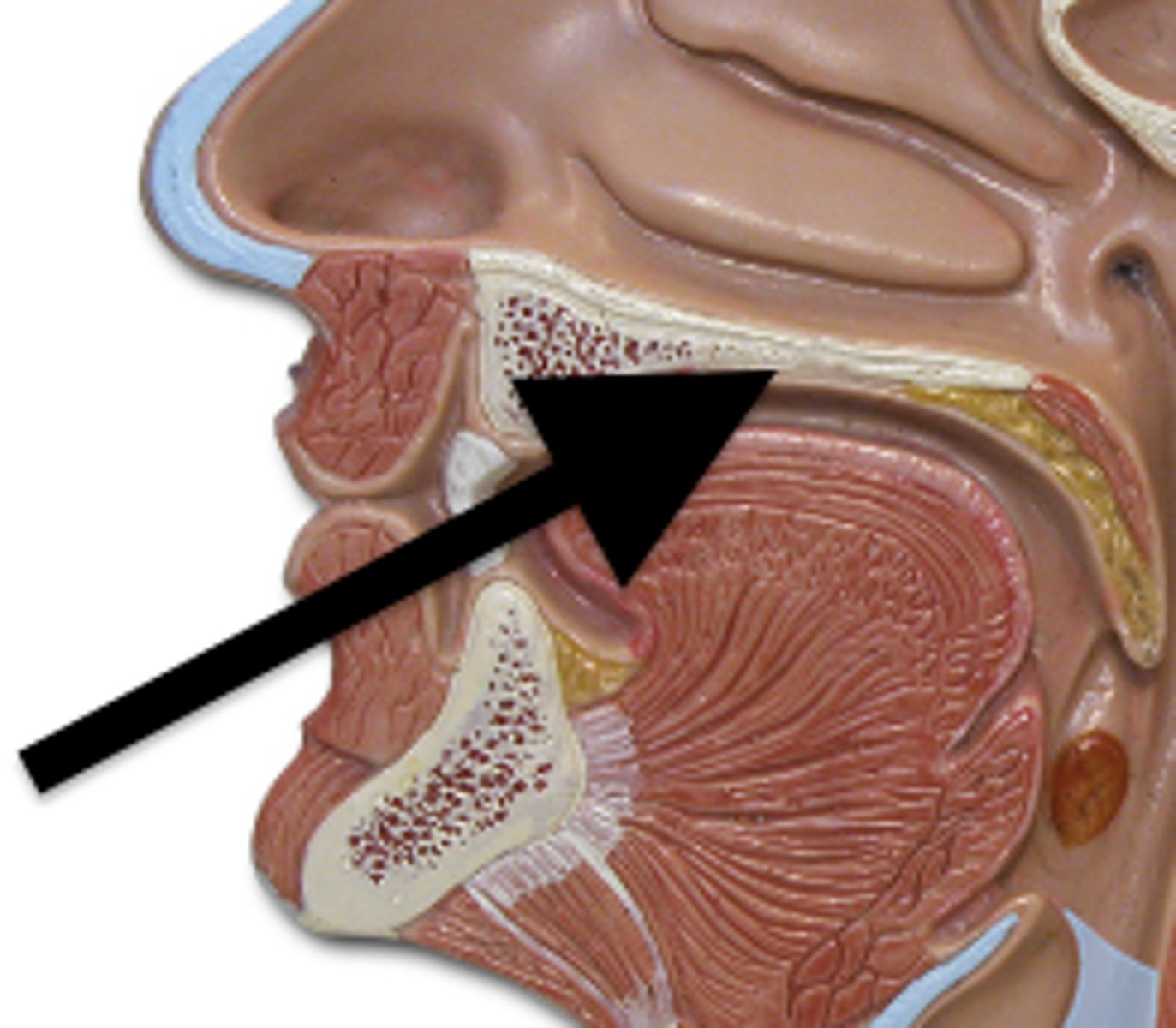
soft palate
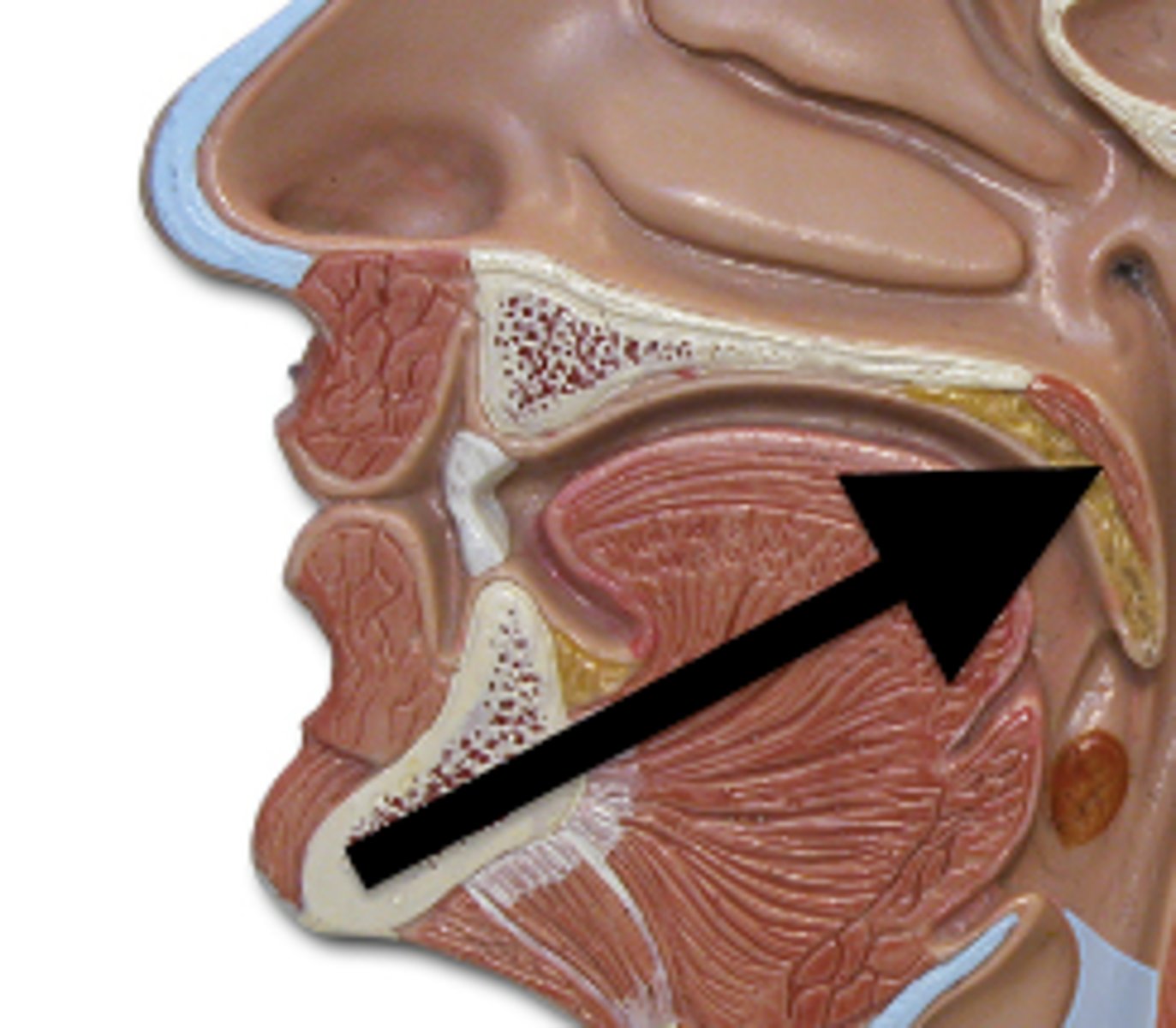
lower esophageal sphincter
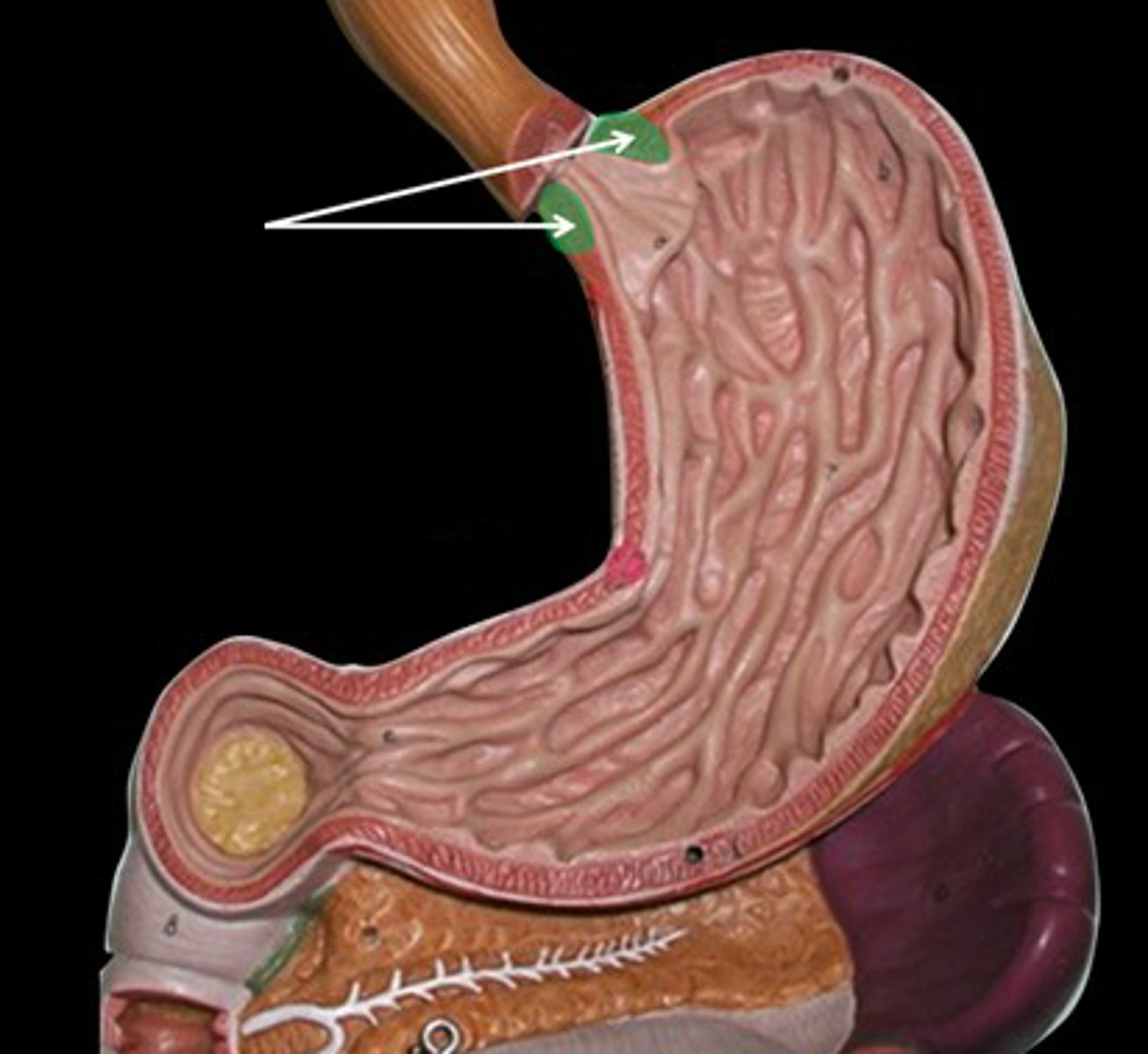
Cadia of stomach
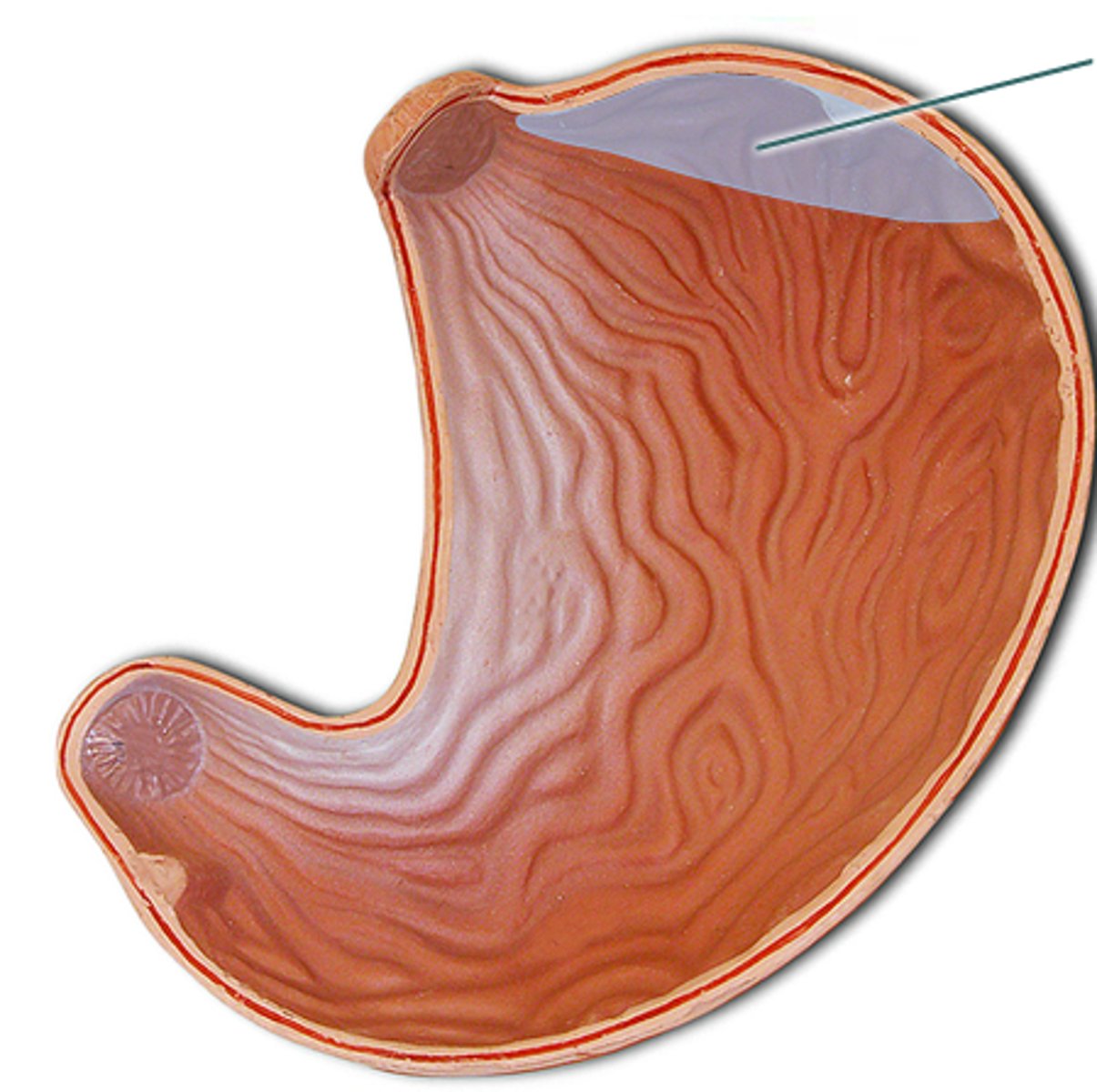
fundus
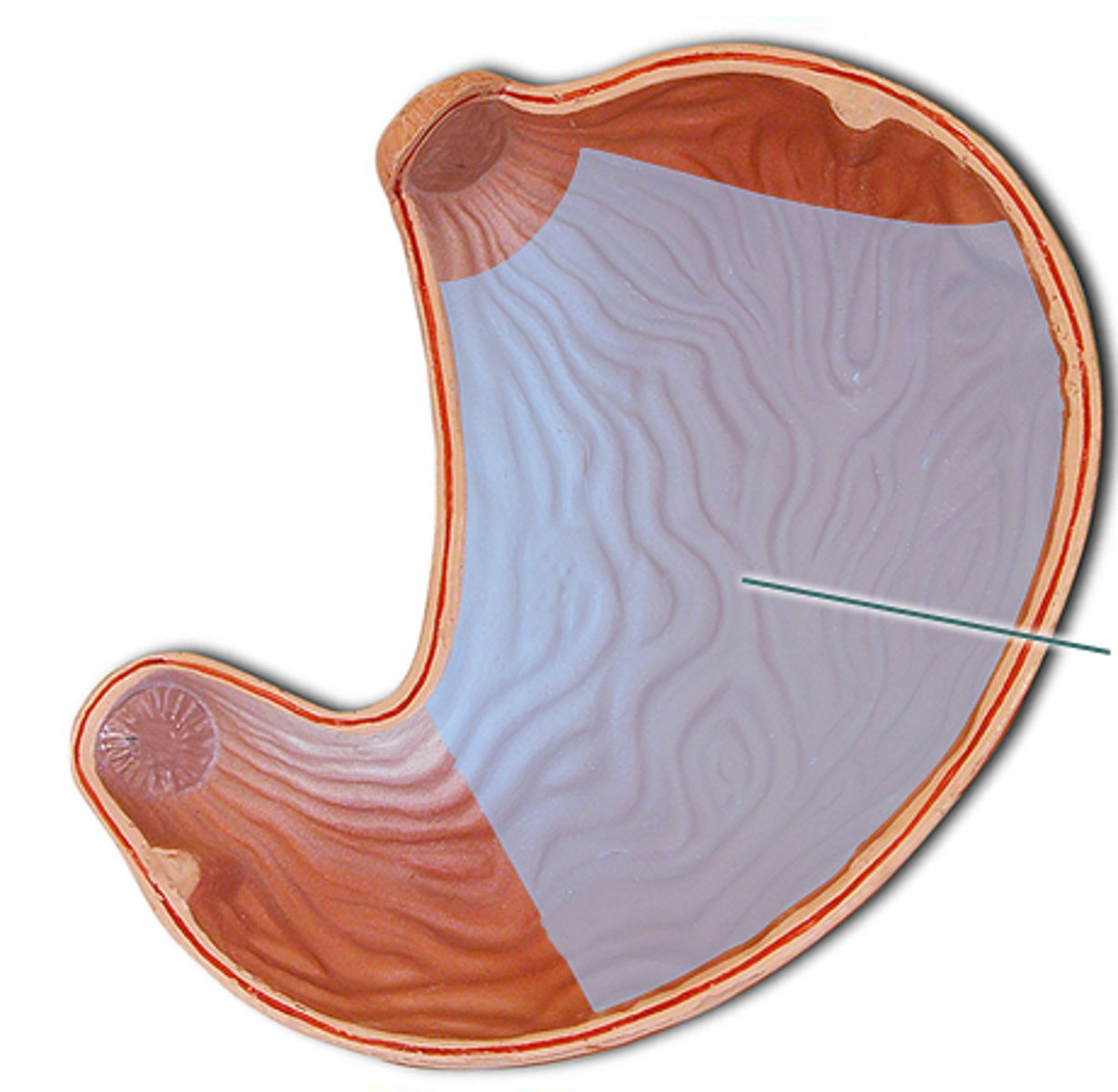
body of the stomach
greater curvature
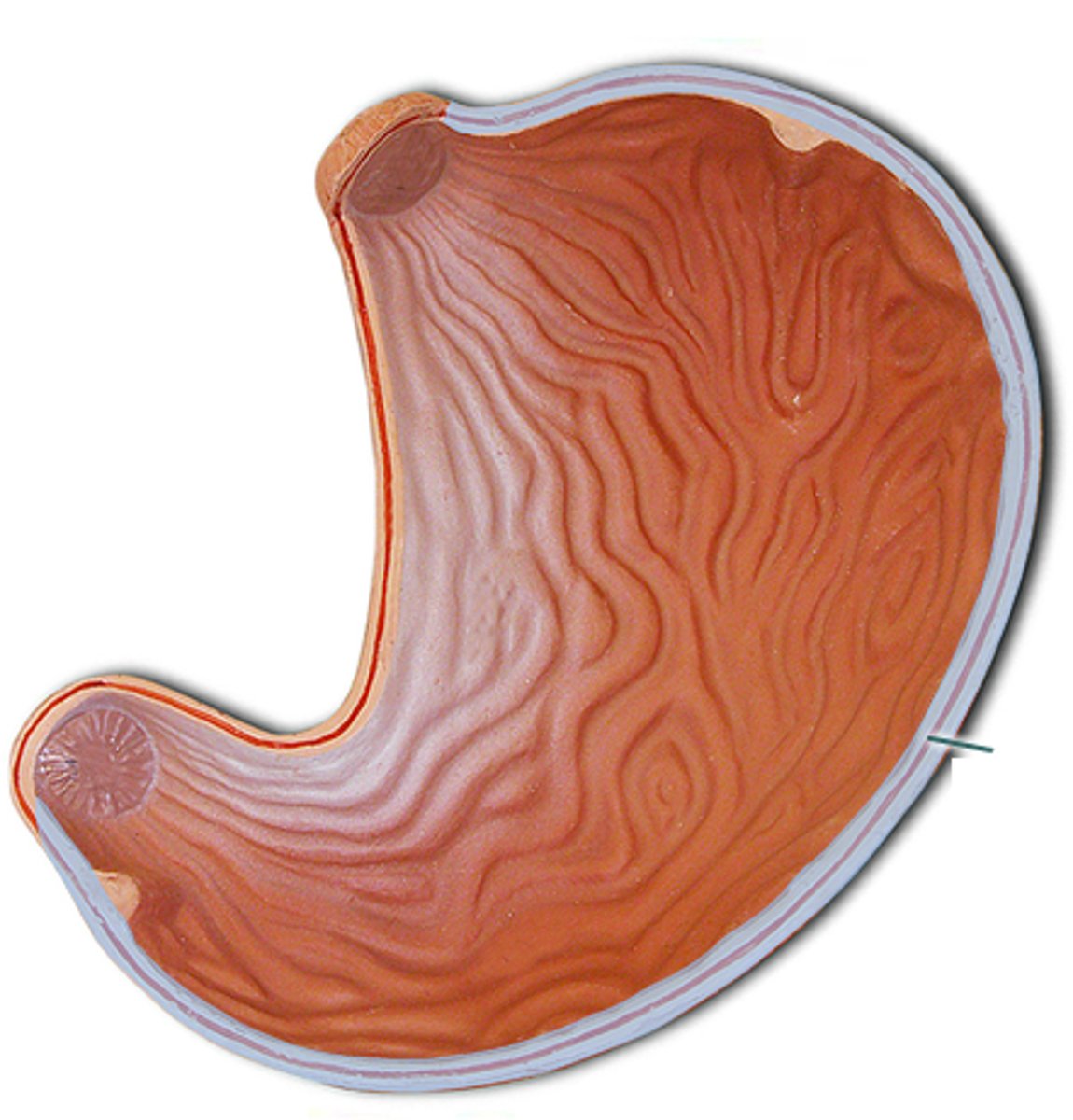
lesser curvature
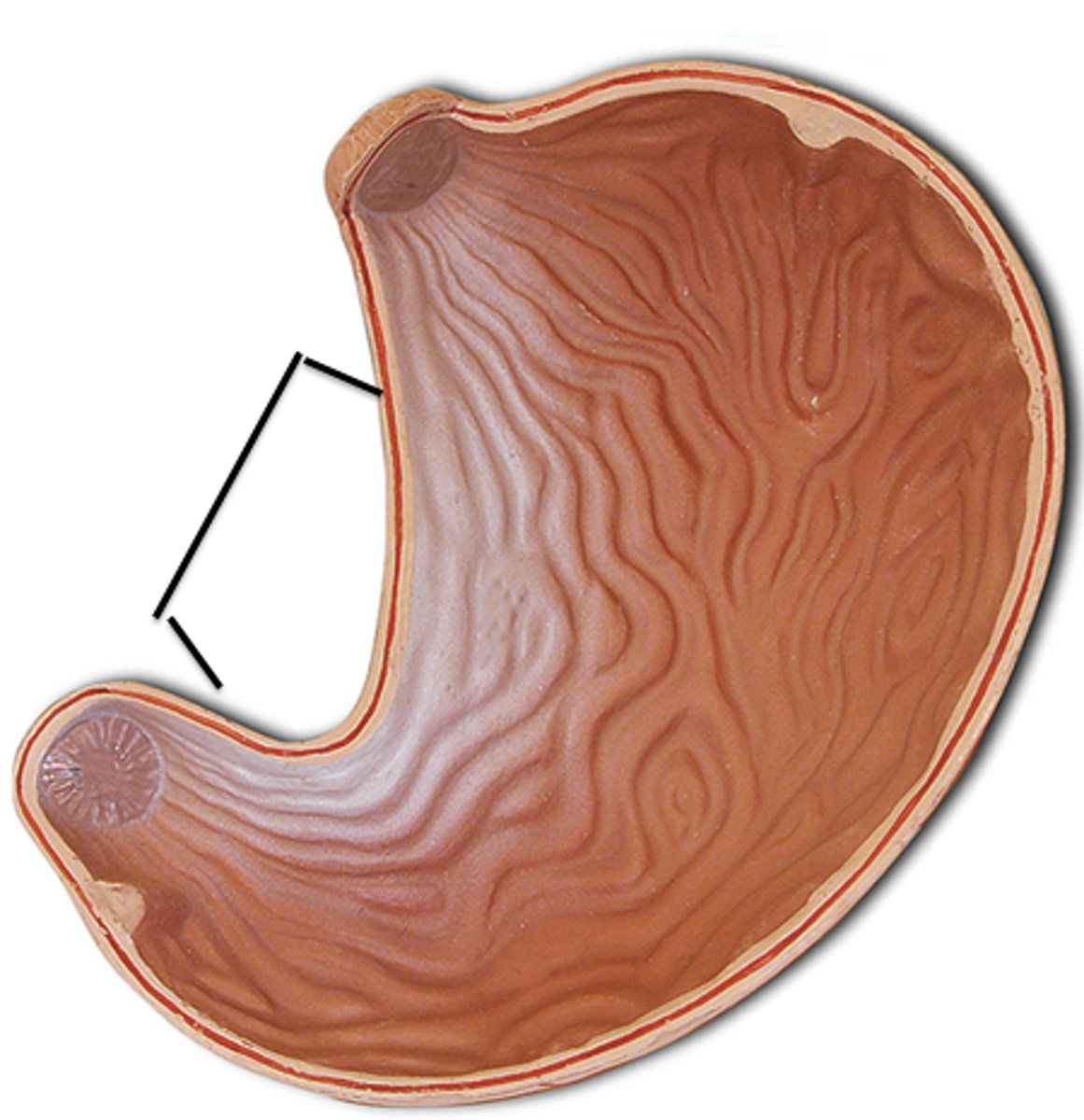
pylorus
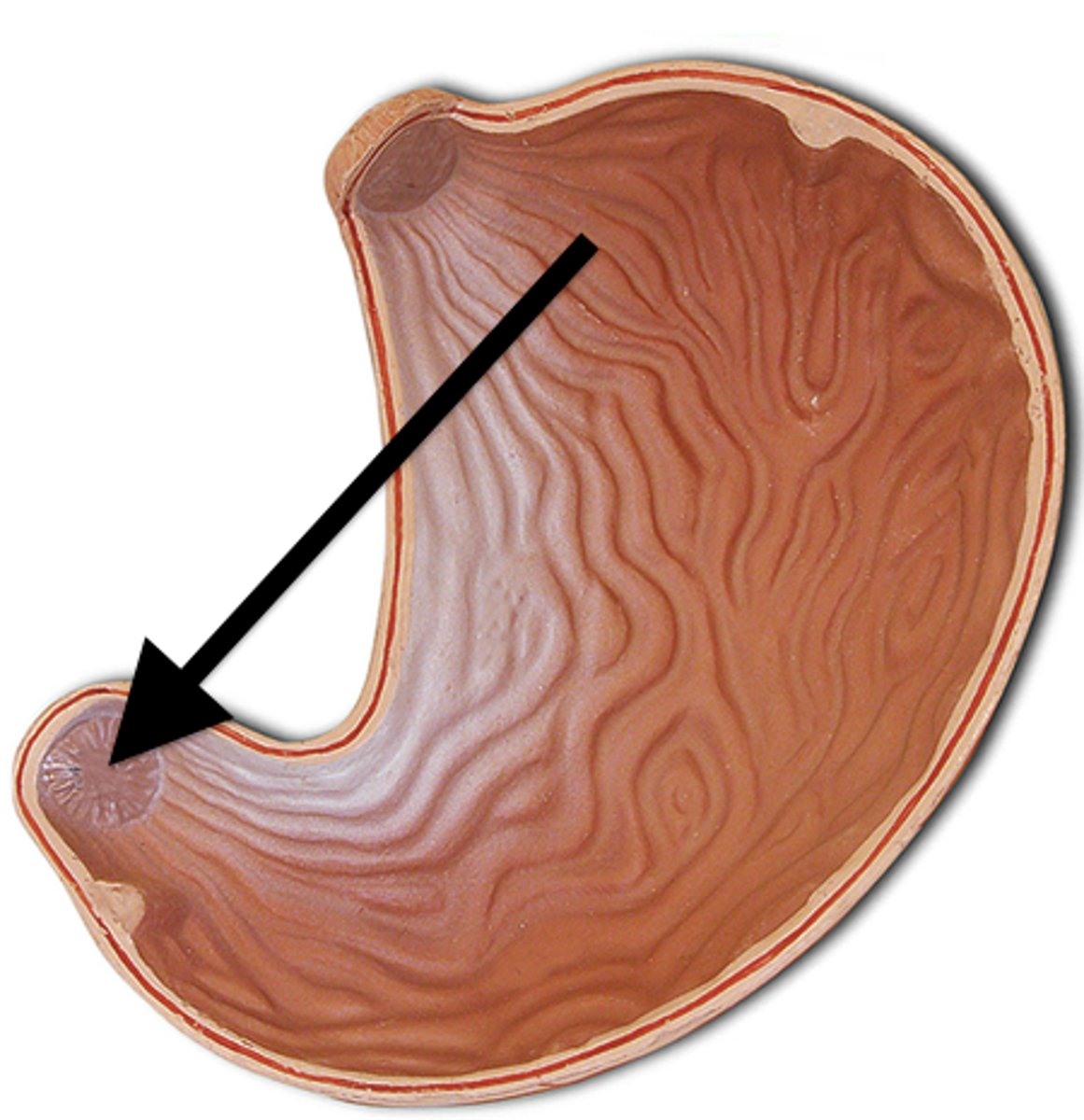
pylorus sphincter
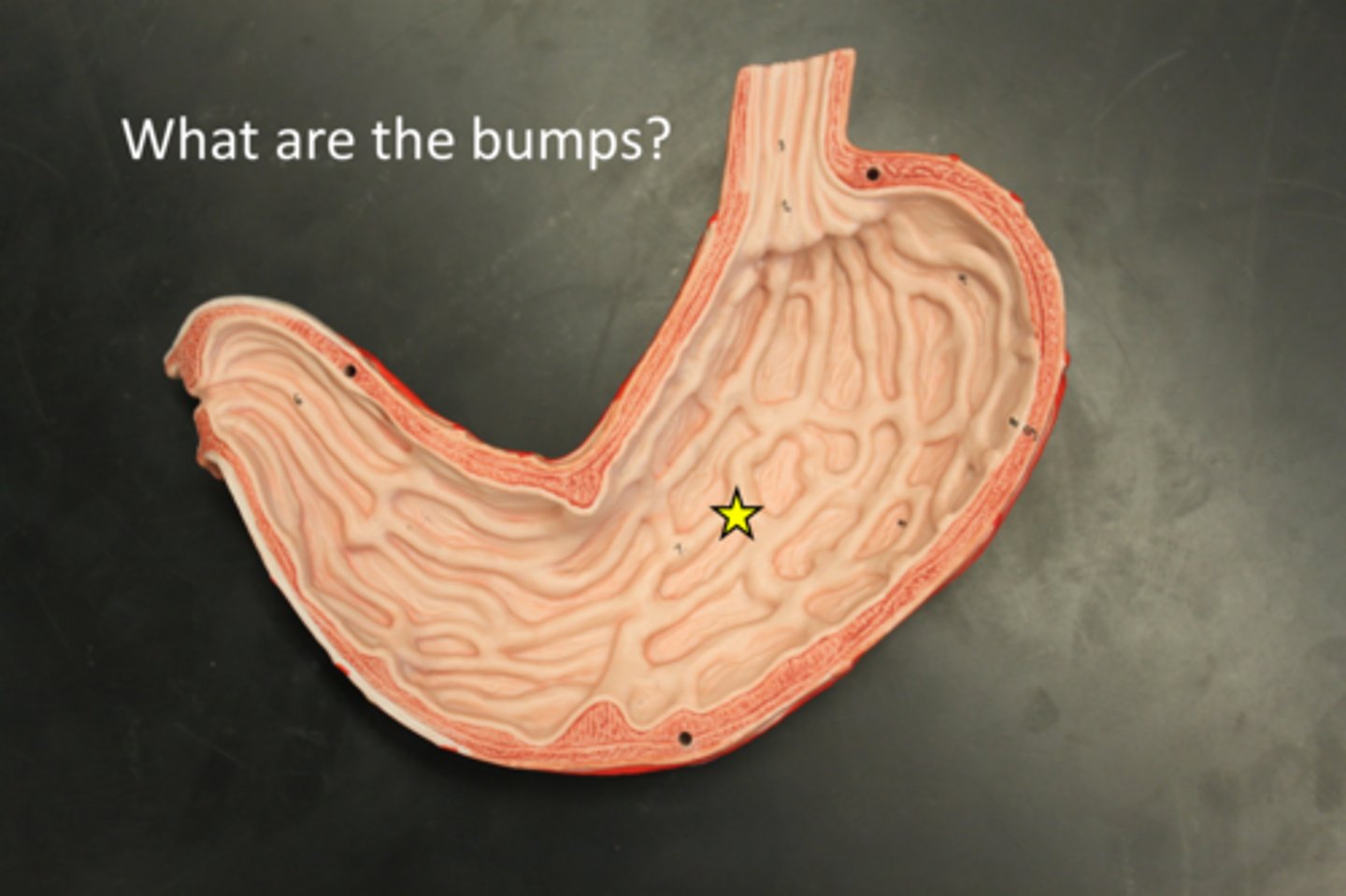
rugea
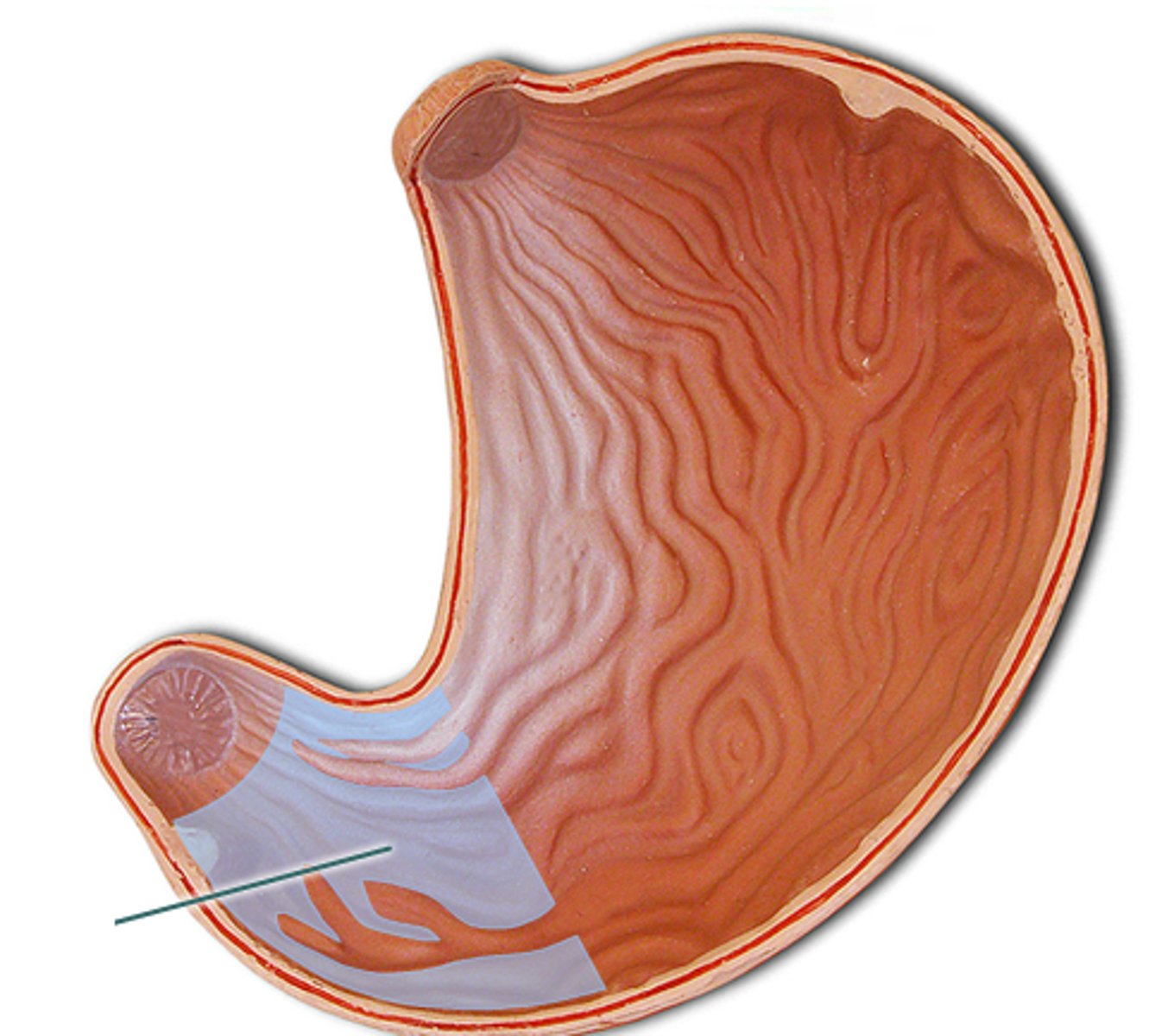
common hepatic duct
