CHEE4S- Sigma flashcard
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
What is shielding?
Electrons in the outer shells spend more time away from the nucleus. Shielding is the repulsion force from inner electrons against the valence electrons which reduces the electrostatic attractions between the outer electrons and the nucleus.
What is Effective Nuclear Charge? (Zeff)
Effective Nuclear Charge is the charge experienced by a valence electron.
Zeff = Z - σ
Zeff - charge experienced by outer e-
Z - actual nuclear charge(atomic number)
σ - # of inner electrons
More shielding, less Zeff
How do anion radii compare to the original atom?
They gain an e-, so the ionic radius increases
How do cation radii compare to the original atom?
They lose e-, so the ionic radius decreases
What is First Ionization Energy?
First Ionization Energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an outermost electron from a gaseous atom.
Energy is always added
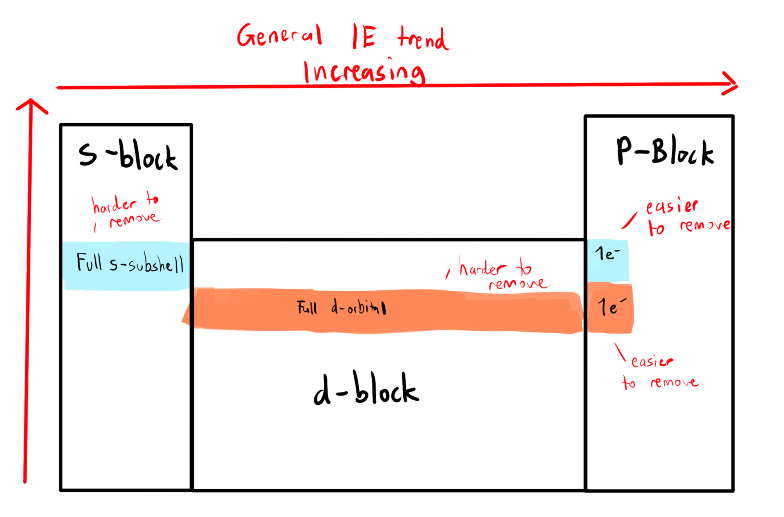
What are the Exceptions to First Ionization Energy?
It requires more energy to pull an electron from a full d-subshell than a single electron in a p-subshell
(in the same period)
It requires more energy to pull an electron from a full s-subshell than a single electron in a p-subshell
(in the same period)
The single e- is easier to remove since it’s the only e- in the higher nrg subshell and is being shielded
How does the 2nd IE compare to the 1st IE?
The second IE is always greater than the first IE because the radius reduces after the first e- is removed (cations get smaller) so the nucleus achieves a stronger pull on the outermost e- because of coulombic attraction
Why does each element have a big increase in IE energy?
Because at a certain point, the IE will be really high because the electron config will drop a principal energy level, which makes the radius shrink much more (the nucleus will have a stronger pull on outer e-)
What is Electron Affinity?
The energy change that occurs when an e- is added to a gaseous atom to form a negative ion
Neg Energy: Exothermic: Wants e-
Pos Energy: Endothermic: Doesn’t want e-
Exceptions for Electron Affinity
Groups 2A and 5A are exceptions
To add e- to group 2A, you need to add it to a whole new p orbital which requires a lot of energy
To add e- to group 5A, it requires more energy because the orbitals are half-filled so they’re already somewhat stable and they don’t want e- as strongly
What is Electronegativity
An elements ability to attract electrons in a chemical a bond
The e- spend more time with the more electronegative element
Noble Gases dont have EN
How to calculate with Heisenberg’s Uncertainy Principle?
We use the uncertainty’s given.
For example, given a percent uncertainty of 5% we use 0.05
Or given an uncertainty of ± 5nm, we use 5nm
Remember the mass is in Kg!!
What is VSEPR?
Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion
The molecules assume the shape that keeps its e- pairs as far apart as possible
a) Double and Triple bonds act in the same way as single bonds but have a bit more repulsion/ will occupy more space
b) Lone electron pairs have more repulsive strength than bonding pairs. Lone pairs occupy more space
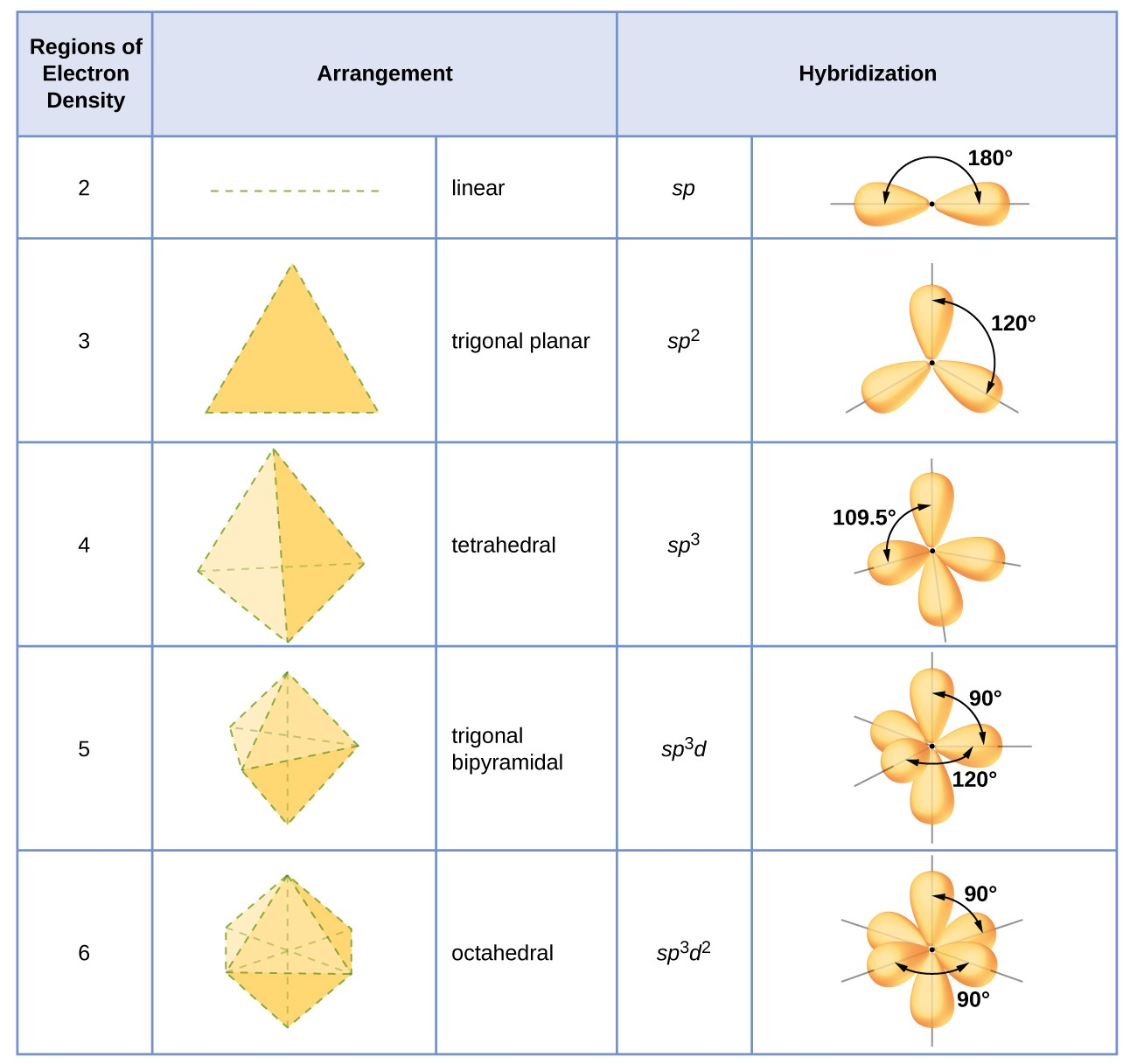
What is Hybridization?
Overlap of orbitals during bonding
The overlapping orbitals are observed on central atom. The orbitals that hybridize depend on the number of bonding pairs & lone pairs.
(eg) sp2 means 3 orbitals are overlapping.
1 s-orbital and 2 p-orbitals
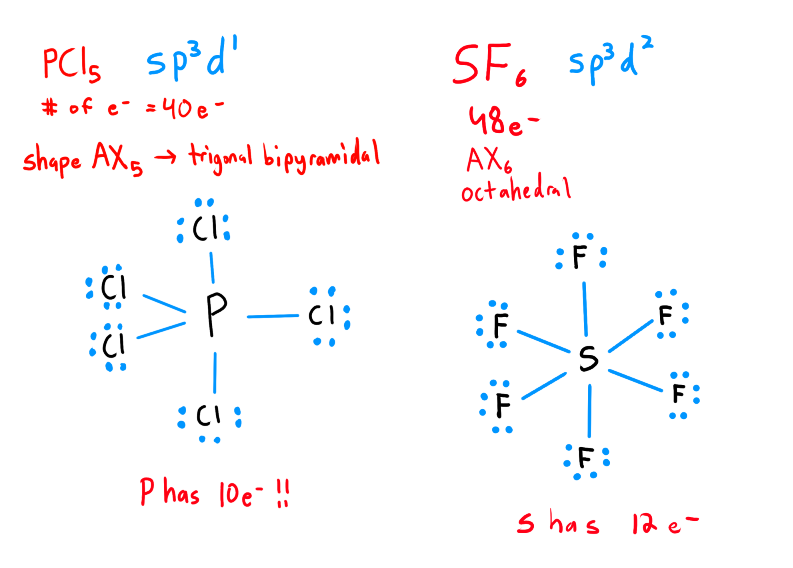
Whats an Expanded Octet?
When excess of e- on the central atom appears after completing the octets on the outer atoms
Only occurs on central atoms usually with d-orbitals available
(eg) PCl5 , SF6
they have 3d orbitals available (?)
What is an Incomplete octet?
Some atoms have a complete outer shell with less than 8e-
Occurs with small central atoms like Beryllium and Boron
(eg) BeH2 , BF3

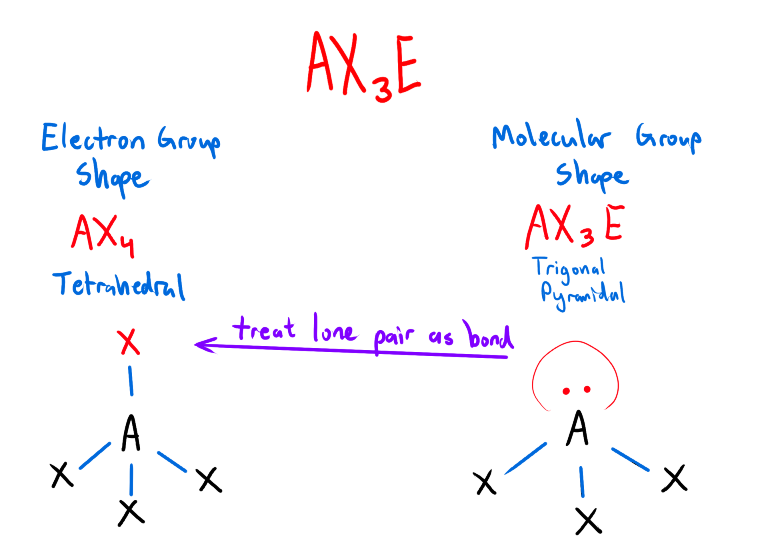
What is Electron-Group Shape and Molecular Shape?
Electron Group Shape/ Electron Domain Geometry
The shape formed by the molecule when all atoms and lone pair electrons on the central atom are considered
(Treat the lone pairs as if they are a bonded pair)
Molecular Shape
Shape formed when only the bonded atoms in the molecule are considered
(ignore the lone pairs, only look at the shape of the bonded pairs)
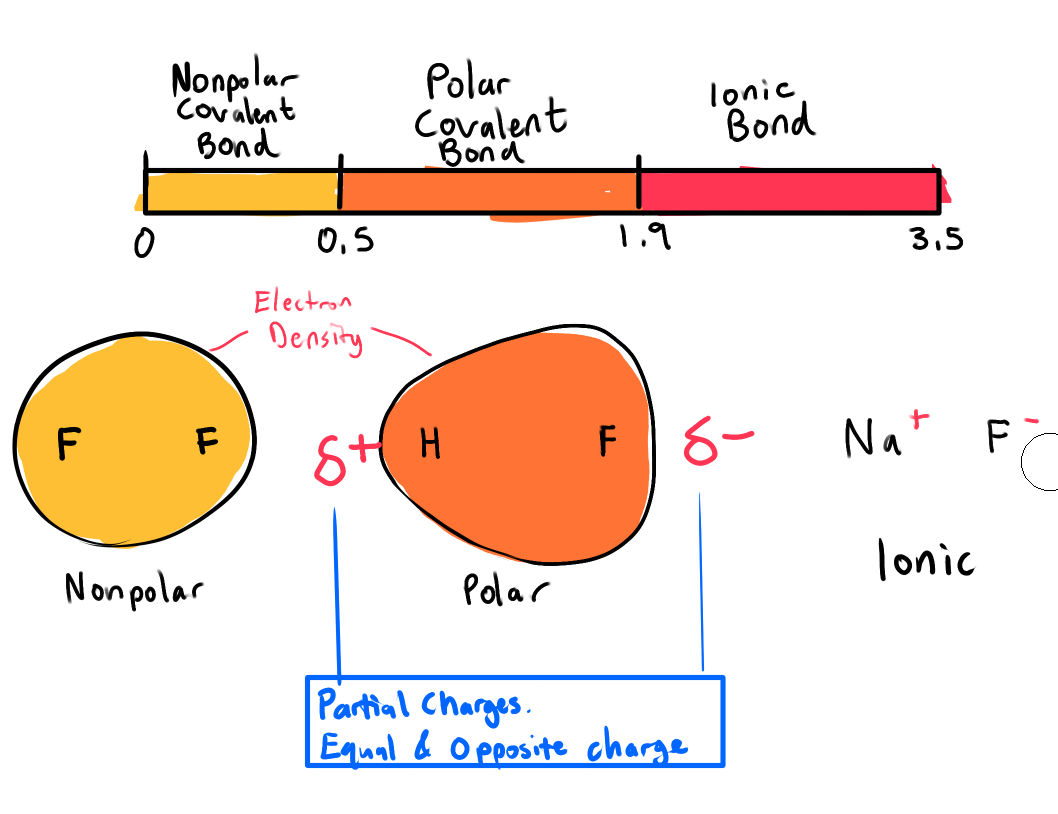
How does EN and Bond Polarity affect the type of bonds formed
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
𝚫EN: 0 – 0.4
Polar Covalent Bond
𝚫EN: 0.5 – 1.8
Ionic Bond
𝚫EN: 1.9 - 3.5
All polar covalent bonds have some ionic character and vice verse
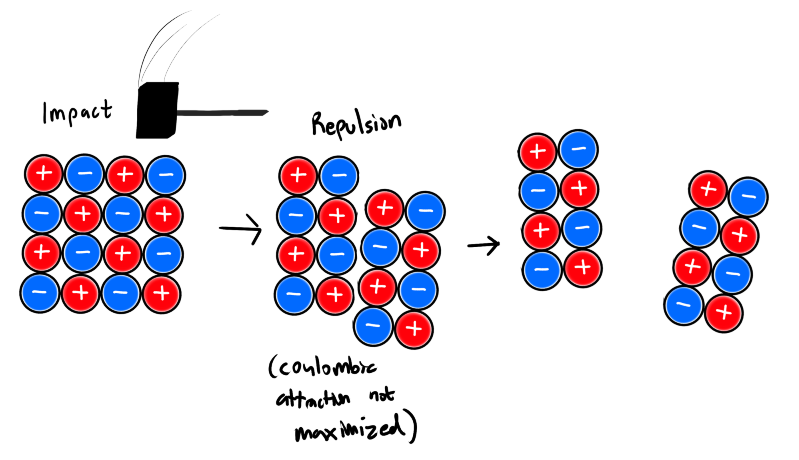
What is an Ionic Solid? What are the properties?
An ionic solid is a solid made up of positive and negative ions held together by strong electrostatic forces (ionic bonds).
Properties
Strong Coulombic forces of attraction
High Melting Points
Very hard
Low votality ( Resistance to change, explains high melting point )
Cleave along planes
Brittle 3D structure
Ions line up repetitively and in a way that maximizes coulombic attraction
Not malleable/ductile
Solubility and Conductivity
Most are soluble in polar solvents
Conduct electricity only when molten or dissolved in a polar solvent (charged particles free to move)
Higher the ion concentration, higher the conductivitry
What are Covalent Compounds and the properties?
Covalent compounds are formed when a NM and another NM share one or more valence e- to fill their octets.
Properties
Lower melting & boiling points compared to ionic compounds
Soft and Flexible
Do not conduct electricity in water EXCEPT FOR ACIDS
What are Crystalline Solids?
Ionic Compounds do NOT exist as individual units/ formula units. (eg) NaCl
Ions are arranged in a repeated pattern in 3D
The segments that repeat are called UNIT CELLS
Usually have flat surfaces with definite angles because of cleaving
What are Metallic Solids? What is a Metallic Bond?
Metallic solids are solids made entirely of metal atoms held together by metallic bonding.
Bonding results from the attractions between the nucleus and delocalized e- (electron sea)
Bond Strength increases as # of bonding e- increases
What is the Electron Sea Model?
Nuclei and inner e- are localized
Valence e- are free to move around
Properties
Conducts electricity
Conducts heat
Malleable & Ductile
Lack directional bonds

What is a Directional Bond?
Directional bond; Atoms are bonded in specific directions Bond only exists between particular atoms and along specific lines.
Covalent (directional)
Atoms share electrons only between specific neighbors.
Each bond points in a specific direction like sticks between atoms.
Example: Diamond each carbon bonds to 4 others in fixed directions (tetrahedral).
If you try to move the atoms, the bonds snap because they only exist along those exact lines.
Metallic (non-directional)
Metal atoms sit in a sea of free electrons that attract in all directions.
electrons flow everywhere.
The atoms can slide without breaking bonds (that’s why metals bend).
Ionic (non-directional)
Each positive ion is surrounded by negatives, attraction happens in every direction between opposite charges.
Whats an Interstitial Alloy?
Atoms with SMALL RADIUS occupy the spaces between atoms with LARGER radius
Steel: Carbon fills in spaces between Iron atoms
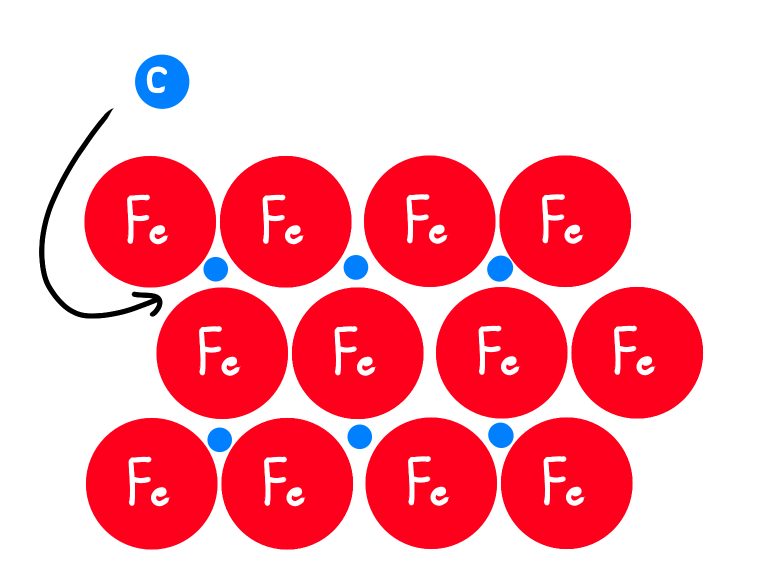
What are Steel’s Properties?
Recall: Steel = interstitial alloy of iron & carbon
Iron lacks directional bonds
Steel is more rigid, less ductile than iron because of the directional bonds between iron & carbon
Density of steel is greater than iron, since carbon doesn’t expand the lattice a lot
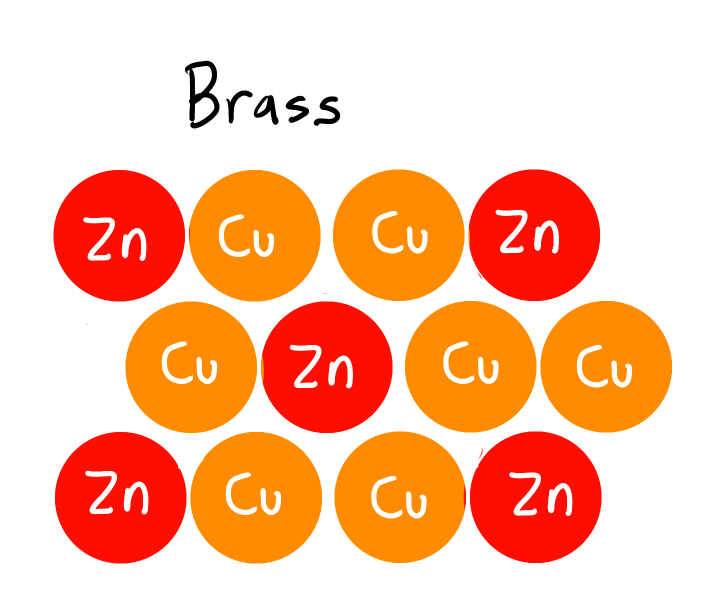
What are Substitutional Alloys?
Similar to Interstitial alloys, but instead of filling in the gaps of the host atom it replaces the atoms.
Radii of solute & solvent are similar
Solvent = subs with more atoms
Solute = subs with less atoms
(eg) Brass: Zinc + Cu
What is formal charge?
Formal charge = (# valence e- of the atom) - (# of dots and lines around atom)
Used to identify the most likely structure of a molecule
More likely structures will have formal charges closer to zero
If there are negative formal charges, they should be on the element with most EN
ADD BONDS OR CHANGE ARRANGEMENT TO ELIMINATE FORMAL CHARGES IF NECESSARY !

What is Bond Energy?
Energy released during the formation of bond. The same amount of energy is needed to break the bond.
Potential energy decreases as atoms are farther
Potential energy increases as atoms are closer
What is a resonance structure?
Two or more possible lewis structures that are equally valid. Most of the time, it’s just rearrangements of the double/triple bonds around an atom.
Must draw all possible structures with two way arrows
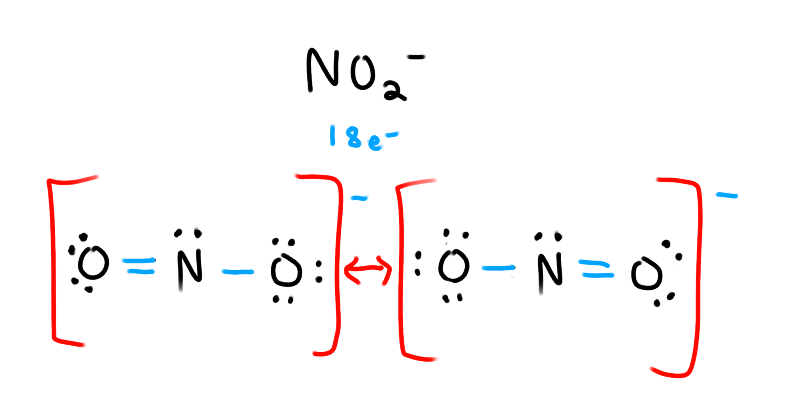
What is Bond Length?
Bond Length is the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms.
Shorter Bond Length, Stronger Bond Energy
Because less distance, stronger bond, more energy required to break the bond
Shorter Bond Length, Larger Bond Order
Larger bond order, more bonding e-, more coulombic attraction, shorter length
What is Bond Order?
The number of chemical bonds between each pair of atoms.
For example O=O has a bond order of two
UNLESS THE MOLECULE HAS A RESONANCE STRUCTURE
Bond Order Formula for Resonance
Bond order = (# of bonds) / (# of outer atoms)
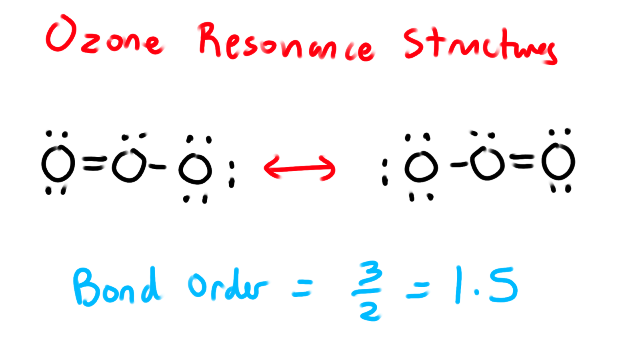
Which period of elements begin to form octets?
Period 3
They have 3s and 3p orbitals being filled, but their 3d orbitals are empty, so they begin to use the 3d orbital during hybridization
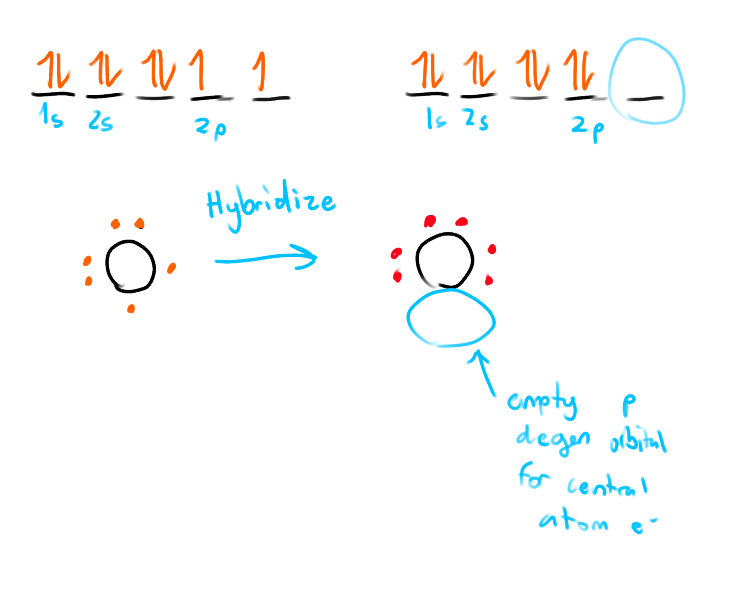
What is a Dative/Coordinate Covalent Bond
Only occurring with oxygen and polyatomic ions.
One atom provides both the bonding e- in a covalent bond.
Oxygen does this because
its the smallest 6A element
high EN value
One empty p orbital where the central atom e- can go when it hybridizes
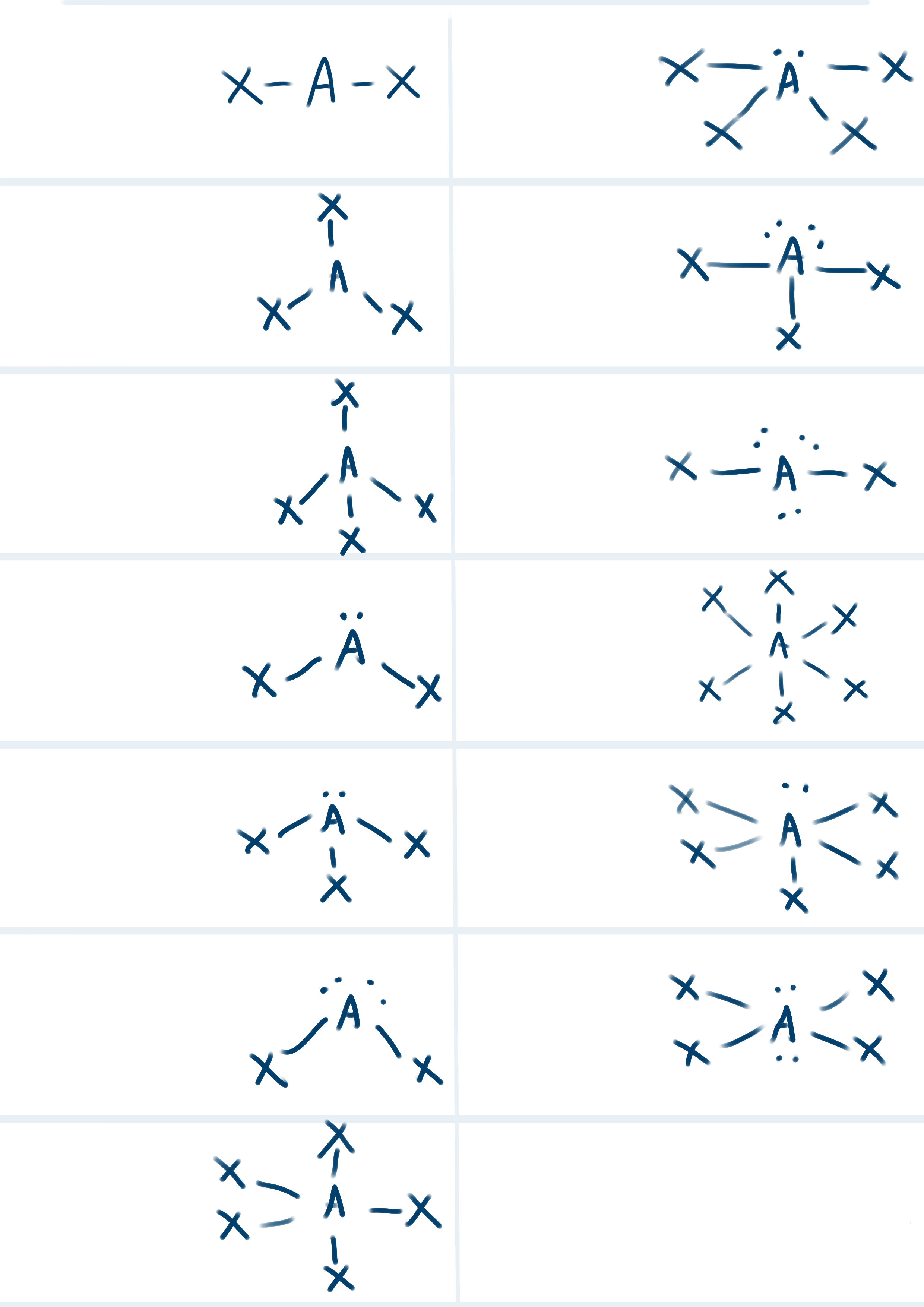
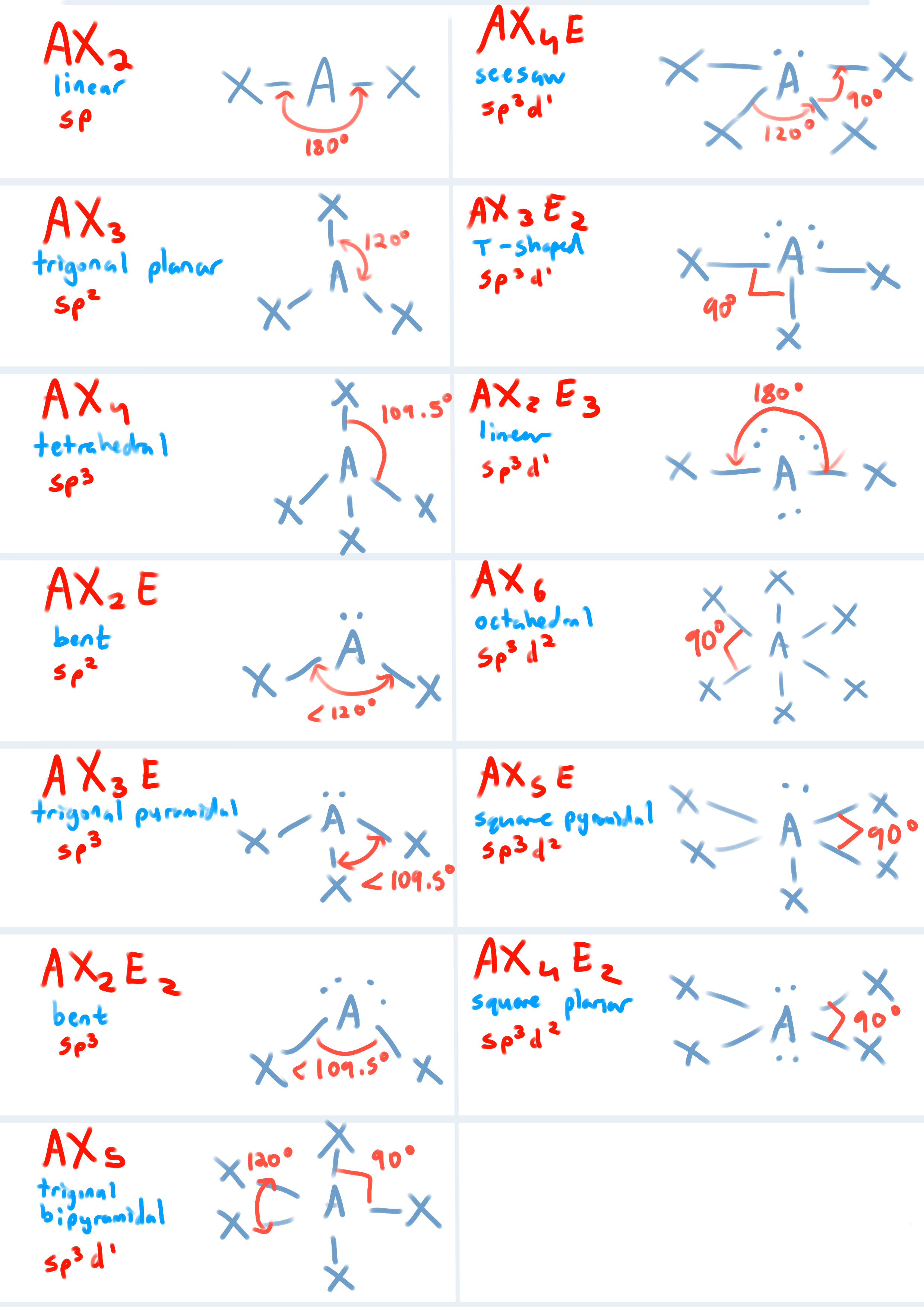
List all the shapes, VSEPR formula, Hybridization and Bond Angles for each structure
What is Lattice Energy?
The energy required to completely separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions.
Based on Coulomb’s Law
Does the formation of Ionic Bonds release or absorb energy?
ionic bond formation is exothermic overall.
When oppositely charged ions come together, they form a stable crystal lattice and release a large amount of lattice energy, which makes the overall process exothermic.
Does lattice energy increase or decrease when cationic & anionic radius increase?
Decreases. The distance between ions increase so the lattice energy decreases.
Coulombs Law.
What is a charge cloud?
A charge cloud is a region around an atom containing a bonding pair or lone pair of electrons. each counts as one electron domain that repels others to shape the molecule.
Lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs
Ideal bond angle & hybridization for an atom with 2 charge clouds?
Ideal angle: 180°
Hybridization: sp
Ideal bond angle & hybridization for an atom with 3 charge clouds?
Ideal angle: 120°
( if there’s a lone pair then <120° )
Hybridization: sp2
Ideal bond angle & hybridization for an atom with 4 charge clouds?
Ideal angle: 109.5°
( if there’s a lone pair then <109.5° )
Hybridization: sp3
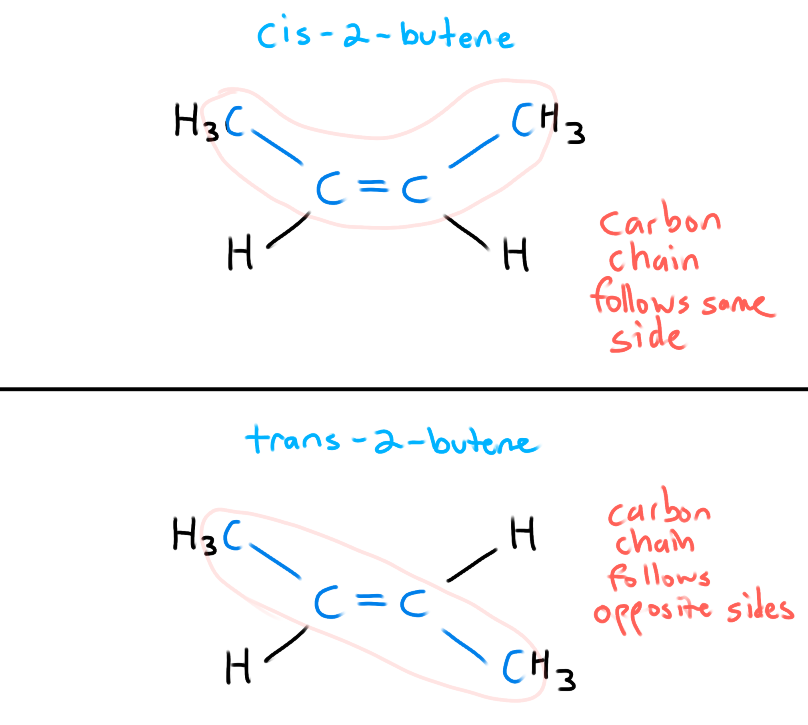
What is a cis and trans isomer?
Are sigma bonds formed by the overlap of orbitals of different atoms?
Yes. A sigma bond (σ bond) is formed by the overlap of orbitals from two different atoms
Are pi bonds formed by the overlap of orbitals of different atoms?
Yes. A pi bond (π bond) forms when p orbitals from different atoms overlap side-by-side
They don’t directly touch, but they interact with one another
Which has more bond energy, sigma or pi?
Sigma bonds have more bond energy than pi bonds because the overlap is stronger, creating a stronger, more stable bond.
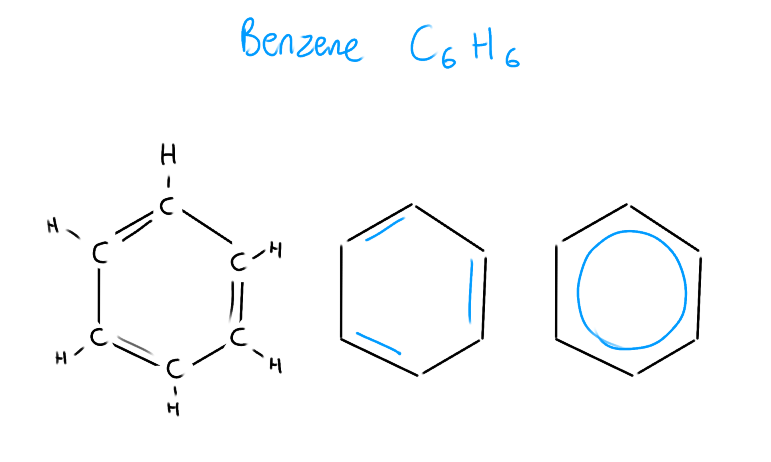
Recall: What is benzene and how do we draw it?
C6H6
CH in each corner
Alternating double bonds that can flip-flop
Each p-orbital overlaps with 2 different p-orbitals
The circle represents delocalization of e-
(Used to explain resonance)
What is Bond Polarity?
Shared e- spend more time around the most ELECTRONEGATIVE element in the bond
Gives the element with greater EN a partial negative charge, and the other with a partial positive EN
Are all molecules with a net charge polar?
Yes. A molecule with a net charge (ion) always has an uneven distribution of electrons, so it is polar.
How do we draw dipole arrows to represent polar bonds?
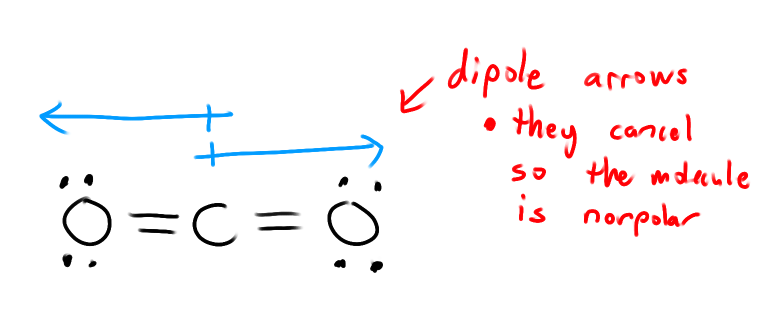
What is a dipole moment?
If a molecule is polar, it must have a dipole moment.
( If dipoles cancel, then no dipole moment, so nonpolar )
μ = Q x r
Q = absolute value of the net partial charge at each end of the molecule
r = distance between positive and negative poles of a molecule
Is the energy needed to break ionic bonds endothermic or exothermic?
Ionic bonds are strong, it requires a lot of energy. Very endothermic
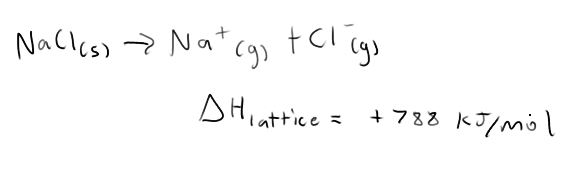
What affects the melting points of ionic solids?
Coulomb’s Law.
In this case, charges of ions affect the melting point more than the distance between the ions
(eg) MgI2 has a higher melting point than NaF because of the 2+ on the Mg, despite being bigger

Which compound in each set has the greatest melting point?
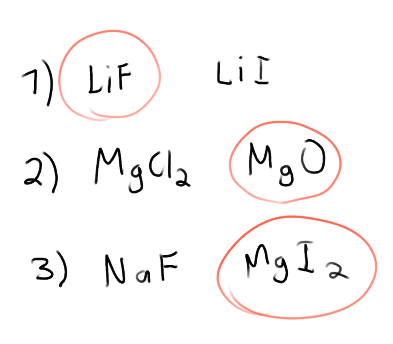
The amount of energy needed to break the bond between two atoms in a molecule is equal to..
The amount of energy released when the bond forms between the two atoms
Conservation of Energy
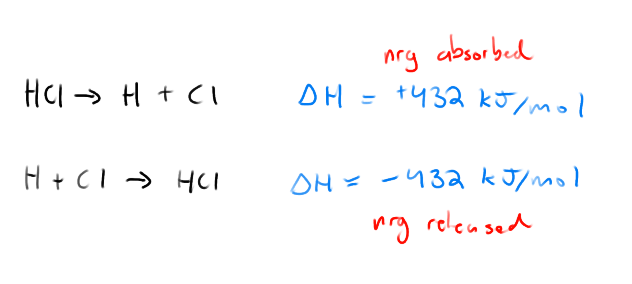
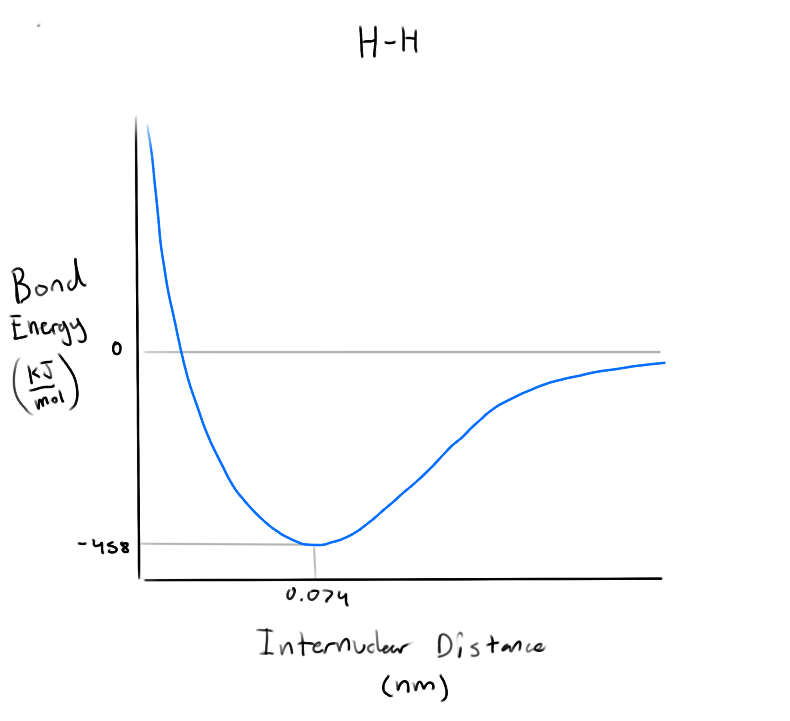
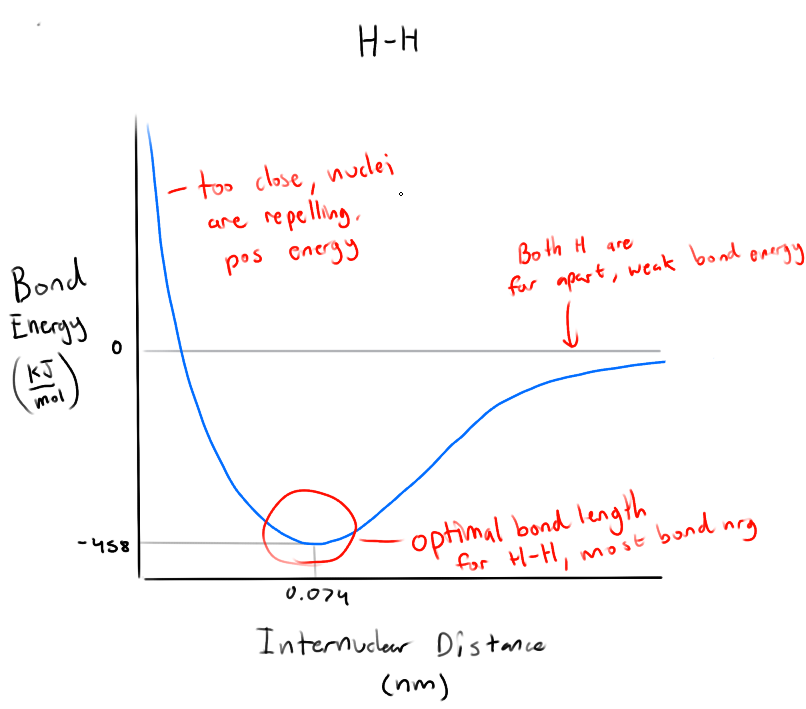
What does the graph of bond energy as a function of bond length tell us? (for H-H)
Lower the energy, more energy needed to break the bond
What do pi bonds do to the rotation of atoms?
Pi bonds prevent the rotation of bonded atoms around the bond axis.
This is because if it rotates, the pi bonds will break
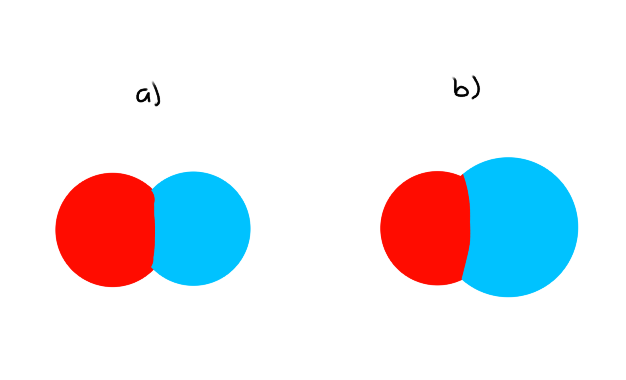
(eg) Space-Filling Model
Which molecule will have the least amount of PE?
Which bond has the lowest bond nrg?
a) Lowest amount of PE because the atomic radii are smaller, so the distance between each atom is smaller
b) Lowest bond energy because of the longer bond length (atomic radius is bigger)
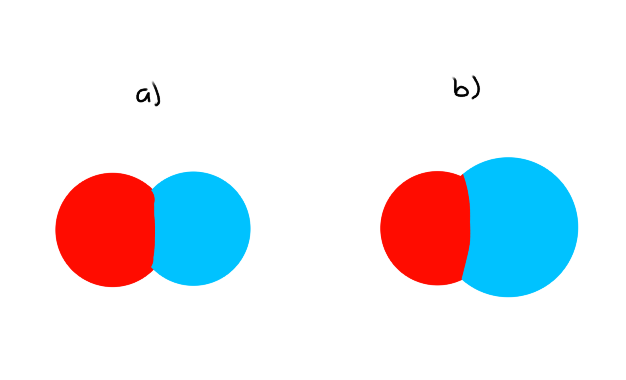
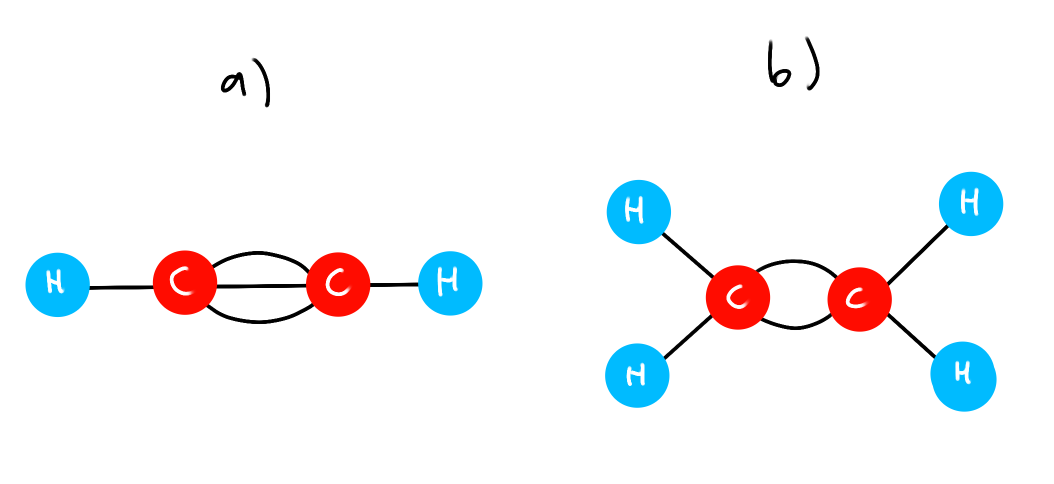
(eg) Ball and Stick model
Which C-C bond has the lowest PE?
Which C-C bond has lowest bond nrg?
a) Lowest PE because high bond order, less bond length, so less distance between the C atoms
b) Lowest bond nrg because a double bond is weaker than a triple bond
Intramolecular Forces vs Intermolecular Forces (IMF)
Intramolecular forces are bonds
Intermolecular forces are the attractions between different molecules
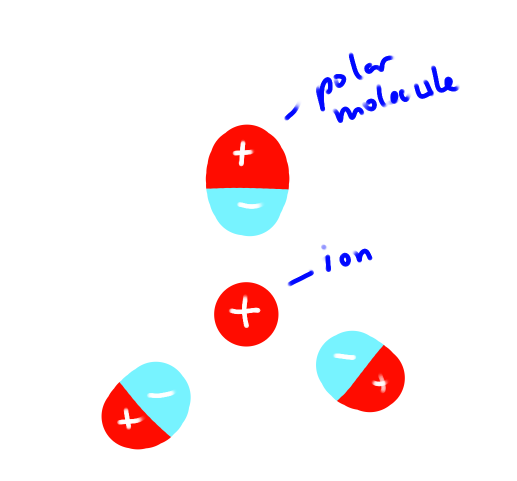
What is an Ion Dipole?
Forces of attraction between an ion and polar molecule.
It’s temporary
(eg) Na+ (aq)
Strength depends on Coulomb’s Law
Radii of ion
Charge of ion
Polar molecule dipole
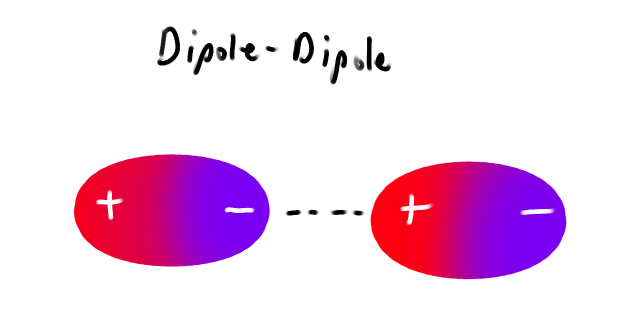
What is a Dipole-Dipole
Attractive forces between the (-) end of one polar molecule and the (+) end of another polar molecule
If they line up well (similar to an ionic solid structure) then they maximize coulombic attraction.
If they don’t line up well they will repel more.
What is a Hydrogen Bond
Occurs between a hydrogen that’s covalently bonded to Fluorine Oxygen or Nitrogen and another F, O or N with at least one lone pair
5-10 times stronger than other dipole-dipole attractions
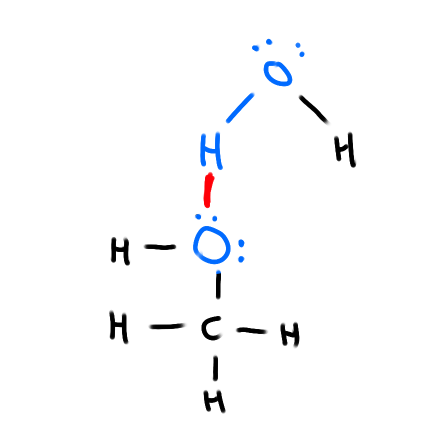
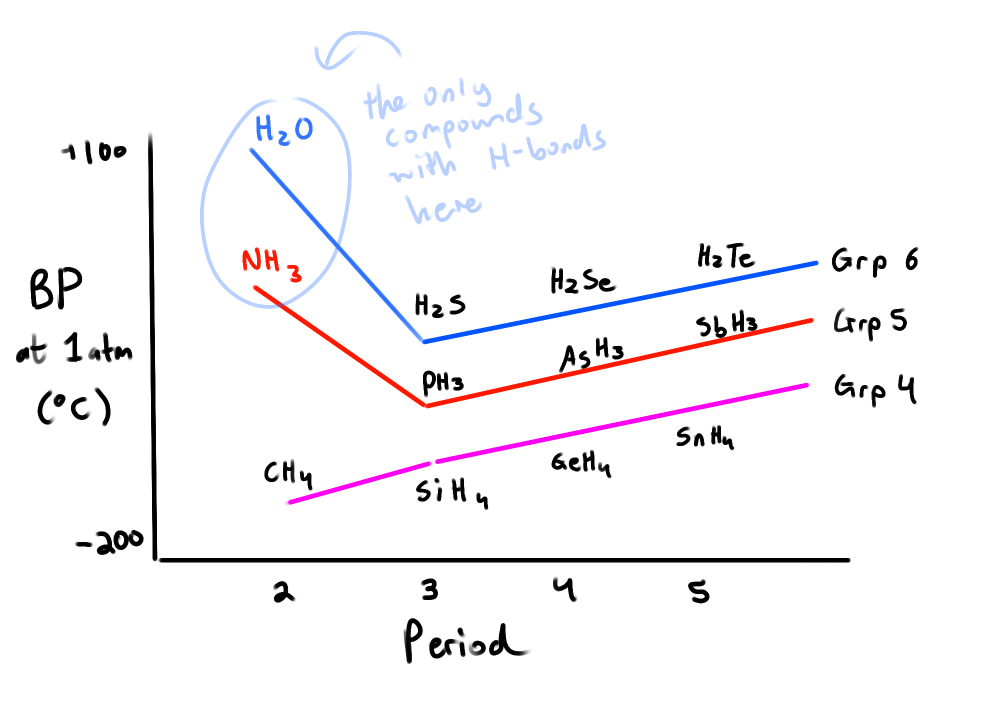
How does the boiling point of compounds with hydrogen change as you move across groups & periods?
Increases across a period
Increases across a group
EXCEPT for the compounds with H-bonds
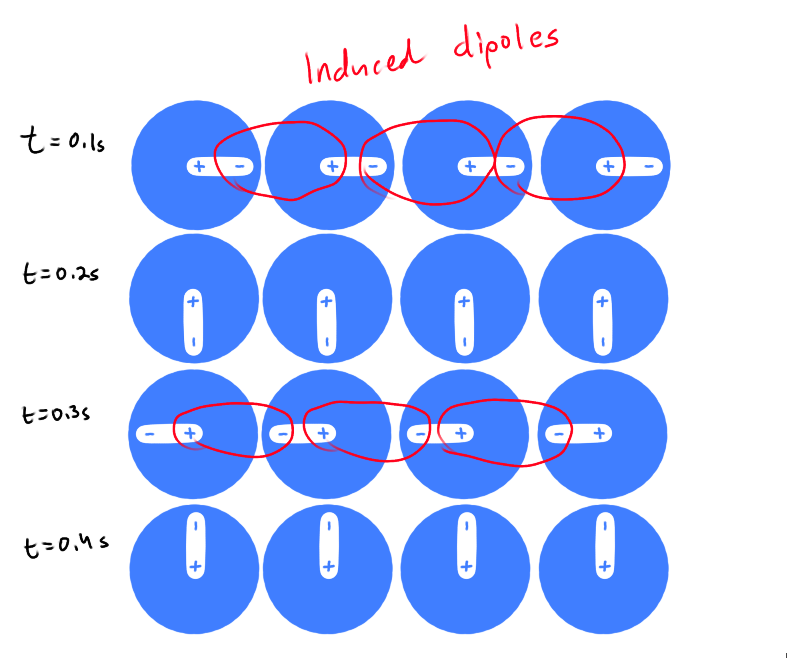
What is a Dipole-Induced Dipole / London Dispersion Forces?
These forces exist between all species/atoms
The only force that attract non-polar species together
Coulombic attractions between the temporarily induced dipoles of neighboring species that result from their electron distributions
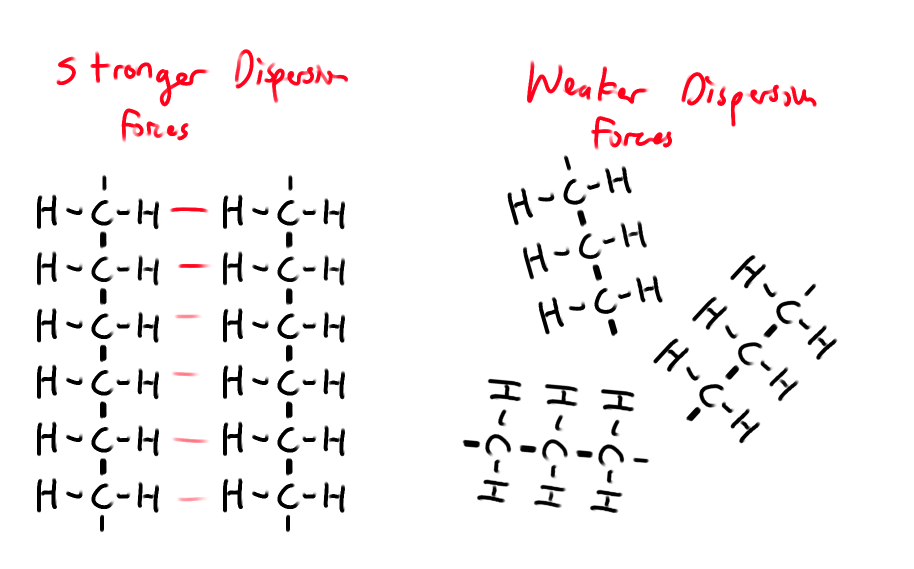
Why are species with more e- and larger e- clouds more polarizable?
The forces are stronger when the nonpolar molecules have bigger electron clouds/bigger molar mass (eg) C4H10 > C2H6
Weaker hold on outer electrons
Follows the trend of atomic radius
How does contact area between molecules affect London dispersion forces?
Dispersion Forces increase as the contact area between molecules increase.
How do Pi-Bonds affect polarizability?
Pi Bonds increase polarizability because they are more delocalized and help with polarization
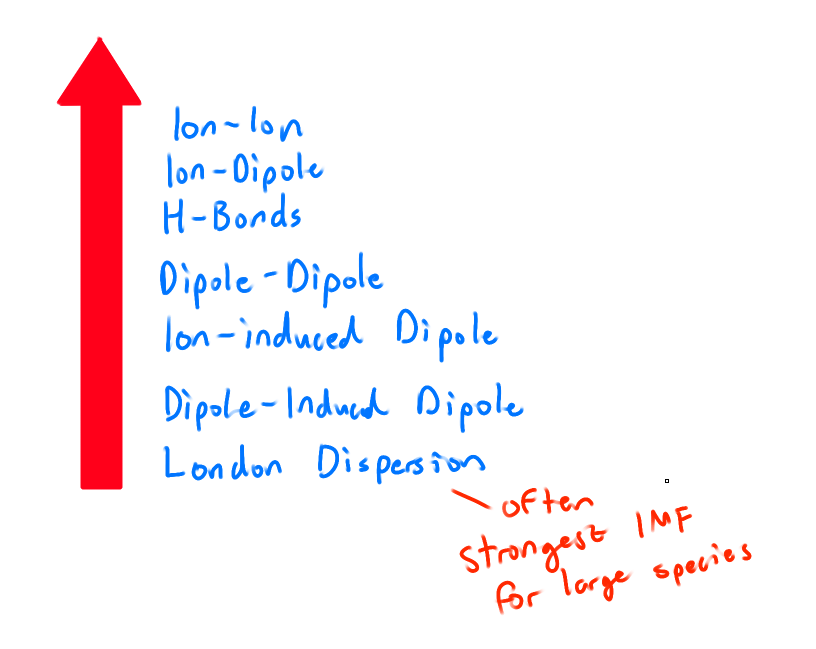
What is the order of the weakest to strongest IMFs?
What is the Born-Haber Cycle?
The compilation of the steps in forming a binary ionic compound.
The change in nrg of ionic bond formation is lattice energy
Lattice energy can be found by combining all the ΔH in the steps of forming an ionic compound
ΔHf = ΔH1 + ΔH2 + ΔH3 ….
ΔHf = overall change in energy/lattice energy
Lattice energy is positive(endo) when the IC is broken
Lattice energy is negative(exo) when the IC is formed
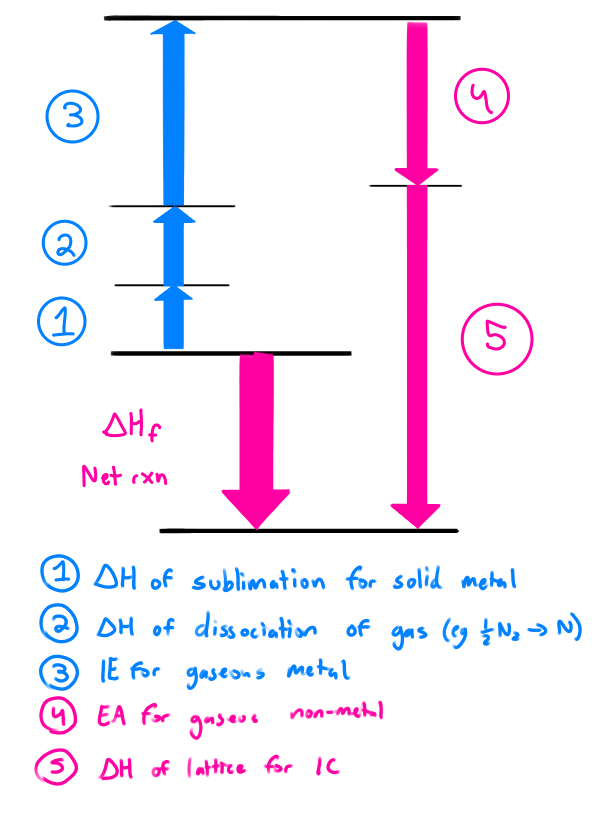
Example of Born-Haber Lattice energy calculation

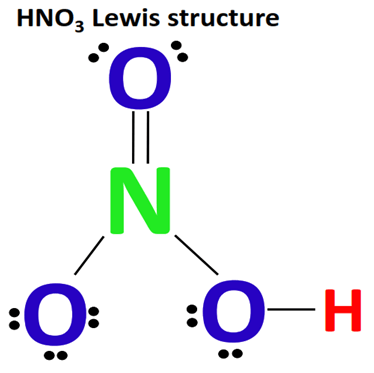
How do we make Lewis Structures for Acidic Species?
(eg) HNO3
The Hydrogen attaches to an outer O atom, NOT the central N atom
Why does CO have a dative bond?
Oxygen donates one pair of its lone pair e- to the empty p-orbital of carbon
Carbon forms a lone pair (it can’t bond any more)
[↑][↑][ ] —> [↑][↑][↑↓]
Carbon p-orbital before and after dative bond (oxygen gives 2 e-
![<p>Oxygen donates one pair of its lone pair e- to the empty p-orbital of carbon</p><p>Carbon forms a lone pair (it can’t bond any more)</p><p>[↑][↑][ ] —> [↑][↑][↑↓]</p><ul><li><p>Carbon p-orbital before and after dative bond (oxygen gives 2 e-</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7692dadd-f1f3-4a88-b344-dd4d2f04f58a.png)
What’s Hess’ Law?
If a rxn can be described as a series of steps, the overall ΔH is the sum of all ΔH of steps

What is Chemical Kinetics?
Area of chemistry concerned with rxn rates.
Certain factors affect how molecules in the rxn collide
Factors affecting reaction rates:
Physical State of reactants
Homogeneous phases react faster (same states)
Diff phase reactants, the rxn rate will depend on area of contact (think of granulated sugar vs sugar cube)
Increased surface area for solids increase rxn rate
Concentration of reactants
Faster if concentration of one or more reactants is greater
Reactant concentration is proportional to collision frequency, faster rxn rate
Temperature
temperature is proportional to rxn rate
KE of molecules increase
Catalyst
Agents that increase the rxn rate without being used up
Affects kinds of collision that lead to rxn
Catalysts provide alternate rxn path
Usually LOWER the activation nrg for a rxn by providing a diff rxn mechanism
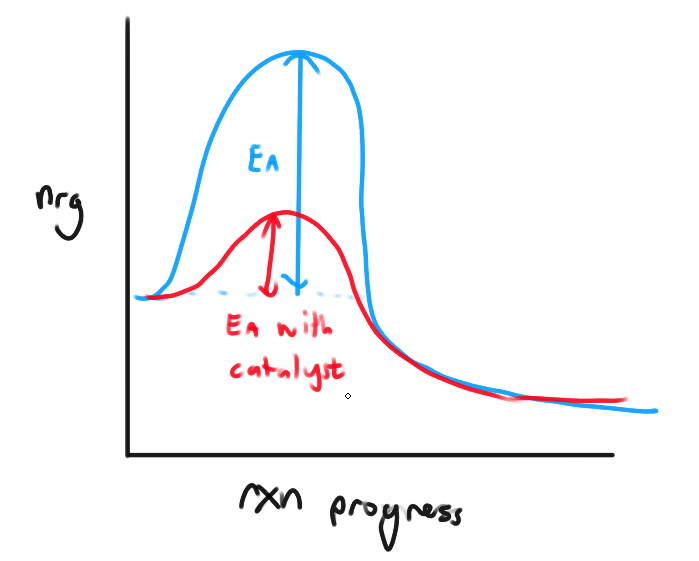
What two things must be satisfied for products to form?
Reactants must collide
Collisions must occur with appropriate energy and in correct orientation (like legos)
Rank all homogenous phases in order of decreasing rxn rates
(g) > (aq) > (l) > (s)
If the particles move faster, the rxn rate is faster
What signs do we assign to the rxn rates of the reactants and products?
negative for the reactants, they are disappearing
positive for the products, they are appearing

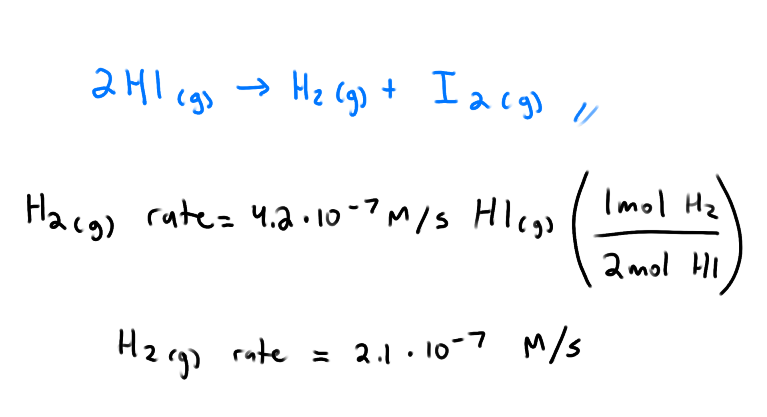
What are the rates of each species?
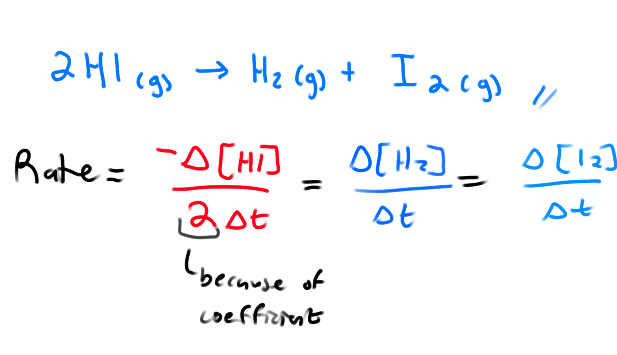
How many ways can the rate of a reaction be viewed?
Rate of disappearance of reactant
Rate of appearance of product
Rate at which the overall rxn proceeds
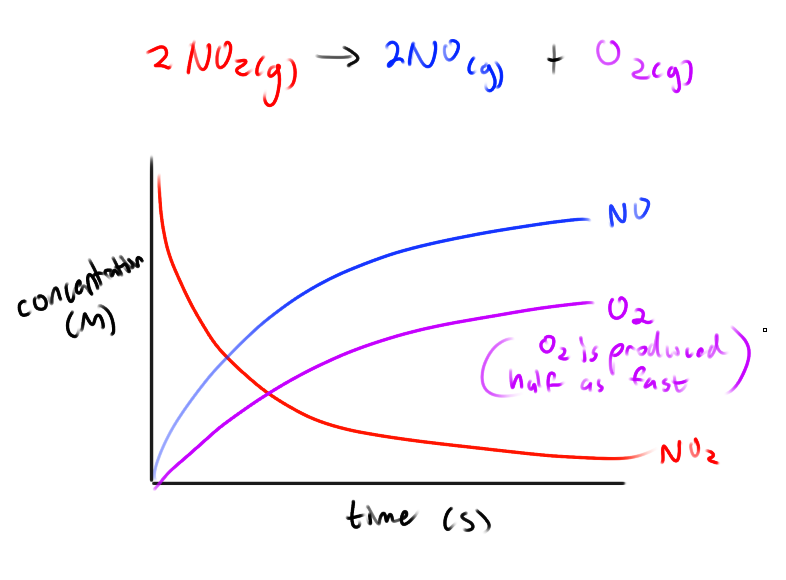
What do the graphs of concentration as a function of time look like for a reaction?
Not linear. The instantaneous rate is the slope of a tangent line at that point
What is the rate formula relating to the rate of disappearance/appearance of species? (not rate law)
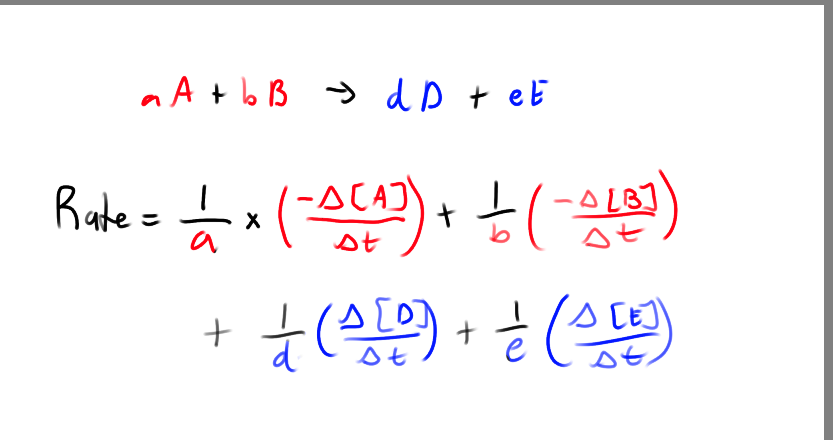
What is the rate law?

If the half life of a rxn is constant, what order is the rxn?
First order rxn
Formula is t1/2 = 0.693/k
k = rate constant
t1/2 = the halflife (time taken for half the material to disappear)

Is this a first order reaction?
Yes, because the half life is constant
How do the half-lifes for different order reactions change over time?
Zero-order: half-life decreases
First-order: half-life stays constant
Second-order: half-life increases
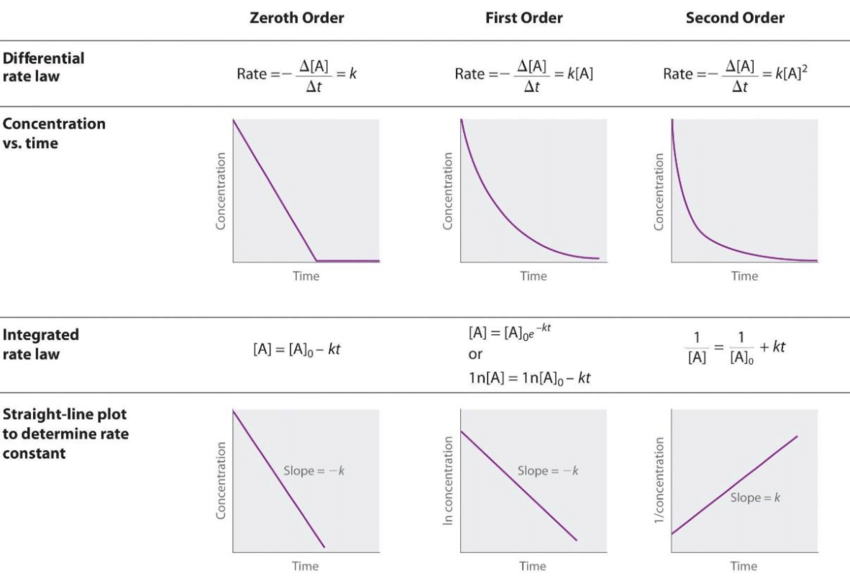
What is half life?
The amount of time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to drop to HALF its initial concentration
Faster rxn, shorter half life and vice versa
The half life for first order reactions is unaffected by initial concentration (half life is constant)

Does the gas pressure follow the half-life trend of the concentration?
Yes ( i think )
Units for the rate constant in each order?
Zeroeth order: Ms-1
First Order: s-1
Second Order M-1s-1
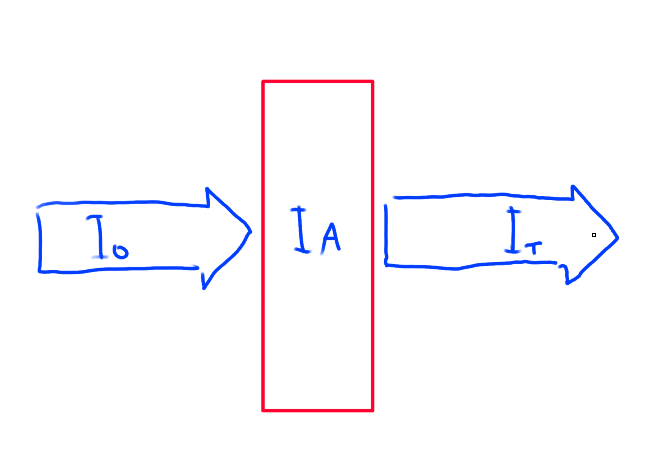
What is spectroscopy?
Method of analysis based on absorbance of EM radiation by matter
I0 = IT + IA
I0 - EM intensity striking sample
IT - EM intensity exiting sample
IA - EM intensity absorbed by sample
What is Beer Lamberts Law?
ONLY APPLIES TO COLOURED SPECIES
ε and b are constant most of the time
A = εbc
A = Absorbance
ε = molar absorptivity (M-1cm-1)
b = path length of sample (width usually) (cm)
c = concentration (M)
How do we draw reaction profile graphs?
LABEL:
x-axis (Rxn Progress)
y-axis (PE) [kJ/mol]
PEreactants
PEproducts
Ea (forward and reverse)
AC (activation complex)
Enthalpy (ΔHrxn)
![<p>LABEL:</p><ol><li><p>x-axis (Rxn Progress)</p></li><li><p>y-axis (PE) [kJ/mol]</p></li><li><p>PE<sub>reactants</sub></p></li><li><p>PE<sub>products</sub></p></li><li><p>Ea (forward and reverse)</p></li><li><p>AC (activation complex)</p></li><li><p>Enthalpy (ΔH<sub>rxn</sub>)</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4c43411b-dd31-43d7-9baa-0a19ed322d13.png)
What equations should you remember relating to Rxn Profile Graphs?
ΔHrxn = ΔHprod - ΔHreac
AC = ΔHreac + Eaf
AC = ΔHprod+ Ear
How do we calculate Activation Energy given two rate constants and temperatures?
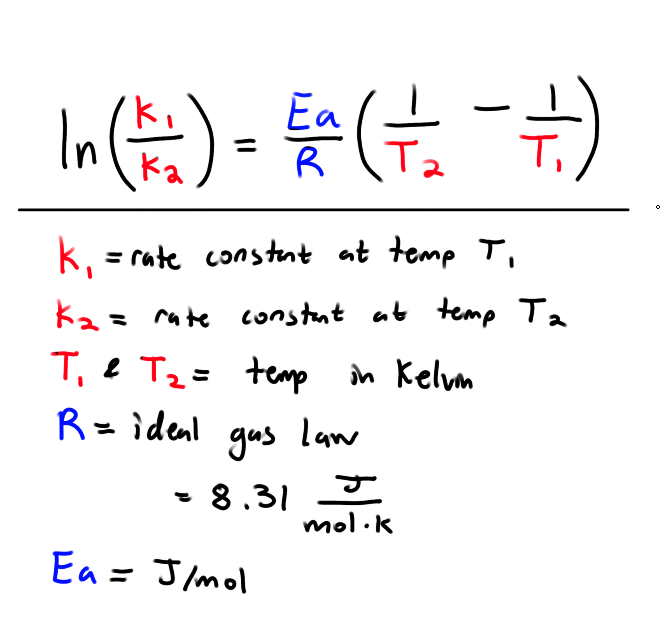
Recall: What is the universal gas constant?
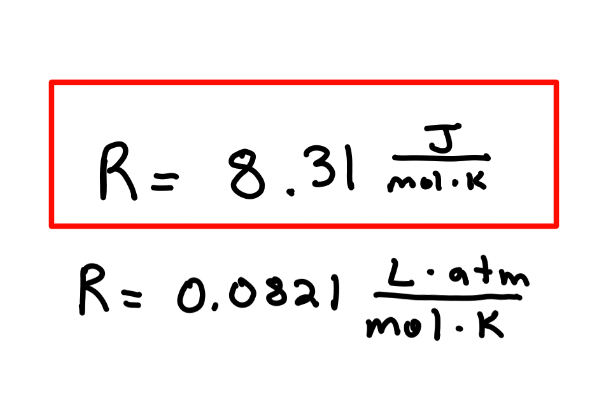
What is the Collision Theory?
Molecules must collide to react
Collisions must have the correct orientation
Collisions must have enough energy
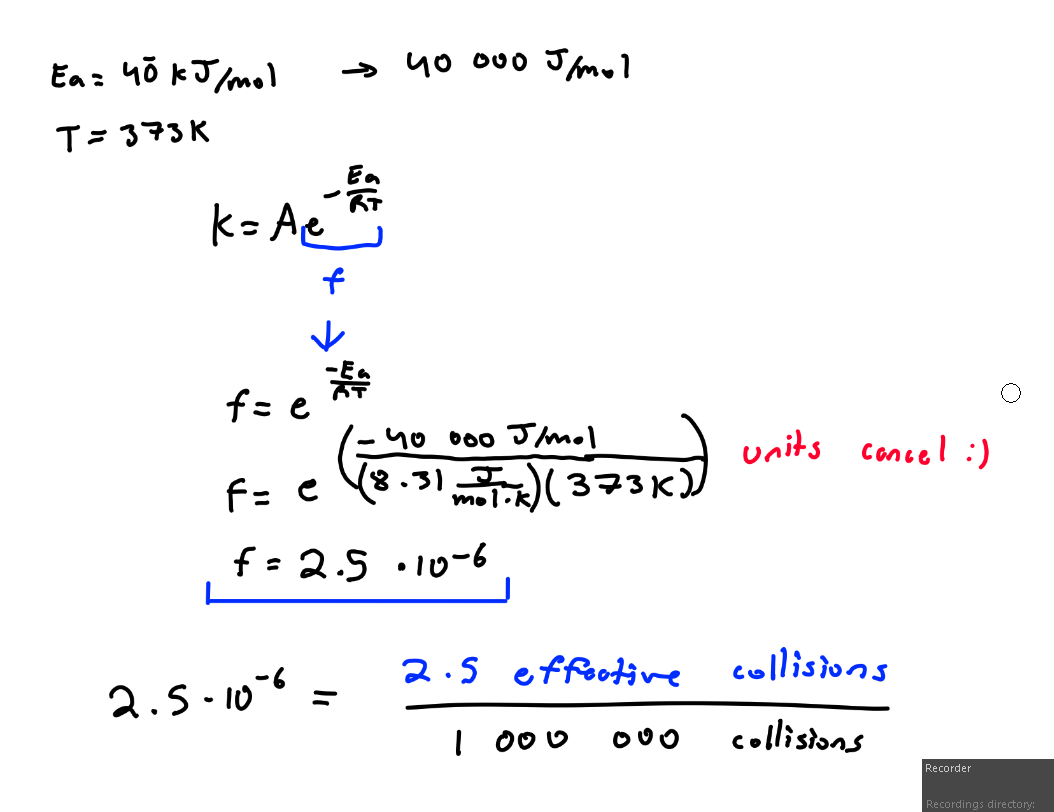
What’s the Arrhenius Equation?
Used to determine how many collisions in the rxn have enough nrg to react. The number of effective collisions.

Given Ea = 40 kJ/mol, T = 373K
Find the frequency factor. (2 sigfigs)