Geol 126 midterm 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/101
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
What is science?
discovery, world is understandable through observations
2
New cards
belief knowledge
knowledge unique to each person
3
New cards
research knowledge
universal knowledge, observable and measurable
4
New cards
good science
doubt, recognize biases, several theories may be raised to explain one observation
5
New cards
observation
facts that should be repeatable from one person to the next
6
New cards
interpretation
hypotheses invented to explain observations
7
New cards
pseudoscience
reference to authority rather than observation, use science to promote a message even though its not based on science
8
New cards
plate tectonics theory
outer portion of the earth is broken into plates
9
New cards
What is a rock?
An aggregate of minerals and mineraloids
10
New cards
What is a mineral?
* Naturally occurring
* inorganic solid
* orderly internal structure (crystal lattice)
* definite chemical composition
* inorganic solid
* orderly internal structure (crystal lattice)
* definite chemical composition
11
New cards
whole earth composition
* iron 32%
* oxygen 30%
* silicon 15%
* magnesium 14%
* sulfur 3%
* oxygen 30%
* silicon 15%
* magnesium 14%
* sulfur 3%
12
New cards
most common silicate materials
quarts and feldspar
* example: granite
* example: granite
13
New cards
earth’s core
solid inner iron core
less dense matter began to flow up from the core to make up the surface
deeper into the core, temps rise and pressure increases
accretion (solids form large objects-planets) , differentiation (melting, separates materials, heavier sink-core and lighter rise-crust), contraction (shrinkage from cooling)
less dense matter began to flow up from the core to make up the surface
deeper into the core, temps rise and pressure increases
accretion (solids form large objects-planets) , differentiation (melting, separates materials, heavier sink-core and lighter rise-crust), contraction (shrinkage from cooling)
14
New cards
crust composition
* Oxygen 47% (O)
* Silicon 28% (Si)
* Aluminum 8% (Al)
* Iron 5% (Fe)
* Calcium 4% (Cl)
* Sodium 3% (Na)
* Potassium 2.5% (K)
* Magnesium 2% (Mg)
* Silicon 28% (Si)
* Aluminum 8% (Al)
* Iron 5% (Fe)
* Calcium 4% (Cl)
* Sodium 3% (Na)
* Potassium 2.5% (K)
* Magnesium 2% (Mg)
15
New cards
common non-silicate minerals
carbonates, oxides, halides (salts), sulfates, sulfides, minerals composed of one element (gold, copper, sulfur)
16
New cards
coal
mineraloid NOT a mineral, made from plants- organic matter
17
New cards
3 types of rocks
igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
18
New cards
igneous rocks
* a melted rock that cools and hardens
19
New cards
What is the difference between magma and lava?
* Magma: molten rock beneath the surface
* pluton- glob of magma
* sill- magma travelling horizontally
* dike- magma traveling vertically
* Lava: molten rock erupted onto the surface
* pluton- glob of magma
* sill- magma travelling horizontally
* dike- magma traveling vertically
* Lava: molten rock erupted onto the surface
20
New cards
two kinds of igneous rocks
* intrusive - cool slowly beneath earth surface
* extrusive, cool quickly on earth surface
* extrusive, cool quickly on earth surface
21
New cards
sedimentary rocks
* made of disaggregated bits of other rock
* form at the earth’s surface
* form at the earth’s surface
22
New cards
sedimentary rock process
* weathering attacks preexisting rocks and produces sediment
* sediment transported by either water, wind, or ice and pile up
* deposited- delivered and stops moving
* once in rest needs to be buried to become a rock
* sediment transported by either water, wind, or ice and pile up
* deposited- delivered and stops moving
* once in rest needs to be buried to become a rock
23
New cards
clastic sedimentary rocks
made from grains (pieces) that came from weathering
* defined by grain size
* sediment: gravel, sand, silt, clay
* after burial: conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, shale
* defined by grain size
* sediment: gravel, sand, silt, clay
* after burial: conglomerate, sandstone, siltstone, shale
24
New cards
chemical sedimentary rocks
made from chemicals that came from weathering of rocks
* chemicals from fluids, and if concentration is high enough, becomes minerals
* ex: carbonates- limestone
* chemicals from fluids, and if concentration is high enough, becomes minerals
* ex: carbonates- limestone
25
New cards
metamorphic rocks
heat and pressure cause preexisting rocks to change
* occurs in solid NOT melted state
* protolith (og rock)>> heat and pressure>> metamorphic rock
* occurs in solid NOT melted state
* protolith (og rock)>> heat and pressure>> metamorphic rock
26
New cards
rock processes
* uplift and weathering
* burial and cementation and compaction
* heat and pressure
* melting
* cooling and crystallization
* burial and cementation and compaction
* heat and pressure
* melting
* cooling and crystallization
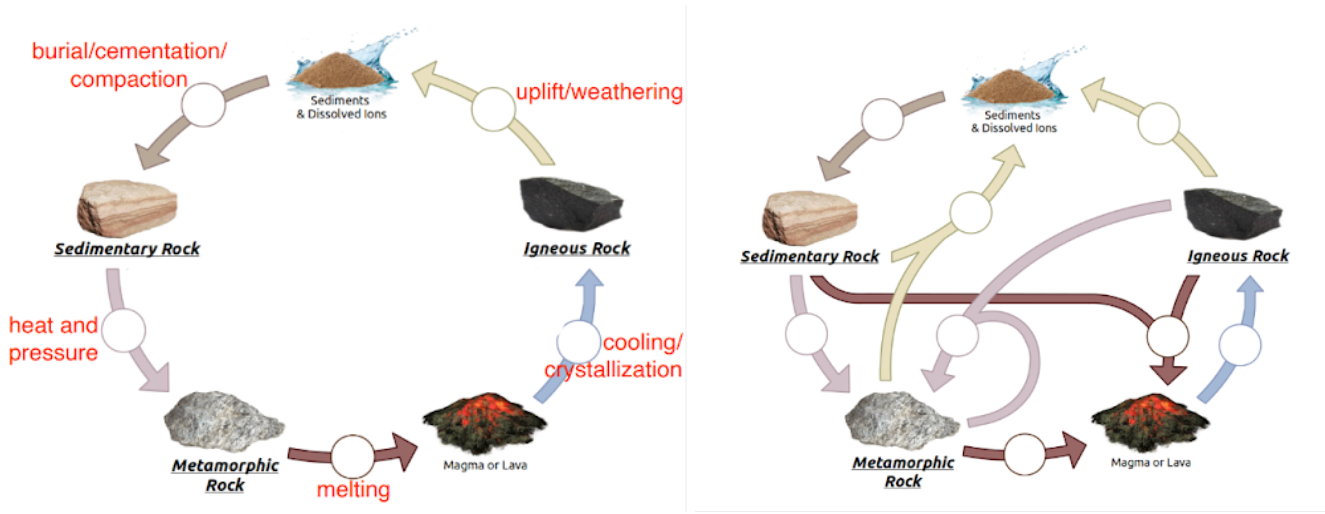
27
New cards
plate tectonics theory
outer portion of earth is broken into plates
* plates move and interact
* plates move and interact
28
New cards
3 kinds of plate boundaries
divergent, convergent, transform
29
New cards
divergent boundary
plates pull apart resulting in the formation of new crust from magma
* passive margin (no effects)
* where?
* ocean, rising magma is cooled by water
* passive margin (no effects)
* where?
* ocean, rising magma is cooled by water
30
New cards
convergent boundaries
when plates collide, plates smash together
31
New cards
types of convergent boundaries
* Ocean Crust vs. Continental Crust
* Oceanic crust will always subduct because it is more dense(volcanos arise from subducting crust)
* Continental Crust vs. Continental Crust
* They collide resulting in the build up of mountains, produce earthquakes
* Oceanic Crust vs. Oceanic Crust
* older plate will give up and be subducted under the younger plate, formation of volcanic islands
* Oceanic crust will always subduct because it is more dense(volcanos arise from subducting crust)
* Continental Crust vs. Continental Crust
* They collide resulting in the build up of mountains, produce earthquakes
* Oceanic Crust vs. Oceanic Crust
* older plate will give up and be subducted under the younger plate, formation of volcanic islands
32
New cards
transform boundary
plates slide past each other, earthquake!
33
New cards
plate tectonics evidence: divergent
mid ocean ridges, age of ocean crust
34
New cards
plate tectonics evidence: convergent
earthquakes, volcanoes
35
New cards
general plate tectonics evidence
hot spots and magnetic strips
36
New cards
importance of plate tectonics
control rock cycle
37
New cards
environment
set of conditions that exist today in a particular location
* controls sorting of sediment
* energy of env controls grain size
* controls sorting of sediment
* energy of env controls grain size
38
New cards
Sorting of sediment
* Windblown sand: very well sorted
* Beach sand: well sorted
* River sand: moderately sorted
* Glacial sediments: very poorly sorted
* Beach sand: well sorted
* River sand: moderately sorted
* Glacial sediments: very poorly sorted
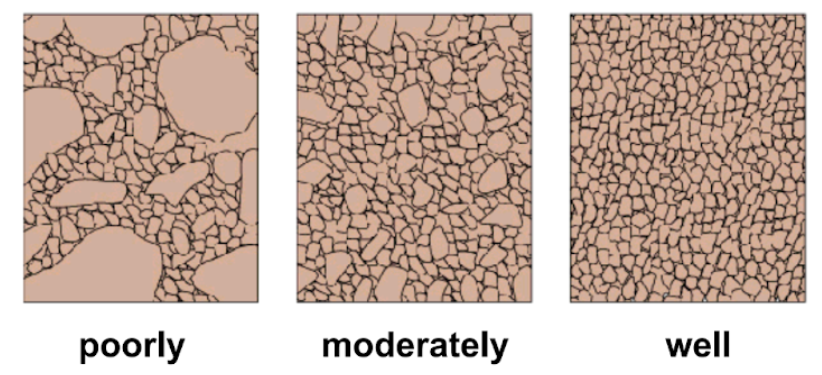
39
New cards
terrestrial environment
on land NOT in the ocean
40
New cards
coastal environment
shallow marine environments, lots of fossils come from here
41
New cards
marine environment
deep sea
42
New cards
paleoenvironments
ancient environments
43
New cards
high energy environment
moves large sediment pieces
* gravel>> conglomerate
* gravel>> conglomerate
44
New cards
intermediate energy environment
movement, but not too much, can move sediment
* sand>> sandstone
* sand>> sandstone
45
New cards
low energy environment
can’t really move sediment pieces
* fine grained sediment
* silt-clay>> siltstone-shale
* fine grained sediment
* silt-clay>> siltstone-shale
46
New cards
sedimentary structures
physical features formed during sediment transport/ deposition
* flat laminations
* ripples
* dunes
* mud cracks
* raindrop impressions
* flat laminations
* ripples
* dunes
* mud cracks
* raindrop impressions
47
New cards
Flat laminations
grains fall out of suspension
* low energy/ quiet water
* low energy/ quiet water
48
New cards
asymmetric ripples
flow in one direction
* cross strata dip in direction of flow
* sediment will be coarser
* not flat or parallel
* medium energy
* cross strata dip in direction of flow
* sediment will be coarser
* not flat or parallel
* medium energy
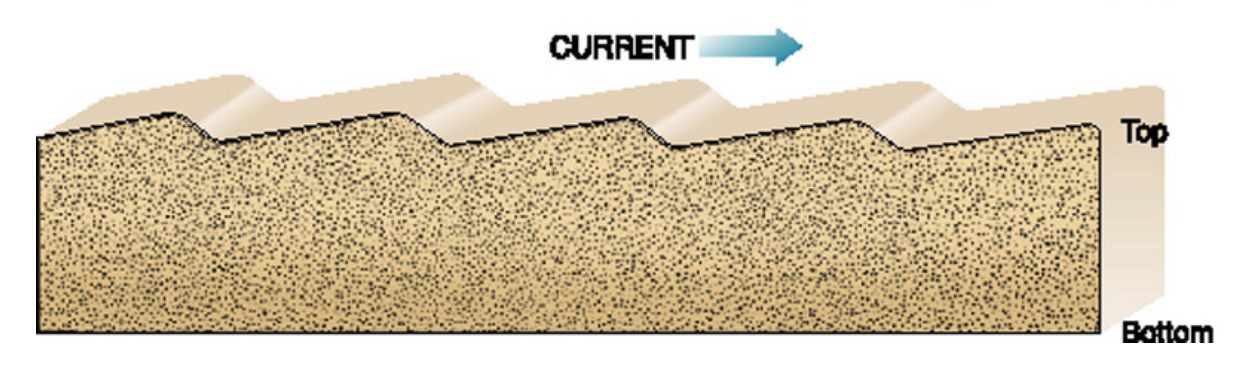
49
New cards
symmetric ripples
back and forth flow
* tuning fork
* medium energy
* tuning fork
* medium energy
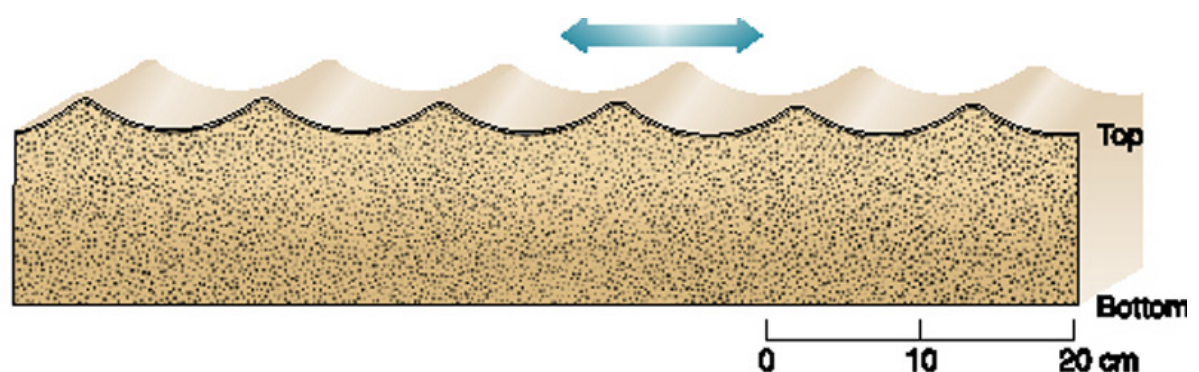
50
New cards
dunes
* asymmetrical
* constrained by depth of flow (air), so can get huge!
* subaerial (windblown)
* high energy
* constrained by depth of flow (air), so can get huge!
* subaerial (windblown)
* high energy
51
New cards
mud cracks
environment dried out!
* no flow and indicates water depth
* no flow and indicates water depth
52
New cards
raindrop impressions
environment dried out but it was also raining
53
New cards
eolian wind environments
* well sorted
* major rock types; sandstone
* frosted grains bc sand is hitting against it
* major rock types; sandstone
* frosted grains bc sand is hitting against it
54
New cards
beaches
* well sorted sandstones
* symmetric ripples indicating oscillatory flow
* symmetric ripples indicating oscillatory flow
55
New cards
braided river
* major rock types: sandstone and conglomerates
* high energy
* moderately to poorly sorted
* asymmetric cross bedding
* murky water bc fine grain is carried by water
* high energy
* moderately to poorly sorted
* asymmetric cross bedding
* murky water bc fine grain is carried by water
56
New cards
glacial environment
* major rock type: tillite
* poorly sorted
* high energy
* rocks are faceted instead of rounded
* flattened instead of like in water where its rounded
* poorly sorted
* high energy
* rocks are faceted instead of rounded
* flattened instead of like in water where its rounded
57
New cards
nils stensen
fossils were remains of past organisms by using the shark tooth
* 17th century
* 17th century
58
New cards
kinds of fossils
body, trace and chemical
59
New cards
body fossils
physical remains of an organism
* ex: shells, bones, compressed plants, petrified wood
informs about morphology
* what It could do when it was alive
* ex: shells, bones, compressed plants, petrified wood
informs about morphology
* what It could do when it was alive
60
New cards
trace fossils
evidence of activity
* not the organism itself
* ex: footprints, worm trails, coprolites (fossil poop)
informs about what the organism did and how it interacted with the environment
* not the organism itself
* ex: footprints, worm trails, coprolites (fossil poop)
informs about what the organism did and how it interacted with the environment
61
New cards
chemical fossils
chemical evidence of past life
* ex: isotopic signatures, organic molecules attributed to life
* only certain chemicals made by life or certain groups
* ex: cholesterol or remains of cholesterol
* informs metabolism
* ex: isotopic signatures, organic molecules attributed to life
* only certain chemicals made by life or certain groups
* ex: cholesterol or remains of cholesterol
* informs metabolism
62
New cards
isotope
Element with same number of protons, different number of neutrons
* life tends to prefer lighter isotopes
* concentration of 12C in a rock could indicate the past presence of life, and would represent a chemical fossil
* life tends to prefer lighter isotopes
* concentration of 12C in a rock could indicate the past presence of life, and would represent a chemical fossil
63
New cards
fossilization potential
* bias towards hard parts rather than soft parts
* bias towards low energy
* bias towards ocean rather than land
* bias towards low energy
* bias towards ocean rather than land
64
New cards
taphonomy processes
* occurs after the organism dies but before it becomes a fossil
* organism must survive this process to become a fossil
* organism must survive this process to become a fossil
65
New cards
types of taphonomy processes
* Biologic attack
* Ex. Borers, scavengers
* Mechanical attack
* Ex. High energy environments
* Chemical attack
* Ex. Weathering
* Ex. Borers, scavengers
* Mechanical attack
* Ex. High energy environments
* Chemical attack
* Ex. Weathering
66
New cards
Steno’s conclusion about geologic time
superposition and original horizontality
67
New cards
superposition
oldest layer at the bottom with successively younger layers above
68
New cards
original horizontality
Sedimentary rocks form horizontal layers \n Thus, inclined sedimentary rocks suffered subsequent disturbance (tectonics!)
69
New cards
crosscutting relationships
Something that cuts across or affects another layer must be younger than the material that’s being affected
70
New cards
stratigraphic columns
Environmental description of each layer
71
New cards
fossil succession
George Cuvier- 1800s
* fossils occur in an order
* some appeared in a layer and then never appeared again
* extinction!
William Smith- 1800s
* rock types change from place to place
* young with young fossil and old with old fossil, always!
* fossils occur in an order
* some appeared in a layer and then never appeared again
* extinction!
William Smith- 1800s
* rock types change from place to place
* young with young fossil and old with old fossil, always!
72
New cards
index fossils
widespread
short lived
can subdivide geologic time into smaller units
* relative time, no date, just sequence of events
short lived
can subdivide geologic time into smaller units
* relative time, no date, just sequence of events
73
New cards
geologic time scale
a record of geologic events and life forms in Earth’s history
* relative
* relative
74
New cards
Eon
Phanerozoic
75
New cards
era
in order from youngest to oldest
* Cenozoic (age of mammals)
* Mesozoic (age of dinosaurs)
* Paleozoic (age of tribolites)
* Cenozoic (age of mammals)
* Mesozoic (age of dinosaurs)
* Paleozoic (age of tribolites)
76
New cards
Paleozoic periods
in order from youngest to oldest
* Permian
* Carboniferous
* Devonian
* Silurian
* Ordovician
* Cambrian
* Permian
* Carboniferous
* Devonian
* Silurian
* Ordovician
* Cambrian
77
New cards
Mesozoic periods
in order from youngest to oldest
* Cretaceous
* Jurassic
* Triassic
* Cretaceous
* Jurassic
* Triassic
78
New cards
Cenozoic periods
in order from youngest to oldest
* Neogene
* Paleogene
* Neogene
* Paleogene
79
New cards
relative time
* The sequence in which events took place
* Chronostratigraphic
* Chronostratigraphic
80
New cards
absolute time
* the actual time (usually measured in years) as determined by radiometric age dating
* Chronometric
* Chronometric
81
New cards
What rocks can be radiometrically dated?
Igneous and Metamorphic
82
New cards
time vs rock
time is continuous but abstract and rock is discontinuous but tangible
83
New cards
meteorites
leftover bits from the formation of solar system
84
New cards
sedimentary record
* sediment accumulation rate varies from place to place
* gives snapshots versus continuous record
* gives snapshots versus continuous record
85
New cards
taxonomy
* the science of classifying organisms
* looks for differences
* looks for differences
86
New cards
phylogeny
the study of the (evolutionary) relationships between groups of organisms
* looks for similarities
* looks for similarities
87
New cards
species
* Basic unit of taxonomy and phylogeny
* Biologic definition
* A population of organism capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
* Genetic definition (better)
* Based on the similarity of DNA in a population
* % of similarity
* Biologic definition
* A population of organism capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring
* Genetic definition (better)
* Based on the similarity of DNA in a population
* % of similarity
88
New cards
morphological species concept
based on similarity of appearance
* morphology = shape
* DNA encodes for shape
* Genes control shape, genes control morphology, so both concepts linked
* morphology = shape
* DNA encodes for shape
* Genes control shape, genes control morphology, so both concepts linked
89
New cards
cladistics
based on parsimony
* simplest is the best
* branching, things don’t directly change, different branches to create more diversity
* simplest is the best
* branching, things don’t directly change, different branches to create more diversity
90
New cards
cladistics vs parsimony
min steps are the best, fewer assumptions
step 1: define characters of taxa
* find characteristic that is either exclusive or common
step 2: construct character matrix
* quantitively assign characteristics to the taxa
step 3: construct tree using parsimony
* how closely taxa are related to each other based on how many characteristics they share
step 1: define characters of taxa
* find characteristic that is either exclusive or common
step 2: construct character matrix
* quantitively assign characteristics to the taxa
step 3: construct tree using parsimony
* how closely taxa are related to each other based on how many characteristics they share
91
New cards
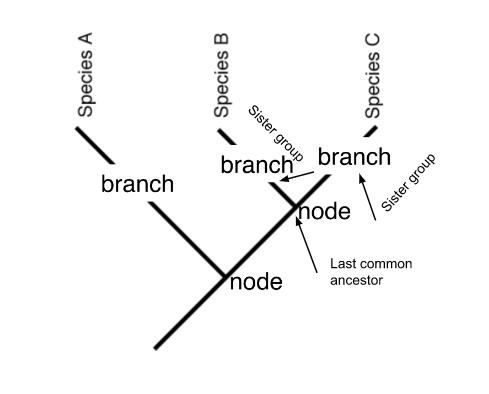
parsimony tree
clade- include the common ancestor and ALL its descendants
92
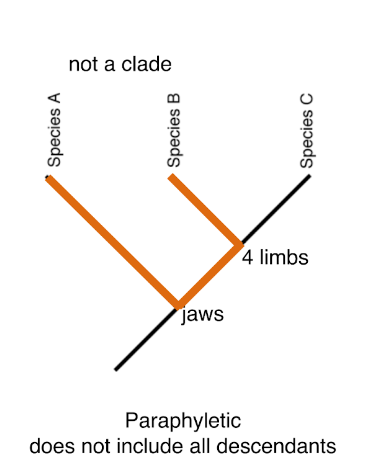
New cards
paraphyletic
does not include all descedants
93
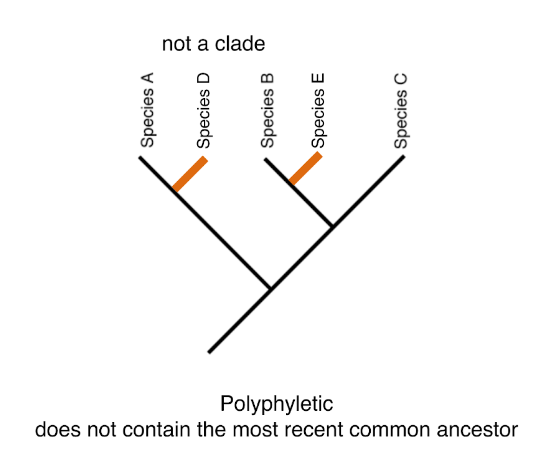
New cards
poyphyletic
does not contain the most recent common ancestor
94
New cards
DNA
* deoxyribonucleic acid
* the blueprint for life
* polymer of nucleotides
* the blueprint for life
* polymer of nucleotides
95
New cards
central dogma of biology
DNA>> RNA>> Protein
96
New cards
who discovered dna?
Rosalind Franklin, James Watson and Francis Crick
97
New cards
code of DNA
pairs of 4 nucleotides
* Sequence of dna catalogs the order of adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine (nucleotides)
* A+t and g+c, only!
* Sequence of dna catalogs the order of adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine (nucleotides)
* A+t and g+c, only!
98
New cards
Replication of DNA
DNA Polymerase copies DNA very accurately
99
New cards
Transcription of DNA
* RNA Polymerase converts DNA to mRNA
* Genes are transcribed into mRNA
* Genes are transcribed into mRNA
100
New cards
Translation of DNA
* Ribosomes translate mRNA into proteins