chapter 20: the heart
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
pericardium
the membrane around the heart, fibrous sac, opaque (not see-through)
2 layers of pericardium
fibrous sac (outside)
serous lining
fibrous sac
outer layer of pericardium - cannot stretch
so if pericardial space fills with fluid, the heart will squeeze
serous lining
second layer of pericardium - serum
produced all the little serous exudate → helps hear beat with no interruption
pericardial shape should have a little fluid, just enough to make it moist
heart layers
epicardium
myocardium
endocardium
epicardium (epi=outside)
thin membrane under the visceral layer of the pericardium
thin, flexible, not super protective
outermost layer
myocardium (myo=muscle)
bulk/mass of heart; cardiac muscle (striated)
thicker on left side (side that produces blood to body)
endocardium (endo=inner)
line heart chambers
forms valves of the heart
inner lining of heart
thickens in heart disease/infection
→ continuous with endothelium (lining of BVs)
platelet plugs in hemostasis stick to this (endothelium)
blood vessels are either
arteries or veins
why is the top of the heart thicker
where blood goes in and out
arteries
take blood away from the heart
thicker walled
veins
return blood to the heart
some goes to lungs to be oxygenated
sinus
a space
superior vena cava
brings blood from head/neck (any tissues above neck), dumps into RA
inferior vena cava
brings blood from body parts below heart, dumps into RA
is the heart an organ?
yes
cardiac veins
go to coronary sinous
all venous blood in heart collects in cardiac veins, dumps into coronary sinus (at the entrace to RA)
“3rd vein” → 3rd source of blood coming into the RA
4 pulmonary veins
bring blood from lungs, go to LA → base of heart
have high O2 b/c just picked it up from lungs to be pumped to the body
still return to heart despite having high )2
aorta
biggest artery
exits on left side of heart
when it comes out it branches (aortic arch) to supply high O2 blood to body
sends arterial blood to all tissues
opposite of vena cavas
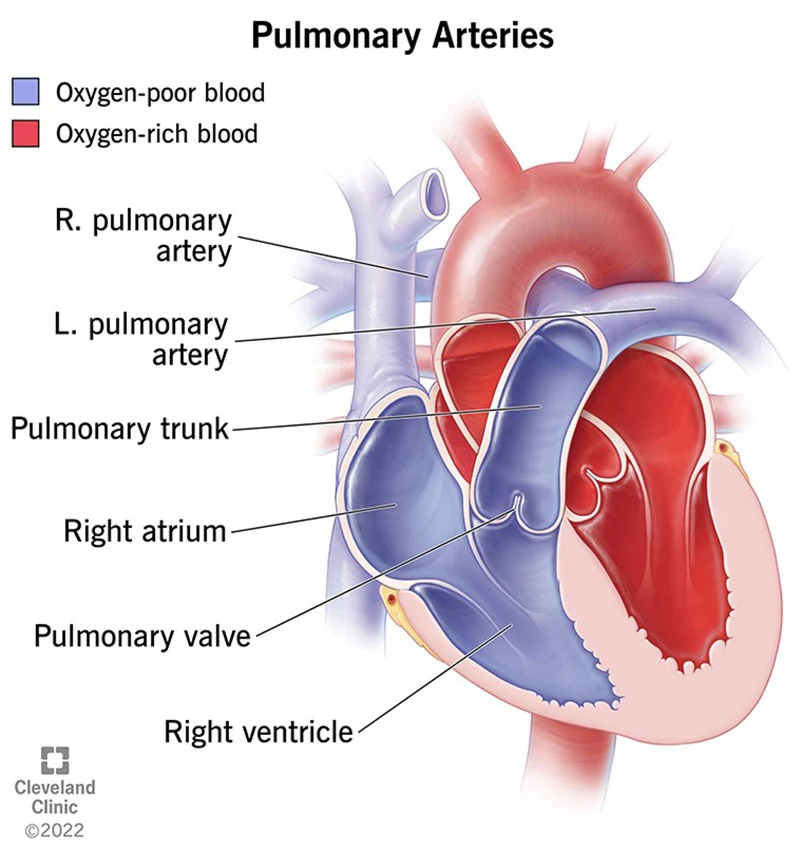
pulmonary trunk/artery
leave the heart to go to the lungs
start deep in the heart, comes up
splits to R/L arteries after leaving heart
comes out RIGHT side to go to lungs
coronary arteries
go to heart muscle
valves
keep blood going in one direction so nothing leaves going in the wrong direction
chambers close as soon as blood is done pumping
semilunar valve
tiny flaps, look like a cup (not solid)
made of endocardium → should see right through them
pused open, heart relaxes, fall back down to collect blood
2 types
aortic __
pulmonic
aortic semilunar valve
in BV heart, keep blood on its way
pumonary semilunar valve
leaving the pulmonary trunk
atrioventricular
as venous comes into the heart, thin endocardium, but have 2 structures attached to them
chordae tendinae
papillary muscles: inside heart chamber
Left AV valve (bicuspid) (mitral)
right AV valve (tricuspid)
left AV valve
mitral valve/bicuspid
when blood comes through pulmonary veins, comes through this
auricles
extra pouches on the outside of the heart - involved with heart conditions; not involved with the direction of flow
chordae tendinae
anchor the AV valves to ventricular papillary muscles and keep the AV valves closed during ventricular systole to prevent the backflow of blood into the atria
papillary muscles
contract and pull the chordae tendinae and help prevent the prolapsing of the AV valves
apex
only on left side of the heart
atria
2 top chambers
more blood comes through the RA
ventricles
LV biggest; pushes blood up and out of the heart
RV pushes blood to lungs