Classification of Living Things
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Taxonomy Levels
D omain
K ingdom
P hylum
C lass
O rder
F amily
G enus
S pecies
scientific naming
binomial
pt 1 - geuns → closest GROUP species belongs to
pt 2 - species → specific epithet within said genus
Domain
Most inclusic taxonomic category; larger than a kingdom level: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
6 kingdoms of living things
Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
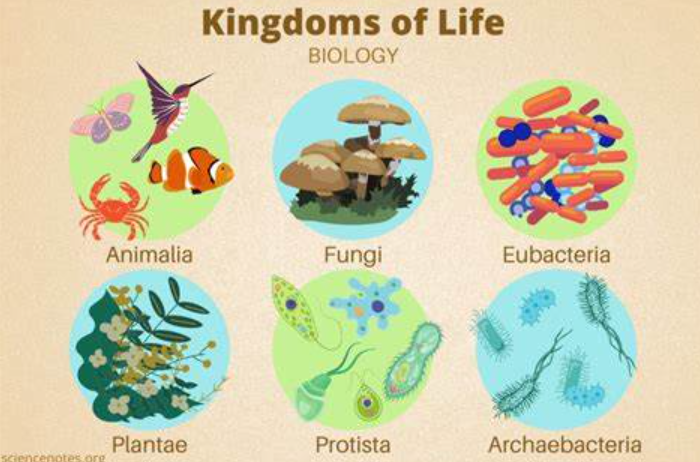
Eubacteria Classifications
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: Eubacteria
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
Heterotroph or Autotroph
Asexual
Ex: cyanobacteria (blue-green algae)
Archaebacteria Classifications
Domain: Archaea
Kingdom: Archaebacteria
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
Heterotroph/Autotroph
Asexual
Ex: thermophiles, methanogens
Protista Classifications
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Eukaryotic
Unicellular
Autotroph + Heterotroph
asexual (except meosis → reduce chromosome to sperm +egg 4 sex)
amoebas
Fungi Classifications
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotroph (decomposer)
Sexual/Asexual (thru spore formation)
Ex: Yeasts, mildews, molds, mushrooms
Plantae Classifications
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Plantae
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Autotroph (photosynthesis)
Sexual/Asexual
Ex: Moss
Animalia Classifications
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Eukaryotic
Multicellular
Heterotroph
Sexual
Animals: Mammals, fish, reptiles, birds
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes: Smaller, simple organisms w/o nucleus or other membrane organs
Eukaryotes: Bigger, complex organisms w/ a membrane-bound nucleus (DNA in nucleus)
Both: can reproduce and respond to the environment
Unicellular vs. Multicellular
Multicellular organisms need specialized organ systems, whereas all the life processes in a unicellular organism take place in that one cell
Autotroph, Heterotroph, and Decomposer
Makes food, consumes food, or breaks up dead matter for energy
Carnivore, Herbivore, Omnivore,
Heterotrophs: eats meat, eats plants, eats both
Scavenger
Heterotrophs: eats dead plants, animals, and carrion but not decomposer bc digests the same as other heterotrophs
Type of reproduction
sexual (pros/cons) creates more diverse genetics but requires more energy and two parents
asexual (pros/cons) faster, more energy-efficient but creates low genetic diversity
symbiotic relationship
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other
mutualism
symbiotic relationship: both organisms benefit (+/+)
parasitism
symbiotic relationship: one organism benefits by living on or in the host and the other is harmed (+/-)
commensalism
symbiotic relationship: one organism benefits and the other is unaffected (+/0)
predation
symbiotic relationship: one organism captures and feeds on another (+/-)
competition
symbiotic relationship: both organisms in the same ecological niche that compete for limited resources (-/-)
ecological niche
A specific role of a species within an ecosystem, including its use of resources, and relationships with other species (food, water, habitat