Session 6: The Autonomic Nervous System
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
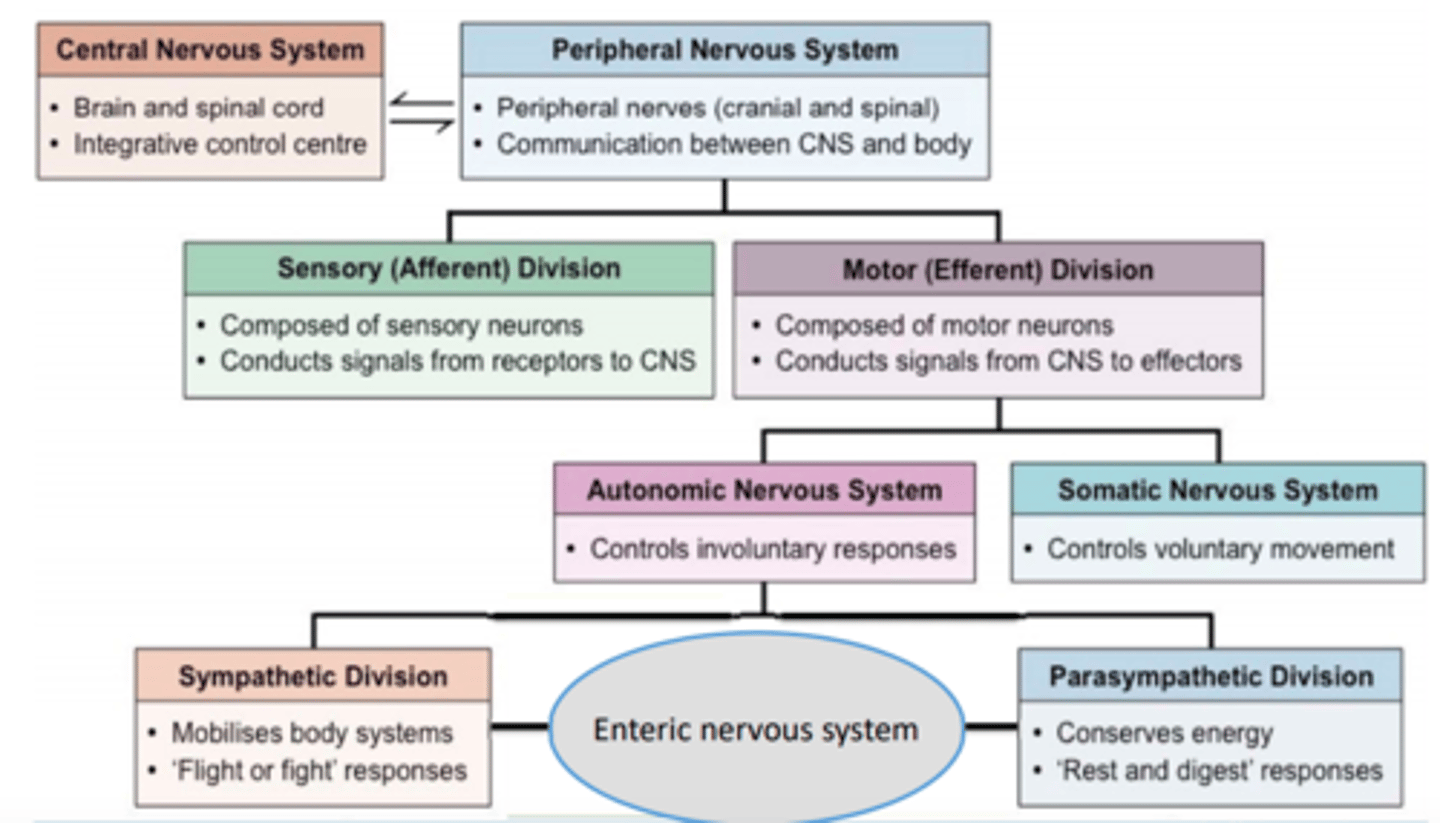
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is comprised of ___ and ___ divisions
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is comprised of sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
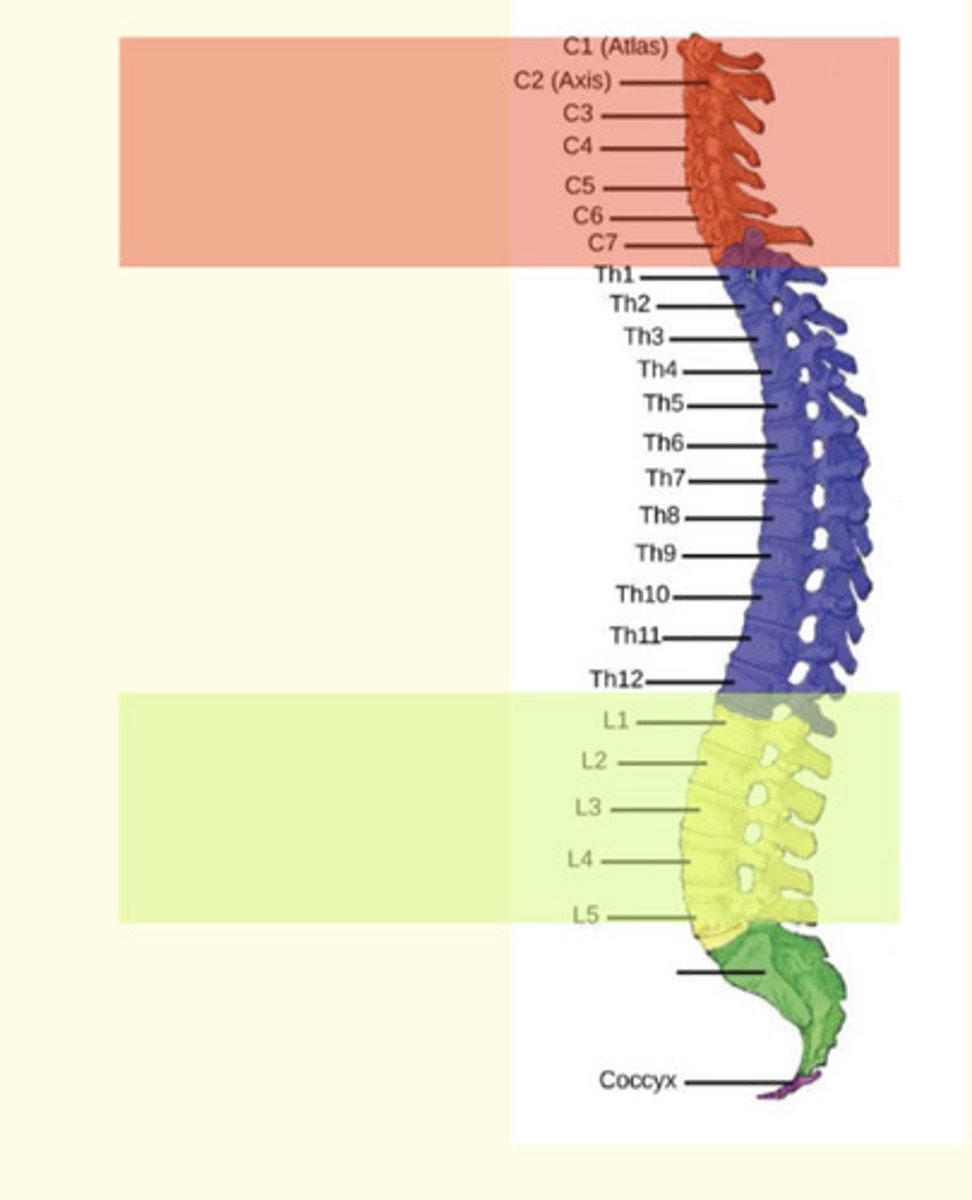
The seven vertebrae directly inferior to the skull are known as the ___ vertebrae
The seven vertebrae directly inferior to the skull are known as the cervical vertebrae
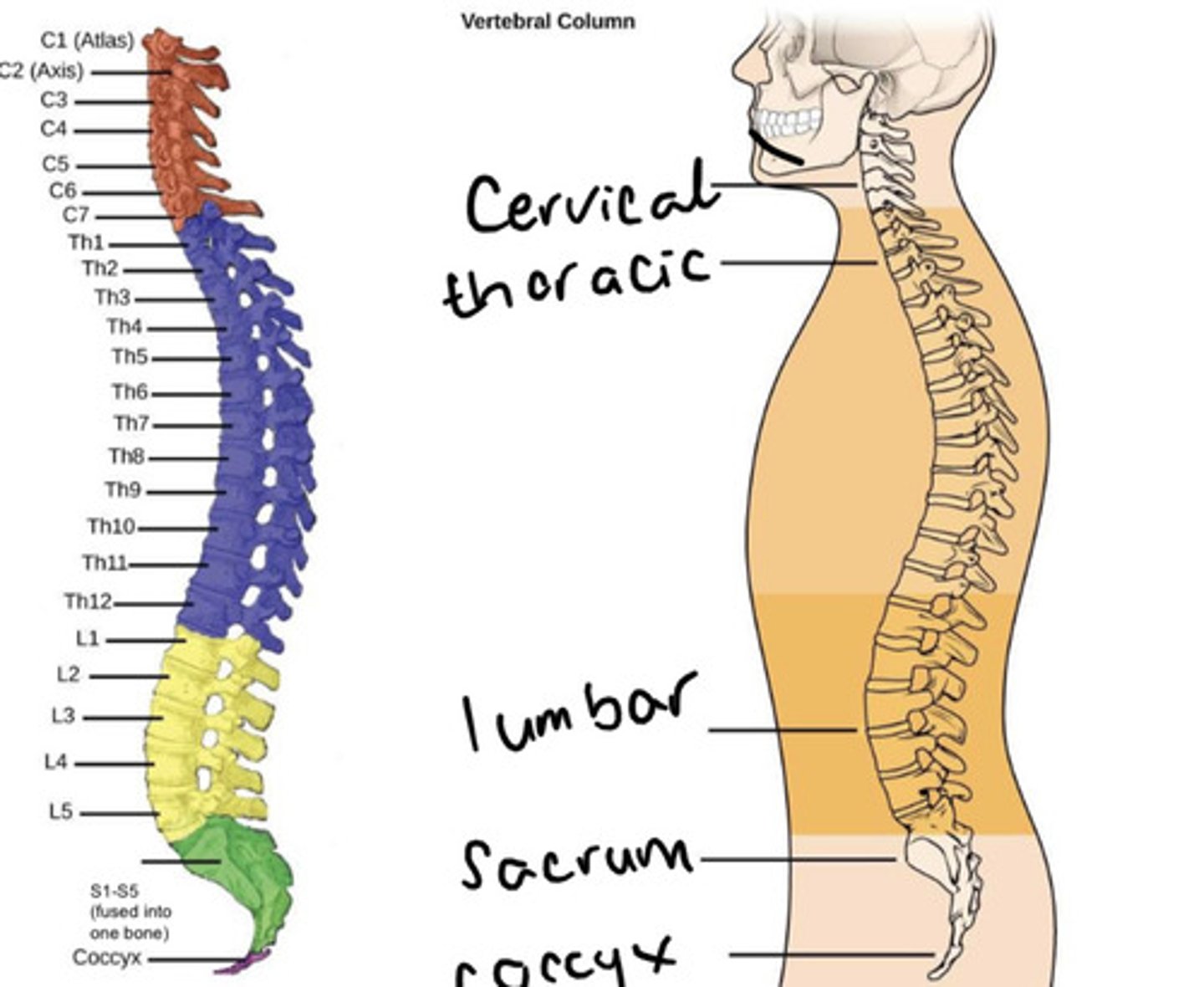
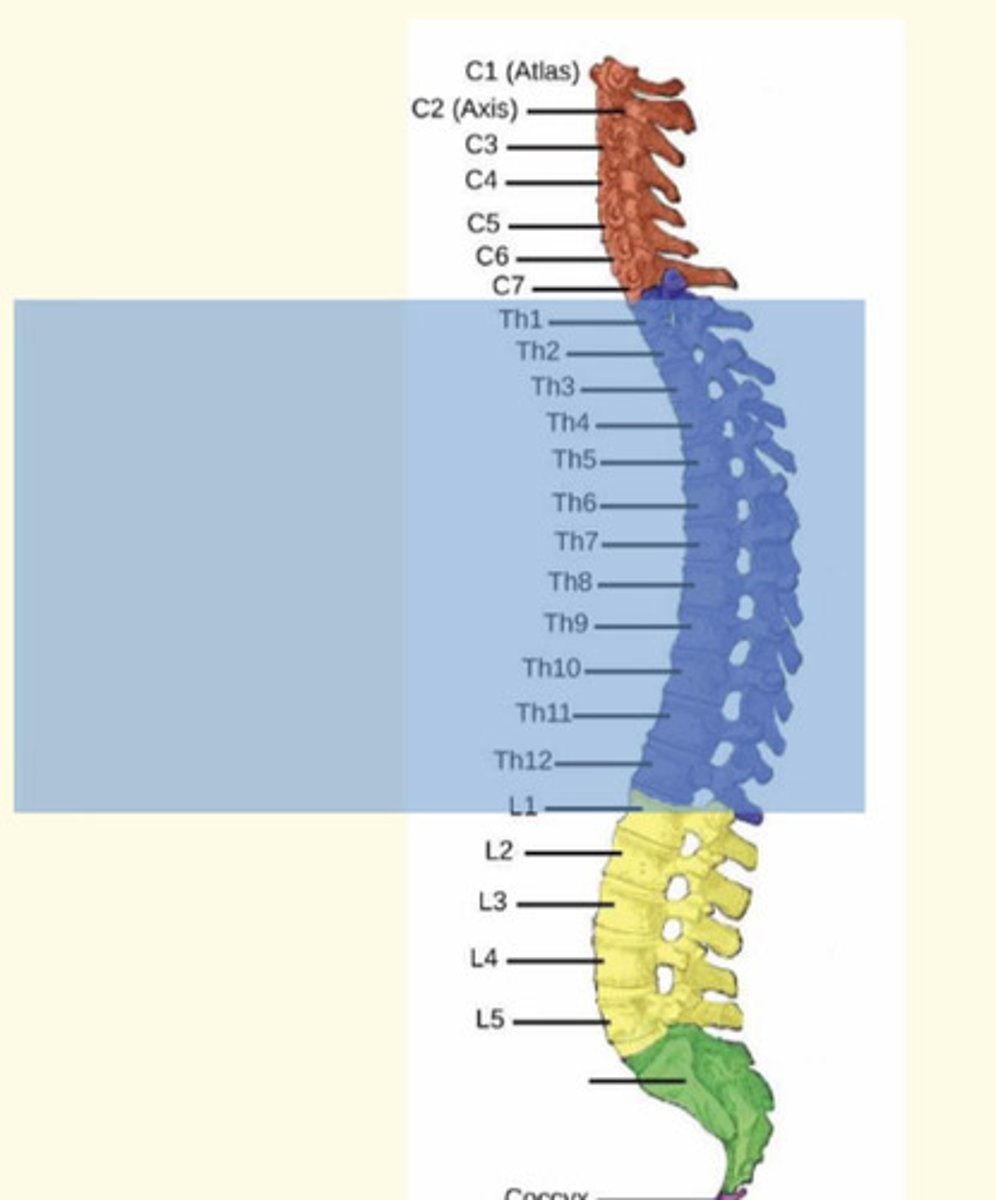
The 12 vertebrae inferior to the cervical vertebrae are known as the ___ vertebrae
The 12 vertebrae inferior to the cervical vertebrae are known as the thoracic vertebrae
The 5 vertebrae inferior to the thoracic vertebrae is known as the ___ vertebrae
The 5 vertebrae inferior to the lumbar vertebrae is known as the lumbar vertebrae
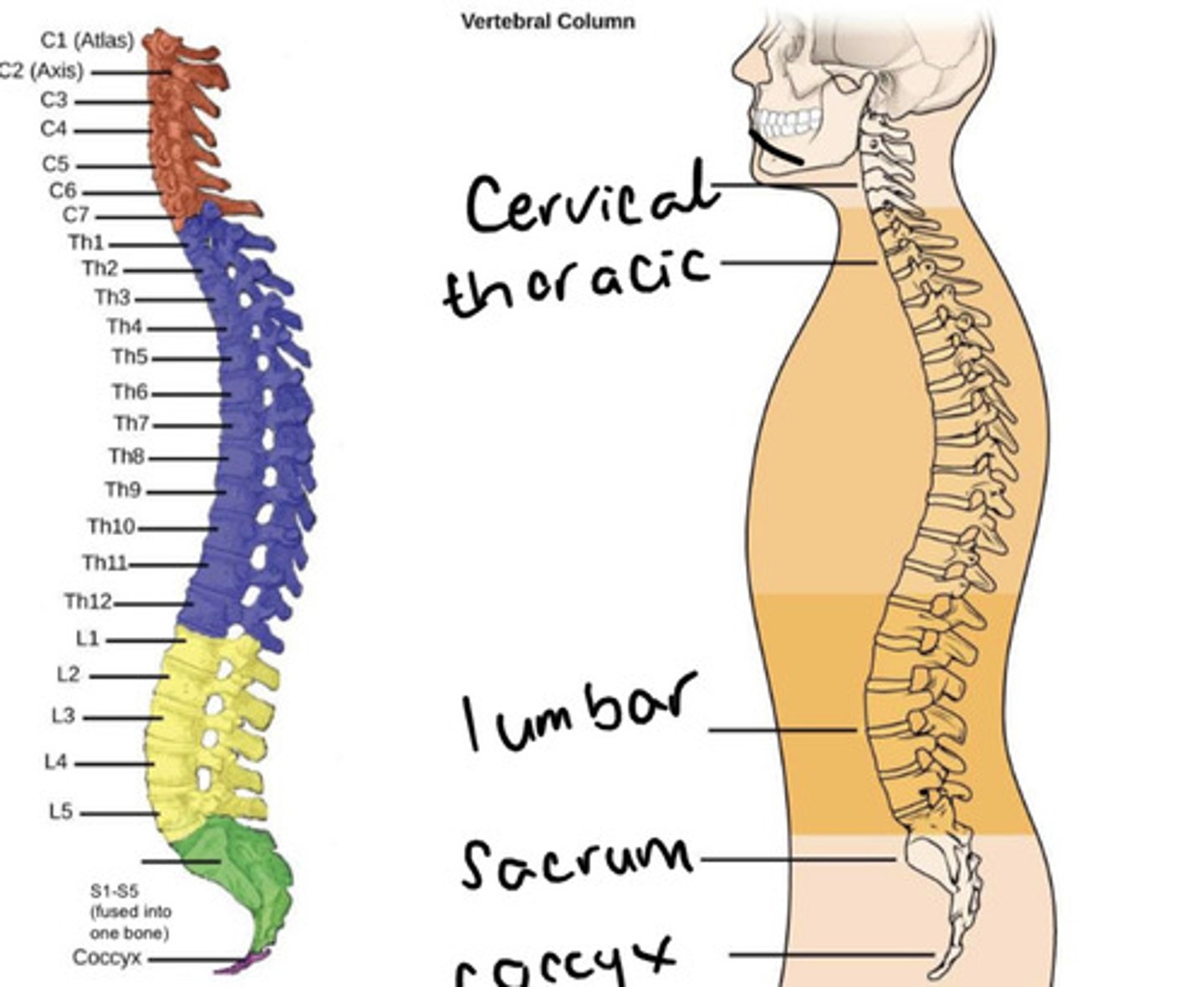
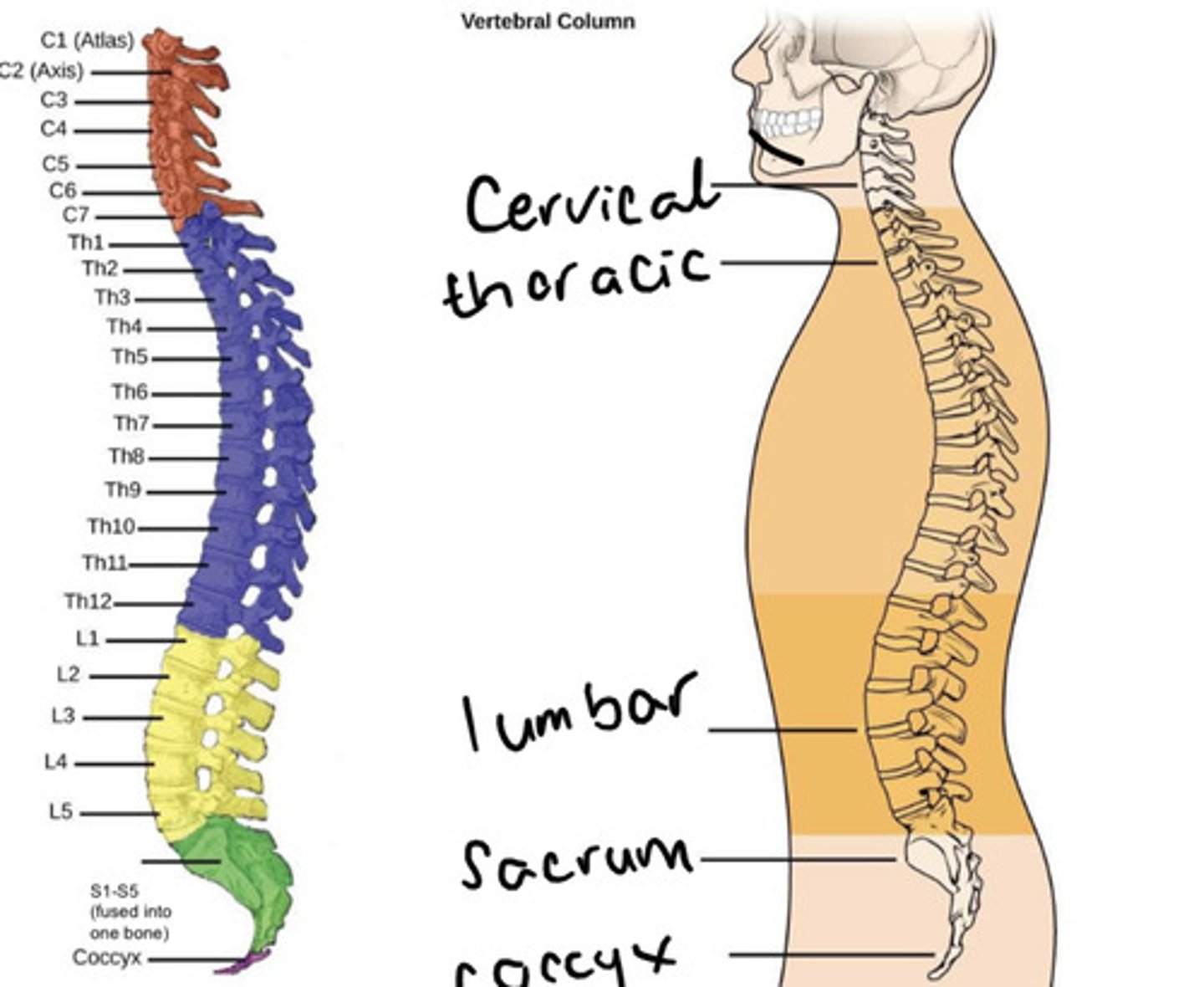
The 5 (fused) vertebrae inferior to the lumbar vertebrae is known as the ___
The 5 (fused) vertebrae inferior to the lumbar vertebrae is known as the sacrum
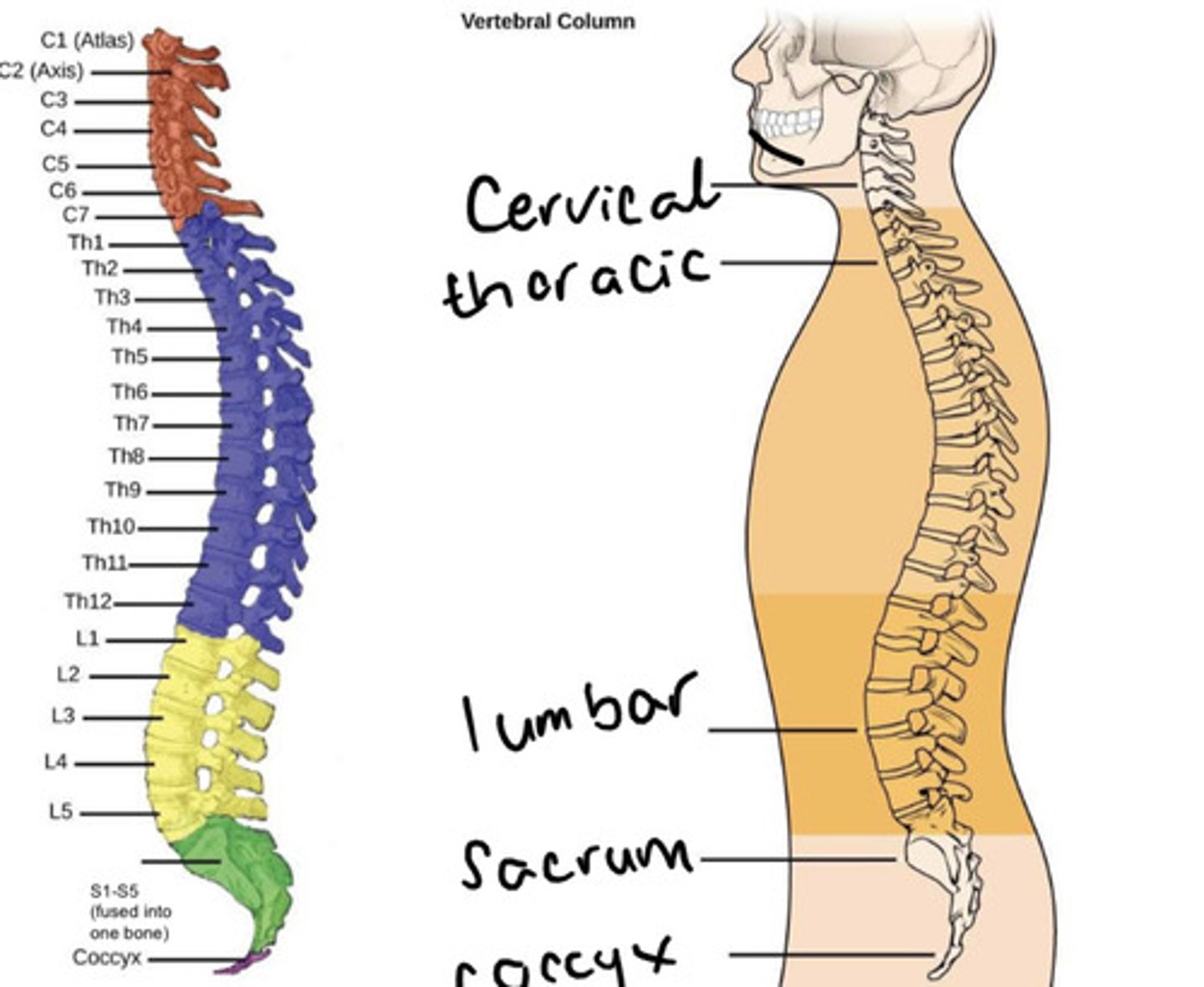
The fused vertebrae inferior to the sacrum are known as the ___
The fused vertebrae inferior to the sacrum are known as the coccyx
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is responsible for ___ or ___
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is responsible for fight or flight
When is the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) triggered?
- Emergency, exercise, excitement, embarrassment, stressful situations
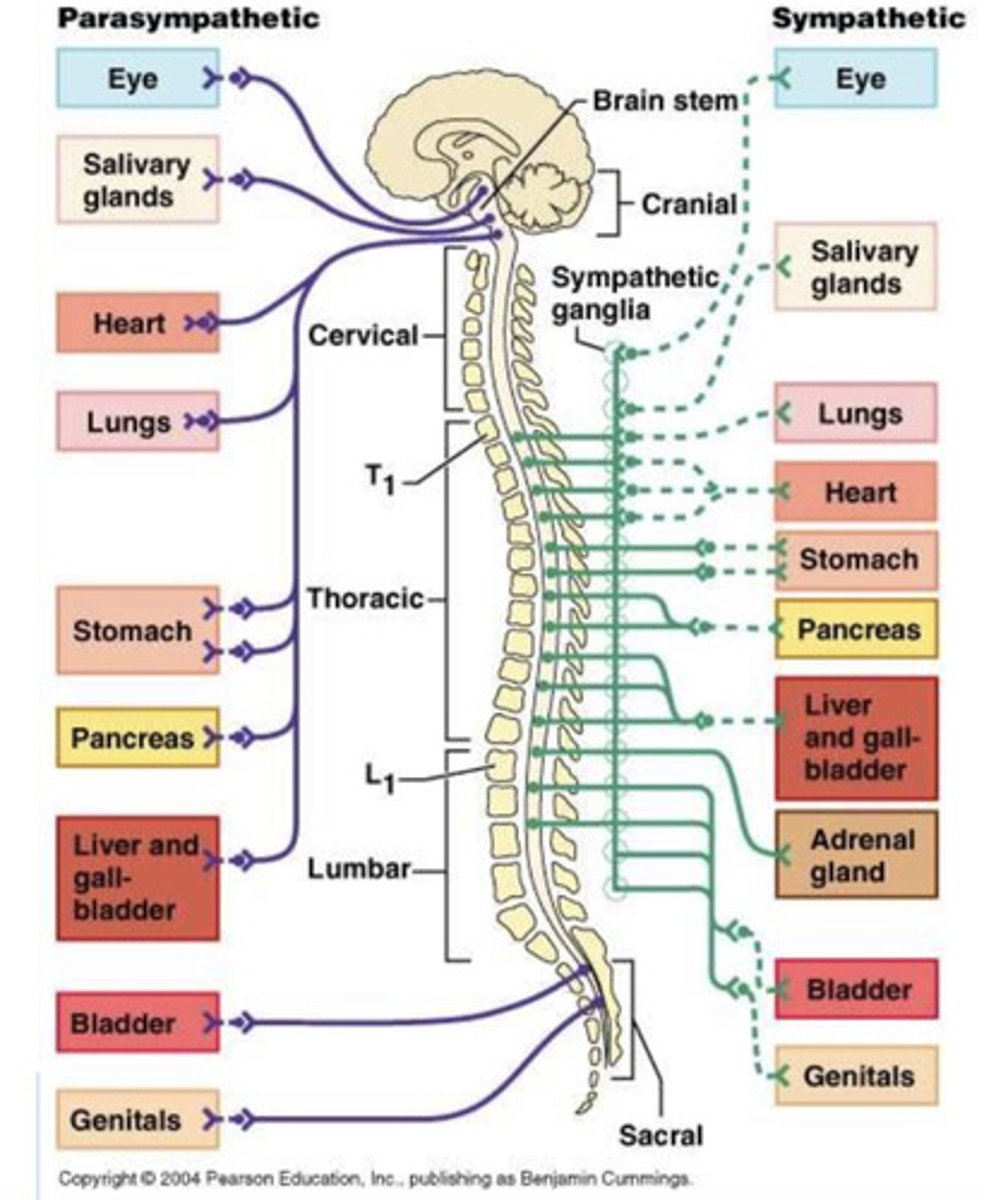
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) nerves emerge from thoracic (T1-T12) and lumbar (L1-L2) known as the ___ division of ANS
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) nerves emerge from thoracic (T1-T12) and lumbar (L1-L2) known as the thoracolumbar division of ANS
The parasympathetic nervous system are triggered for ___ and ___
The parasympathetic nervous system are triggered for rest and digest
The parasympathetic nervous system has ___ anatomical origins
The parasympathetic nervous system has craniosacral anatomical origins
Some general actions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Establishes and maintains our homeostasis through the regulation of...
- BP
- HR
- Breathing rate
- Body temperature
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Urination
- Defecation
- Sexual responses

Most organs have both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. Exceptions to this include the ___ ___ and sweat glands, which have ___ supply only
Most organs have both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation. Exceptions to this include the adrenal medulla and sweat glands, which have sympathetic supply only
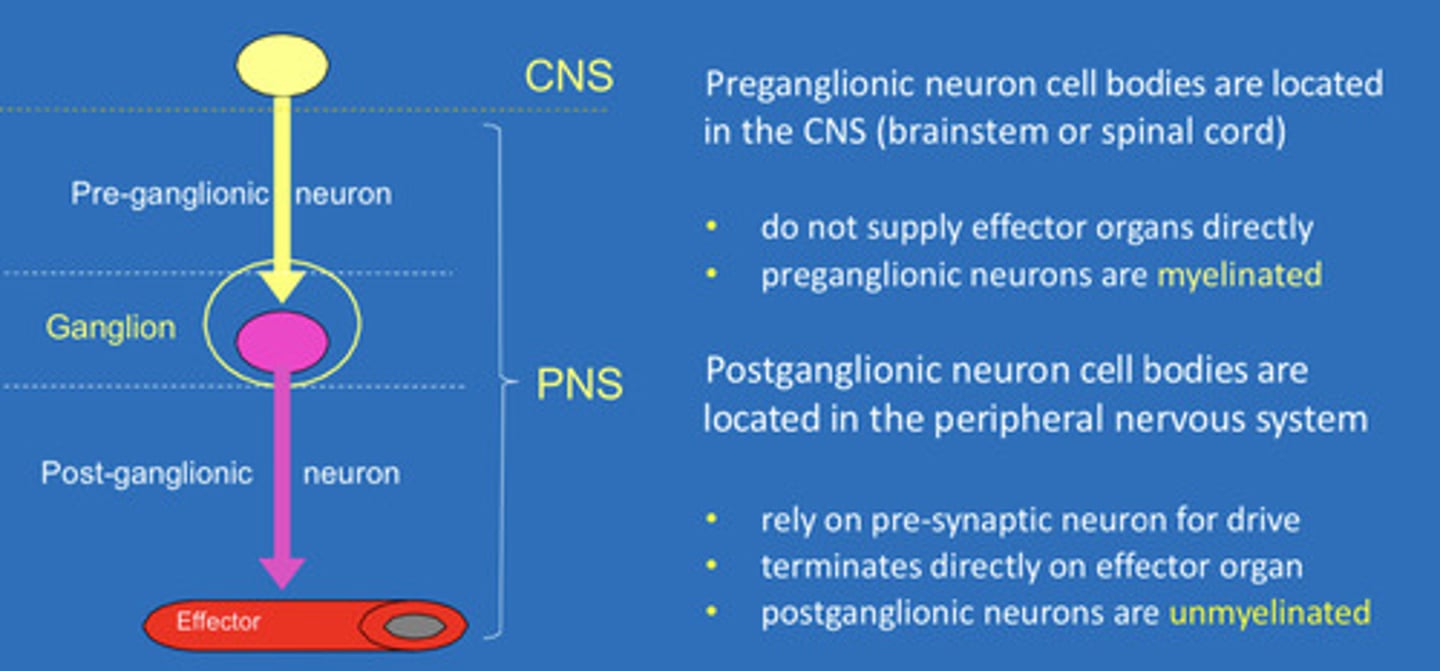
All autonomic pathways are made up of a ___-neuron chain
All autonomic pathways are made up of a two-neuron chain
Preganglionic neuron cell bodies are located in the CNS. They do not supply effector organs directly. Preganglionic neurons are ___
Preganglionic neuron cell bodies are located in the CNS. They do not supply effector organs directly. Preganglionic neurons are myelinated
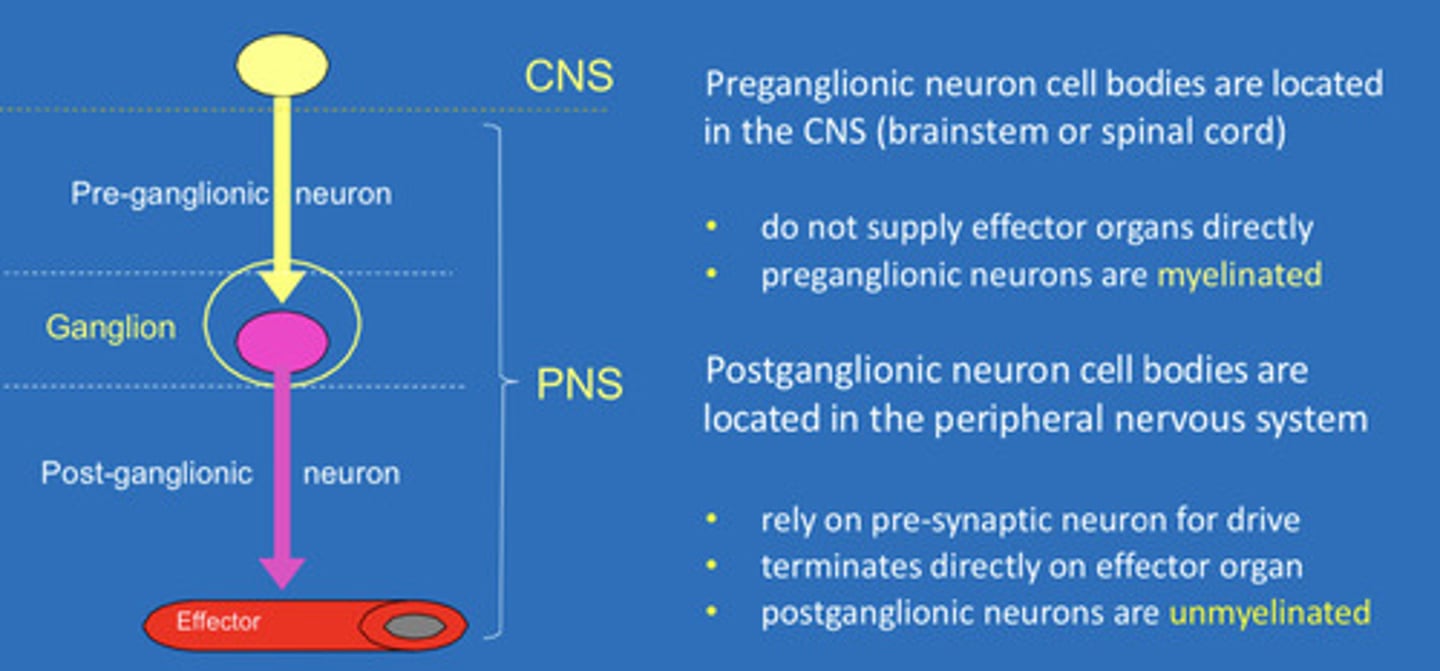
Postganglionic neuron cell bodies are located in the PNS. They rely on pre-synaptic neuron for drive. They terminate at the effector organ. Postganglionic neurons are ___
Postganglionic neuron cell bodies are located in the PNS. They rely on pre-synaptic neuron for drive. They terminate at the effector organ. Postganglionic neurons are unmyelinated
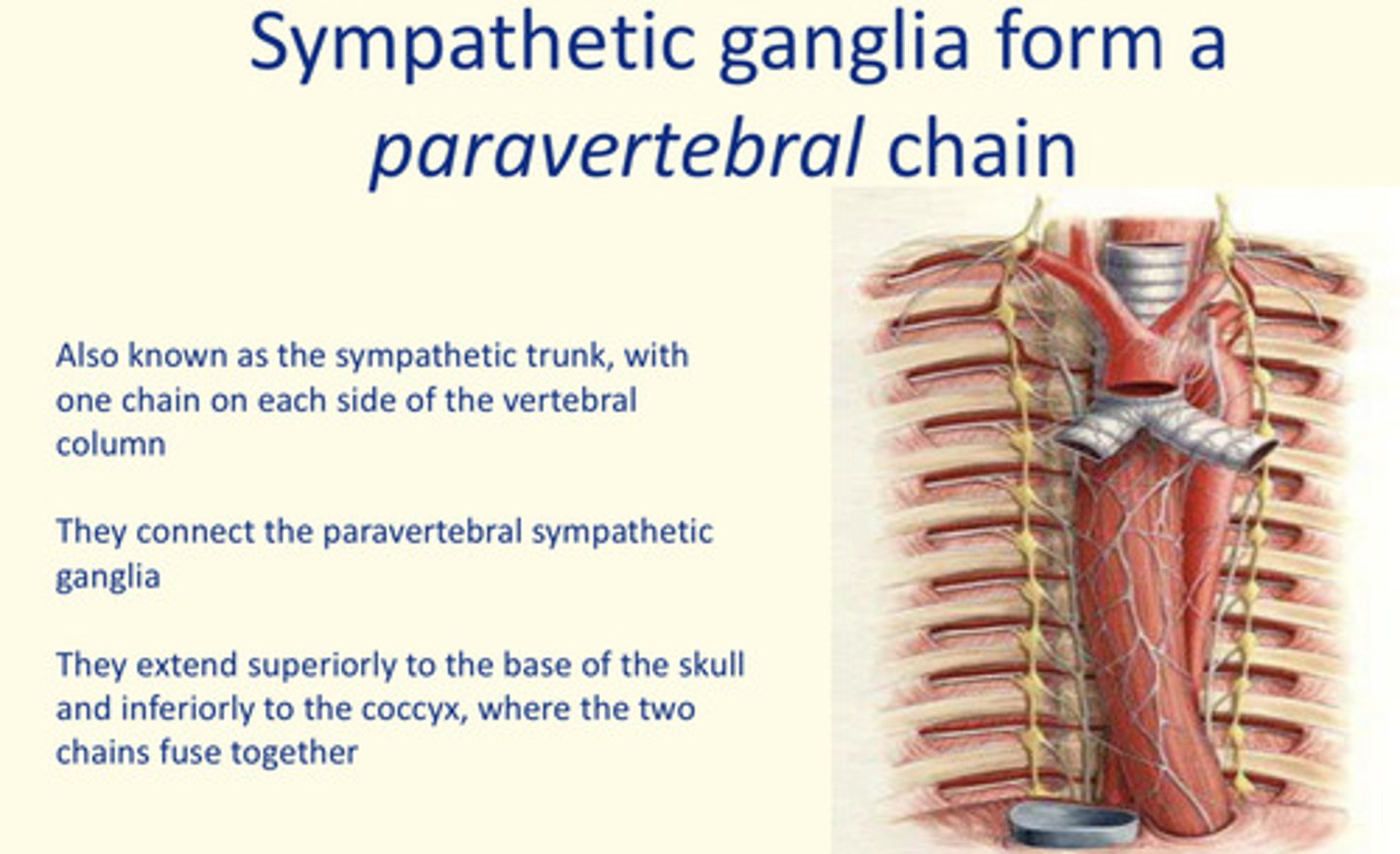
Sympathetic ganglia form a ___ chain
Sympathetic ganglia form a paravertebral chain
Some outcomes of sympathetic innervation
- Increased flow of blood to skeletal muscle
- Increased energy expenditure
- Diversion of blood to heart
- Increase in HR
- Increase in BP
- Reduced blood flow to GI tract/skin
- Stimulation of chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla - release catecholamines (adrenaline and noradrenaline) into blood

Four of the pairs of the 12 cranial nerves have a ___ component
Four of the pairs of the 12 cranial nerves have a parasympathetic component (3, 7, 9, 10)
Cranial nerve 3
Oculomotor nerve
Cranial nerve 7
Facial
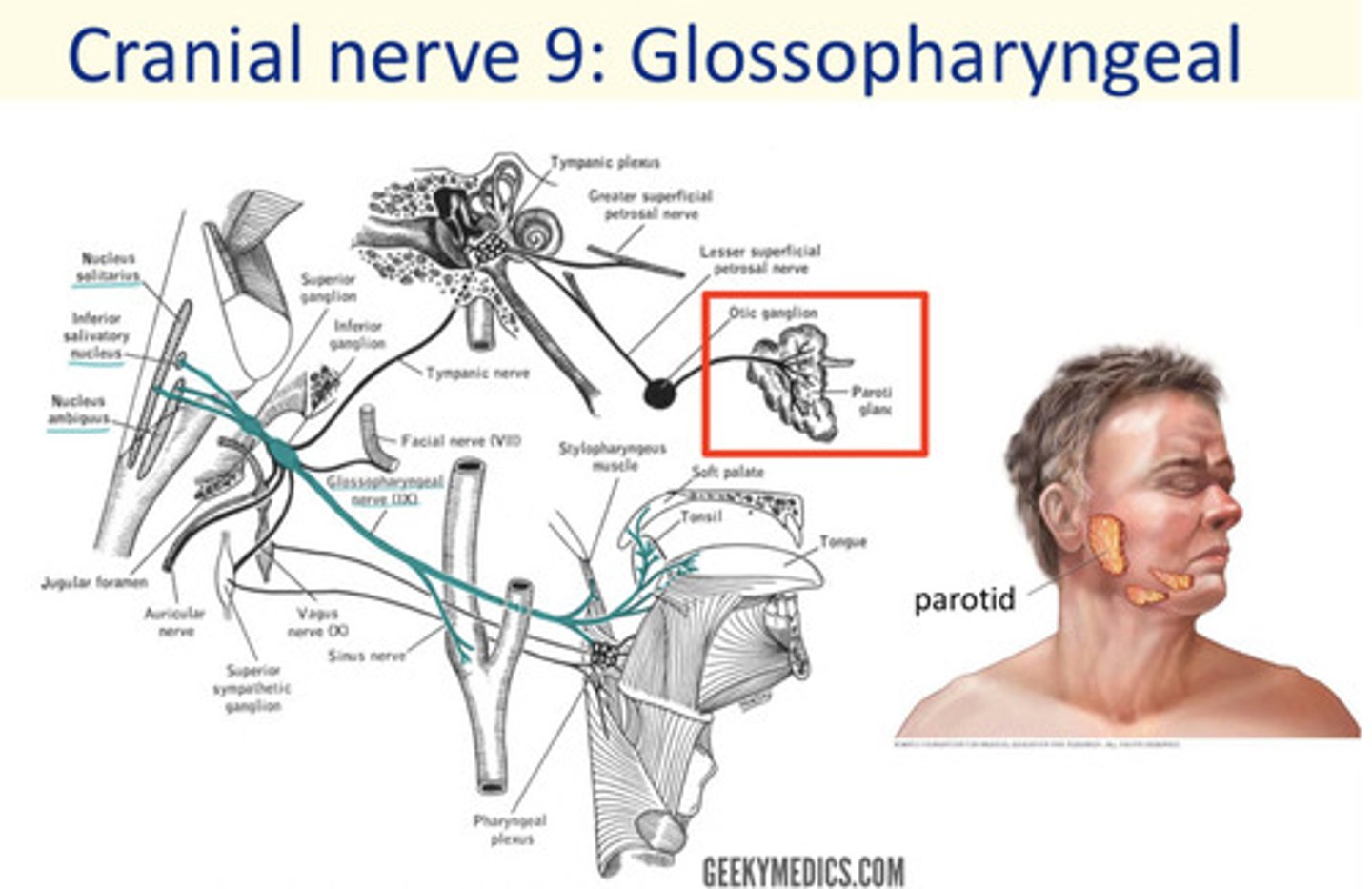
Cranial nerve 9
Glossopharyngeal
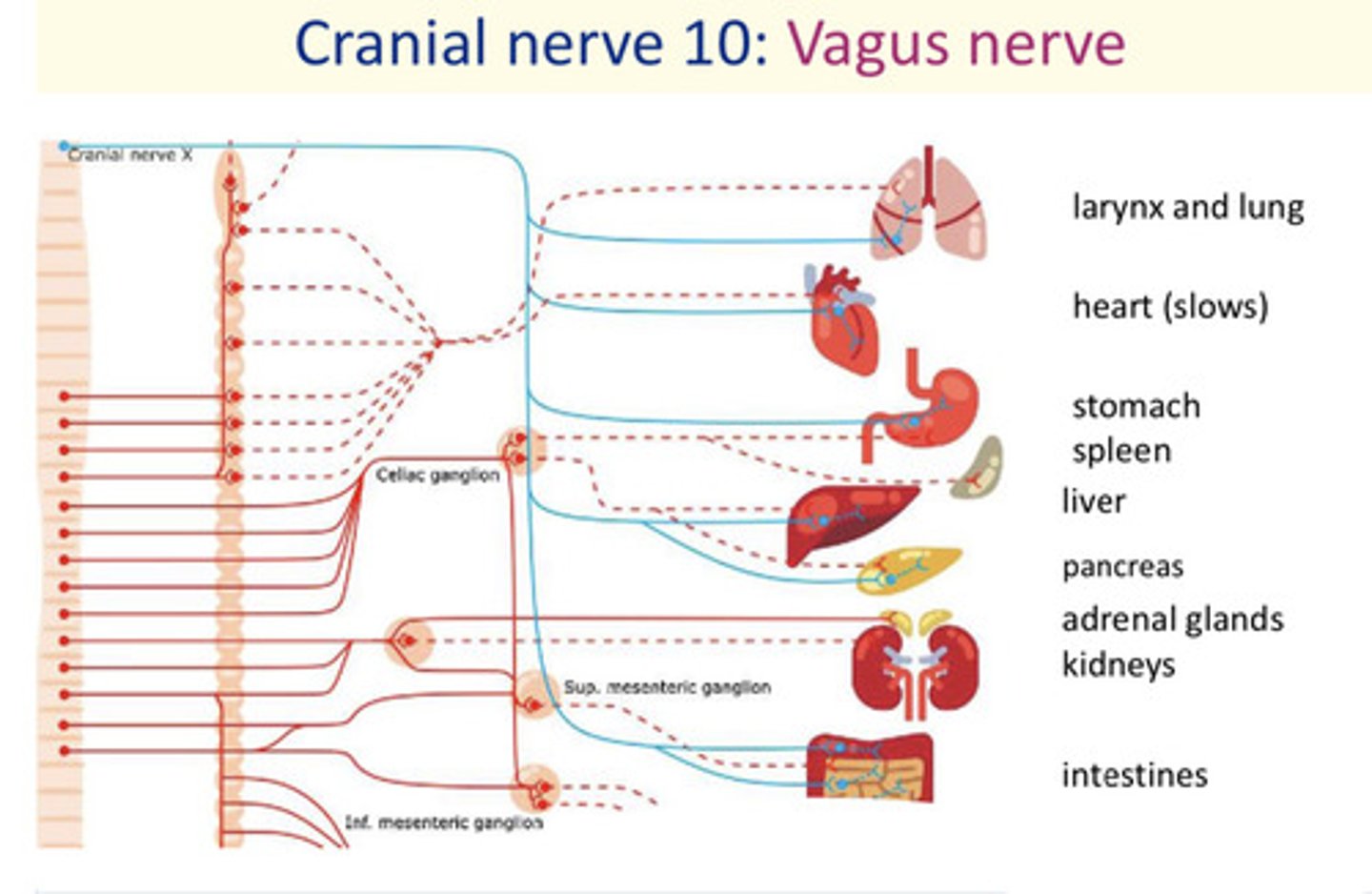
Cranial nerve 10
Vagus nerve
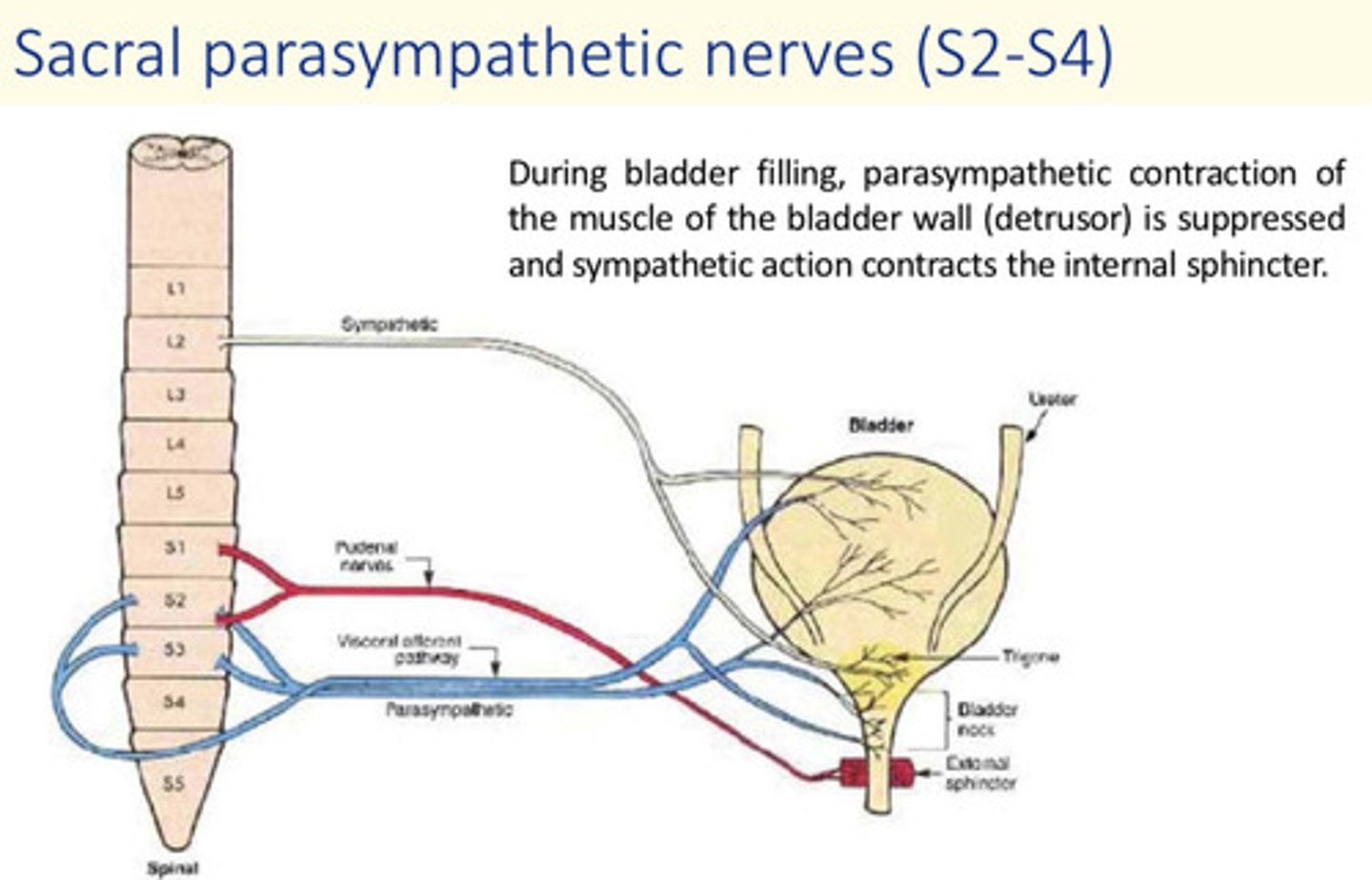
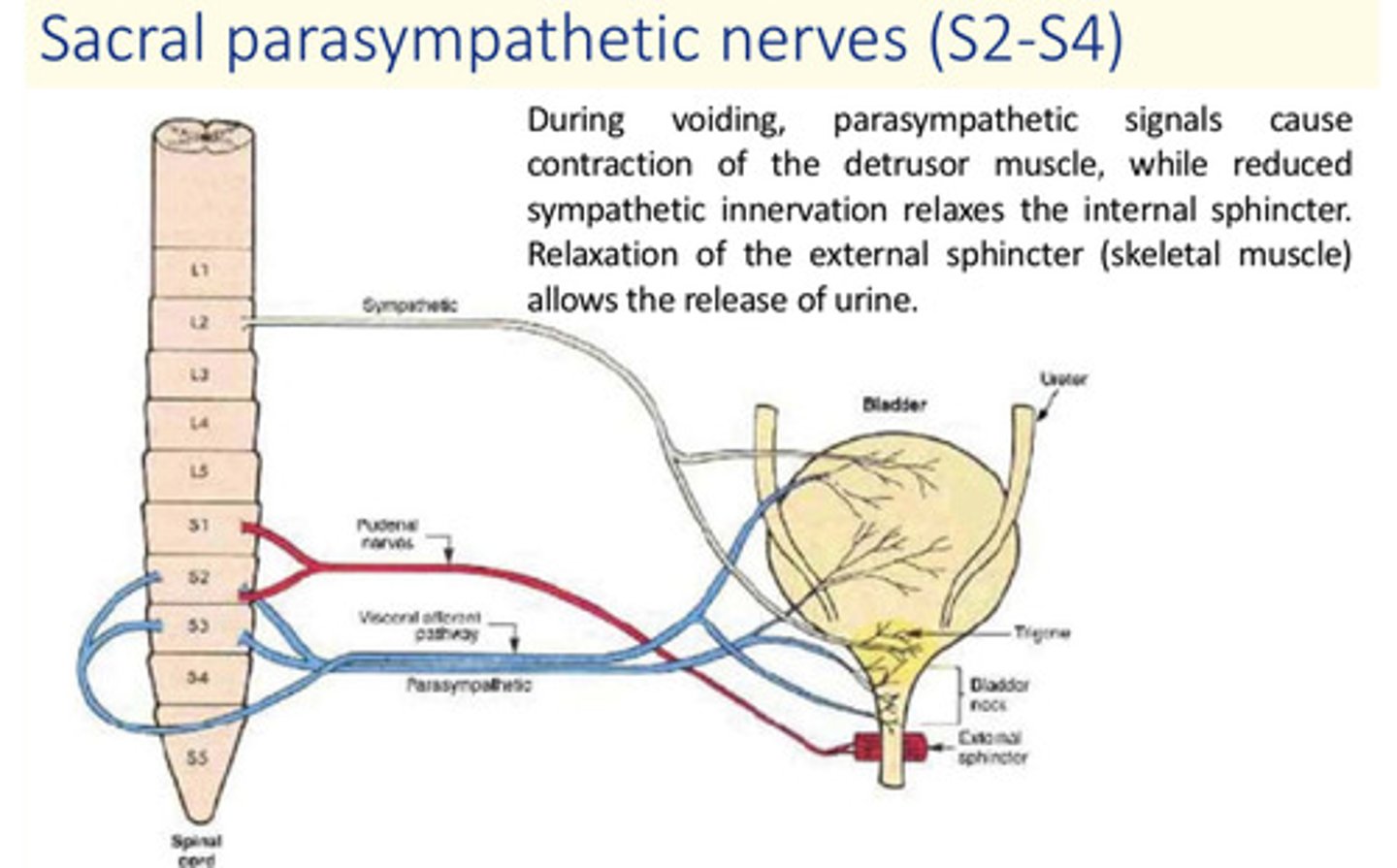
During bladder filling, ___ contraction of the muscle of the bladder wall (detrusor) is suppressed and ___ action contracts the internal sphincter
During bladder filling, parasympathetic contraction of the detrusor is suppressed and sympathetic action contracts the internal sphincter
During voiding, ___ signals cause contraction of the detrusor muscle, while reduced ___ innervation ___ the internal sphincter.
Relaxation of the external sphincter (skeletal muscle) allows ___ of urine
During voiding, parasympathetic signals cause contraction of the detrusor muscle, while reduced sympathetic innervation relaxes the internal sphincter.
Relaxation of the external sphincter (skeletal muscle) allows release of urine
___ glands of the skin and ___ ___ receive ___ drive only!
Sweat glands of the skin and adrenal medulla receive sympathetic drive only!
Vasovagal syncope is also known as
Neurocardiogenic syncope
Common cause of vasovagal syncope
Fear, severe pain, blood/needle phobia, sudden unexpected sight/sound/smell
Other causes of vasovagal syncope
Orthostatic causes: prolonged standing or when in crowded, hot places
Vasovagal syncope mechanism
Initial increase in sympathetic activity is reduced by feedback mechanism
This doesn't balance an increase in parasympathetic activity, causing vasodilation, bradycardia and hypotension leading to fainting
Raynaud syndrome symptoms
Pallor, cyanosis and redness of digits
Pain, numbness, paresthesia (tingling) and difficulty moving affected area

What occurs in chronic, severe Raynaud disease?
Tissue infarction and finger loss

Cause of Raynaud syndrome?
Spasm of the digital arteries in the fingers - precipitated by cold and relieved by heat
Raynaud syndrome affects ___% of the population and is more common in ___
Raynaud syndrome affects 5% of the population and is more common in females
What surgery can be performed in severe cases of Raynaud syndrome?
Peripheral sympathectomy
Prevention/treatment of Raynaud's syndrome
Staying out of the cold
Vasodilators
Extreme case of vasoconstriction is ___ syndrome
Extreme case of vasoconstriction is Raynaud’s syndrome

Sympathetic
- Arise in spinal cord segments T1-L2
- Form synapses close to spinal column
- Can be seen as paravertebral chain running adjacent to spinal column (sympathetic trunk)
Stressful situations activate the
sympathetic nervous system
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons mainly release ___ to stimulate target organs
noradrenaline
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons mainly activate ___ or ___ adrenergic receptors (adrenoreceptors)
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons mainly activate a- or b- adrenergic receptors (adrenoreceptors)
beta-1 adrenergic receptor
myocardium
agonism leads to increased HR
alpha-1 adrenergic receptor (sympathetic)
smooth muscle
agonism leads to contraction (vasoconstriction)
beta-2 adrenergic receptor - receptor for catecholamine like epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine, found in smooth muscles
smooth muscle
agonism leads to relaxation, broncho and vaso-dilation
What drug is an agonist of beta-2 adrenergic receptors?
salbutamol
Effect of sympathetic stimulation
Reduced blood flow to GI tract & skin
Increased BP/HR
Fight/flight
Increased energy expenditure
Stimulation of chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla - release catecholamines (adrenaline & noradrenaline) into blood
Parasympathetic
- Originate in the brain or sacral region (craniosacral) of spinal cord
- Form synapses in ganglia located close to target organs (presynaptic fibres tend to be very long)
Relaxed situations 'rest and digest'
Parasympathetic system
Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons mainly release ___
Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons mainly release acetylcholine (ACh)
Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons activate ___ receptors
muscarinic
Compare sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of ANS
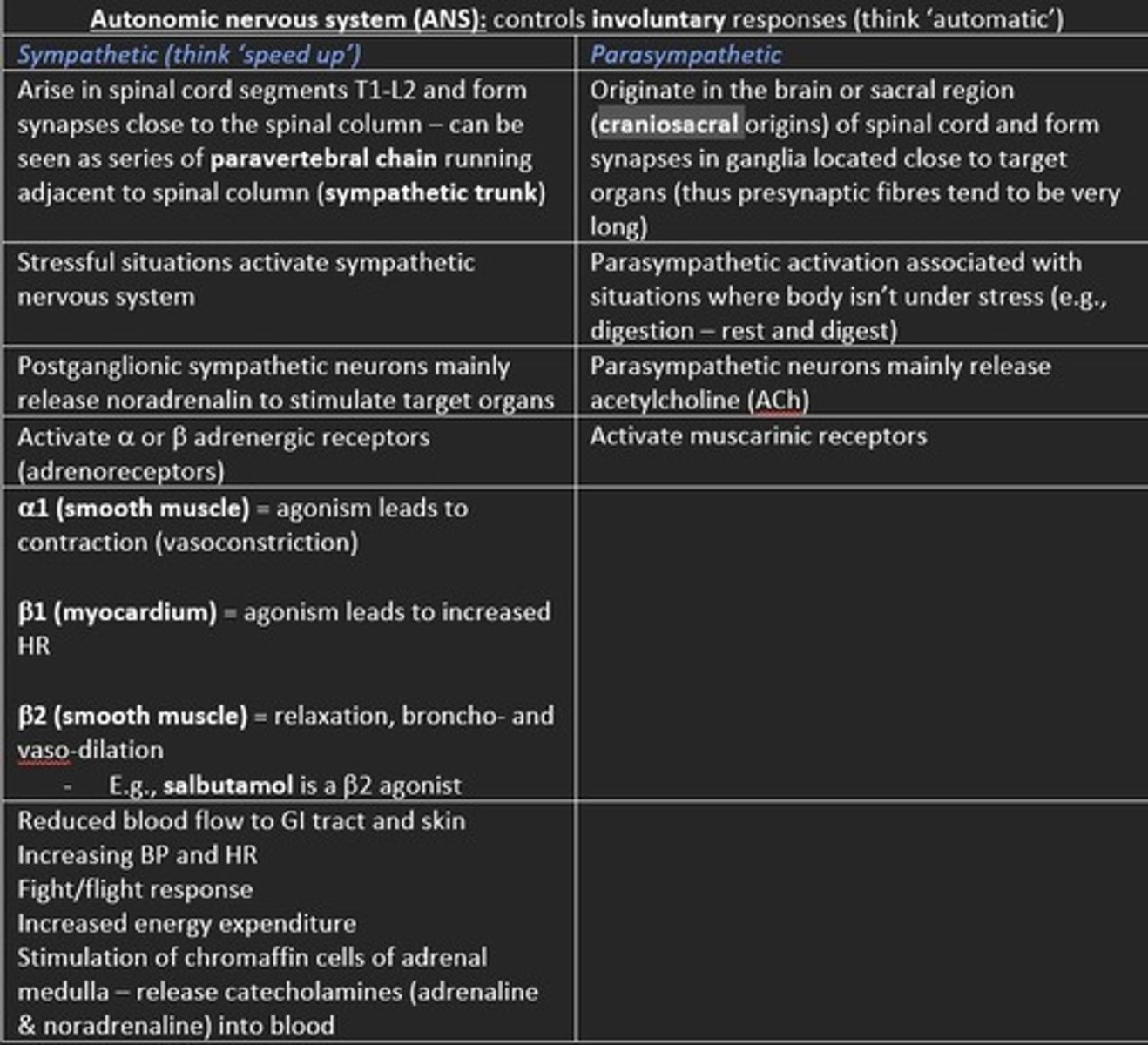
Sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
Thoracolumbar division of ANS
Parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
C1-C7
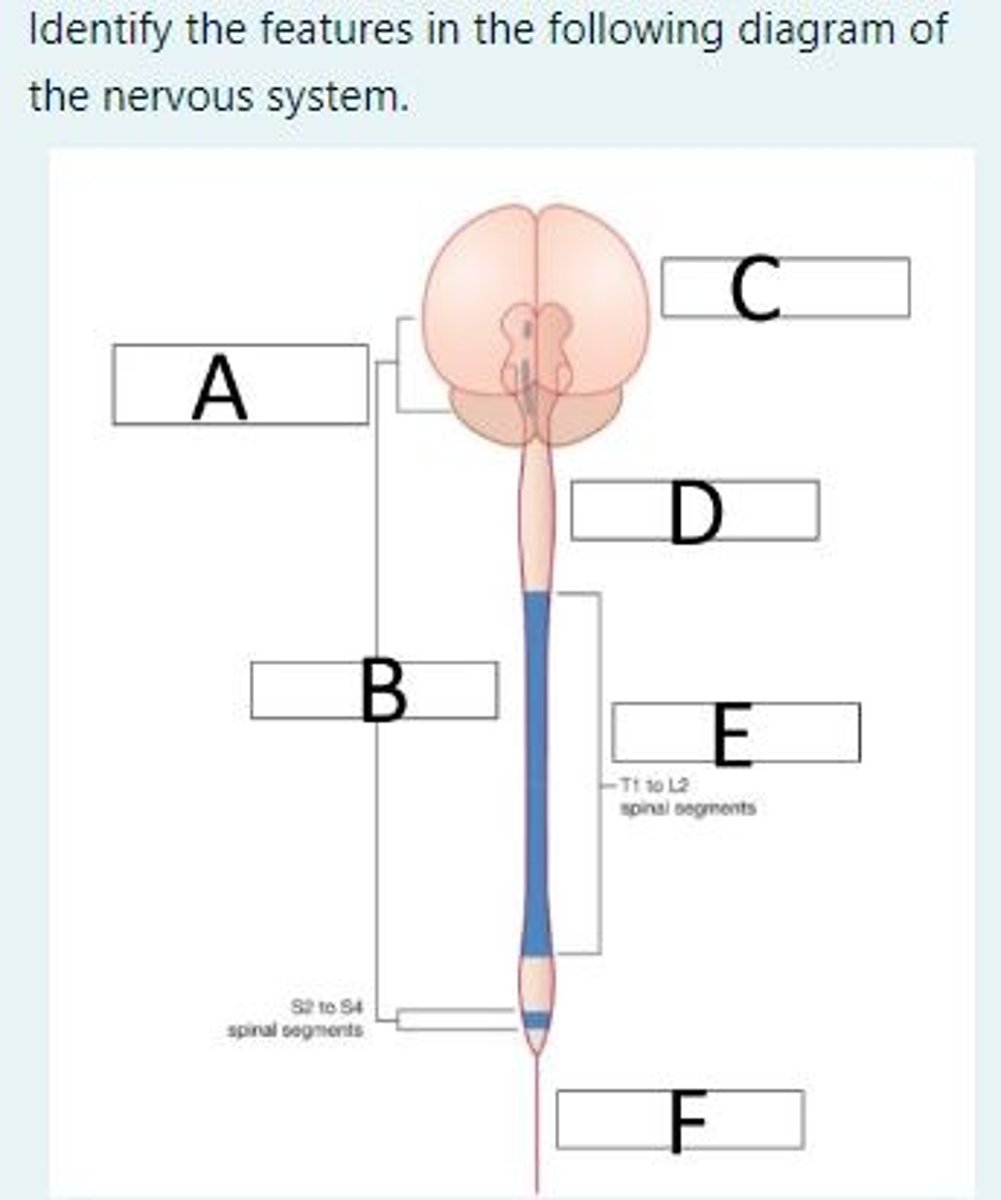
Identify the features in the following diagram of the nervous system
A = Cranial nerves associated with parasympathetic outflow (3, 7, 9 and 10)
B = Parasympathetic nervous system
C = Brain
D = Spinal cord
E = Sympathetic nervous system
F = Filum terminal
The presence of Nissl substance is evidence that neurons are highly biosynthetic. Of what is Nissl substance comprised?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Which of the following organs has sympathetic but NOT parasympathetic innervation, according to the diagram?
A) Pancreas
B) Lungs
C) Adrenal glands
D) Bladder
E) Heart
C) Adrenal glands
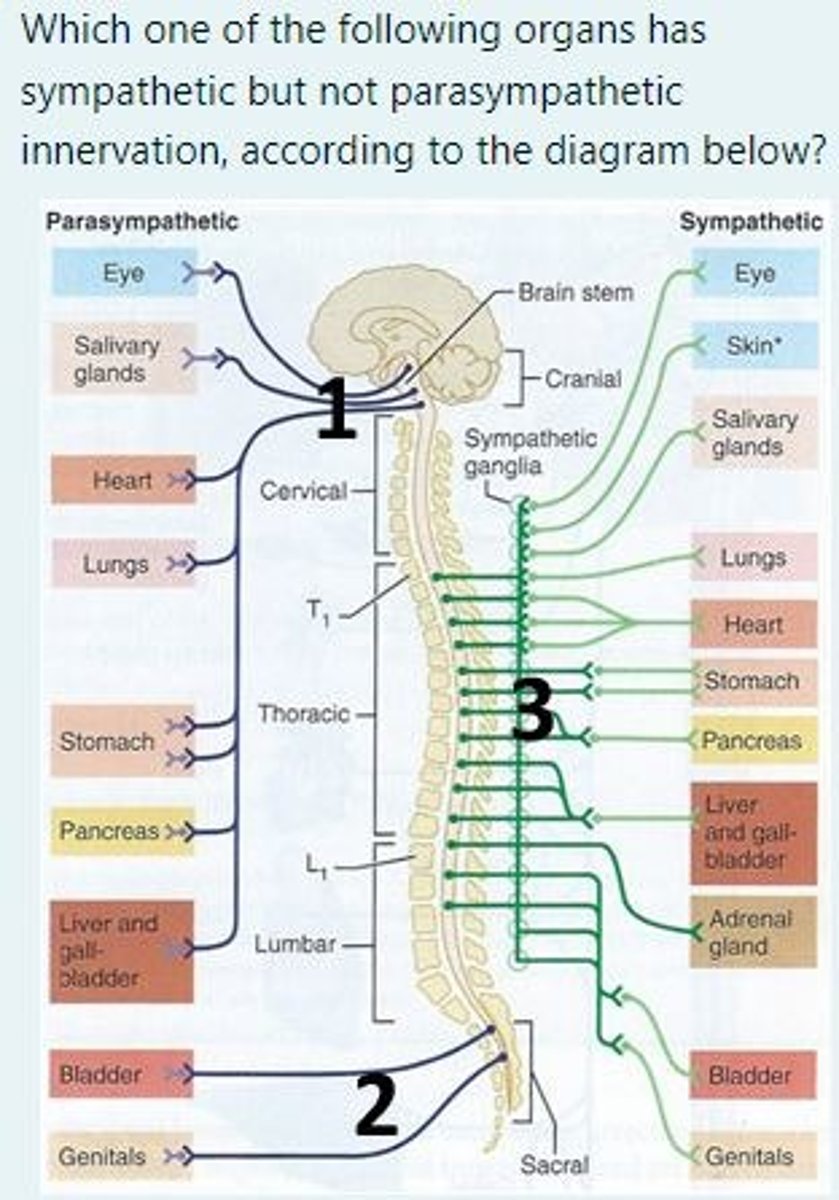
Four cranial nerves supply parasympathetic innervation. Which two cranial nerves supply the salivary glands?
VII: Facial nerve
IX: Glossopharyngeal nerve
Anatomically, where are most parasympathetic ganglia located?
Close to end organs
Which division of the nervous system is responsible for...
A) Voluntary movement
B) Fight or flight
C) Rest and digest
A) Voluntary movement = somatic
B) Fight or flight = sympathetic
C) Rest and digest = parasympathetic
Match the cell to the most common type of receptor with which it's associated
A) Sympathetic effector organ
B) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neuron
C) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neuron
D) Parasympathetic effector organ
A) Sympathetic effector organ → adrenergic
B) Post-ganglionic sympathetic neuron → cholinergic (nicotinic)
C) Post-ganglionic parasympathetic neuron → cholinergic (nicotinic)
D) Parasympathetic effect organ → cholinergic (muscarinic)
Alpha-1 receptor
Smooth muscle contraction
Beta-1 receptor
Increased heart rate
Beta-2 receptor
Smooth muscle relaxation
Damaged axons are able to regrow at what rate?
1-5mm per day
Which layer of connective tissue in neurons provides a channel for the regrowth of damaged axons?
Endoneurium
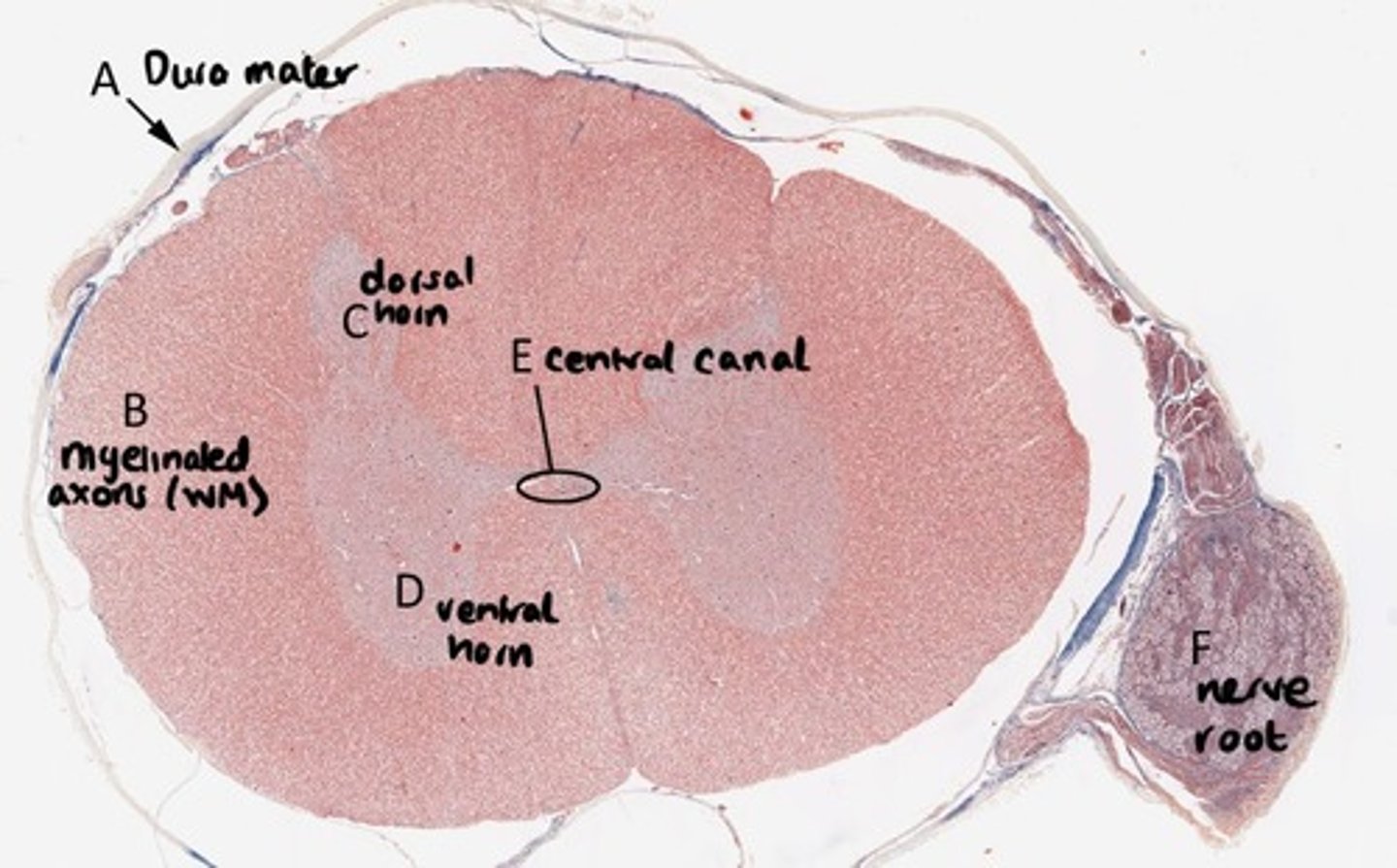
A = Protection to spinal cord (dura mater)
B = Region containing myelinated axons (white matter)
C = Sensory neuron cell bodies (dorsal horn)
D = Motor neuron cell bodies (ventral horn)
E = CSF circulates (central canal)
F = Nerve root
A = Dura mater
B = White matter
C = Dorsal horn
D = Ventral horn
E = Central canal
F = Nerve root
What name is given to pain that arises from damage to the somatosensory system, rather than by activation of pain receptors (the latter is called nociceptive pain).
Neuropathic pain
The sciatic nerve carries both motor and sensory fibres. What is the name given to this type of nerve?
Mixed
Autonomic nervous system
controls involuntary responses
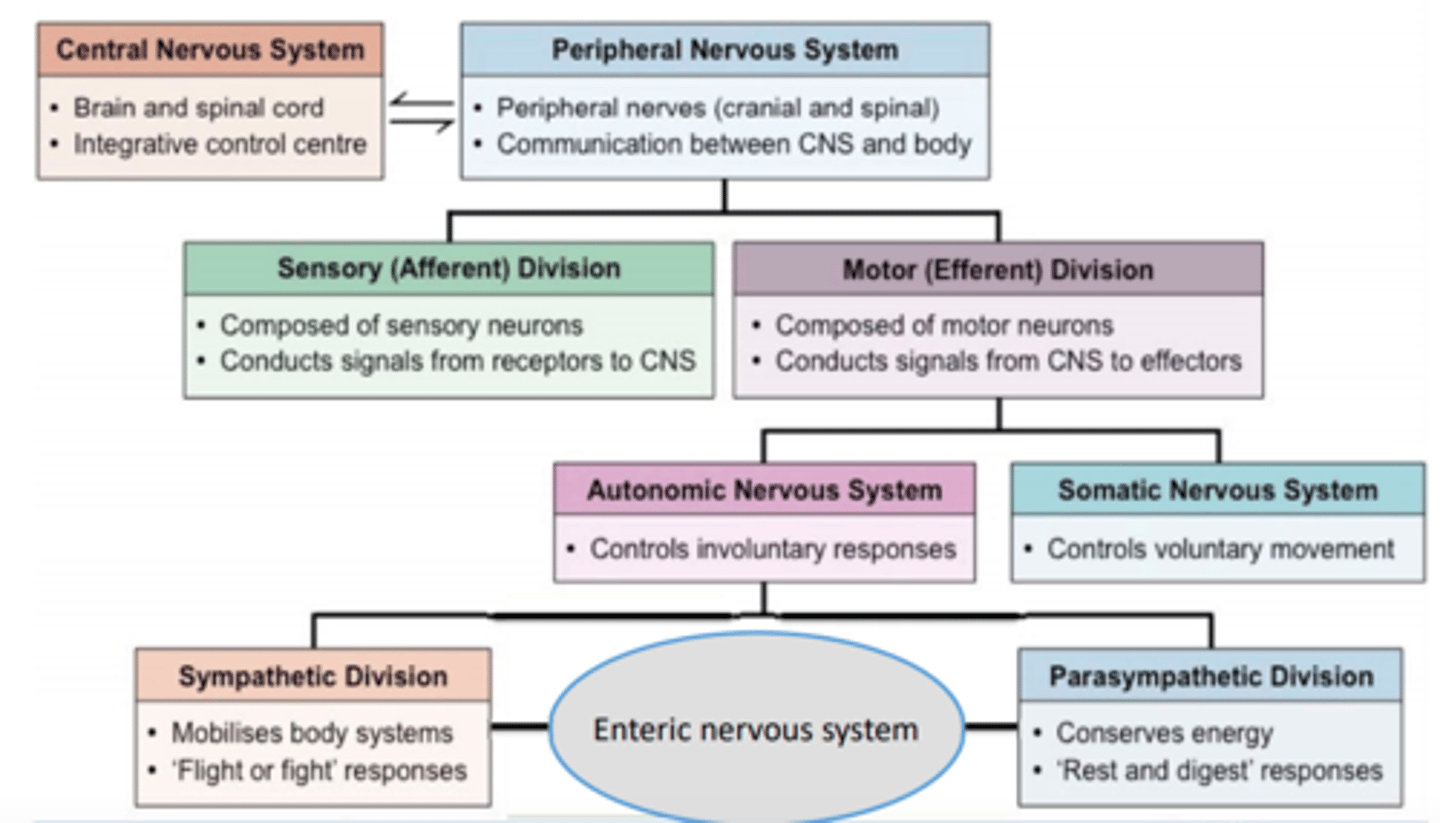
Somatic nervous system
controls voluntary movement