Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
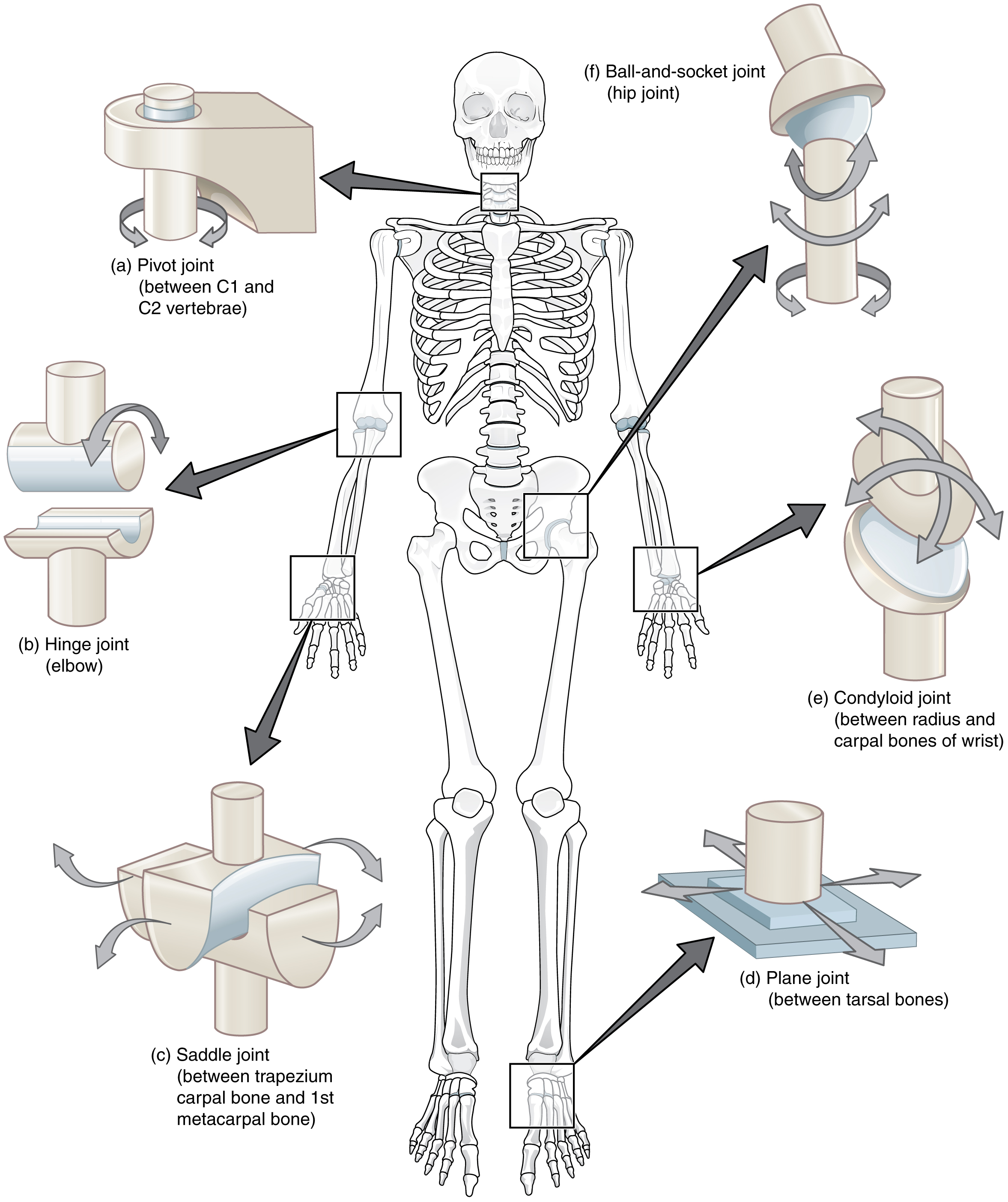
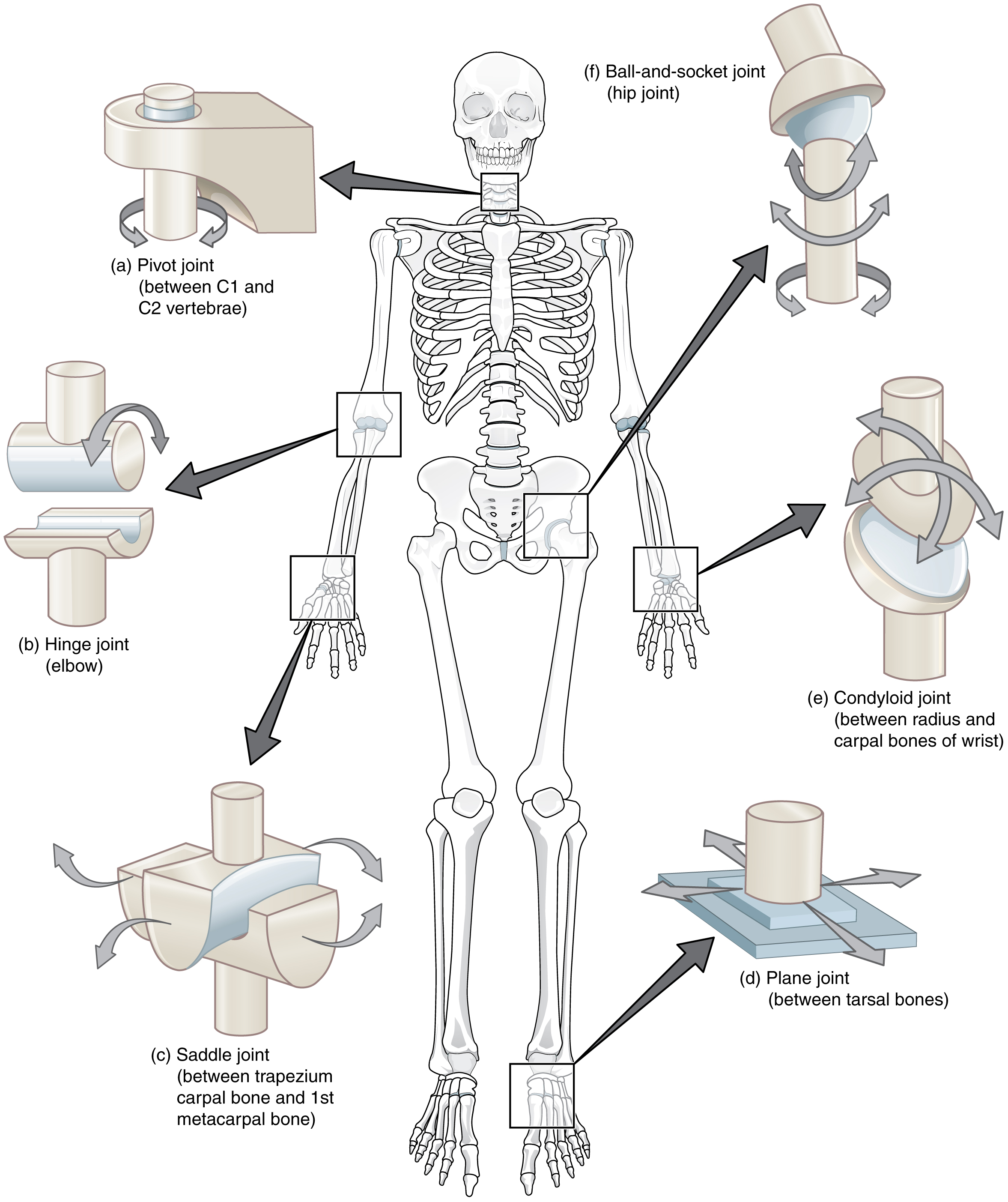
Where is the hinge joint found?
elbow
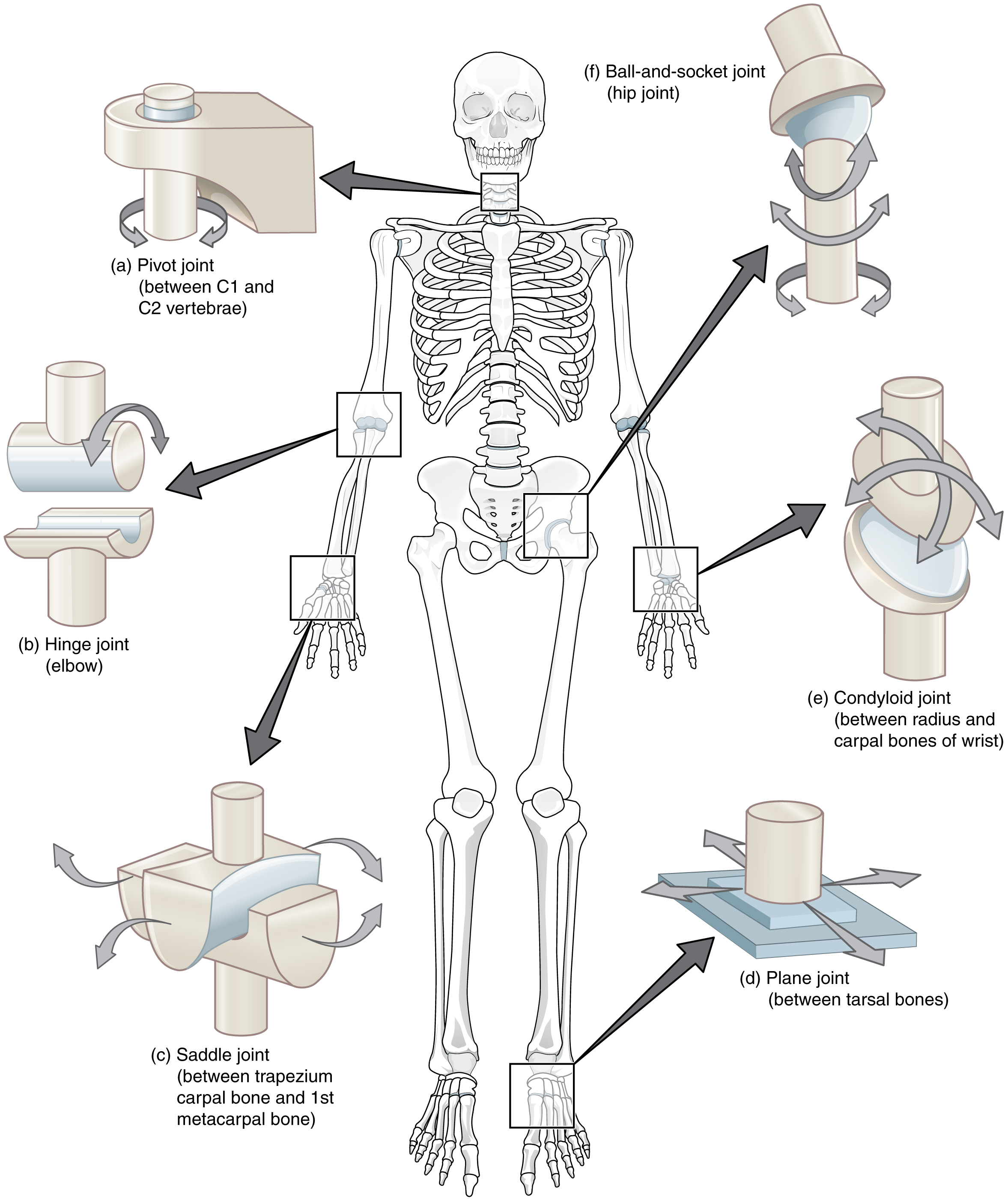
Where is the pivot joint found?
Between C1 and C2 vertabrae
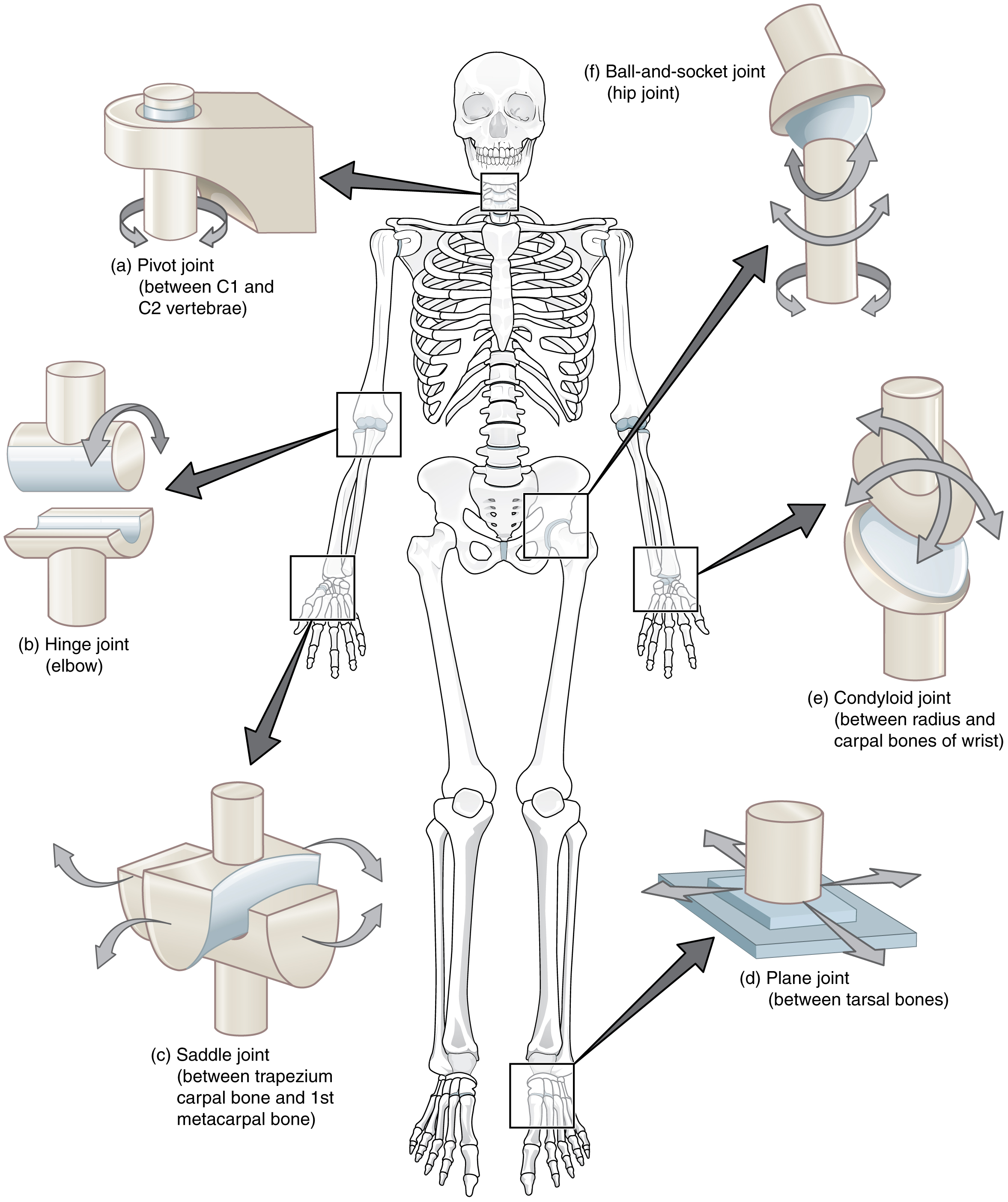
Where is the ball & socket joint found?
Hips and shoulders
Where is the gliding joint or plane joint found?
Feet/Heel
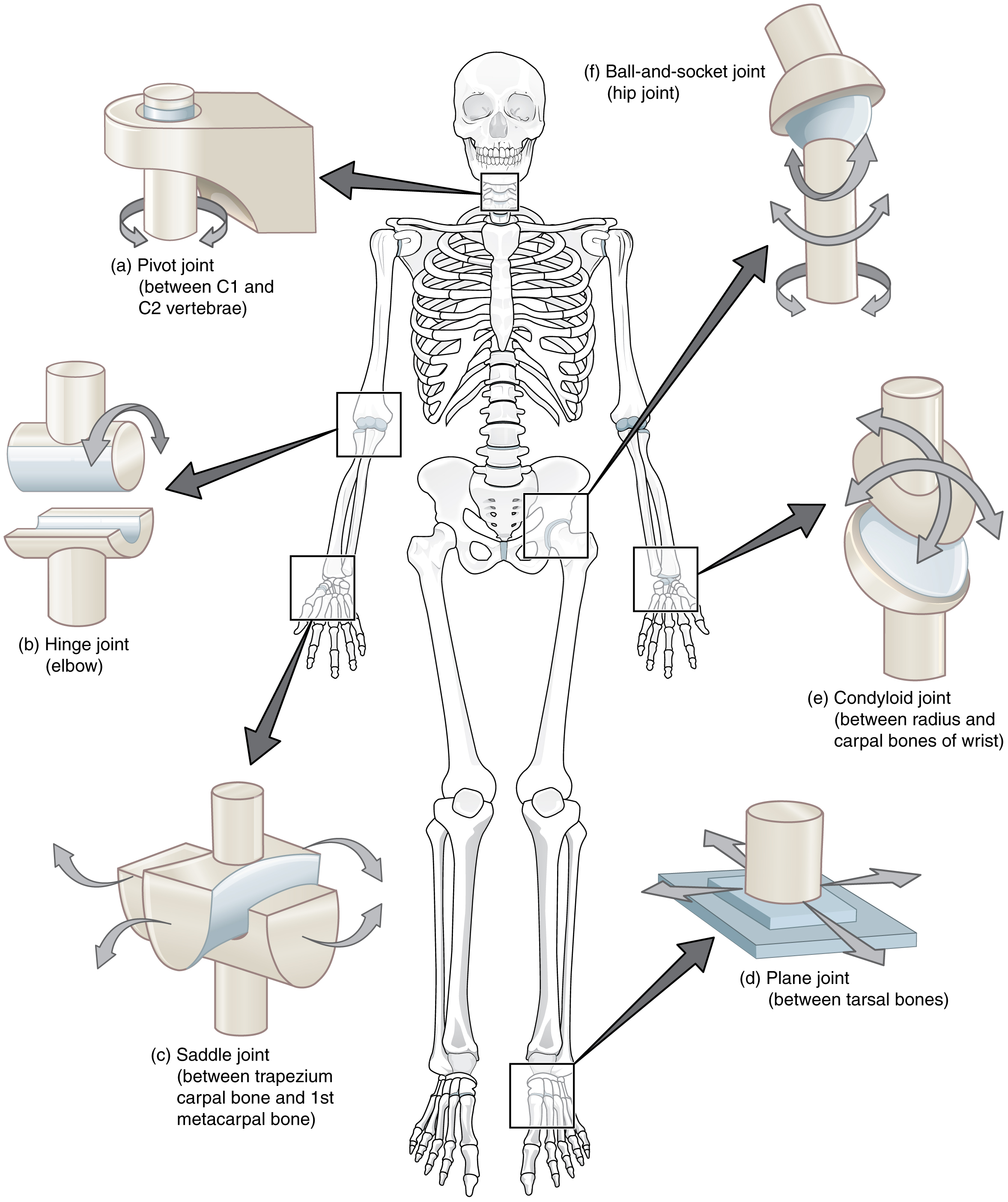
Where is the condylar joint found?
Wrist
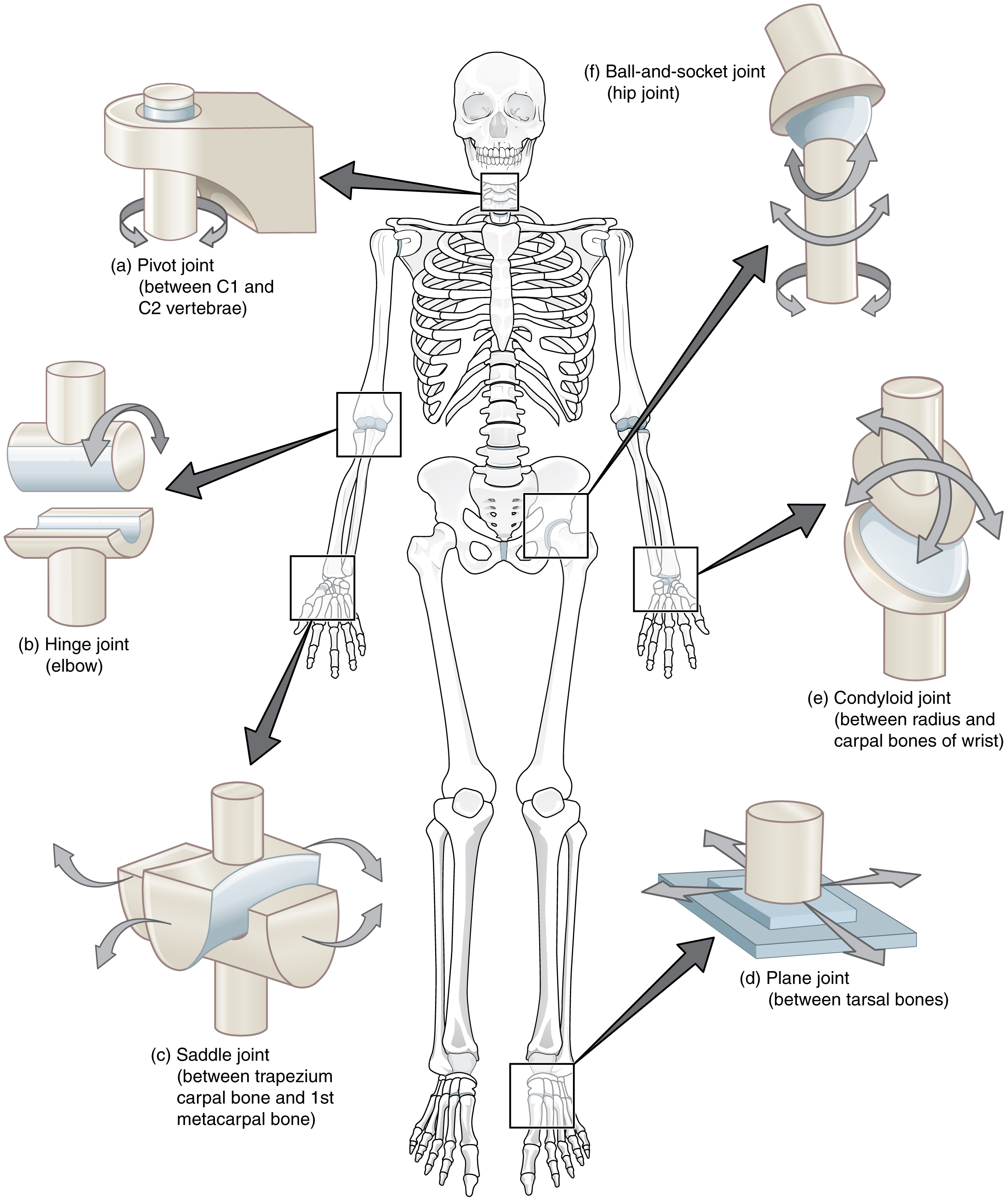
Where is the saddle joint found?
Wrist
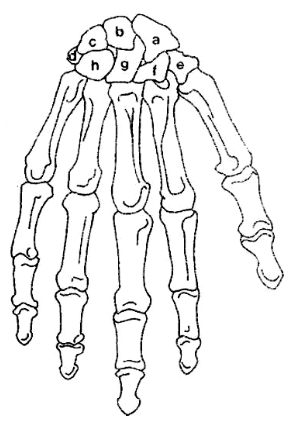
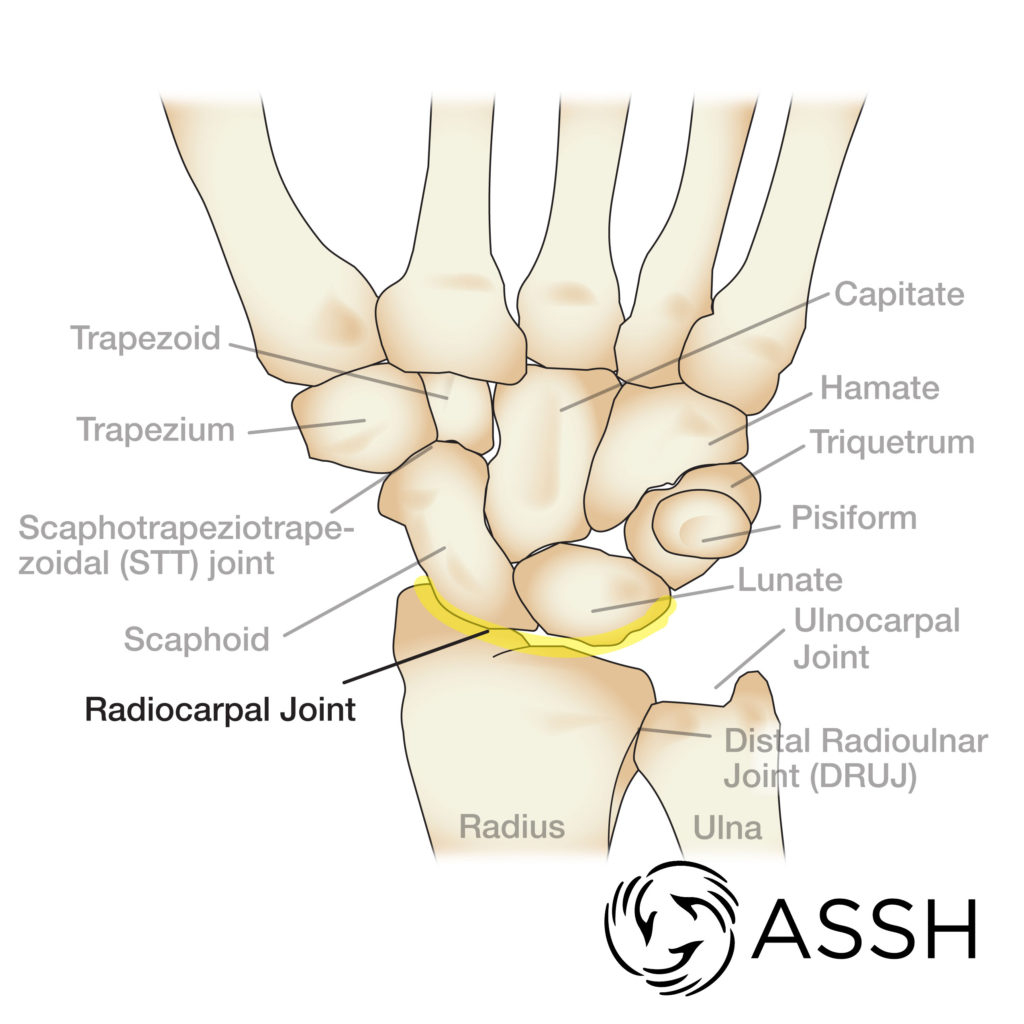
What is A?
Scaphoid
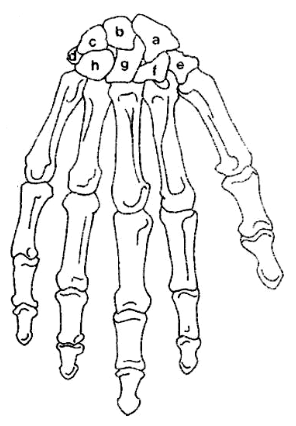
What is B?
Lunate
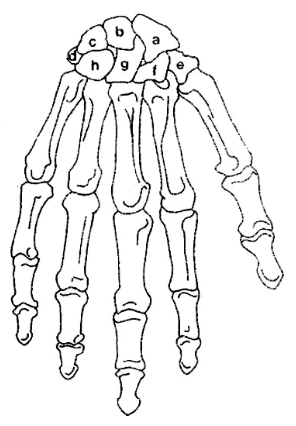
What is C?
Triquetrum
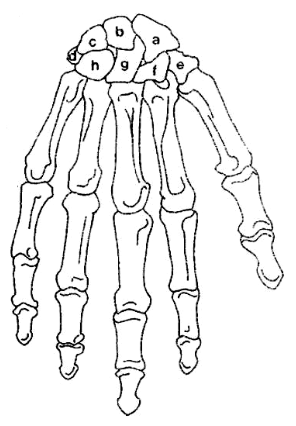
What is D?
Pisiform
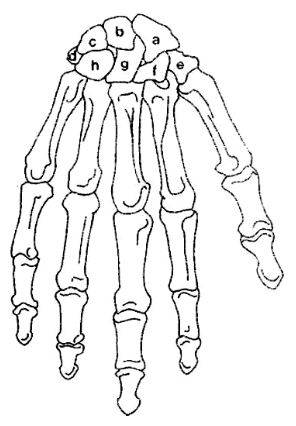
What is E?
Trapezium
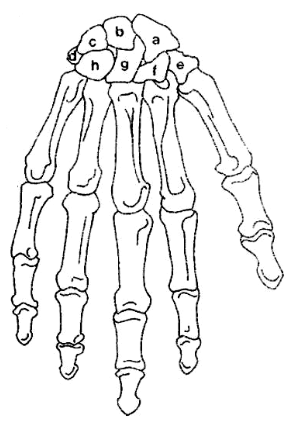
What is F?
Trapezoid
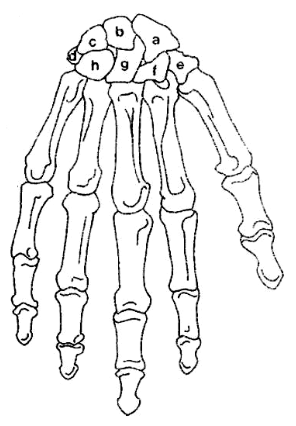
What is G?
Capitate
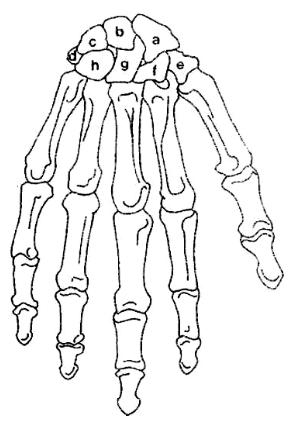
What is H?
Hamate
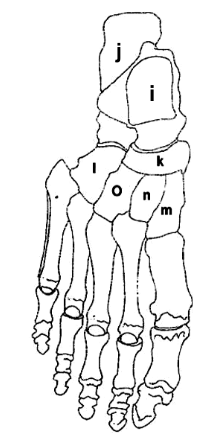
What is I?
Talus
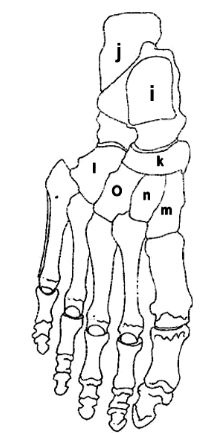
What is J?
Calcaneus
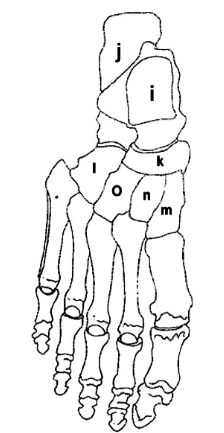
What is K?
Navicular
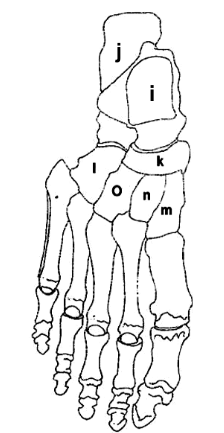
What is L?
Cuboid
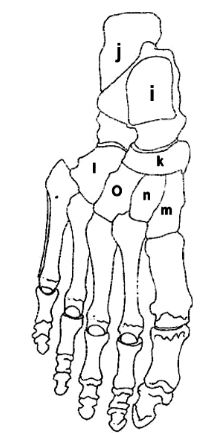
What is M?
Medial Cuneiform
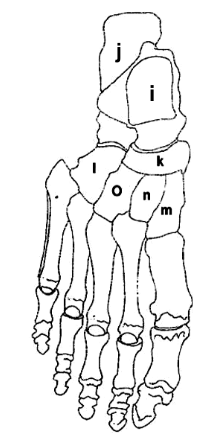
What is N?
Intermediate Cuneiform
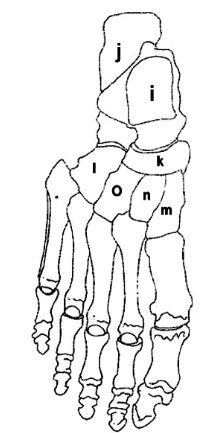
What is O?
Lateral Cuneiform
What is a common joint found in the wrist?
Radiocarpal Joint (condyloid joint)
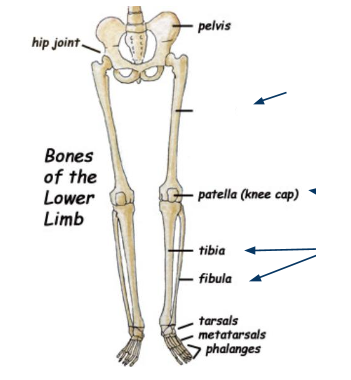
What bone is this?
Femur
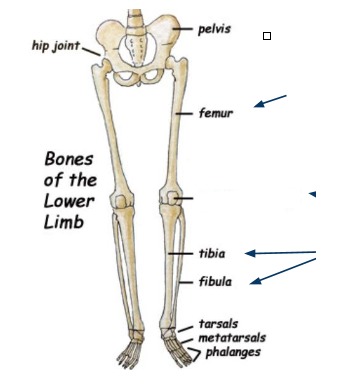
What bone is this?
Patella
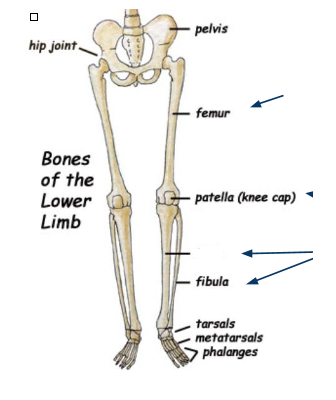
What bone is this?
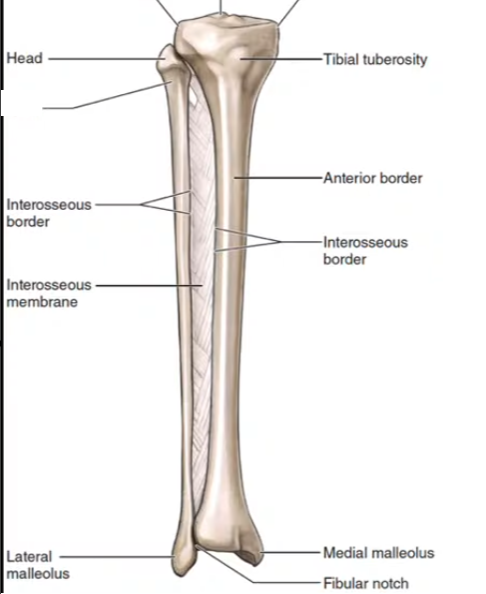
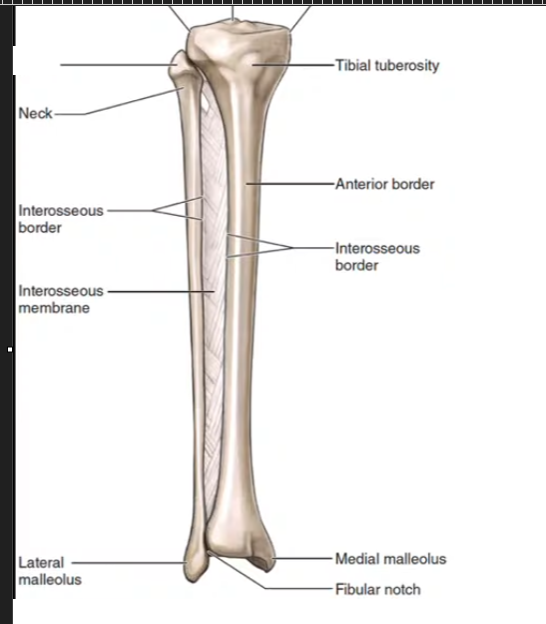
Tibia
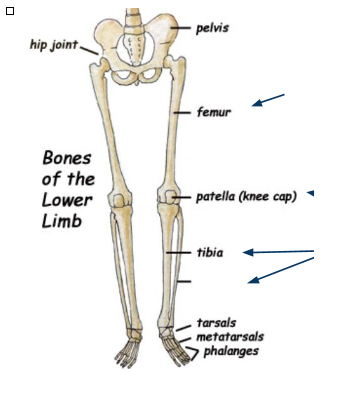
What bone is this?
Fibula
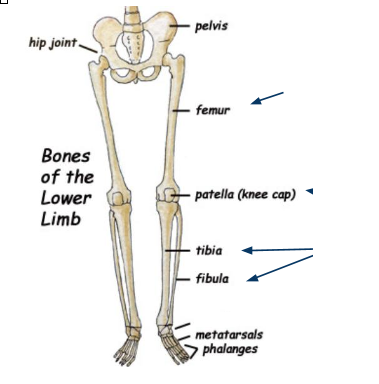
What bone is this?
Tarsals
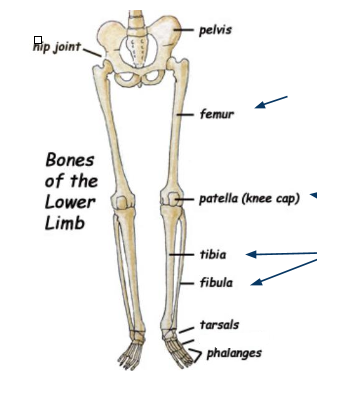
What bone is this?
Metatarsals
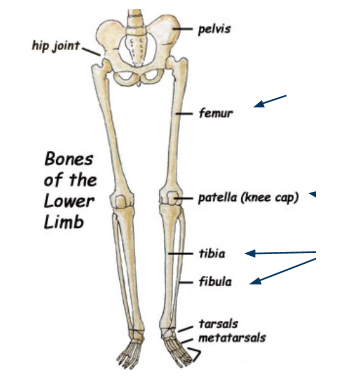
What bone is this?
Phalanges
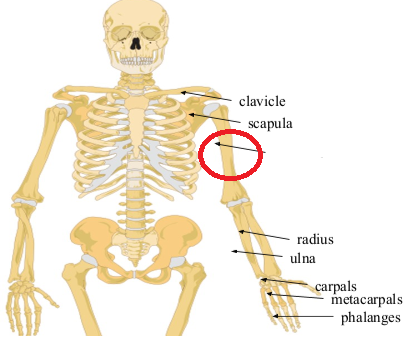
What bone is this?
Humerus
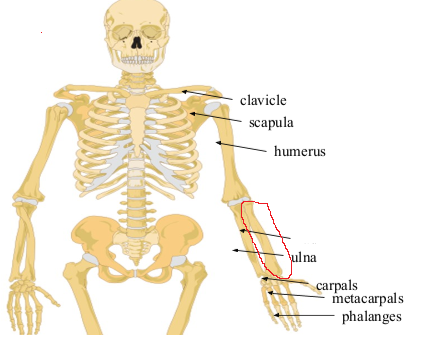
What bone is this?
Radius
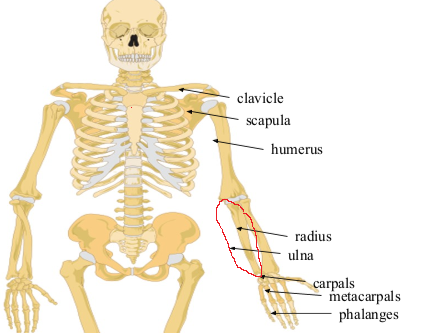
What bone is this?
Ulna
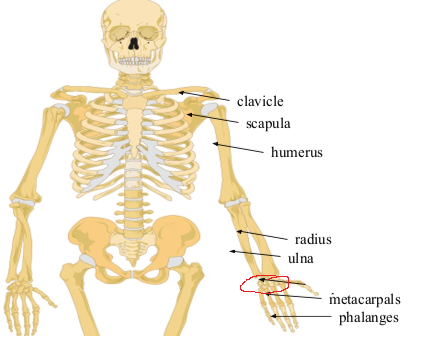
What bone is this?
Carpals
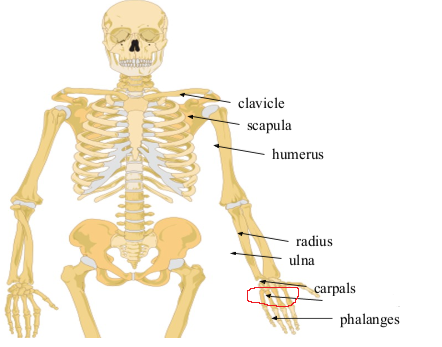
What bone is this?
Metacarpals
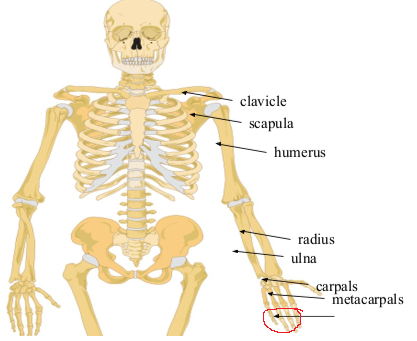
What bone is this?
Phalanges
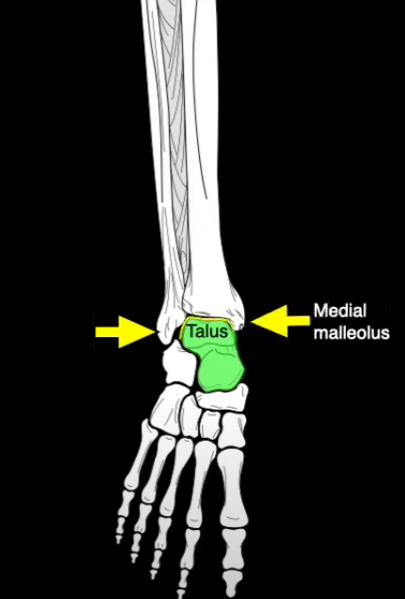
What section of the fibula is this?
Lateral Malleolus
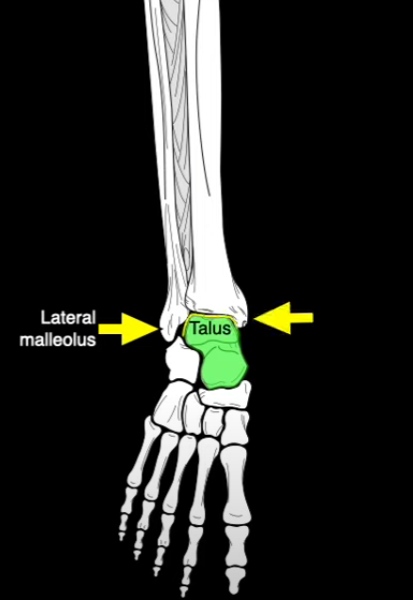
What section of the tibia is this?
Medial Malleolus
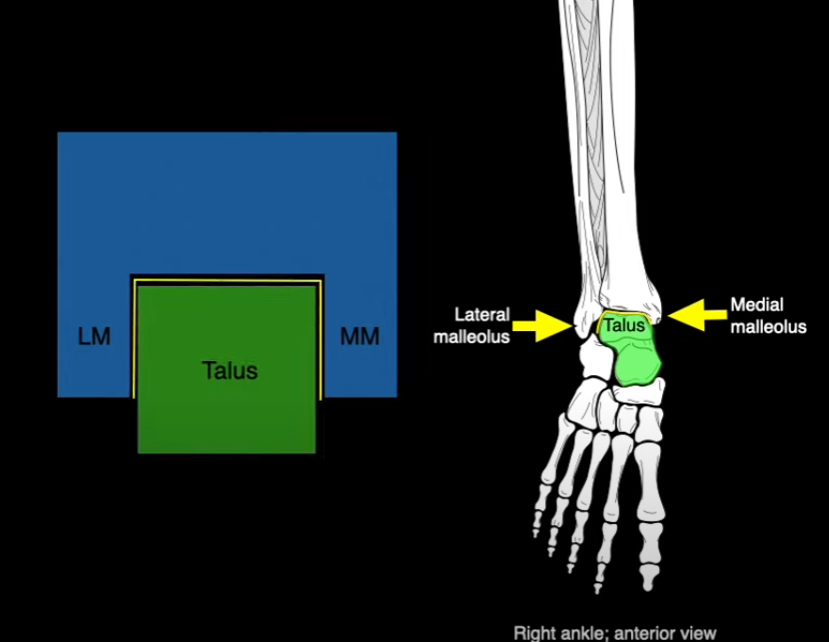
What joint is this?
Tibiotalar joint - Mortis joint
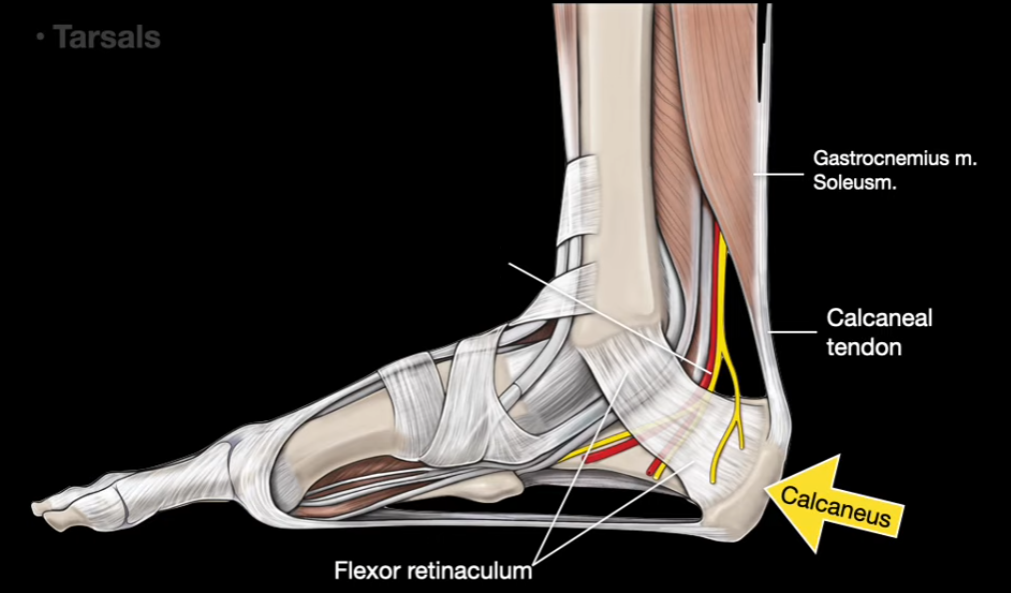
What is the nerve called?
Tarsal Tunnel
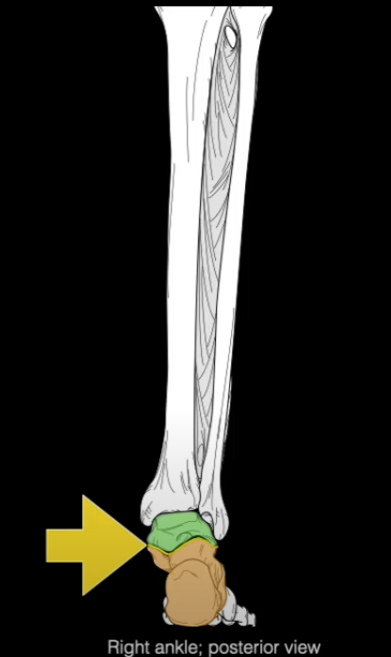
What joint is found here?
Subtalar Joint (Talocalcaneal joint)
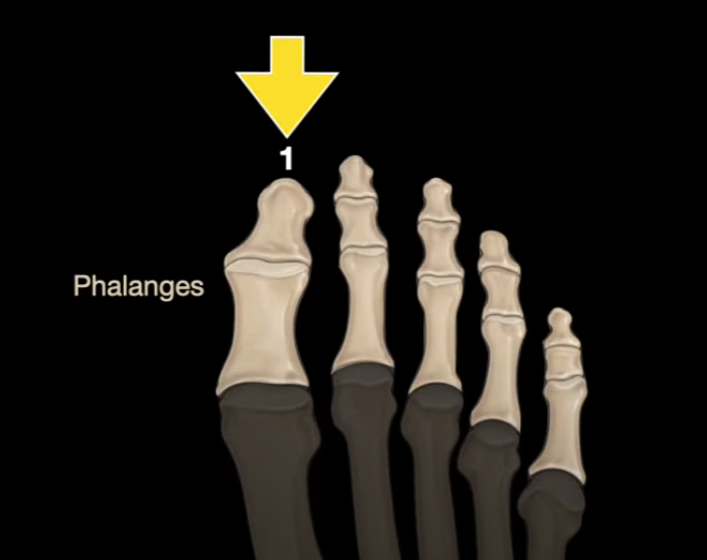
What is the name for the big toe?
Hallux
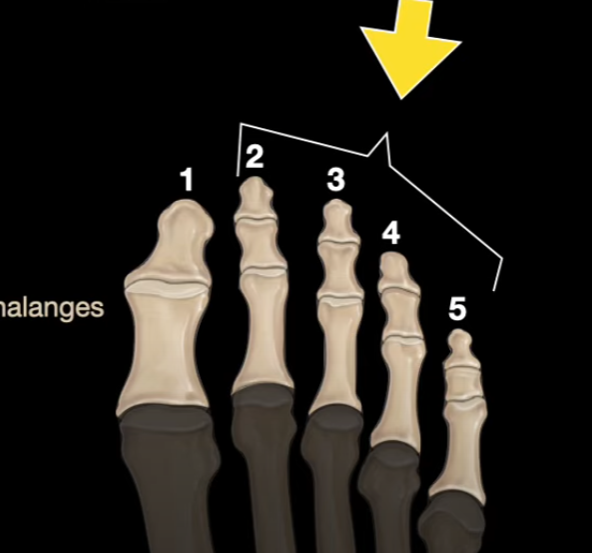
What is the name of the other toes not including the big toe?
Lesser Toes (2-5)
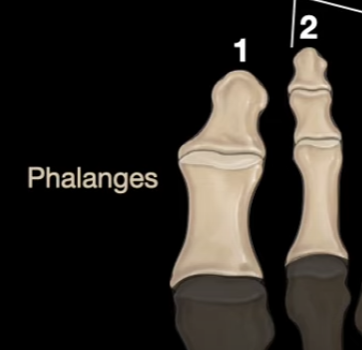
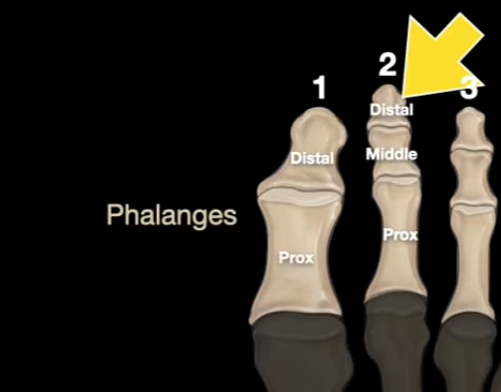
How are the toes labeled according to their location?
Big toe = Distal + Prox
Lesser toes = Distal + Middle + Prox
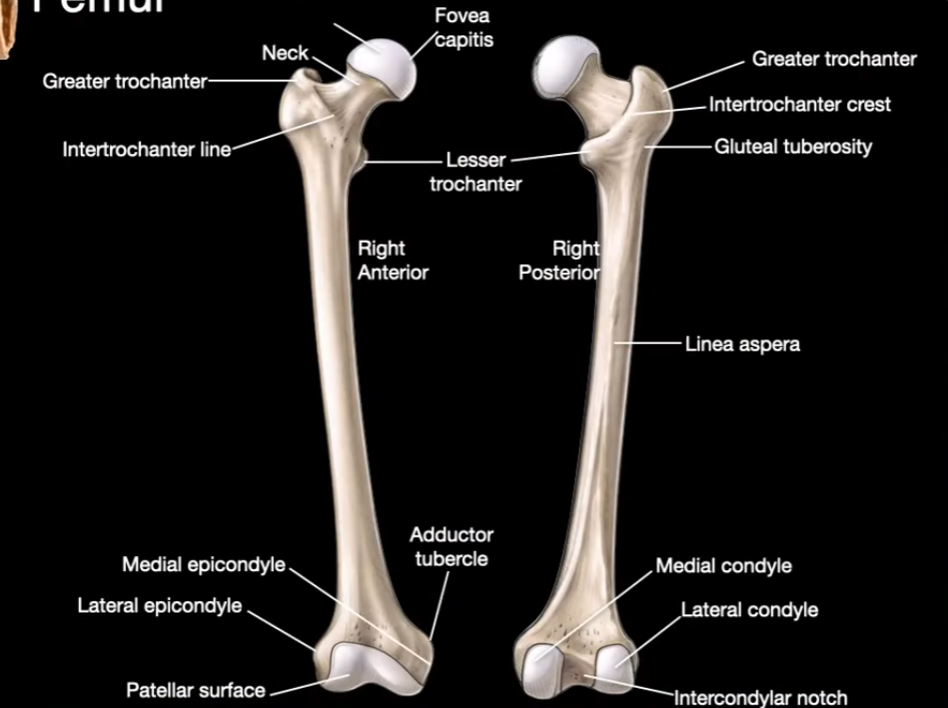
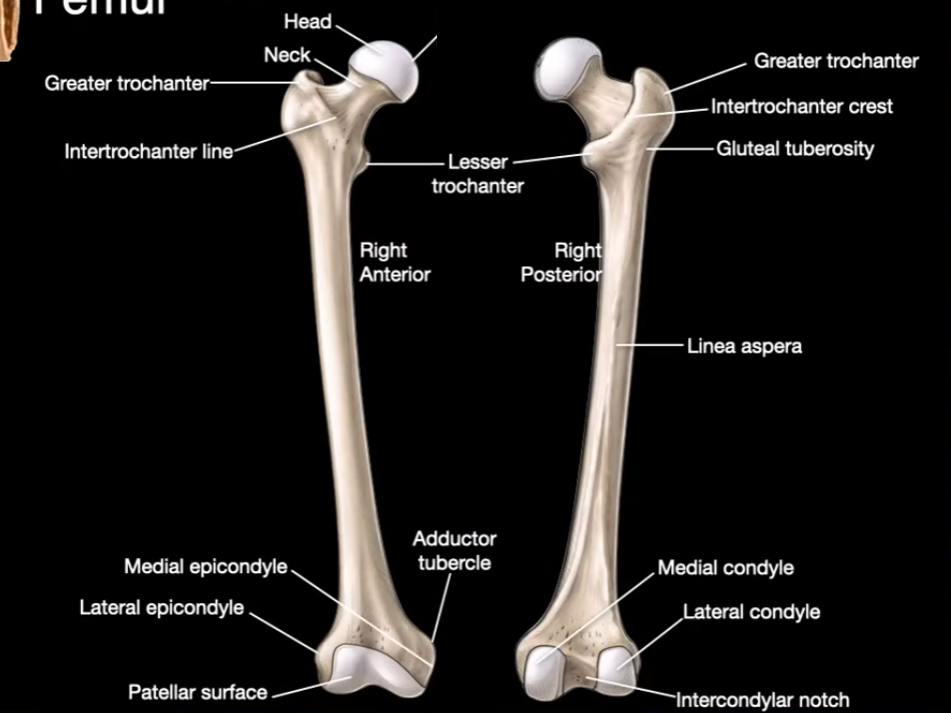
Head
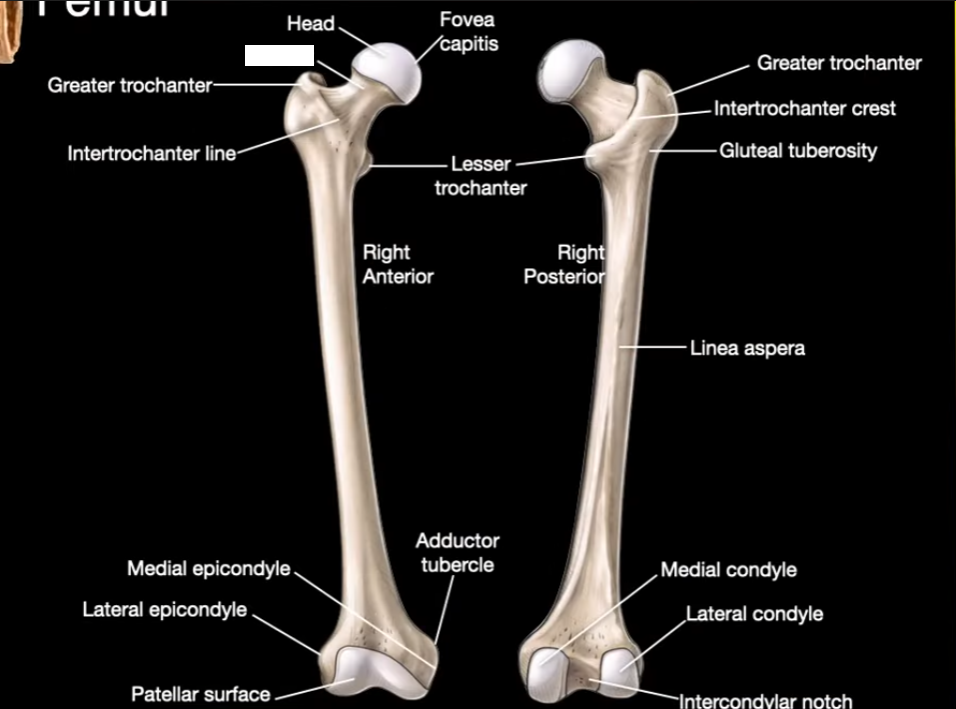
Neck
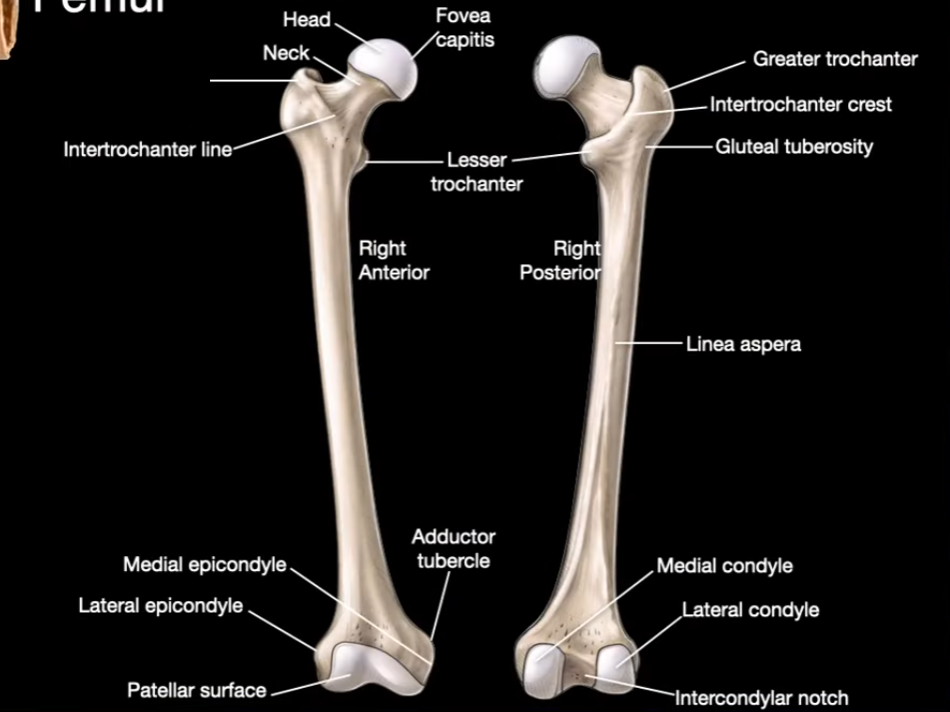
Greater trochanter
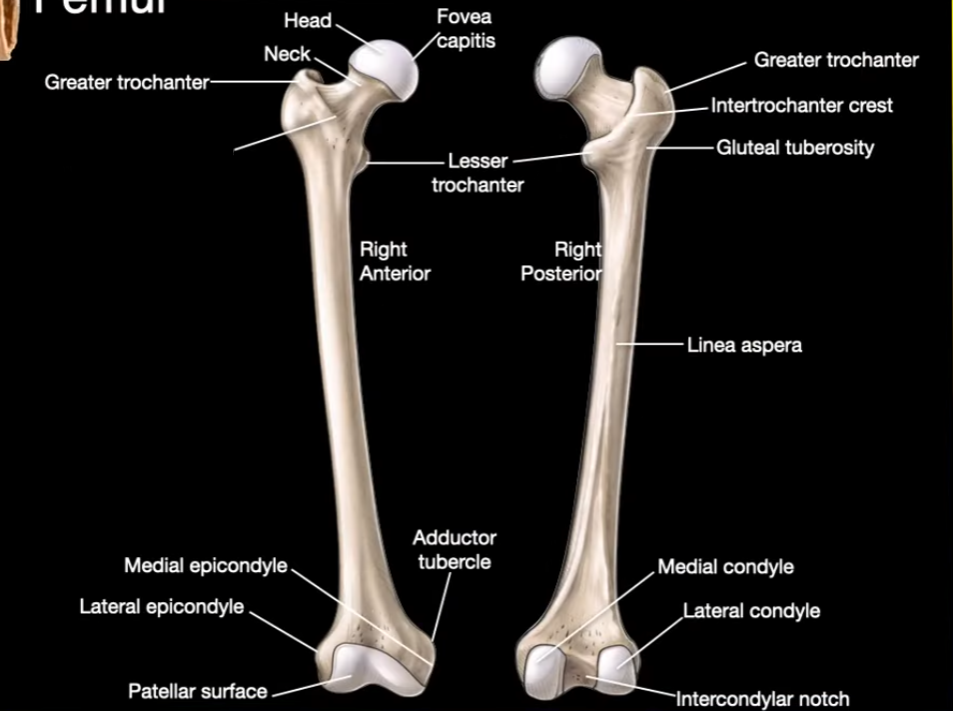
Intertrochanter line
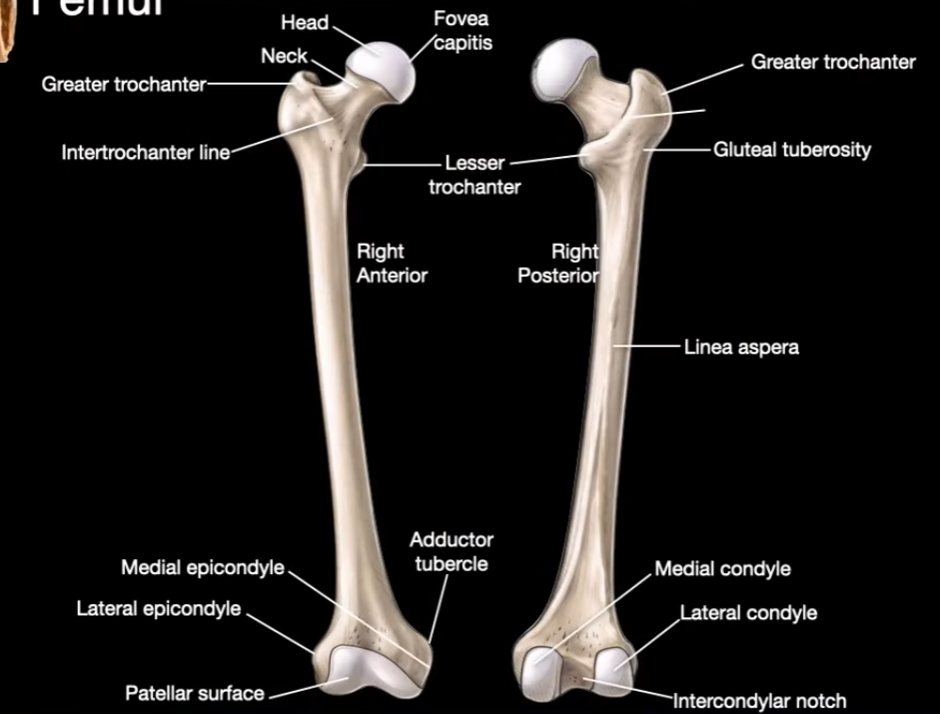
Fovea capitis
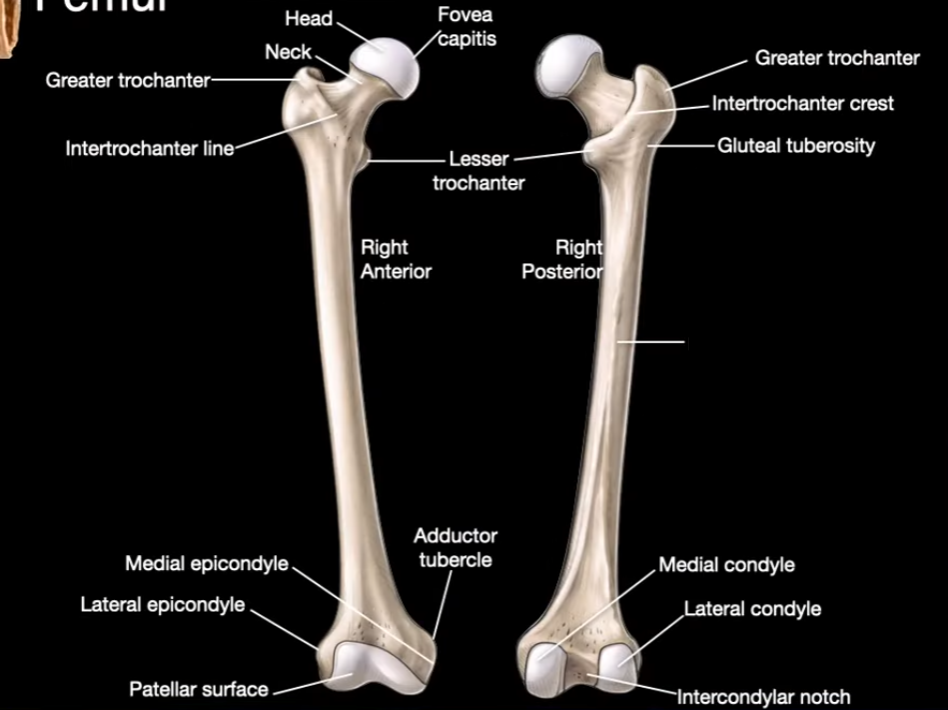
Intertrochanter Crest
Linea aspera
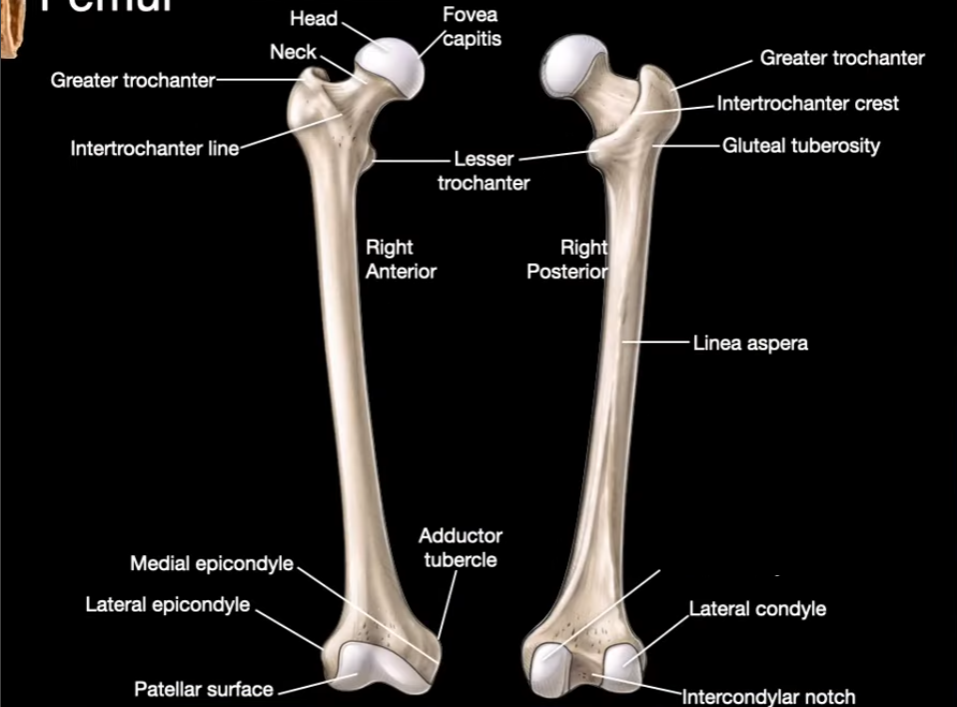
Medial Condyle
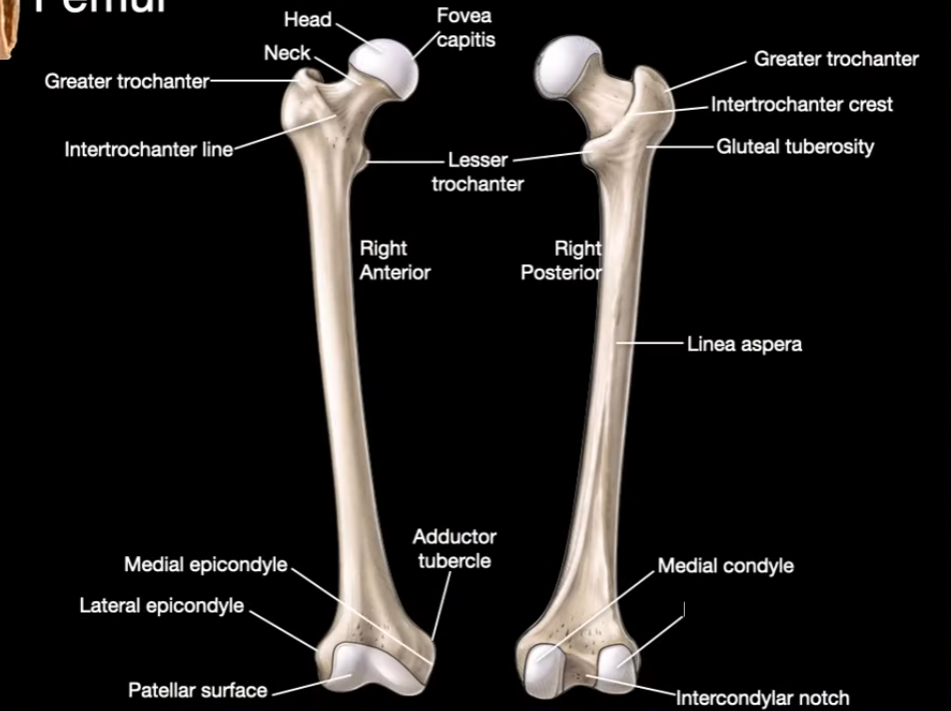
Lateral Condyle
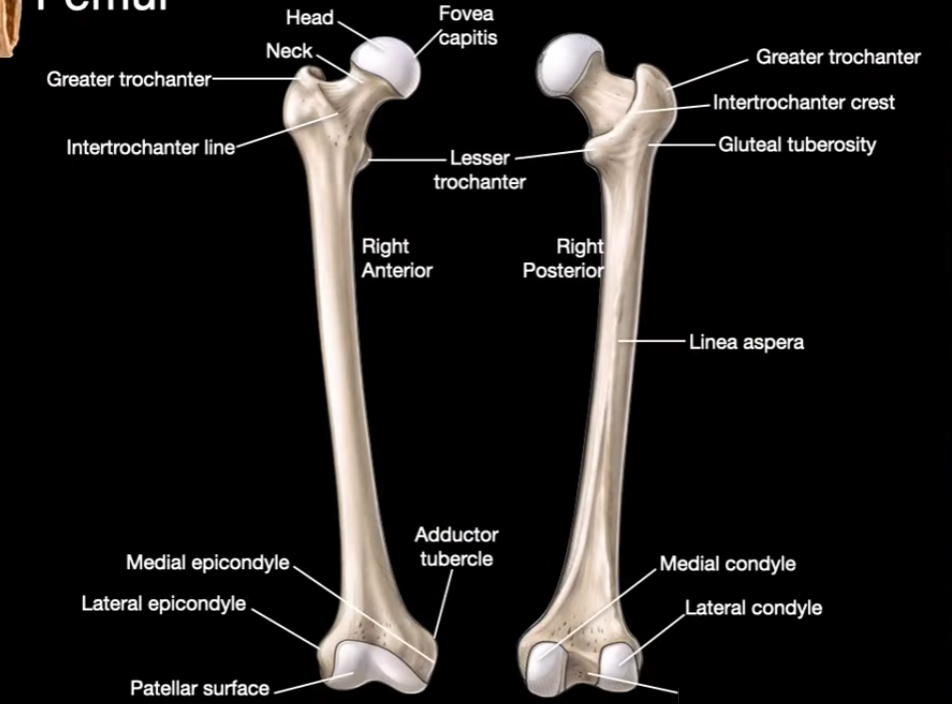
Intercondylar notch
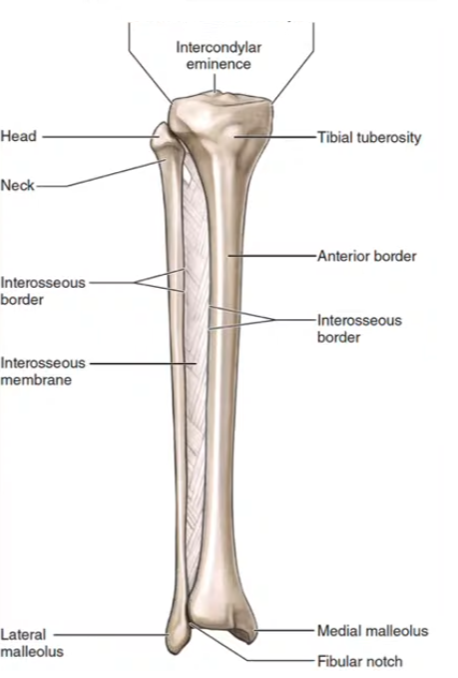
Lateral and medial condyles
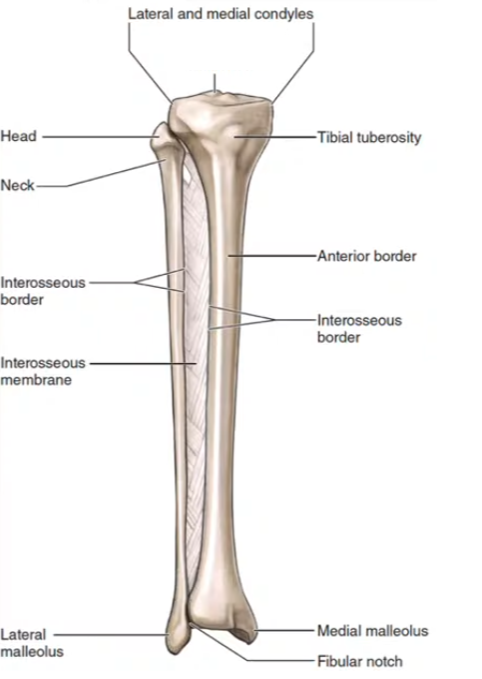
Intercondylar eminence
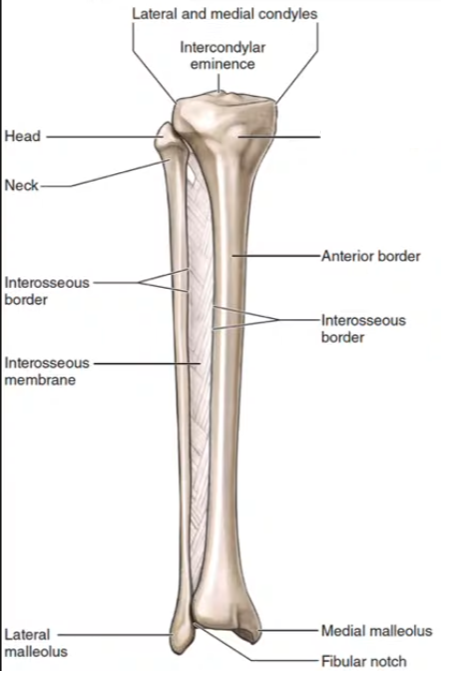
Tibial tuberosity
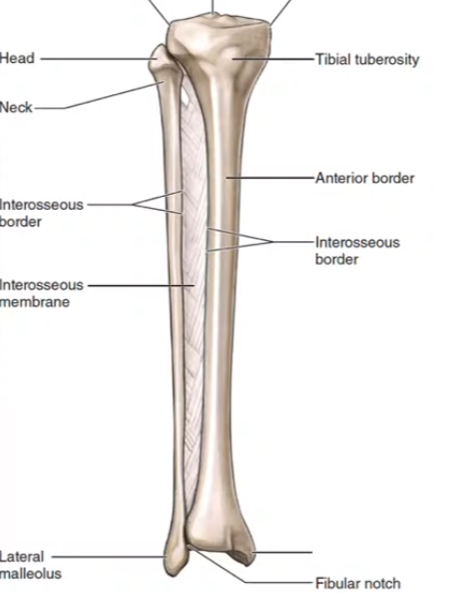
Medial malleolus
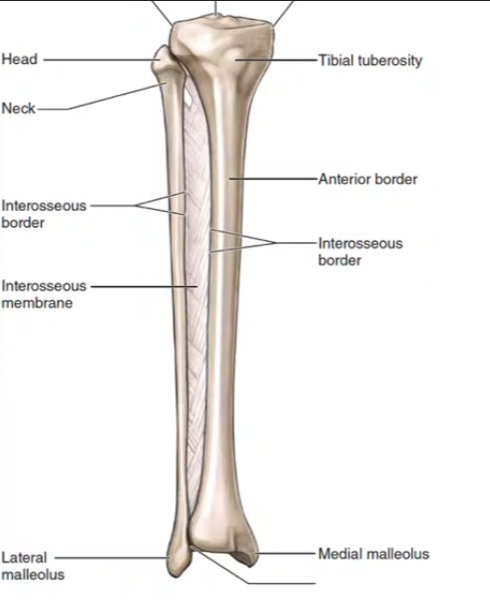
Fibular Notch
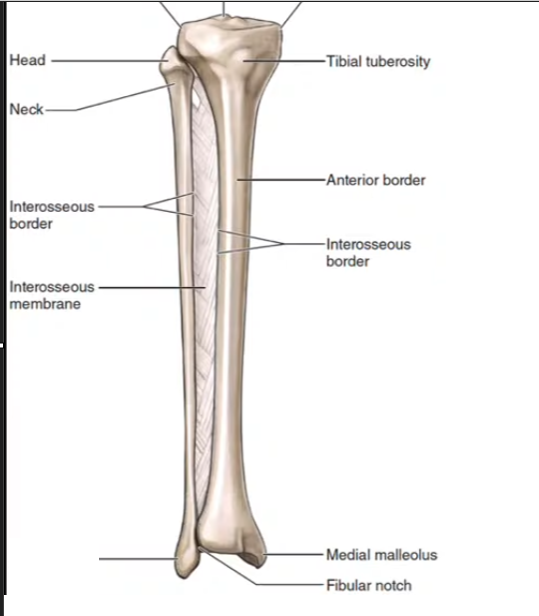
Lateral malleolus
Neck
Head
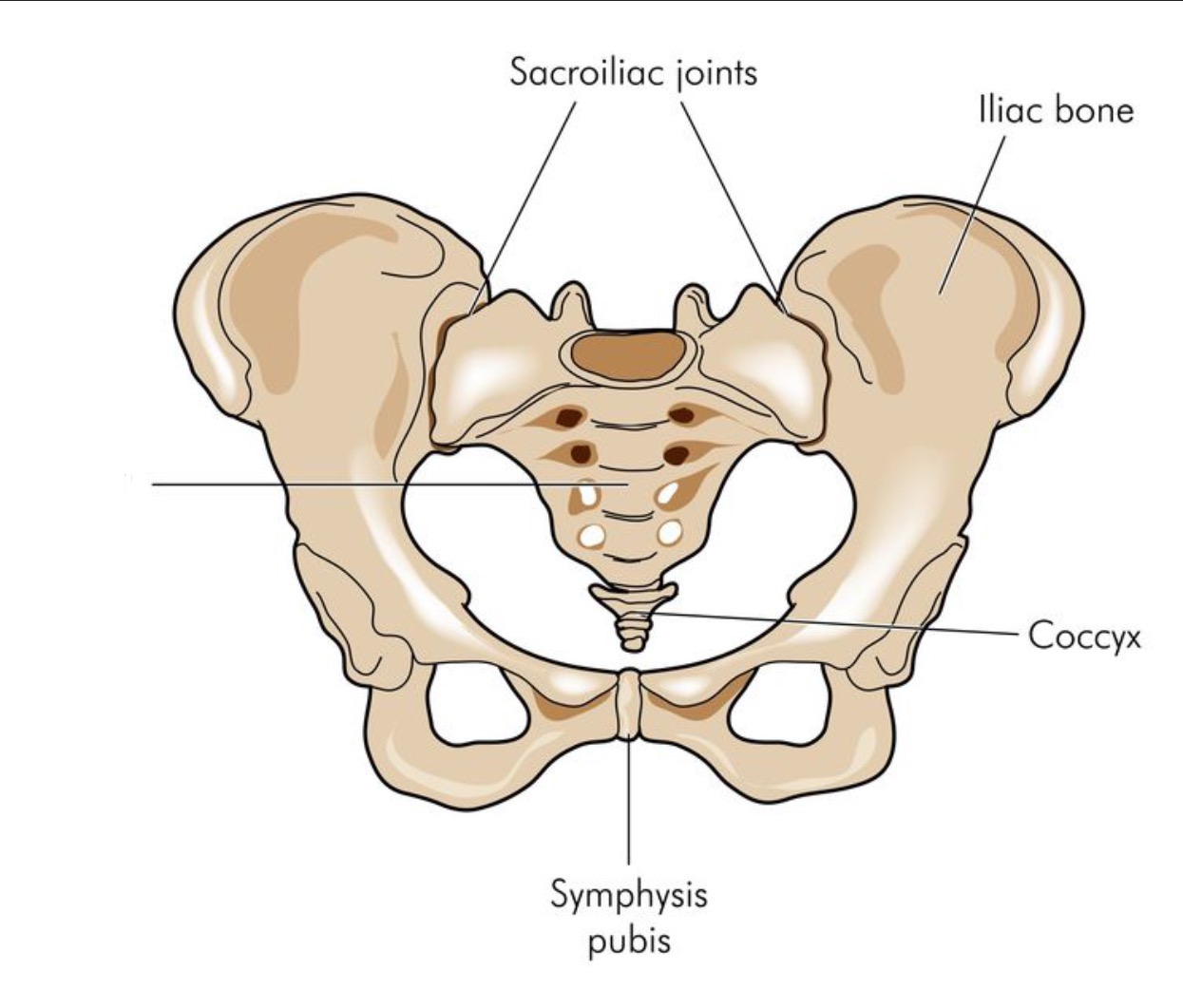
Sacrum
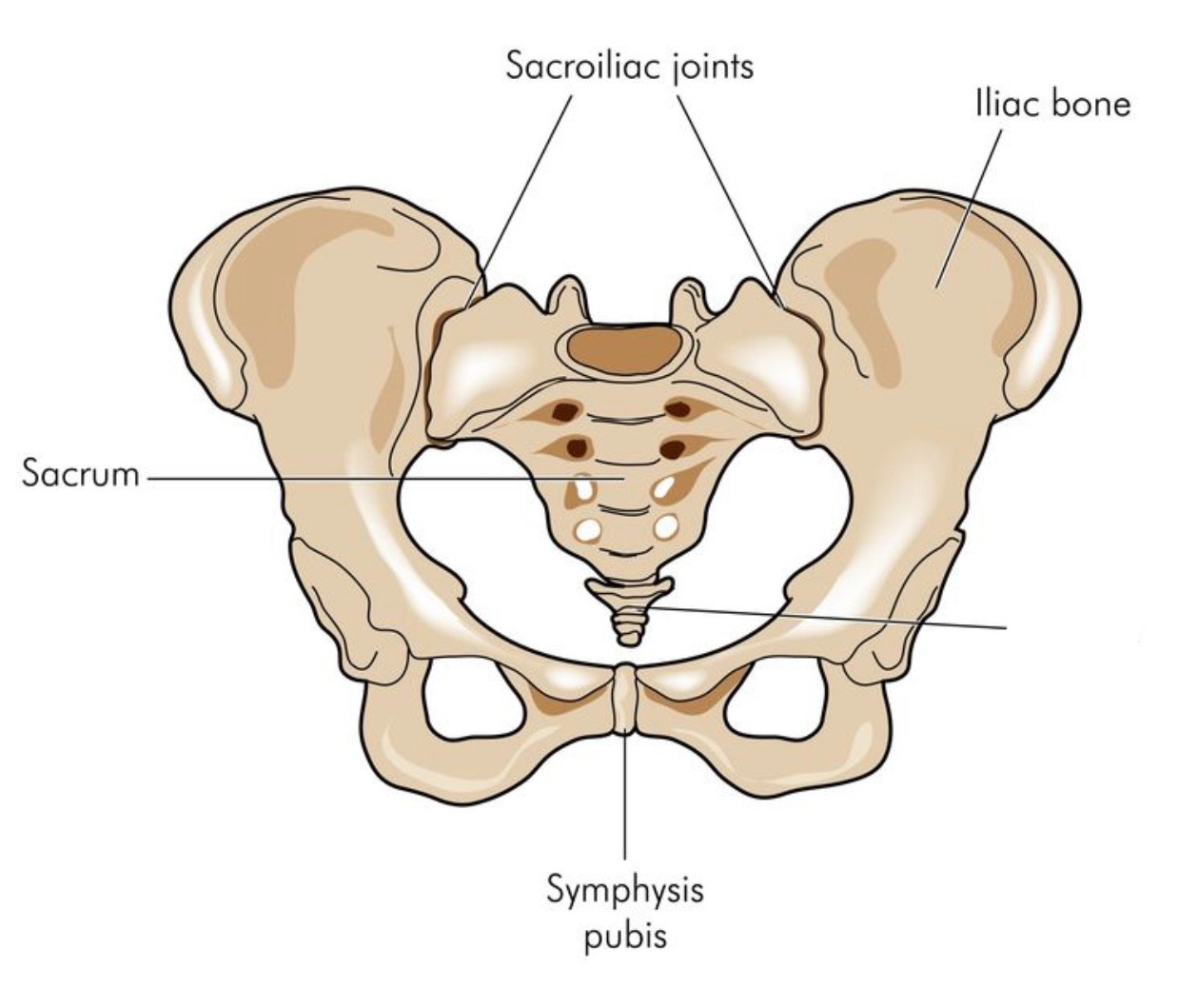
Coccyx
PTH Hormone
Bone hormone that controls whether or not bone breaks down to release calcium into the bloodstream
Fracture common in osteoporotic bones (spongy bone)
Compression fractures
What type of tissue covers the epiphysis of bones and reduces friction to bones?
Articular cartilage
What is the technical term for the matrix of the spongy bone? And what is its function?
Trabeculae which supports and aids in weight distribution and stresses on the bone. It also plays a part in blood cell production, storage of minerals, and remodeling and housing marrow.
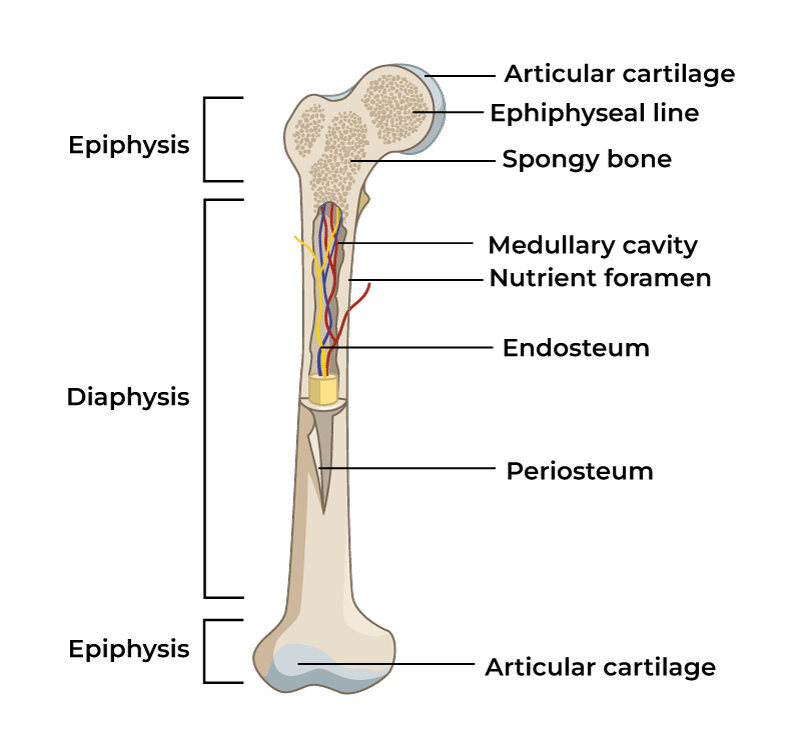
Diaphysis vs epiphysis
Epiphysis is the top and bottom part of the bone
Diaphysis is the middle of the bone
Styloid process
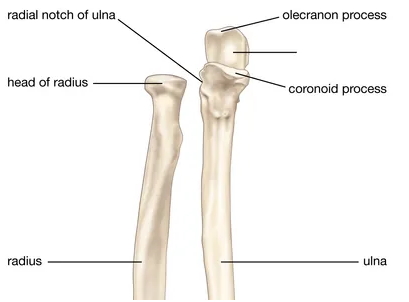
What part of the bone is this?
trochlear notch
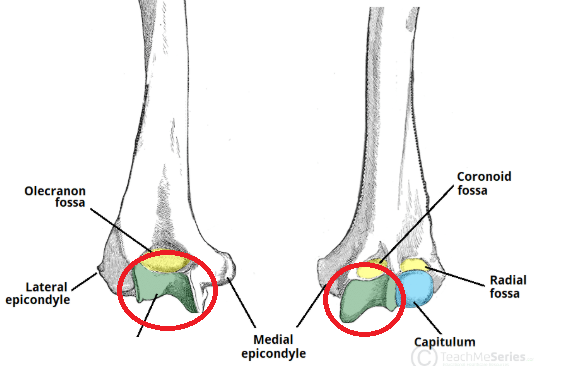
a pulley-shaped or grooved structure over which a bone, tendon, or muscle slides or articulates, functioning similarly to a pulley system
this bone is the humerus
trochlea
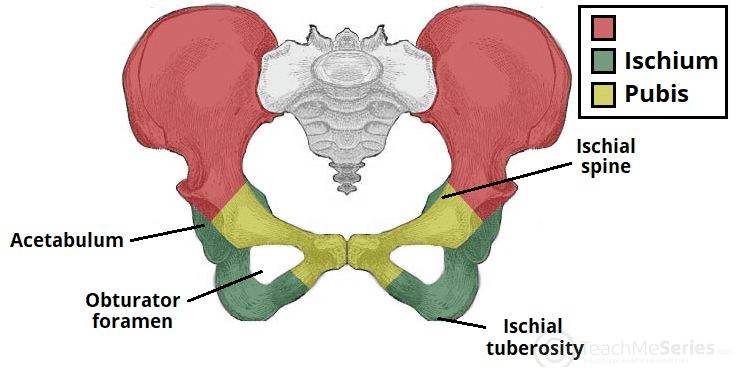
Ilium
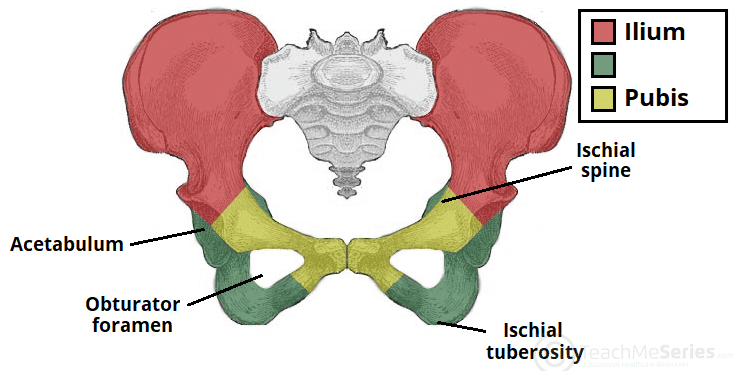
Ischium
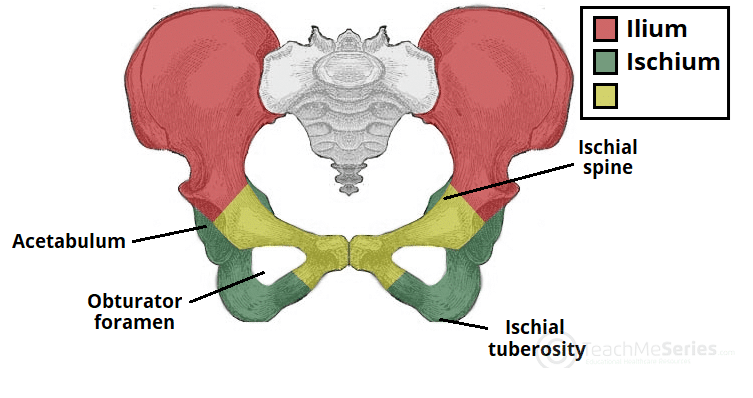
Pubis
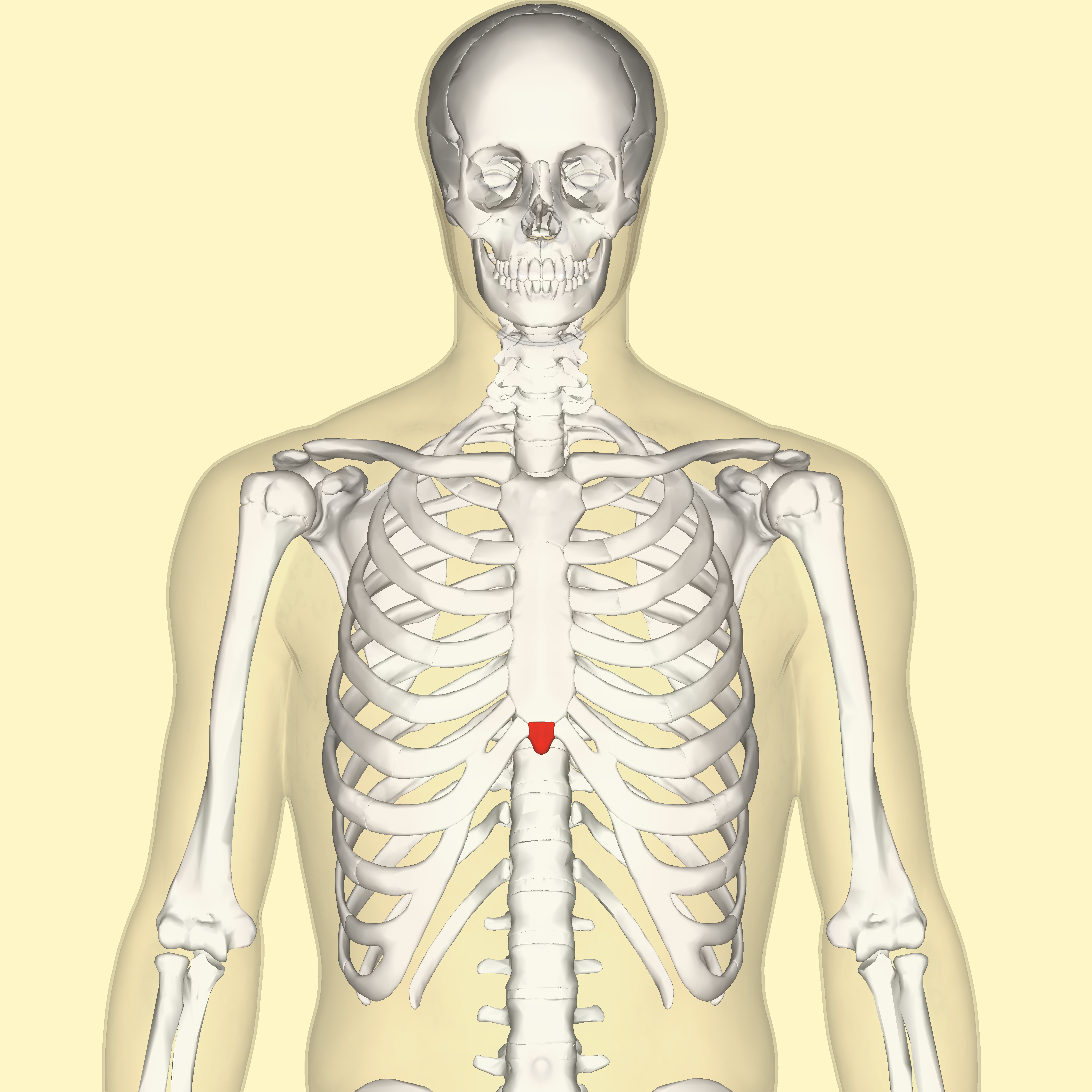
What is the pointy part of the sternum
Xiphoid process
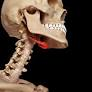
Only free floating bone that doesn’t articulate with any other bone
Hyoid bone
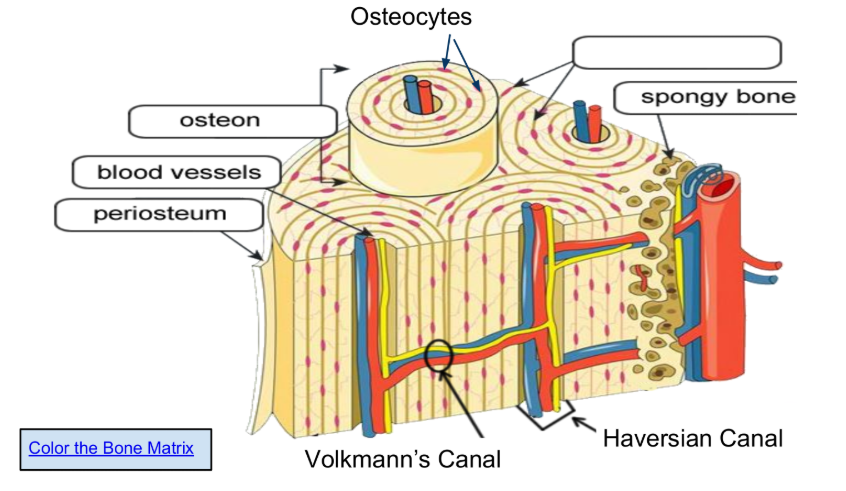
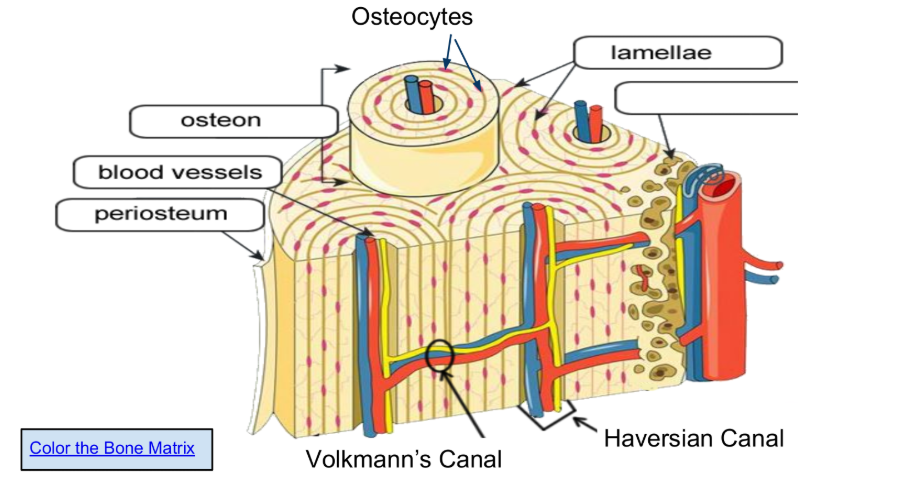
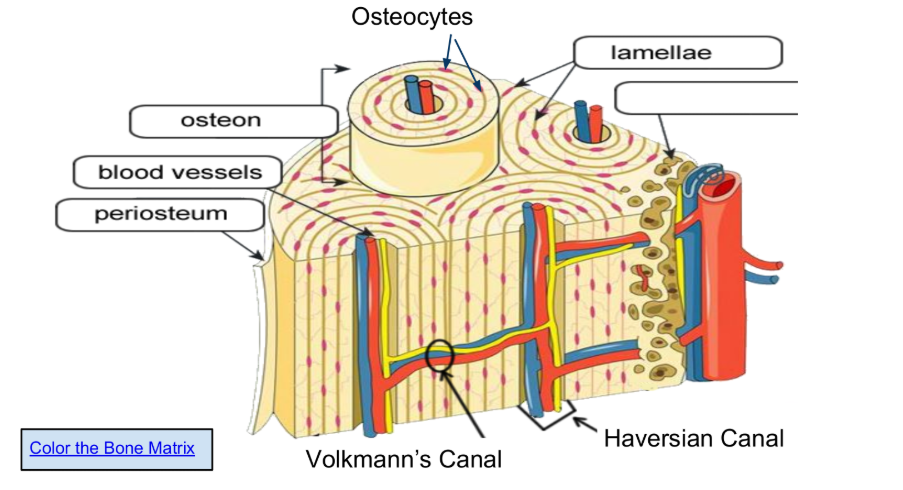
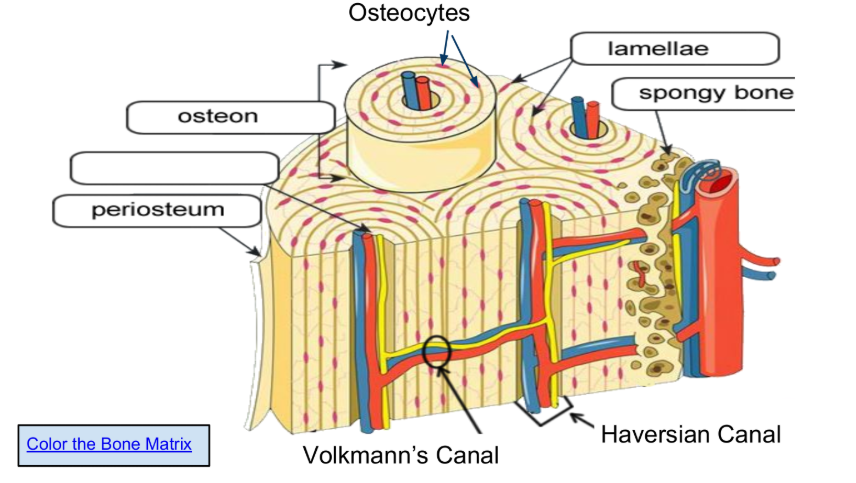
Osteons are arranged in concentric circles called lamellae.
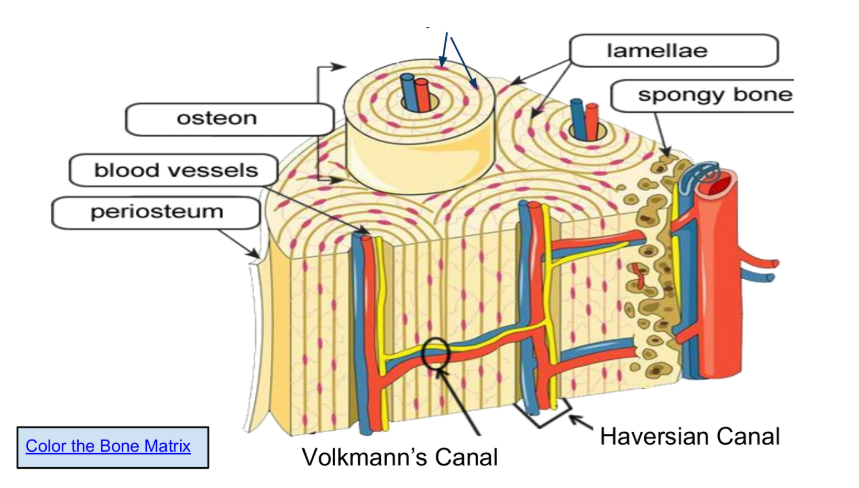
Osteocytes (in lacunae) are mature bone cells make up the
majority of the bone structure
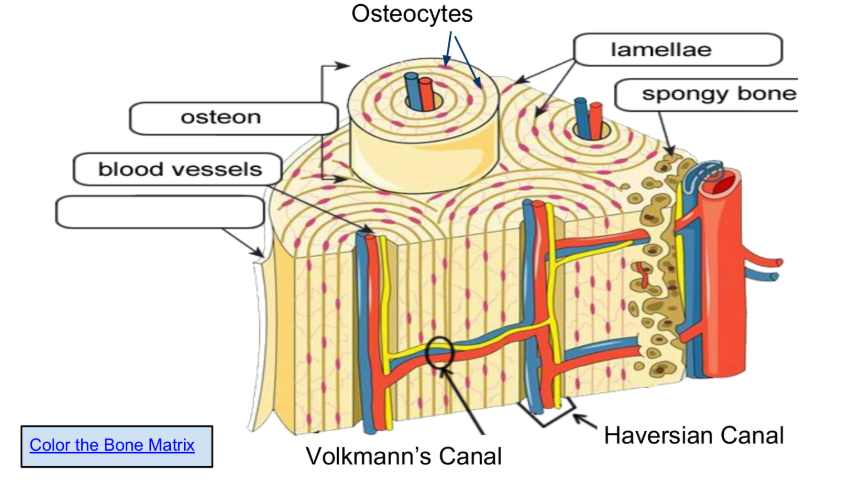
The periosteum is a vital sheath covering bones, essential for bone growth, healing, and maintenance by providing a blood supply, housing osteogenic cells (like osteoblasts), and supplying sensory innervation that causes pain and enables the sense of touch
The function of the spongy bone is to house the bone marrow, allow for RBCs formation or erythropoiesis, and allow bones to be less dense and more light. Spongy bone also allows for flexibility.It consists of a network of trabeculae that help distribute stress and improve structural integrity.
Blood vessels, which supply essential oxygen and nutrients for the living bone tissue, remove metabolic waste products, and facilitate the transport of hormones and immune cells.
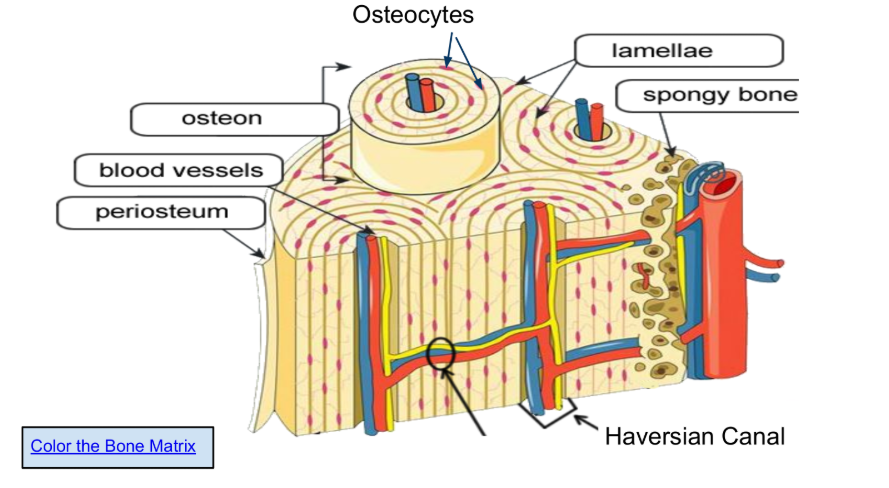
Volkmann’s Canal, function to create a vascular network within the compact bone tissue by connecting Haversian canals (central canals of osteons) to each other, the periosteum (outer bone layer), and the endosteum (inner bone lining), allowing blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics to supply and nourish the bone cells, remove waste, and sustain bone health
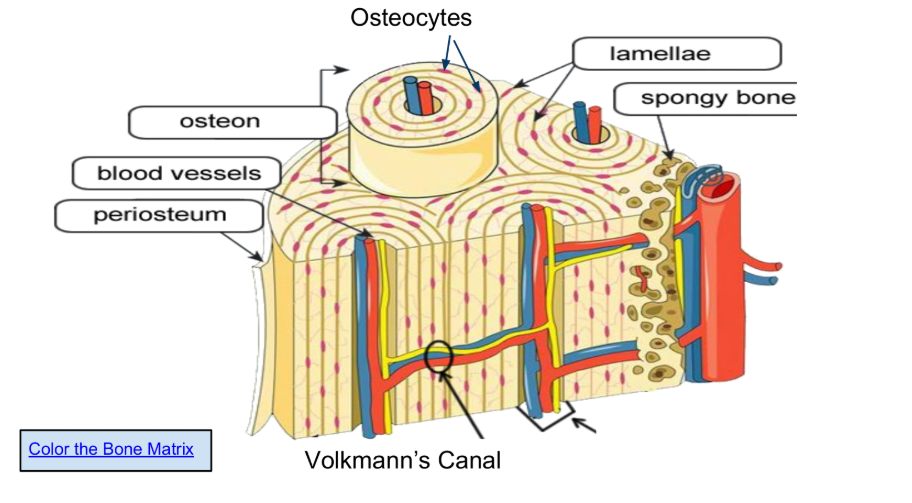
Haversian Canal, a tiny, central channel within a microscopic structural unit of compact bone called an osteon, which contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves to provide nourishment, oxygen, and waste removal to bone tissue
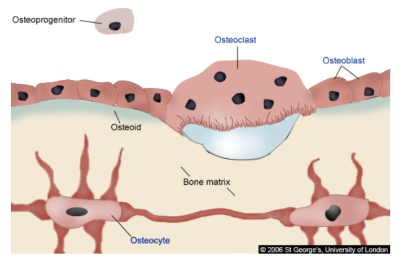
Function of osteoclasts?
To break down/consume bone by secreting acid. It’s useful so that it can release calcium into the bloodstream if there is not enough calcium in the body.
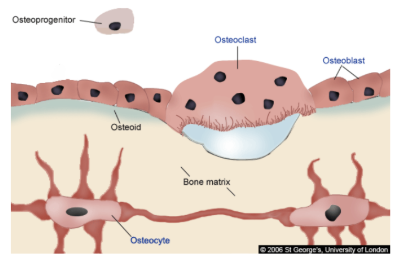
Function of osteoblasts?
To build up bone
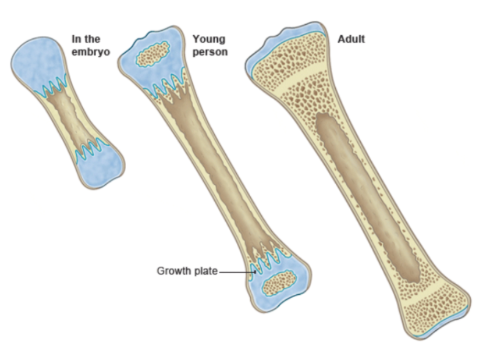
What is ossification?
As bones grow, the cartilage is replaced by bone
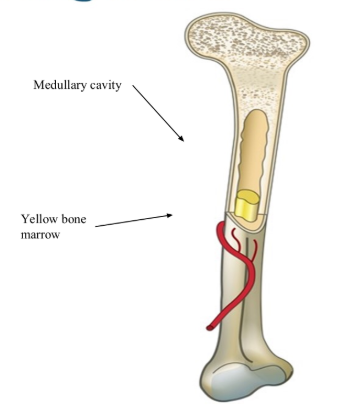
In the diaphysis of the long bone, a hollow medullary cavity is found.
What are the functions of yellow bone marrow?
Fat storage, blood cell production, bone formation and repair, immune function, regulation of metabolism, and mineral storage
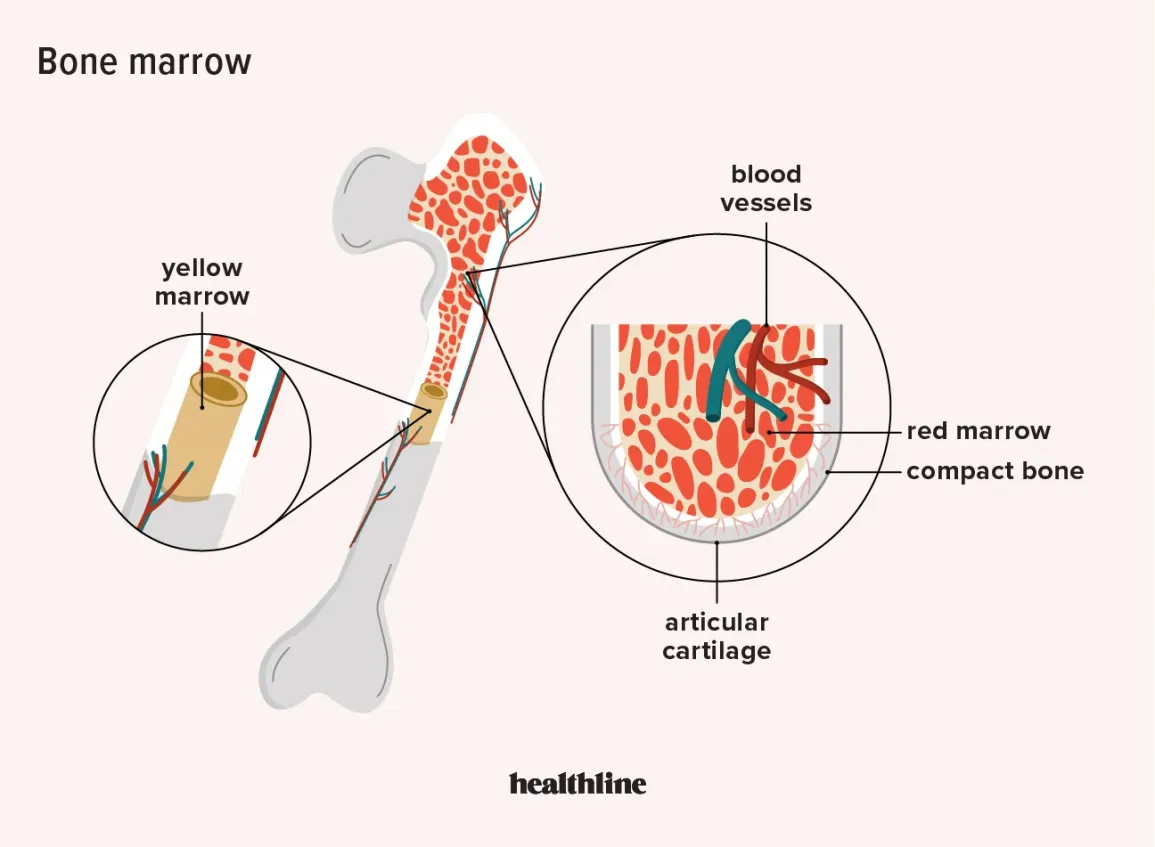
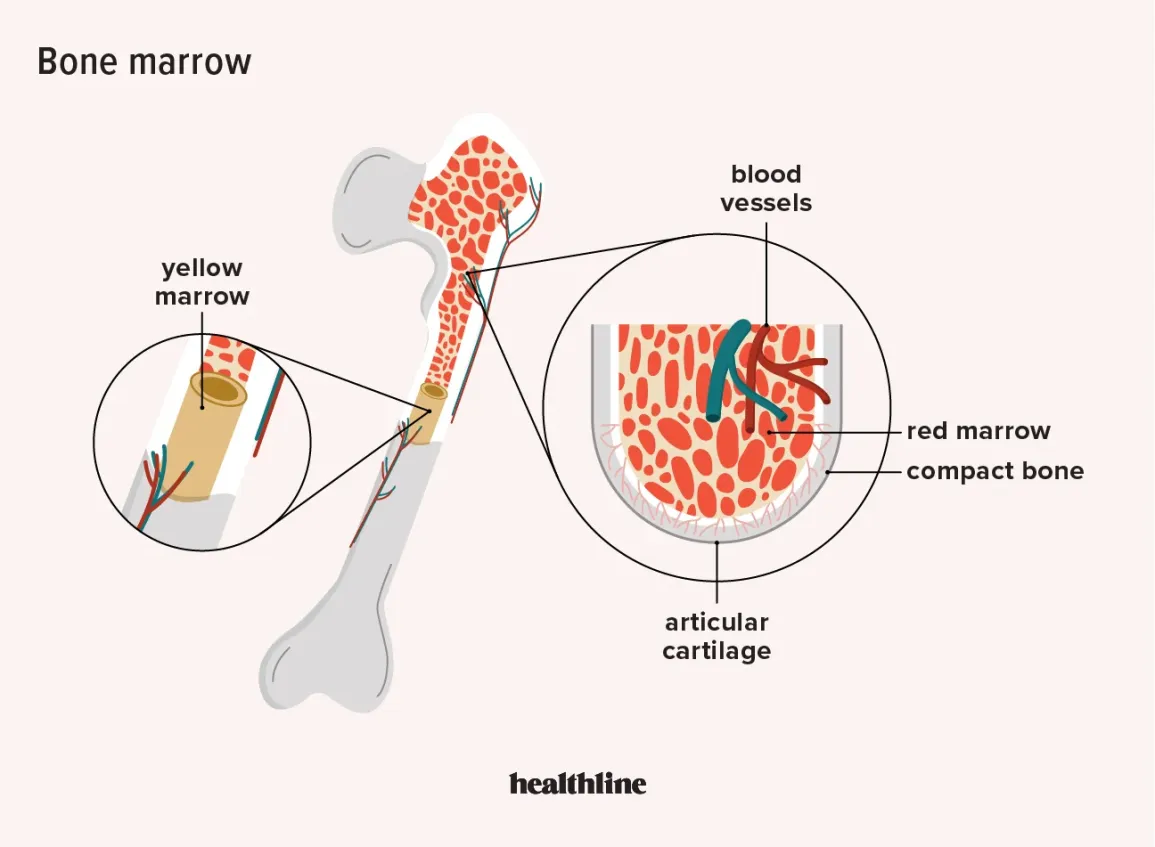
What are the functions of red bone marrow?
Blood cell production, immune response, and hematopoiesis, regulation of RBC production, and support for bone structure.
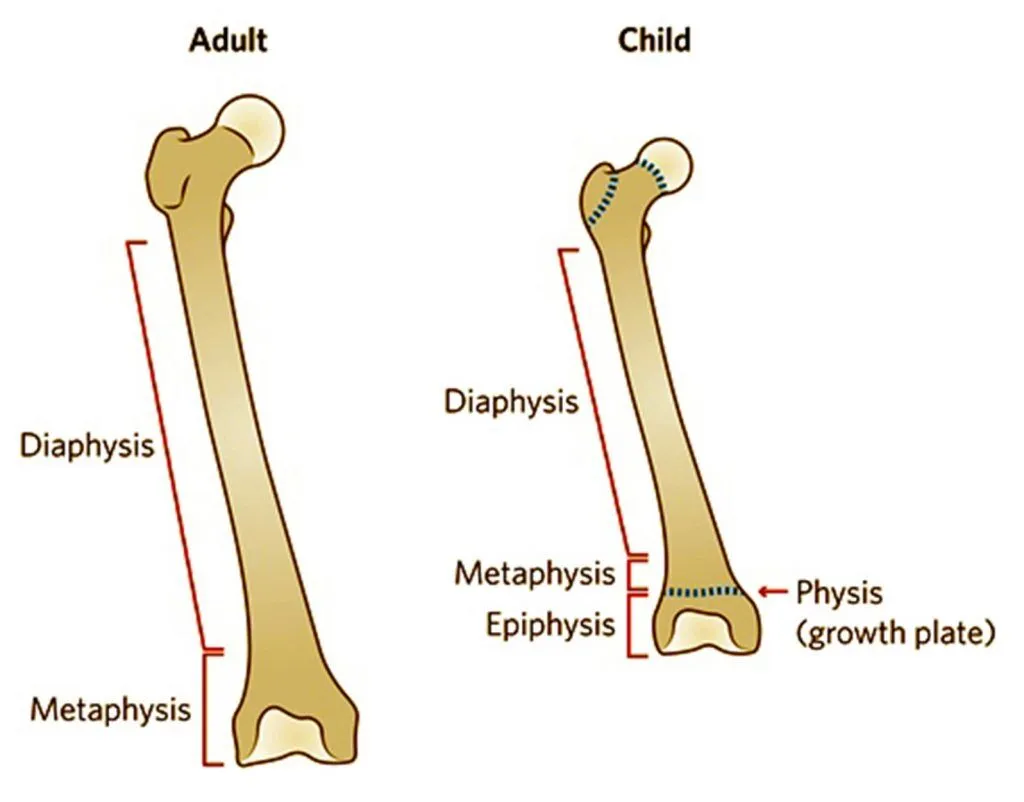
Adolescent vs adult bones
Adolescent bones are still growing and contain open growth plates (physes), have a more flexible and less dense structure due to higher Haversian canal volume, and a thicker, more supportive periosteum. In contrast, a full adult bone has closed growth plates, a harder and more rigid structure with a lower proportion of porous woven bone replaced by dense lamellar bone, making it more brittle. Adolescent bones exhibit greater flexibility and less density, making them more susceptible to injury compared to adult bones, which are fully formed and more rigid.
Number of bones adults vs adolesence
Adolescence = 270 to 300 bones
Adults = 206 bones
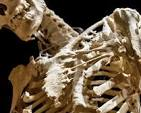
What is FOP, or Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
A rare, disabling genetic disorder where muscle and connective tissue, like tendons and ligaments, gradually turn into bone, creating a "second skeleton" that traps the body
Proper splinting techniques involve:
immobilizing a fracture site by securing a rigid object to the limb, ensuring the joints above and below the injury are immobilized, and checking circulation and sensation in the limb frequently. Key techniques include padding the limb generously, applying the splint material without excessive tension, molding it to the limb's shape, and securing it with an elastic bandage. For an open fracture, the wound must be covered with a sterile dressing before splinting, and the limb should be splinted in the position it was found.
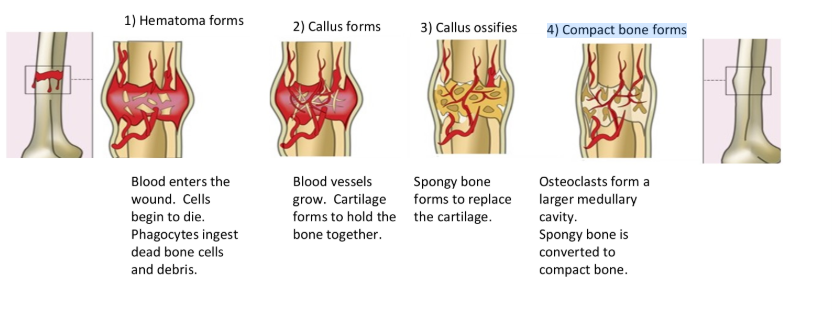
How is a broken bone repaired?
1) Hematoma forms
2) Callus forms
3) Callus ossifies
4) Compact bone forms

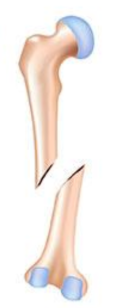
Comminuted fracture
Open fracture, oblique, displaced
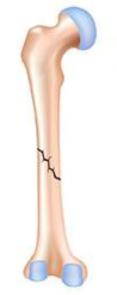
oblique, nondisplaced
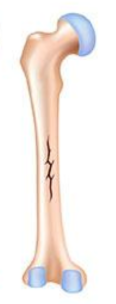
linear
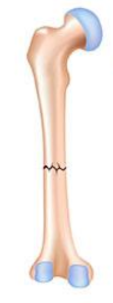
transverse
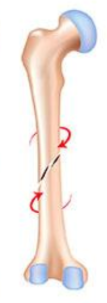
spiral