Prescribing in Pregnancy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
unchanged, decrease, increases, decreased, increased, CYP, output, glomerular, renal, uterine
ADME Changes in Pregnancy
Absorption
May be _________
May _________ d/t decreased peristalsis and delayed gastric emptying
Distribution
Plasma volume __________ by up to 50% (bag of water)
Increased plasma volume = _______ drug levels
Decreased protein binding = increased free drug levels = __________ drug effects
Metabolism
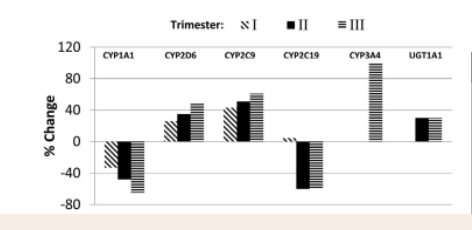
____ enzymes change dramatically from trimester to trimester
Elimination
Maternal physiologic changes that affect pharmacokinetics by trimester of pregnancy
Cardiac _______, _________ filtration rate, effective ______ plasma flow, creatinine clearance, _________ blood flow
caffeine, acetaminophen, codeine, fluoxetine, warfarin, omeprazole, progesterone, bilirubin
Representative drugs metabolized by CYP450 enzymes
CYP1A1/2
_________, aflatoxin B1, ___________
CYP2D6
_________, hydrocodone, flecainide, propranolol, carvedilol, ___________
CYP2C9
Phenytoin, _______, tolbutamide
CYP2C19
__________, pantoprazole, phenobarbital, diazepam, propranolol, clopidogrel, citalopram, bupropion
CYP3A4
Fentanyl, midazolam, cyclosporin, tacrolimus, carbamazepine, ___________
UGT1A1
_________, irinotecan
pregnancy, lactation, reproductive
New Labeling for Specific Population Use
_________ → includes Labor and Delivery
_________ → includes Nursing Mothers
Females and Males of ___________ potential
genotype, developmental stage, embryogenesis, deleterious, environmental, dosage
Wilson’s Principles of Teratology
1st Principle
Susceptibility to a teratogen depends on the _________ of the conceptus
2nd Principle
Susceptibility of the conceptus to teratogenic agents varies with the _____________ _______ at the time of exposure
3rd Principle
Teratogenic agents act in a specific way on developing cells and tissues in initiating abnormal ___________
4th Principle
Irrespective of the specific ___________ agent, the final manifestations of abnormal development are death, malformation, growth restriction, and/or functional disorder
5th Principle
Access of adverse ___________ influences to developing tissues depends on the nature of the influence
6th Principle
Manifestations of abnormal development increase in degree from the no-effect level to the lethal level as ________ increases
androgens, lithium, thalidomides, cytotoxic, retinoids, warfarin, streptomycin, valproate/topiramate, mycophenolate
1st Trimester Exposure to Teratogens in Pregnancy
_________
Virilization
________
Ebsteins anomaly (cardiac)
_________
Limb reduction
____________ drugs
Abortion, Growth stunting, Stillbirth
________
Craniofacial, cardiac, CNS defects
________
Nasal hypoplasia, skeletal defects
___________
Deafness
____________/__________
facial and neurobehavioral effects, renal
___________
Cardiac, ear, eye, orofacial, renal
warfarin, NSAIDs, salicylates, sulfonamides, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, narcotics, lithium, ACEi, phenothiazines, benzodiazepines, antidepressants
2nd and 3rd Trimester Exposure to Teratogens in Pregnancy
________
Fetal hemorrhage, CNS abnormalities
_________ and __________
prolongation of gestation and labor, neonatal pulmonary HTN
___________
kernicterus, hyperbilirubinemia
_________
Staining of teeth, impaired bone growth
___________
deafness, vestibular damage
_________
withdrawal and respiratory depression
_________
Hypotonia and hyporeflexia
____
Growth stunting, lung and kidney deformities, convulsions, hypotension
___________
Withdrawal
____________
Withdrawal, respiratory depression
_____________
Withdrawal
pyridoxine, ginger, doxylamine, dimenhydrinate, diphenhydramine, promethazine, ondansetron, metoclopramide
N/V Pharmacologic Options
Vitamins and nutritional supplements
Vitamin B6 (__________)
________
Antihistamines
_________ (Unisom)
_________ (Dramamine)
____________ (Benadryl)
Combination medication that is expensive when OTC products exist
Phenothiazine Antipsychotics
__________
Prochlorperazine
Chlorpromazine
Serotonin (5HT3) receptor antagonists
___________
Dopamine antagonist
______________
folic acid, ginger, pyridoxine, doxylamine, prochlorperazine
N/V Pharmacologic Options
First Line
Nonpharmacologic Therapy
Use ______ _____ supplement only
_________ capsules 250 mg four times daily (reduces nausea)
Second line
__________ with or without _____________
Third line
____________
Dimenhydrinate
Promethazine
dehydrated, oral, B6, doxylamine, dimenhydrinate, metoclopramide, ondansetron
N/V → Have you had any water?
Pts who are _________ are treated differently from those who are hydrated
Hydrated
______ medications
Vitamin ____ + __________
If sx persist, add one oral agent at a time:
Antihistamines (__________)
Dopamine antagonists
____________
Promethazine
___________ (secondary/third line per guidelines)
hydration, parenteral, normal, lactated ringers, thiamine, dextrose, electrolytes, antiemetics, ondansetron, promethazine, corticosteroids, 10, feeding
N/V → Dehydrated Patient
Inpatient or ED management
Focus shifts to IV __________ and __________ medications
IV Fluid resuscitation
________ saline or ________ _________
Add IV __________ BEFORE giving __________ if prolonged vomiting
Correct __________ (K+, Mg2+)
Parenteral ___________
Given IV or IM because PO cannot be tolerated
____________ IV
Metoclopramide IV
___________ IV
Dimenhydrinate IV
Escalation (if vomiting is uncontrolled):
____________ (methylprednisolone) after __ weeks of gestation
Consider enteral tube _________ if severe
MONITOR
neural tube, brain, spina bifida, anencephaly
Why is folate important?
_______ _____ defects are serious birth defects that affect the spine, spinal cord, or ______ and may cause death
These include
_______ ________ →
Condition happens when an unborn baby’s spinal column does not fully close during development in the womb, leaving the spinal cord exposed
_________ →
Most or all of the brain and skull does not develop in the womb. Almost all babies with this condition die before or soon after birth.
bypass, diabetes, malabsorptive, alcohol, methotrexate
Folate Deficiency Risk Factors
Medical Conditions
Hx of gastric _______
Pre-pregnancy _________
_________ disorders
________ use disorder
Medications
Anticonvulsants
__________
Sulfasalazine
early, treat, cure, 5-7
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnancy → Treatment and Screening
Screen once in ______ gestational visit
_______ if colony counts >100,000 CFU/mL
Unclear if test of _____ is needed
Treat for _-_ days, shorter duration may not be adequate
nitrofurantoin, bactrim, cephalexin, fosfomycin, amoxicillin
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Pregnancy Treatment Options
___________
Avoid during weeks 38-42 gestation
________
Consider avoiding during 1st and 3rd trimester
__________
_________
___________ (± clavulanate)
Only if culture shows sensitivity
high, less, weak, lipid, diffuse, basic, acidic, lower
Medications and Breastmilk
Plasma protein binding
Drugs with ____ plasma protein binding are ____ likely to be transferred into breast milk
Ionization
Most drugs are _____ acids or bases that are present in solution as both nonionized and ionized species
The nonionized molecules are usually ______ soluble and can _______ across the milk-plasma membrane
Acidity
______ drugs are more likely to be transferred into breast milk d/t milk being more ________ than plasma
Molecular weight
The _______ the molecular weight the more easily the drugs will be transferred
yes, yes, no, yes, yes, no, yes, yes, no
Medications in Breastmilk
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Claritin and Benadryl
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Note: observe infant for drowsiness
Sudafed
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Notes: Can decrease milk supply
Amoxicillin, ampicillin, cephalexin, erythromycin, penicillin, zithromax
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Fluconazole
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Prozac
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Notes: Zoloft or Paxil are preferred alternatives
Zoloft and Paxil
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
Depo-Provera and Progestin-only oral contraceptivs
Breastfeeding friendly? ___
St. John’s Wort
Breastfeeding friendly? ___