Motor Spinal Cord (Sosnowski)
1/228
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sosnowski
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
_ cervical spine nerve and _ cervical vertebrae
8; 7
__ thoracic spine nerves and vertebrae
12
_ lumbar spinal nerves and vertebrae
5
Spinal cord ends around ___
L1
__ pairs of sacral spinal nerves
5
_______ compress spinal cord in canal itself
Myelopathy
_________ Compression of nerve roots
Radiculopathy
Spine disease at or below vL2 does not produce _______, only _______!
myelopathy; radiculopathy
C1 spinal nerve is ____ C1 vertebrae
above
C8 spinal nerve exits ____ C7 vertebrae
below
T2 spinal nerve exits ____ T1 vertebrae
below
Lumbar nerves are contained in the ____ ____
Lumbar cistern
___ mater directly connected to spinal cord
Pia
Most peripheral is ____ mater
dura

Pia arachnoid and dura mater
Dentate (denticulate) ligament collection of arachnoid creating a tuft along cord triangle holds spinal cord in the _____ connecting pia to dura
middle
Cona ______ is where the spinal cord end
medullaris
______ ________ are the lumbar nerves
Cauda equina
pia mater that attached to the cord tethered to the sacrum (coccyx)
Filum terminale
Termination of pia mater holding conus medullaris in place.
Filum terminale
Too tight growing up can pull on conus medullaris and have fecal incontinence etc.
Tight Filum Terminale Syndrome
Dorsal and ventral roots come together to form _____ ______
spinal nerve
Dorsal root ganglia sensory ___ order neurons bringing in sensory
first
Vertebral body is ______ to spinal cord
anterior
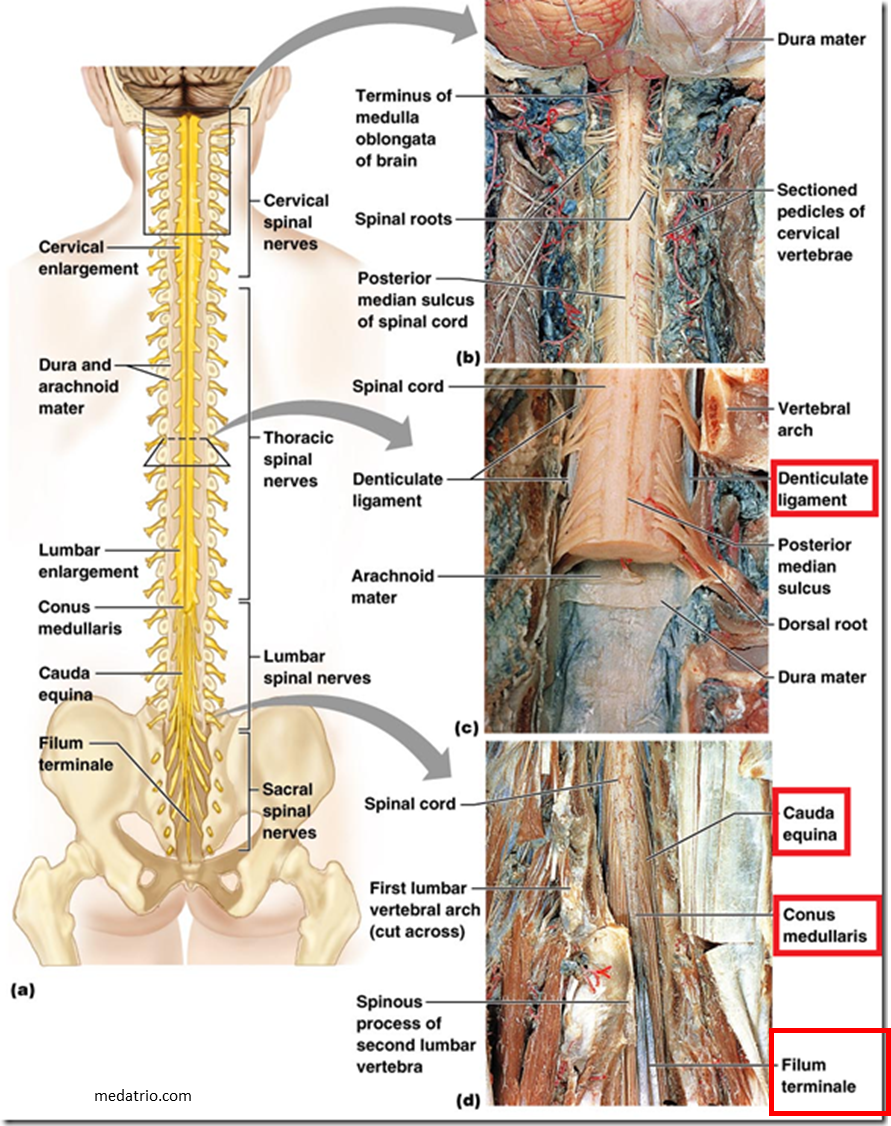
Spinal cord images
Spinal cord is diameter of ______
pencil
Largest diameter of spinal cord is at ___
C8 because it contains the cervical enlargements for arms and legs.
Where is the enlargement for arms and legs?
Cervical enlargement C8
___ all axons coming in for lower extremities bulges are the enlargements where motor neuron cell bodies are kept
L4
Where is the enlargement for legs?
L4 Lumbar enlargement
What spinal region has the most white matter?
Cervical
Honda symbol has lateral cell column where sympathetic neurons are between T1 and L2
Thoracic spine
Honda symbol
Thoracic spine
Sympathetic neurons are between ___ and __
T1 and L2
Round, no lateral columns, half the white matter.
Lumbar enlargements
Cord levels C8 and L4 have the largest _____ horns (neuronal soma) for serving the arm and leg
ventral
The ____ horn is present from T1-L2
Lateral
The higher the cord level the more _____ fibers it contains
vertical
The tip of the conus medullaris descends to the inferior limit of the __ vertebral body
L1
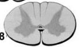
Cervical C8
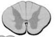
Thoracic T2
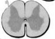
Lumbar L4
Gray matter location in spinal cord?
Inside
C1 is ____: ring with no vertebral body fused with ligaments to occipital bone
Atlas
C2 ____ rotates the head on ____ through dens
axis; atlas
Dens is what __ rotates on
C1
no room for __ to slip off base of the skull fused with strong ligaments
C1 atlas
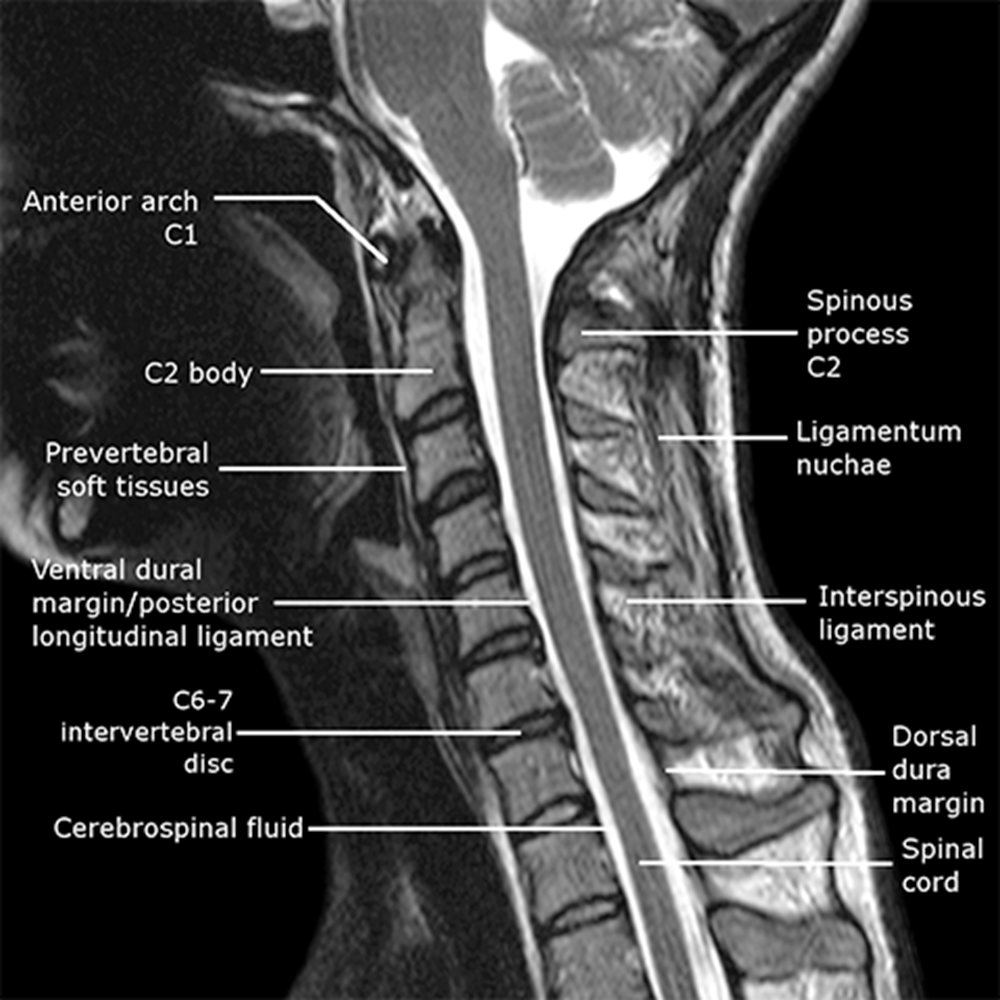
Cervical cord landmarks
largest vertebrae
Lumbar
Angle between sacrum and L5 count back
how to count lumbar vertebrae
Lumbar puncture spinal tap in _____ _______ access to CSF. Between L3 and L4 (slowly nerves move around the needle) Dural tap
lumbar cistern (subarachnoid space)
Spinal anesthesia is in _____ plane above injecting anesthesia around the dura as nerve routes come out get bathed in anesthesia
epidural (do not want to get into the subarachnoid space because it can travel up)
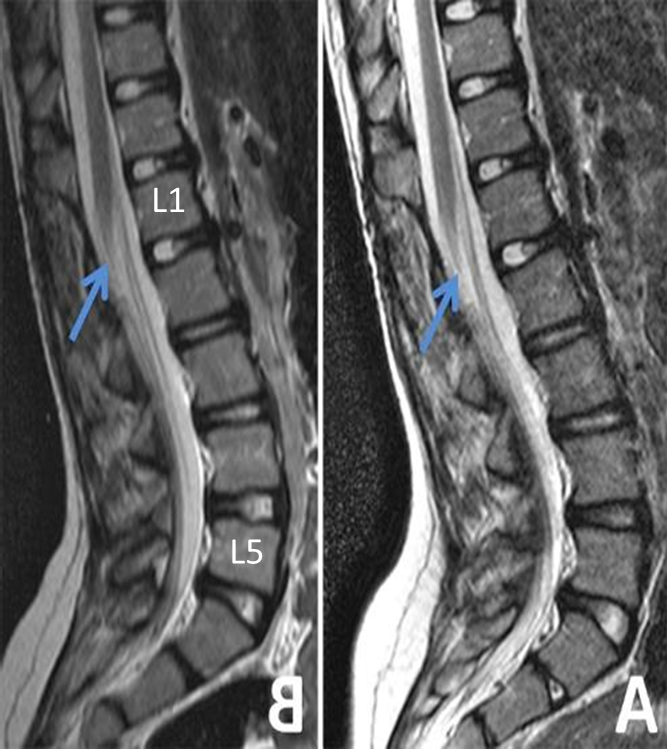
How to count lumbar spine vertebrae
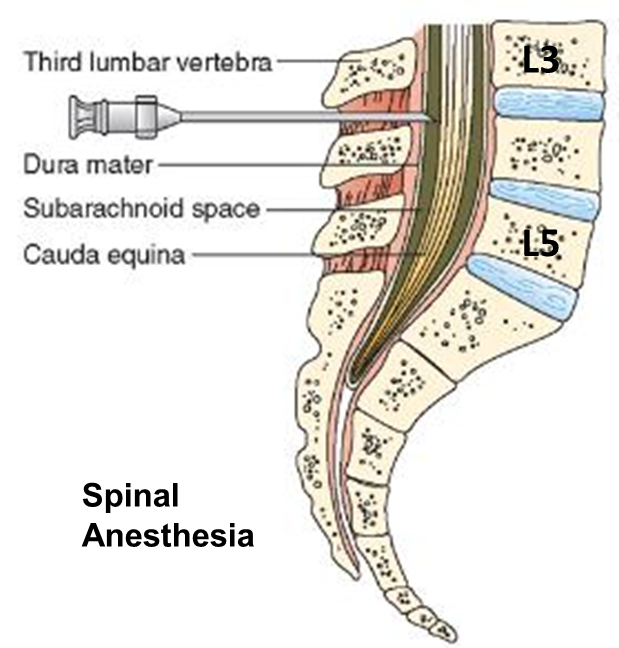
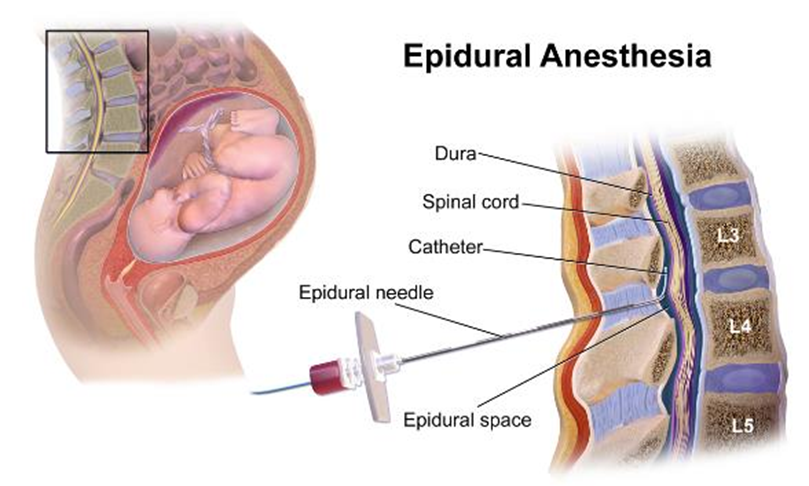
Lumbar lifting injury can cause _____
herniation
Grandparent picking up grandchild and hears a pop and feels the pain
Could be lumbar herniation
Nerve roots come out of _______ inbetween vertebrae
foramina
In Lumbar L4/L5 intervertebral disk herniate laterally pinch ___, herniate medially (paracentral) pinch __
L4 (match)
L5
Cervical C5/C6 intervertebral disk herniate lateral or central pinch ____
C6 (mismatch)
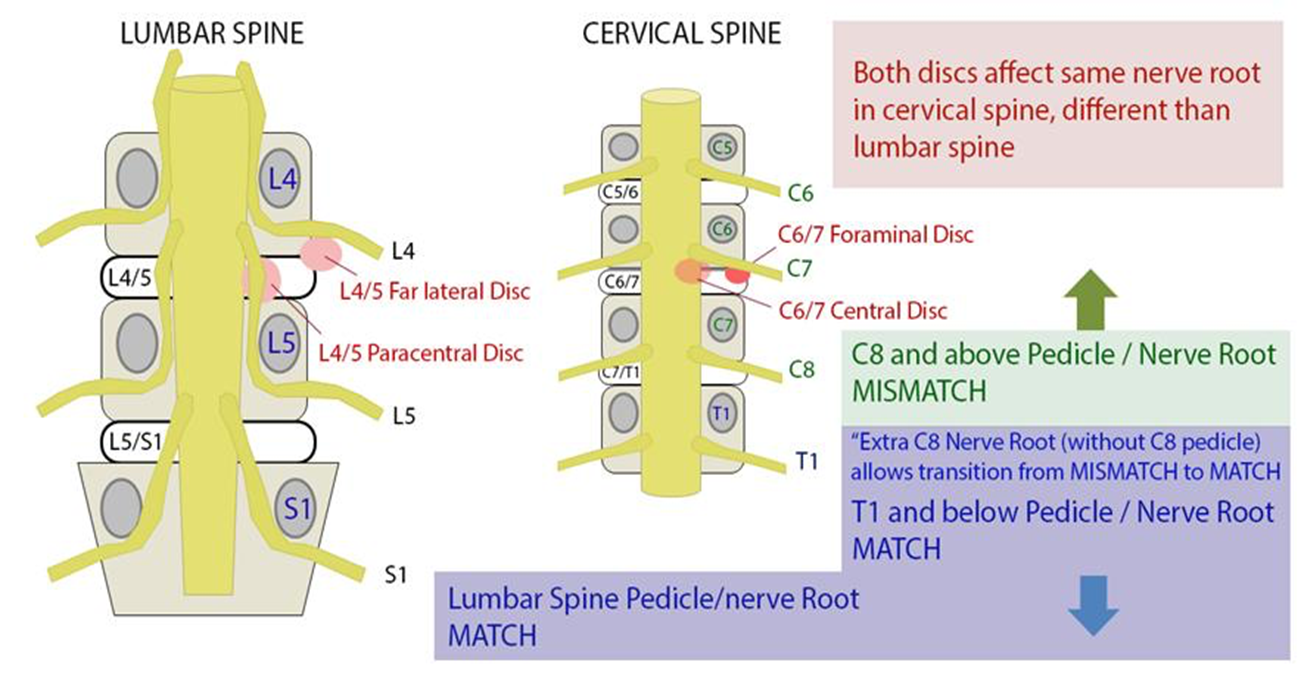
Lumbar vs cervical spine herniation
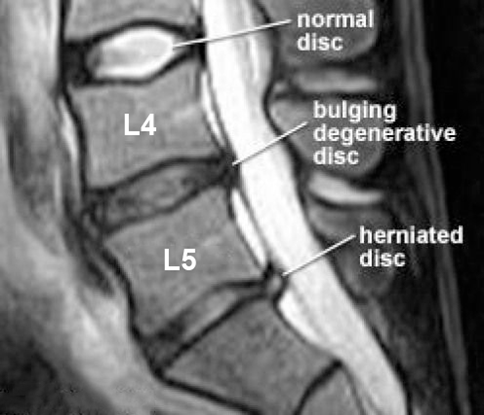
What nerve would L4-L5 intervertebral lateral herniated disk compress?
L4 (medial would be L5)
Immediate temporary loss of motor and sensory at level and below of injury (I cannot move or feel anything after injury)
Spinal shock
Sudden loss of sympathetic tone (maybe drug related)
Neurogenic shock
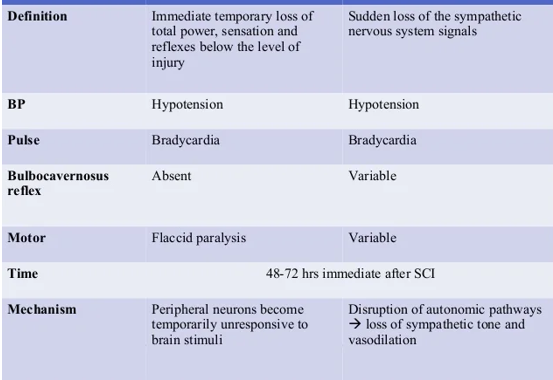
Spinal shock left
Neurogenic shock right
What happens to BP and pulse in spinal shock and neurogenic shock
Hypotension
Bradycardia
perineal region gloved finger do digital rectal exam stimulate clitoris or penis and cause anal sphincter to contract (normally it does contract)
Bulbocavernosus reflex
absent in spinal shock
variable in neurogenic shock
______ primary neurons are between T1 and L2 (hr breathing etc)
Sympathetic
Lesions between ___ and __ shut down adrenals (homeostasis and stress events cannot manage stress)
T1 and T6
Lesions above ___ eliminate all sympathetic outflow
T1
Lesions between T1 and T6 block sympathetic flow to the _____ and lower extremities
adrenals
Lesions below ___ block sympathetic flow to the lower extremities
T6
______ spinal artery is 1 artery supply by many different branches
Anterior
intercostal artery in the thoracic region that is very pronounced and supply a good portion of the anterior spinal artery to the thorax
Adamkiewicz artery
Important during surgery, trauma, cancer because injury could result in anterior cord stroke.
Adamkiewicz artery
__ posterior spinal arteries
2
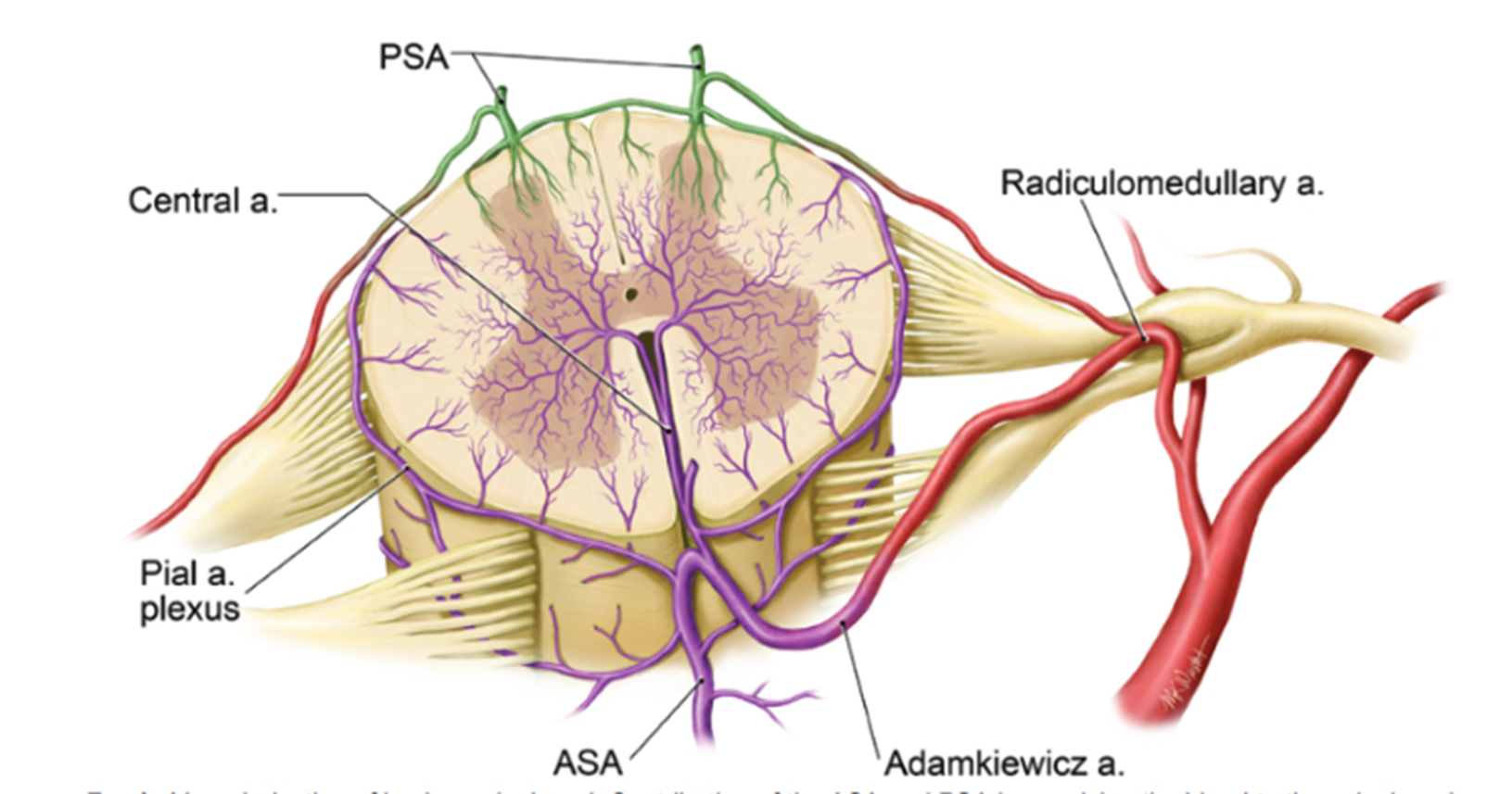
ASA vs. PSA Perfusion Territories
Anterior spinal stroke can be caused by damage to _____ artery
Adamkiewicz
______ funiculus All sensory all axons bundled up in highways to make mega highways
posterior
tend to be motor some sensory and autonomic but mostly motor
Lateral and anterior funiculus
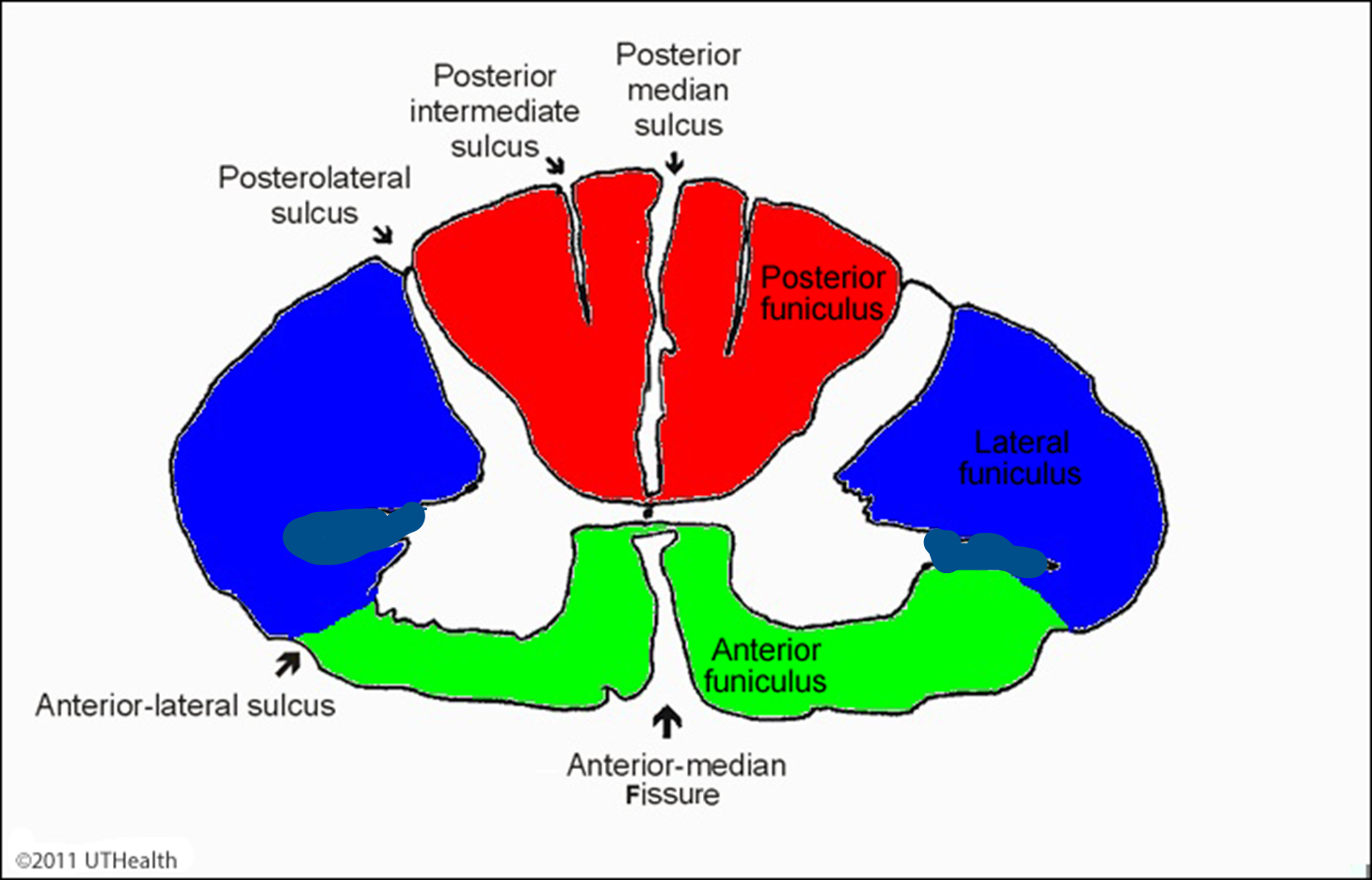
Anterior funiculus and lateral funiculus tend to be motor some sensory and autonomic but mostly motor
Posterior funiculus all sensory
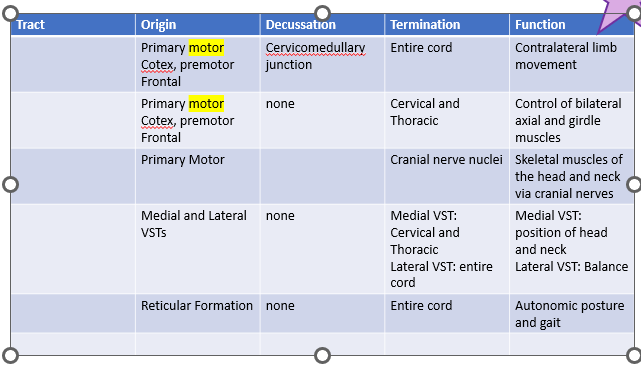
Lateral corticospinal
Anterior corticospinal
Corticobulbar
Vestibulospinal
Reticulospinal
Origin of lateral corticospinal tract
Primary motor Cotex, premotor Frontal
Origin of anterior corticospinal tract
Primary motor Cotex, premotor Frontal
Decussation of lateral corticospinal tract
Cervicomedullary junction
Termination of lateral corticospinal tract
Entire cord
Function of lateral corticospinal tract
Contralateral limb movement
Contralateral limb movement
Lateral corticospinal tract
Termination of anterior corticospinal tract
cervical and thoracic
Function of anterior corticospinal tract
Control of bilateral axial and girdle muscles
Control of bilateral axial and girdle muscles
Anterior corticospinal tract
Origin of corticobulbar tract
Primary motor
Termination of corticobulbar tract
Cranial nerve nuclei
Function of corticobulbar tract
Skeletal muscles of the head and neck via cranial nerves
Skeletal muscles of the head and neck via cranial nerves
Corticobulbar tract
Origin of vestibulospinal tract
Medial and Lateral VSTs
vestibular nuclei in pons and medulla
Termination of vestibulospinal tract
Medial VST: Cervical and Thoracic
Lateral VST: entire cord
Function of vestibulospinal tract
Medial VST: position of head and neck
Lateral VST: Balance
position of head and neck
balance
Medial vestibulospinal tract
Lateral vestibulospinal tract
Origin of reticulospinal tract
Reticular formation
Termination of reticulospinal tract
Entire cord