Bio 1711- Special senses I
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Stimulus
Perception of event
Sensation
Initial physical and neral reception
Receptors
Structures that respond to stimuli and initial sensory input to CNS
Somatic sensory receptors
Skeletal muscles
Visceral sensory receptors
Smooth muscle
Special sensory receptors
Located in the head (complex sense organs)
Exteroreceptors
External environment
Interoreceptors
Internal organs
Chemoreceptors
Chemical environment
Thermoreceptors
Temperature changes
Mechanoreceptors
Physical stimuli
Baroreceptors
Pressure changes
Nociceptors
Very painful stimuli
Refered pain
Pain is felt on skin in another part of body due to visceral sensory neurons sharing a tracts in spinal cord
Olfaction
Sense of smell
Olfactory gland
Clears out odourants
Cibriform place
Bony plate part of olfaction
Basel cells
Replace support cells
Support cells
Columnar epithileum
Mucous
Sticky odourant adhesion
Olfactory receptor cell
Picks of chemical smell
Frontal lobe (olfactory cortex)
Interprete smell
Limbic system (olfactory cortex)
Emotional response to smell
Gustation
Taste (requires dissolved substances)
Papillae
Bumps on tongue
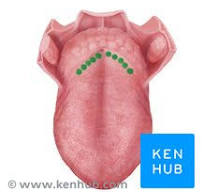
Vallate
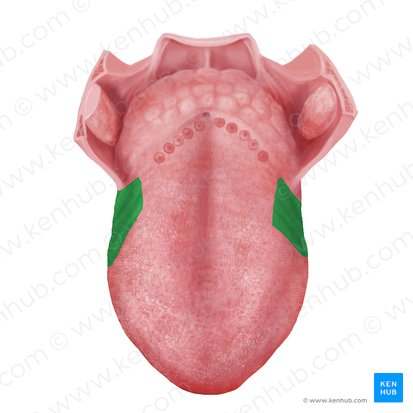
Foliate
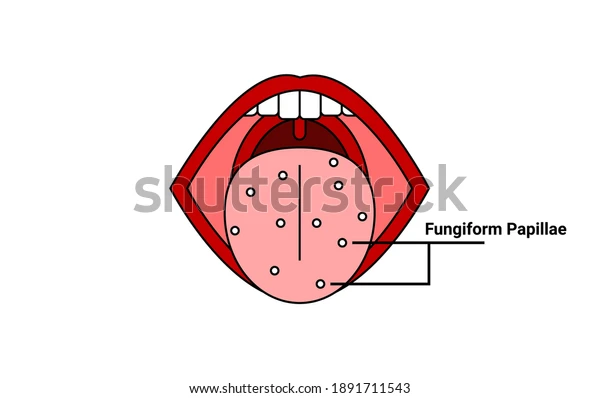
Fungiform
Filiform
Part of the tongue that has no taste buds
Sweet
organic compounds
Salty
Metal ions
Sour
Acids
Bitter
Alkaloids
Umami
Meaty flavour
Lacrimal gland
Secretes tears
Tears flow across eyeball with
Gravity, and blinking
Lacrimal punctum
Tear exit eyeball
Lacrimal sac
Tears drain into
Nasolacrimal
Tears get dumped into nasal cavity
Conjunctiva
Thin membrane lining eye and inner eyelids
Layer 1 of eye
Fibrous tunic
Layer 2 of eye
Vascular tunic
Layer 3 of eye
Nervous tunic
Cornea
Reduces refraction to focus light
Sclera
Gives the eye its shape
Choroid
Provides nutients and absorbs light in eye
Ciliary body
Ciliary process & Ciliary muscles
Ciliary processes
Secretes aqueous humour fluid
Ciliary muscles
Smooth muscles that alters lens shape
Sensory ligament
Connects ciliary muscles and lens
Iris
Regulates light coming into eye
Sphincter pupillae
Closes pupils
Dilater pupillae
Dilates pupils
Lens
Focuses light on retina
Flattened lens
Looking far
Rounded lens
Looking close
Nearsightedness (myopia)
Eyeball is slightly longer that normal
Farsightedness (hyperopia)
Eyeball is slightly shorter than normal
Astigmatism
Cornea is uneven
Retina
Vision receptor
Optic disc
Blind spot
Macula lutea
Best vision (straight on)
Peripheral retina
Best low light vision
Pigmented layer
Retinal layer that absorbs access light
Neural layer
Retinal layer of 3 layers
Rods
Shapes and movement
Cones
Sharp, color vision
Anterior cavity
Filled with aqueous humorous
Posterior cavity
Filled with vitreous humour
Scleral venous sinus
Drains fluid from eye
Brain pathways of vision
Eyeball nerves from both eyes go to both sides of brain