Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxide, Nitrile Reactions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
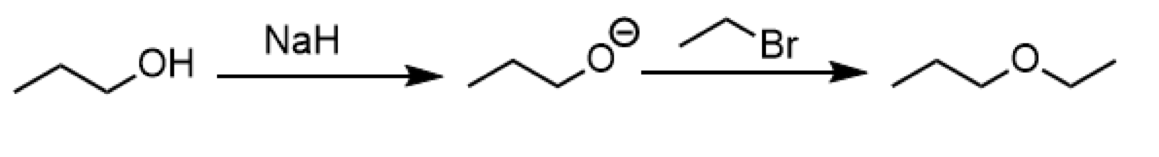
williamson ether synthesis (SN2 reaction)
reagent:
Step 1: NaH
Step 2: alkyl halide
conversion of an alcohol to an ether
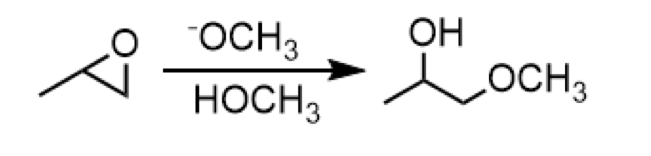
base catalyzed opening of epoxide (nucleophile attacks less substituted side)
reagents: -OCH3 (above) and HOCH3 (below)
opening of epoxide to form a 2o alcohol with an ether
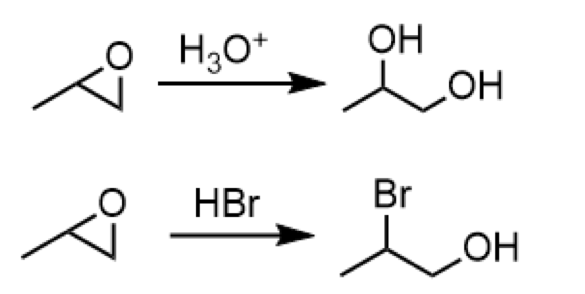
acid-catalyzed opening of epoxide (nucleophile attacks more substituted side)
reagents: H3O+ or HBr
opening of an epoxide to form a dialcohol olecule or a 2o carbon with a bromine group and a primary alcohol
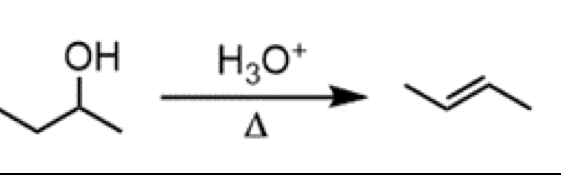
acid-catalyzed alcohol dehydration (E1 reaction)
reagents: H3O+ (above), delta (below)
conversion of a 2o alcohol to a trans alkene
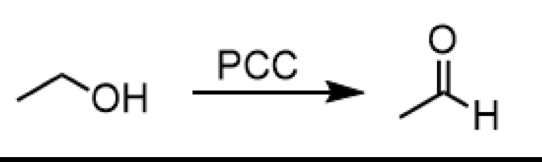
oxidation of 1o alcohol to aldehyde
reagent: PCC
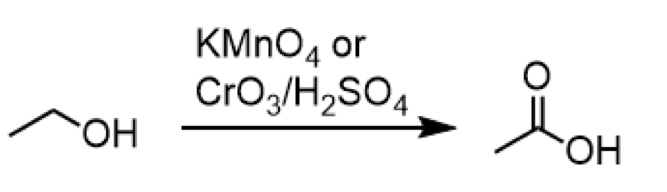
oxidation of 1o alcohol to carboxylic acid
reagents: KMnO4 or CrO3/H2SO4
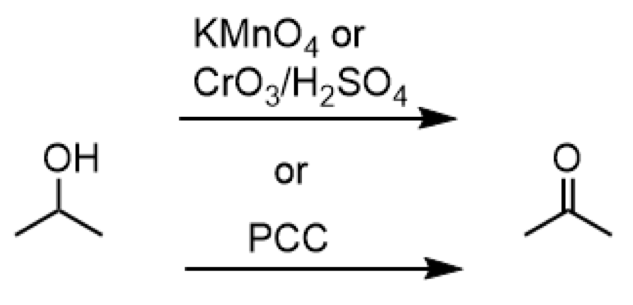
oxidation of 2o alcohol to ketone
reagents: KMnO4 or CrO3/H2SO4 or PCC
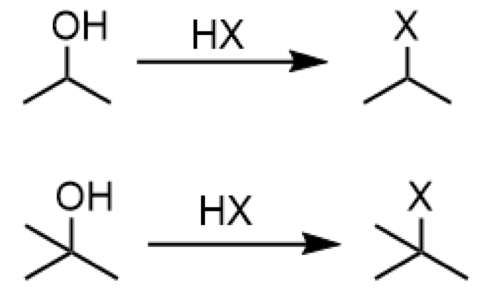
converting 2o/3o alcohols to alkyl halides (SN1) reaction
reagents: HX
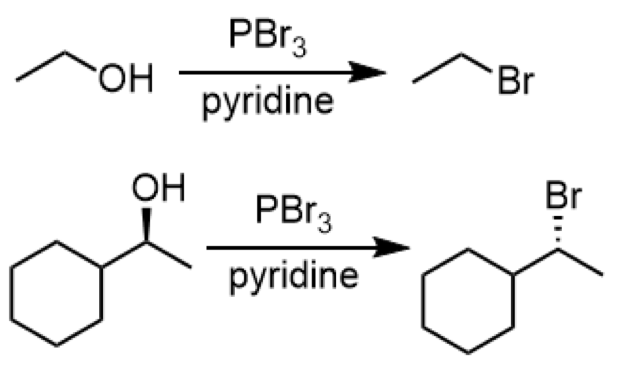
converting 1o/2o alcohols to alkyl bromides (SN2 reaction)
reagent: PBr3
for stereochemistry: causes an inversion of stereochemistry
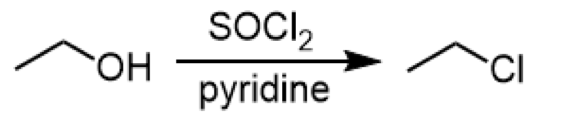
converting 1o/2o alcohols to alkyl chlorides
reagent: SOCl2 (above), pyridine (below)
for stereochemistry: causes an inversion of stereochemistry
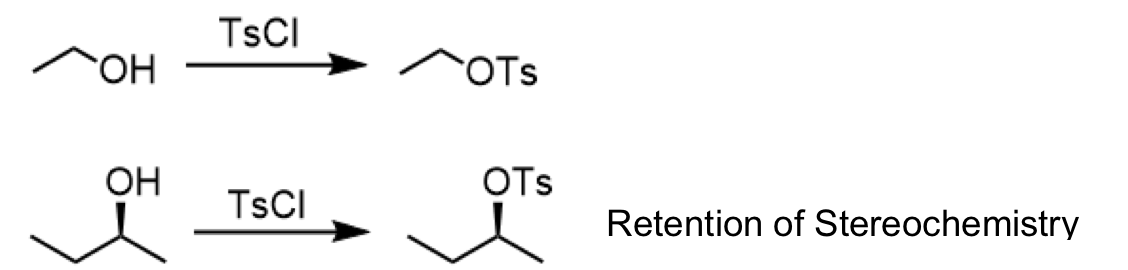
tosylate ester formation
reagents: TsCl
for stereochemistry: retention of stereochemistry
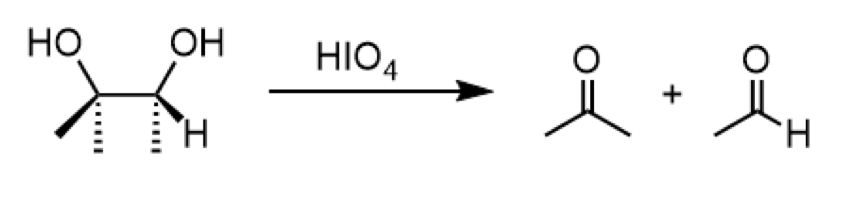
oxidative cleavage of 1,2 diol
reagents: HIO4
conversion of 1,2 diol to a ketone and aldehyde
swern oxidation
reagents: 1. DMSO, COCl2 2. Et3N
conversion of a primary alcohol into an aldehyde or secondary alcohol into a ketone
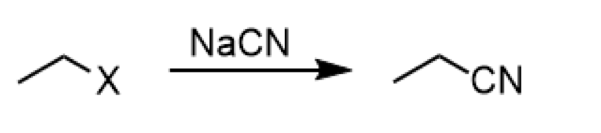
SN2 formation of nitrile with cyanide and alkyl halide
reagent: NaCN
conversion of alkyl halide to nitrile with cyanide
acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles
reagents: H3O+ , heat
conversion of nitrile to carboxylic acid
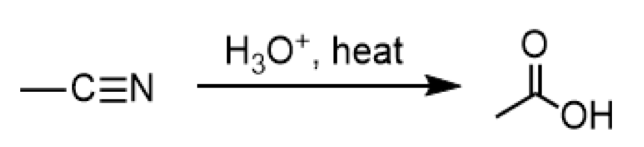
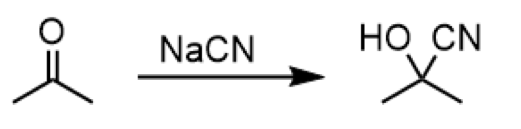
cyanohydrin formation using aldehydes/ketones and cyanide
reagent: NaCN
formation of a cyanohydrin from an aldehyde or ketone