Moving Charges & Magnetism
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Lorentz force
Force experienced by a charged
Biot Savart’s Law
Magnitude of the magnetic field due to a small current carrying element is
directly proportional the current I
directly proportional the length element
inversely proportional to square of the distance
|dB| = μ₀Idlsinθ/4πr²
μ₀/4π = 10⁻⁷ Tm/A
Magnetic Field due to a Circular loop
At axial line:
μ₀IR²/2(R²+x²)³/²
At the centre of the loop with N turns:
B = N(μ₀I/2R)
Magnetic Field due to a Circular Arc
B = (μ₀I/4πR) x θ
Ampere’s Circuital Law
Ampere’s law states that the integral of magnetic field over a loop is equal to μ₀ times the total current passing through the surface
∮ B . dl = μ₀I
It is used when:
B is tangential
B ≠0
B is normal to the closed loops
Magnetic Field due to an Infinitely Long thin Current Carrying Wire
B = μ₀I/2πr
Magnetic Field due to an Infinitely Long Thick Current Carrying Wire
B (in) = (μ₀I/2πR²) x r
B (surface) = μ₀I/2πR
B (outside) = μ₀I/2πr
R => Radius of circle
r => Distance between centre and point P
Magnetic Field due to a Finite Current Carrying Wire
B = μ₀I/4πR(sinΦ₁+ sinΦ₂)
Magnetic Field due to a Solenoid
nμ₀I
n = N/l (turns per unit length)
Magnetic Force
F = q (v × B) = Bqvsinθ n^
[B] = [F/qv]
S.I. unit: Tesla (T)
Tesla is a rather large unit
Smaller unit: Gauss
1 gauss = 10^-4 T
It is zero if:
Charge moves parallel or anti-parallel
Charge is at rest
Particle is neutral
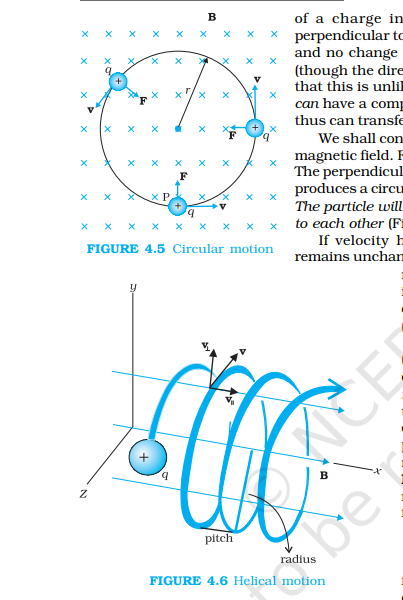
Motion of a Charge in Magnetic Field
r = mvsinθ/Bq
T = 2πm/Bq
f = Bq/2πm (1/T)
ω = Bq/m
pitch, x = v (parallel) x T = Vcosθ x 2πm/Bq
Path of Charge:
Straight Line (θ = 0°)
Circular Path (θ = 90°)
Helical Path (θ ≠ 0°/90°/180°)
Magnetic Force on a Current Carrying Conductor
F = I(current) (l(length vector) x B)
F = BIlsinθ (remember as billsinθ)
l => length vector, the same direction as the current
B => External magnetic field, not the field produced by the rod
Force Between Parallel Two Current Carrying Wires
F/l = μ₀I₁I₂/2πd
Current in the same direction => Attract
Current in different directions => Repel
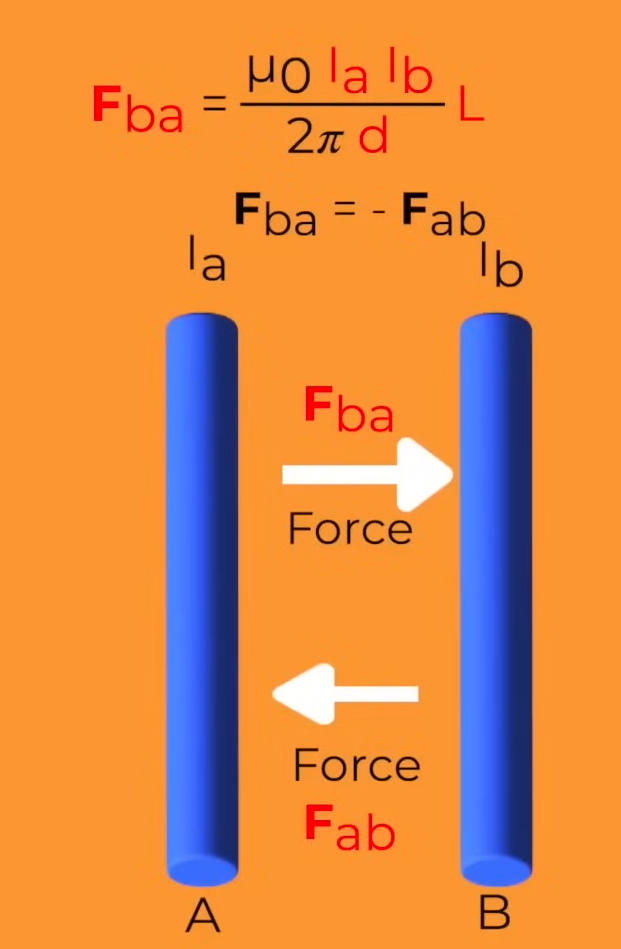
1 Ampere
1A is the current passing through 2 parallel wires which are separated by 1m and they experience a force of 2×10⁻⁷ N/m
Magnetic Dipole Moment
m = NIA
Torque Acting On A Current Carrying Loop In A Magnetic Field
𝜏 = IAB
𝜏 = IABsinθ
𝜏 = mbsinθ
Circular Current Loop As A Magnetic Dipole
(μ₀/4π)(2m/x³)
Moving Coil Galvanometer
Device used to measure small currents/detect current flow
Φ (deflection) ∝ I (current flowing)
Current Sensitivity (Iₛ)
Deflection per unit current
Iₛ = Φ/I = NBA/K
Voltage Sensitivity (Vₛ)
Deflection per unit voltmeter
Vₛ = Φ/V = NBA/KRg
Figure of Merit (K)
Current required to create unit deflections
K = I/Φ = K/NBA
Galvanometer to Ammeter
By adding a shunt resistance in parallel
Rₛ = (Ig/I-Ig) Rg
Rₛ => Required shunt resistance
I => Total current to be measured
Ig => Current flowing through galvanometer
I-Ig => Remaining current flowing through resistor
Total resistance of ammeter:
Rₐ = Rg x Rₛ/Rg+Rₛ (since they are parallel)
Galvanometer to Voltmeter
By adding a resistance in series
V = Ig(R+Rg)
R = V/Ig - Rg
R => Unknown resistance to be measures
Rg => Resistance of galvanometer
Rᵥ = R + Rg