Secondary Hemostasis (Exam 2)
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
If there is a small "a" next to a coagulation factor, it means it is ______.
activated
Coagulation factors circulate as inactive ______ until the need for repair arises.
zymogens
Coagulation factor activation occurs when the single peptide chain gets ______ by proteases.
cleaved
What are the three groups of coagulation factors?
- Vitamin K Dependent
- Contact Factor
- vWF: Factor VIII
Factor I
Fibrinogen
Factor II
Prothrombin
(IIa is thrombin)
Factor III, tissue factor
Tissue Thromboplastin
Factor IV
Calcium ions
Factor V
Proaccelerin, Labile Factor
Factor VII
Proconvertin, Stabile Factor
Factor VIII:C
Anti-Hemophilic Factor (AHF)
Factor VIII R:Ag Factor VIII vWF
Von Willebrand Factor
Factor IX
Christmas Factor, Anti-Hemophilic Factor B
Factor X
Stuart-Prower Factor
Factor XI
Plasma Thromboplastin Antecedent (PTA)
Factor XII
Hageman Factor
Factor XIII
Fibrin Stabilizing Factor
Prekallikrein (PK)
Fletcher Factor
HMWK (High Molecular Weight Kininogen)
Fitzgerald Factor
What factors make up the Vitamin K Dependent group?
- Factor II (prothrombin)
- Factor VII
- Factor IX
- Factor X
- Proteins C, S, and Z
These factors need vitamin K for their ______.
activation
The Vitamin K Dependent group are also called the ______ group.
Prothrombin
The Contact Factor group is involved in the contact activation step of the ______ pathway of the coagulation cascade.
intrinsic
What are the Contact Factor group factors?
- Factor XII
- Factor XI
- HMWK
- PK
Factor XII and PK are ______.
proteases
HMWK is a ______.
cofactor
The Contact Factor group bind to ______ surfaces
negatively charged
Factor VIII: von Willebrand Factor group
- Factor VIII
- vWF
vWF is a glycoprotein composed of multiple subunits synthesized by ______ and ______.
megakaryocytes, vascular endothelial cells
Factor VIII is synthesized by the ______, driven by the X chromosome.
liver
vWF and Factor VIII are ______ in circulation.
covalently bound
What are the cofactors?
- Factor V (Factor Xa)
- Factor VIII (Factor IXa)
- HMWK (Factor XIIIa and XIa)
- Protein S (activated Protein C)
- Tissue Factor (Factor VIIa)
Interaction of protease with cofactor significantly increases ______ activity.
enzyme
______ is the only coagulation protein that does not become an activated enzyme.
Fibrinogen
What are the serine proteases?
- Thrombin
- Factor VIIa
- Factor IXa
- Factor Xa
- Factor XIa
- Factor XIIa
______ is a trans-glutaminase.
Factor XIIIa
Coagulation Cascade
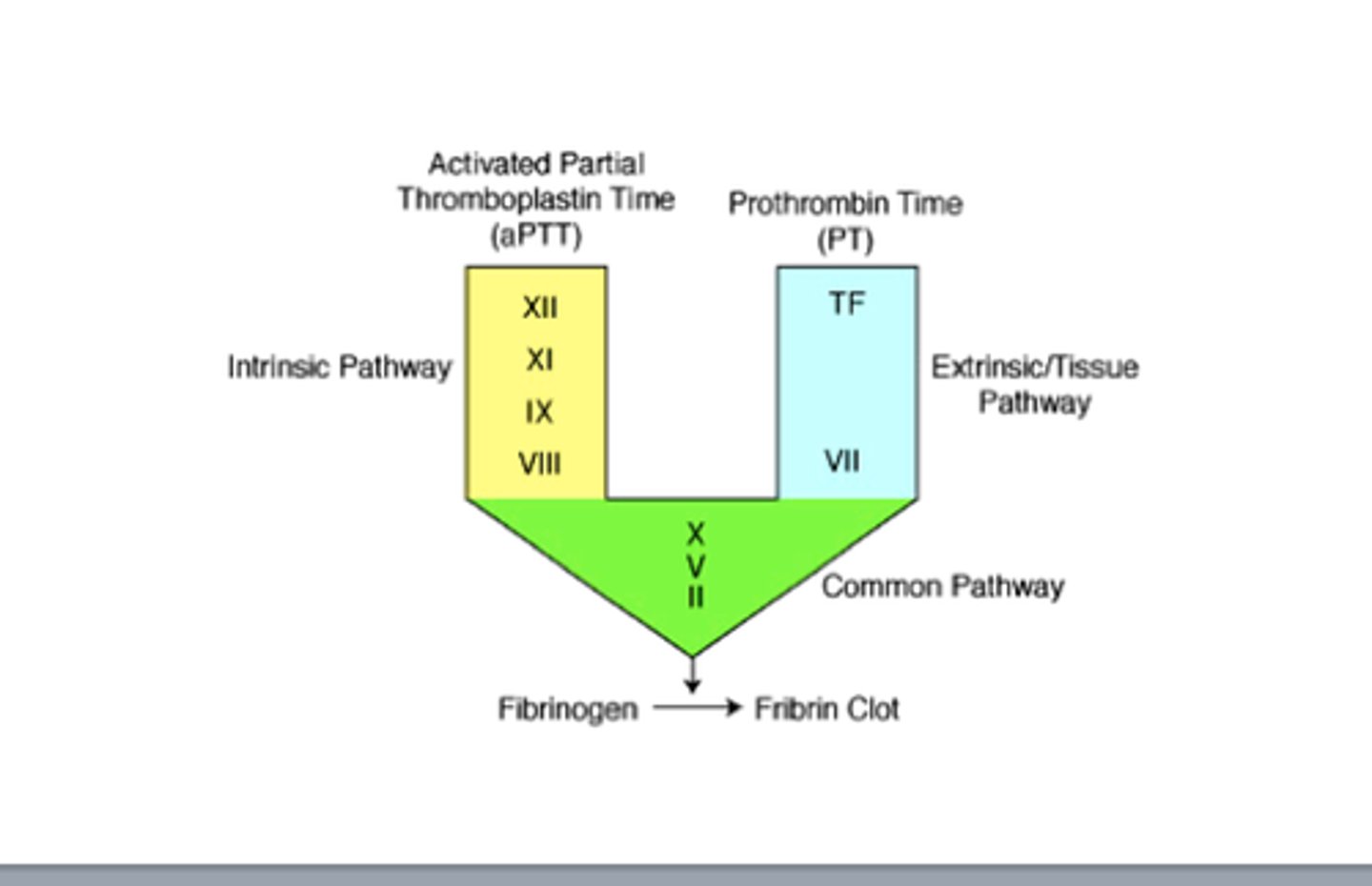
The intrinsic pathway molecules are all found in ______.
plasma
What are the factors involved in the intrinsic pathway?
- Factor XII
- Factor XI
- Factor PK
- Factor HK
These factors are activated when exposed to ______ surfaces.
negatively charged
Lack of these factors does not cause ______ problems.
bleeding
These factors are more active in ______, ______ and ______ activation.
fibrinolysis, inflammation, complement
Intrinsic Pathway steps
1. Factor XII --> XIIa
2. XIIa activates prekallikrein to kallikrein
3. XIIa converts XI --> XIa (requires HMWK)
4. XIa converts IX --> IXa (with Ca2+)
5. IXa + VIIIa + Ca2+ binds to platelets to activate X --> Xa
The extrinsic pathway requires ______ which is not normally found in blood or on cells exposed to blood.
Tissue Factor
Tissue Factor is constitutively expressed on ______ cells.
nonvascular
Monocytes and endothelial cells are induced to express Tissue Factor by ...
- Endotoxin
- C5a
- IL-1
- TNF
Tissue Factor is the cellular receptor and cofactor for ______ and ______.
Factor VII, Factor VIIa
Extrinsic Pathway steps
1. Factor VIIa + TF cleaves X --> Xa
2. Factor VIIa + TF can also cleave IX --> IXa
Common Pathway
Xa + Factor Va + Ca2+ + phospholipid = Prothrombin (Factor II) --> Thrombin (Factor IIa)
As a procoagulant, thrombin induces platelet ______ and ______.
activation, aggregation
Thrombin activates PLT aggregation through promoting the secretion of ______ and ______, both of which are procoagulants.
serotonin, TXA2
As a procoagulant, thrombin activates cofactor ______ to ______.
VIII, VIIIa
As a procoagulant, thrombin converts fibrinogen to ______.
fibrin
Activation of fibrinogen by thrombin involves the removal of the ______ subunits on fibrinogen.
A and B
Fibrin
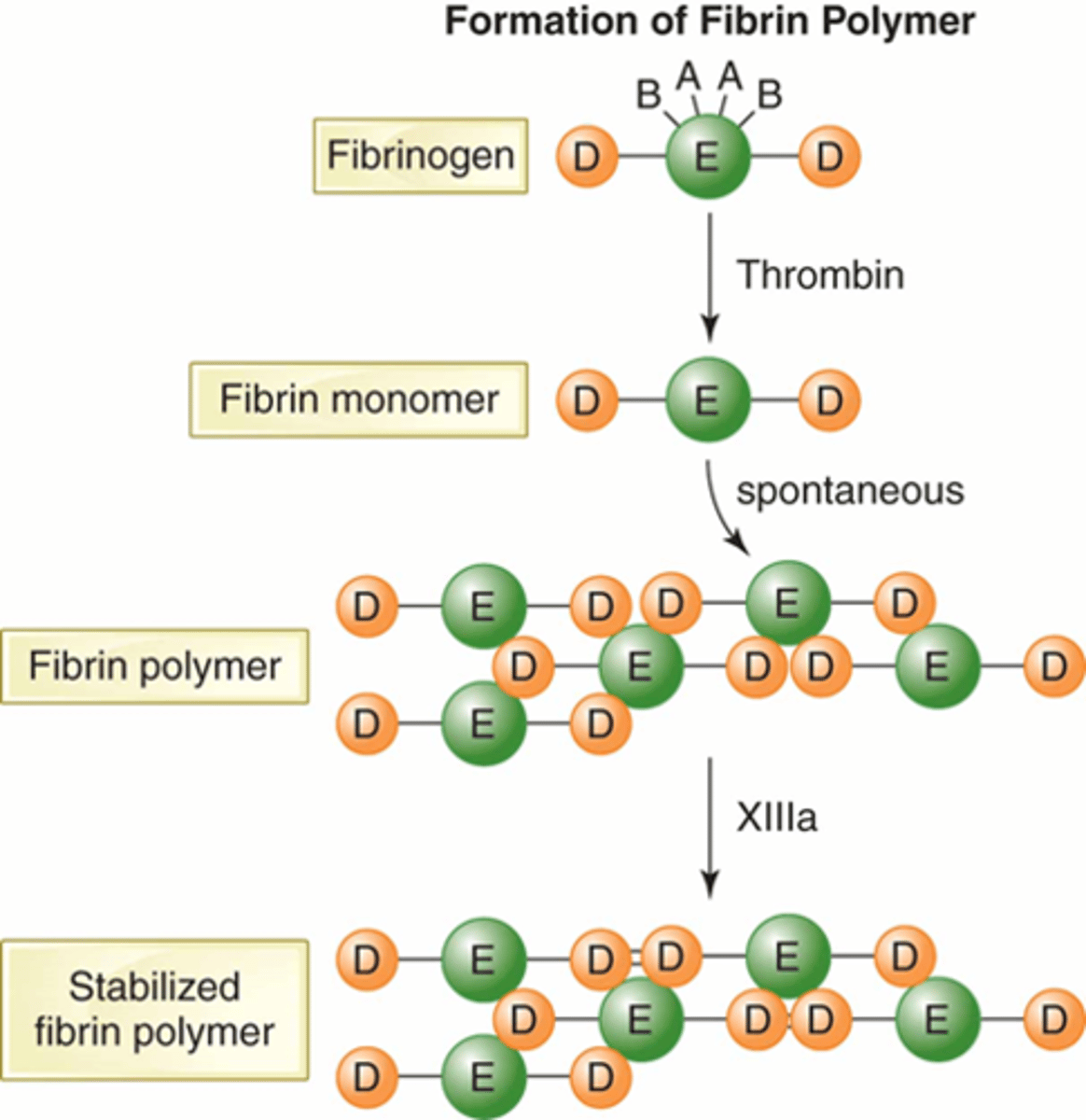
Thrombin stabilizes the fibrin monomer by activating factor ______.
XIII
Activated Factor XIII arranges the fibrin polymer in a lattice formation so that the ______ line up to form a dimer, making the clot stable.
D fragments
Once, formed, thrombin can go back into the cascade and further activate which factors?
- Factor VIII
- Factor V
- Factor XI
- Factor XIII
Common pathway
As a procoagulant, thrombin converts prothrombin to ______ through autocatalysis.
thrombin
As an anticoagulant/fibrinolytic component, thrombin binds with AT III to inhibit ______.
serine proteases
As an anticoagulant/fibrinolytic component, thrombin promotes endothelial release of ______.
t-PA
As an anticoagulant/fibrinolytic component, thrombin binds to thrombomodulin to activate ______.
protein C
The main physiologic inhibitor of thrombin is ______.
Antithrombin III (AT III)
AT III also inhibits ...
- Factor Xa
- Factor IXa
- Factor XIa
- Factor XIIa
- Protein C
- Prekallikrein
Neutrophils and monocytes respond to ______ and undergo chemotaxis.
thrombin
These cells mediate ______ release, which stimulate the proliferation of fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells.
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF)