Sectional Anatomy Unit 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Before, During, After & Terminology of Anatomy and Sonography
Last updated 9:56 PM on 6/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
Ordering Practioner
physician (doctor) PA, nurse practitioner who sees the patient and orders the exam
2
New cards
Sonographer
performs and records ultrasound study
3
New cards
reading physcian
provides final legal interpretation of ultrasound findings. creates final report
4
New cards
Exam order
Ultrasound request form
Has patient identification (NAME and DOB)
Symptoms/Reason for exam
Has ICD 10 Code (Code of diagnosis or symptoms)
Type of exam requested
physician signature
Has patient identification (NAME and DOB)
Symptoms/Reason for exam
Has ICD 10 Code (Code of diagnosis or symptoms)
Type of exam requested
physician signature
5
New cards
Patient chart (medical record)
Patient info (identifying and contact info)
medical history
physical exam results
symptoms
previous imaging results
lab results
medical history
physical exam results
symptoms
previous imaging results
lab results
6
New cards
electronic medical record (EMR)
digital computerized medical record
7
New cards
Standard precautions
treat every patient as though they may have a blood borne or infectious disease
clean/disinfect ultrasound system between patients
wear appropriate PPE
handwashing
clean/disinfect ultrasound system between patients
wear appropriate PPE
handwashing
8
New cards
Curved transducer
Abdominal exam, trans abdominal pelvicl
9
New cards
linear transducer
vascular and small parts
10
New cards
sector transducer
cardiac
11
New cards
endocavity transducer
transvaginal
12
New cards
protocol
anatomic images and measurements required for the ordered exam
13
New cards
Preliminary findings
technical observations, comments, may include worksheet of measurement
\
\
14
New cards
PACS system
computerized method of storing,transmitting and displaying medical images
15
New cards
DICOM
PACS are stored in this format
16
New cards
Differential diagnosis
other possible cause of finding
17
New cards
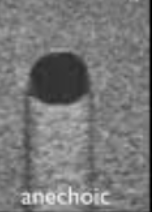
anechoic
echo free appearance
18
New cards
echo texture
sonographic appearance of tissue within the body
19
New cards

hypoechoic
less echogenic
darker than another structure
darker than another structure
20
New cards
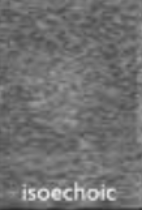
isoechoic
the same echogenicity, the same shade as another structure
21
New cards
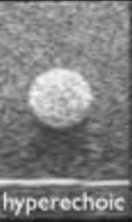
hyperechoic
more echogenic, brighter than another structure
22
New cards
pulsed wave doppler
aka spectral (speed and direction of blood flow)
23
New cards
Color doppler
presence and direction of blood flow
24
New cards
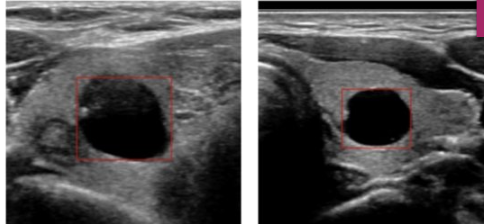
cystic
fluid filled
25
New cards
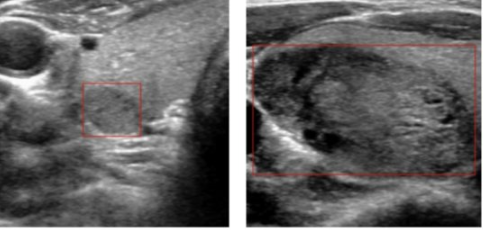
solid
composed of tissue
26
New cards
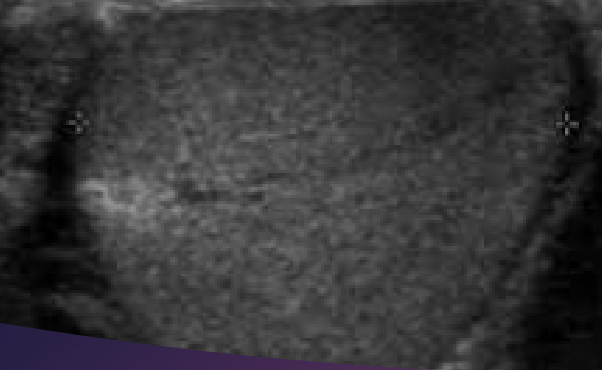
Homogeneous
similar or uniform echo pattern
27
New cards
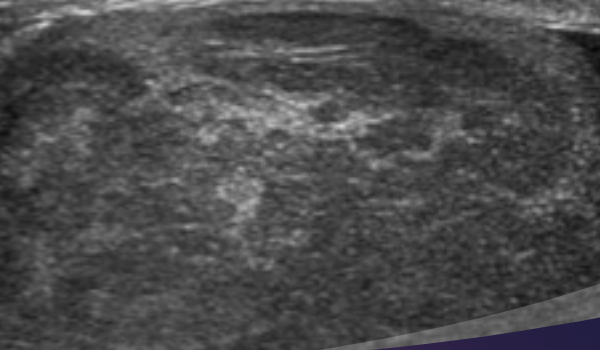
heterogeneous
irregular or mixed echo pattern
28
New cards
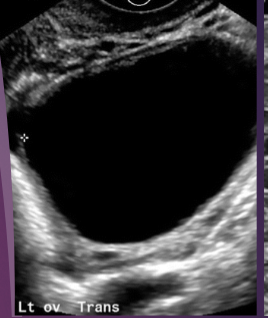
simple
uncomplicated, usually referring to cysts
anechoic, unilocular, thin smooth wall, no blood flow
anechoic, unilocular, thin smooth wall, no blood flow
29
New cards
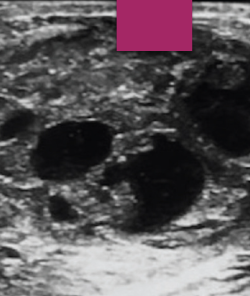
complex
composed of both tissue and fluid
30
New cards
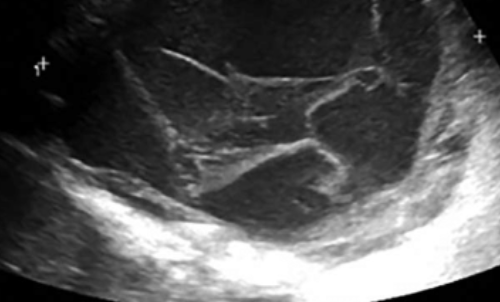
septations
thin membranes within a mass
31
New cards
ipsilateral
on the same sideco
32
New cards
contralateral
on the opposite side
33
New cards
NPO
nothing by mouth
34
New cards
neoplasm
any abnormal growth
35
New cards
benign
non-cancerous
36
New cards
malignant
cancerous
37
New cards
diffuse disease
disease throughout an organ
38
New cards
superior or cephalic
towards the head
39
New cards
inferior or caudal
towards the feet
40
New cards
anterior or ventral
front of body
41
New cards
posterior or ventral
back of body
42
New cards
medial
towards middle of body
43
New cards
lateral
towards edge of body
44
New cards
proximal
towards the heart
45
New cards
distal
further from the heart
46
New cards
subcostal
beneath or below the ribs
47
New cards
intercoastal
between the ribs
48
New cards
midline
vertical line- center of body
49
New cards
midclavicular
vertical line- middle of clavicles
50
New cards
xiphoid process
lower end of sternum
51
New cards
umbilicus
belly button
52
New cards
sternal notch
top of sternum
53
New cards
iliac crest
top of hip bones
54
New cards
symphysis pubis
joint of Lt and Rt pubic bones
55
New cards
Right hypochondriac region
upper left
56
New cards
epigastric region
top middle
57
New cards
left hypochondriac region
top right
58
New cards
right lumbar region
middle left
59
New cards
umbilical region
middle middle
60
New cards
left lumber region
right middle
61
New cards
right iliac region
lower left
62
New cards
hypogastric region
lower middle
63
New cards
left iliac region
right bottom
64
New cards
sagittal plane
longitudinal, long
divides body into left and right
the transducer is towards patients head
divides body into left and right
the transducer is towards patients head
65
New cards
transverse plane
divides body into superior and inferior
notch is towards machine
notch is towards machine
66
New cards
coronal plane
divides body anterior to posterior
67
New cards
Supine
laying on back, indicator towards machine
68
New cards
prone
laying on belly, indicator towards machine
69
New cards
left lateral decubitus (LLD)
patient lays on left side
70
New cards
right lateral decubitus (RLD)
patients lays on right side