aggression
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Blackburns description of violence
the forceful infliction of physical harm
andersons description of aggression
a behaviour that is intended to harm another person who wants to avoid harm
alllens forms of aggression
minor (such as name calling) to serious (kicking, punching), to sever (stabbing, killing)
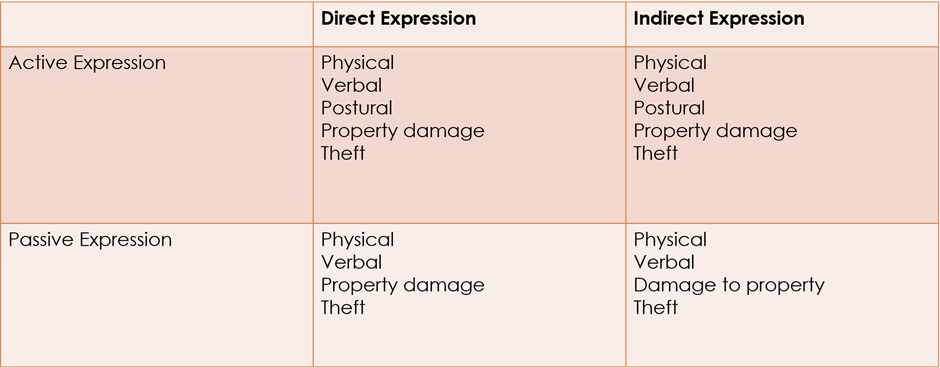
parrots taxonomies
split aggressive behaviour in four types, based on two dimensions, active vs passive and direct vs indirect
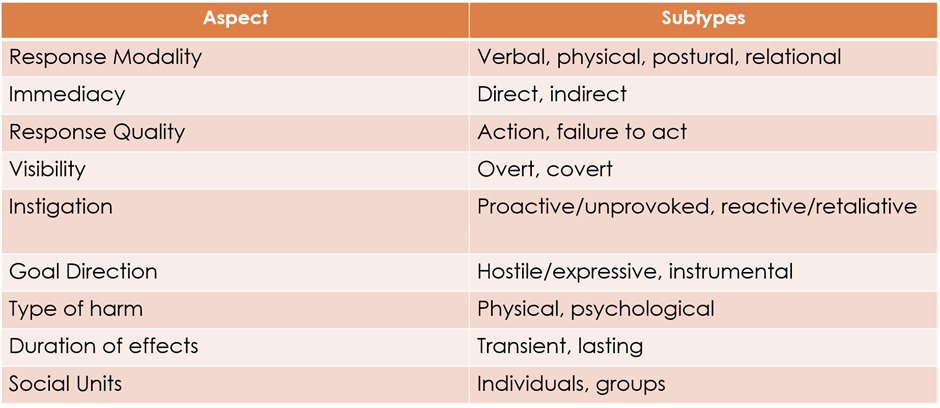
Kraches taxonomies
outlined aspects of behavioural responses and the subtypes of these. For example, visibility (covert, or overt), and type of harm (physical, psychological).
two subtypes of violence
instrumental and reactive
elbert and instrumental violence
violence is used as a way to gain somethin
elbert and reactive violence
response to escape a situation where someone feels dear or anger, this type of violence is often impulsive
socio - Heuer and violence
interpretation of violence is dependent on the individual because people view the world in very different ways
socio - bandura and aggression
aggression is learnt and established through rewards, making violence a behaviour taught through social interactions.
socio cog - huesmann and aggression
aggressive behaviour is gained through early socialisation, individuals develop cognitive scripts
Scripts?
s mental templates which influence decision and the way situations are read by the individual
socio cog - dodge and scripts
environment shapes cognitive scripts within an individual, cues are encoded, interpreted, classify a goal and construct and select an appropriate response
socio cog - dodge and youth
antisocial youth were found to encode fewer cues, and interpret intentions as hostile, they also activate harmful goals and respond and select aggressive responses.
socio - excitation transfer and Zillmann
arousal is a stimulant of aggression, anger is seen as a function of both the strength of the physiological arousal and the way that this arousal is labelled by the individual.
Aggressive response to arousal and misattribution
An aggressive response to arousal can be increased when an individual incorrectly attributed the arousal they experience and misattribute it to an incorrect source
socio excitation - Dollard
aggression is triggered by frustration, frustration can be from any event that prevents an individual from achieving a goal and the reinforcement they would get from this goal. Aggressive behaviour is a result of a person attempting to remove the source that is interfering with the achievement of this goal.
socio interactionist theory - Felson
focuses on the function of coercive actions rather than aggression.
socio interactionist theory - why use coercive strategies
to control a persons behaviour
as a means of restoring justice
to protect the aggressor’s positive identity
socio interactionist theory - decision making
coercive actions are often used as an outcome of a decision making process, the first decision being whether to use coercive action or not, and the second being to decide on a form of coercive action.
bio hormones - shoal and cortisol
low cortisol levels has been found to be linked to risk taking and fearlessness, these two characteristics can be predictors of aggressive behaviour over
bio hormones - archer and testosterone
high levels of testosterone have been found in highly aggressive men
bio hormones - ratio of cortisol and testosterone
Low levels of cortisol cannot counterbalance high levels of testosterone, which will increase the likelihood of aggressive behaviour
bio hormones - Lorenz
compared human and animal behaviour and put forward a model to explain how aggressive energy is developed and released
model stated that organisms build aggressive energy, and the release and response of this energy depends on the energy level and the strength of the external stimuli. If this aggressive energy rises above a certain level and is not released by an external stimulus, it can lead to spontaneous aggression.
bio natural selection theory
was derived from Darwin (1859), stating that a behaviour has to be adaptive for it to be passed down genetically
bio natural selection - Archer
Aggression has been considered as an adaptive behaviour, as fighting off competition can help reproductive success
bio twin studies - Miles
meta-analysis
found that there was a strong genetic link that accounted for 50% of the variance in aggression.
Self-report and parental ratings showed that both genes and the family environment were important during childhood, but with age the influence of the family environment decreased, whilst the genetic influence increased
bio twin studies - Rhee
found that genetics explained 41% of the variance in aggression
the environment explained 59% of the variance.
bio male warrior hypothesis theory
states that men’s psychology has been shaped to gain and protect reproductive resources
bio male warrior hypothesis - Vugt
human brain has evolved through natural selection, with a strong emphasis on sociality and forming associations.
The human brain is inherently social, and this can be seen through the human tendency to create alliances, historically this was important in gaining and protecting resources
bio male warrior hypothesis - Machiavellian Intelligence hypothesis
states that the human brain increased in size through evolution to manage these complex social networks.
Men are thought to have developed cognitive mechanisms with help with the formation of alliances with other men, which enables coordination of planning, and succeeding in intergroup conflicts.