nucleic acid detection and eukaryotic transcription (16-17)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lec 16 - 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what does qualitative analysis of nucleic acids tell us? (4)
structure
conformation
nature/size of molecules
nucleotide composition
what does quantitative analysis of nucleic acids tell us? (2)
levels of gen products
over/underexpression
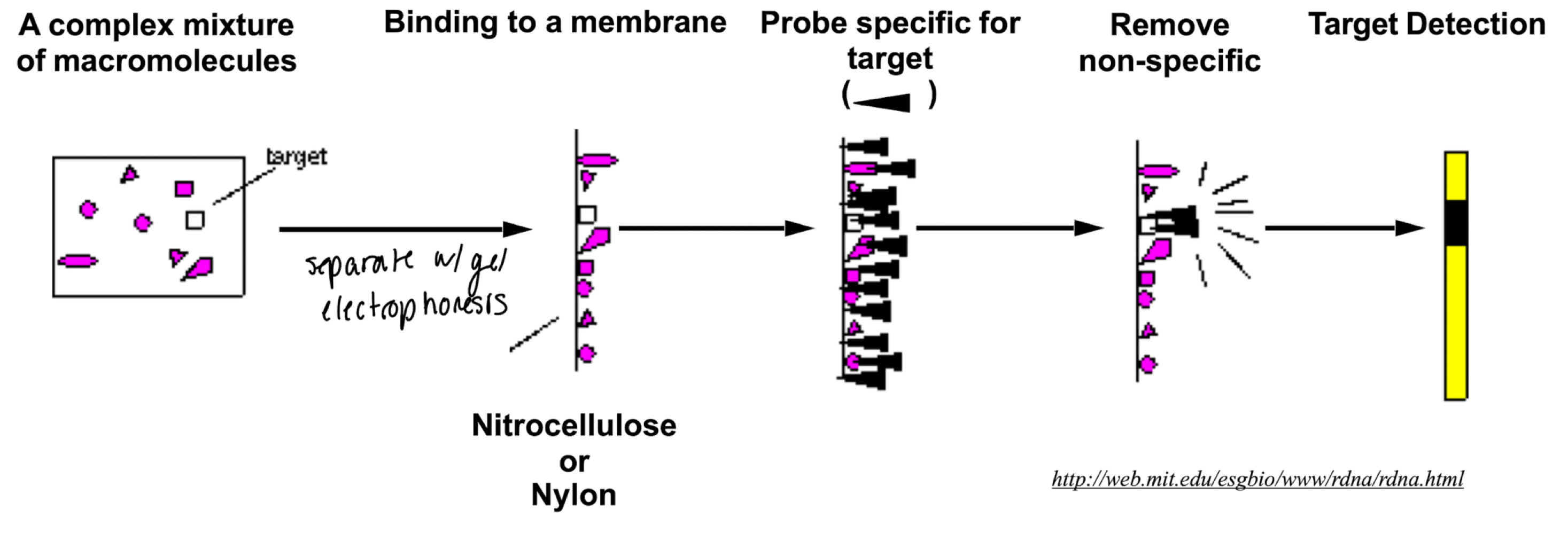
general scheme of how probes work
2 simple ways of making probes
ss oligonucleotides
pcr
how can ss oligo-nt be used as probes?
make ss oligonucleotide reverse complimentary sequence to target
polynucleotide kinase phosphorylates the free OH on the 5’ end with a radioactive gamma phosphate
PNK
polynucleotide kinase
how can pcr be used to make probes?
amplify dna that is compliment to target dna
introduce labelled dNTPs into PCR amplified dna
can use radiolabelled dCTPs
can use fluorescentlylabelled dNTPs
what are solid supports usually made of?
nylon or nitrocelluslose
do agarose gels need to be marked after the gel has been run?
yes
to use as a reference for interpreting the positions, lane numbers, and well locations of blot later
how does dna get onto a solid state support?
run an agarose gel
with rna there must be formaldhyde in gel
dna gets pulled onto membrane through capillary action
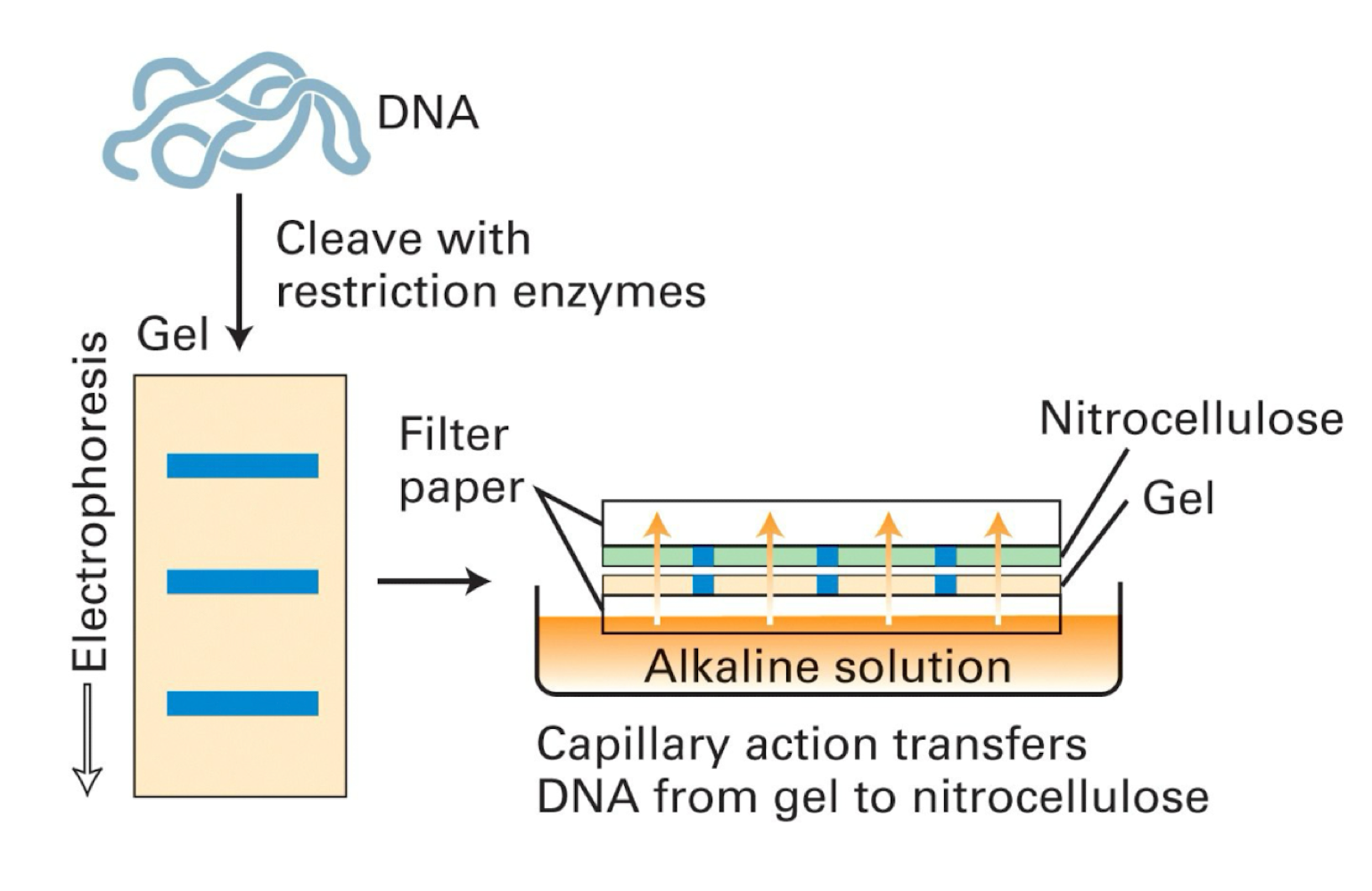
UV crosslinking
ensures nucleic acids are permanently bound to solid state support
once bound, level and positions are recorded
hybridization
letting a probe interact w/ nucleic acid on a solid support then removing the membrane and washing
only target dna remains
autoradiography
used to detect the target dna left behind after hybridization
amount of radioactivity represents the number of copies in the sample
southern analysis
dna only blotting technique
follows agarose gel, membrane transfer method
probe doesnt need to bind 100%
used for polymorphisms
digest dna, run in gel, then denature
northern analysis
rna only blotting technique
follows agarose gel, membrane transfer method
rna doesnt need to be digested before gel
RT- qPCR
reverse trancriptase quantitative pcr
determines mRNA levels
make cDNA then do PCR using a fluorescent dye
knowing how many PCR cycles occur before Ct tells how much starting material you had
Ct
threshold cycle seen in PCR
point where growth becomes exponential
faster ct is reached, more starting mrna u have
cDNA stands for
complimentary dna
how is cdna made
poly A tail of mrna is primed with a ss poly T oligonucleotide
RT uses that primer to make compolimentary ssdna
mrna is removed
poly dG adapter anneals to 3’ ends of cDNA
poly dC primer intiates synthesis of second strand
e coil
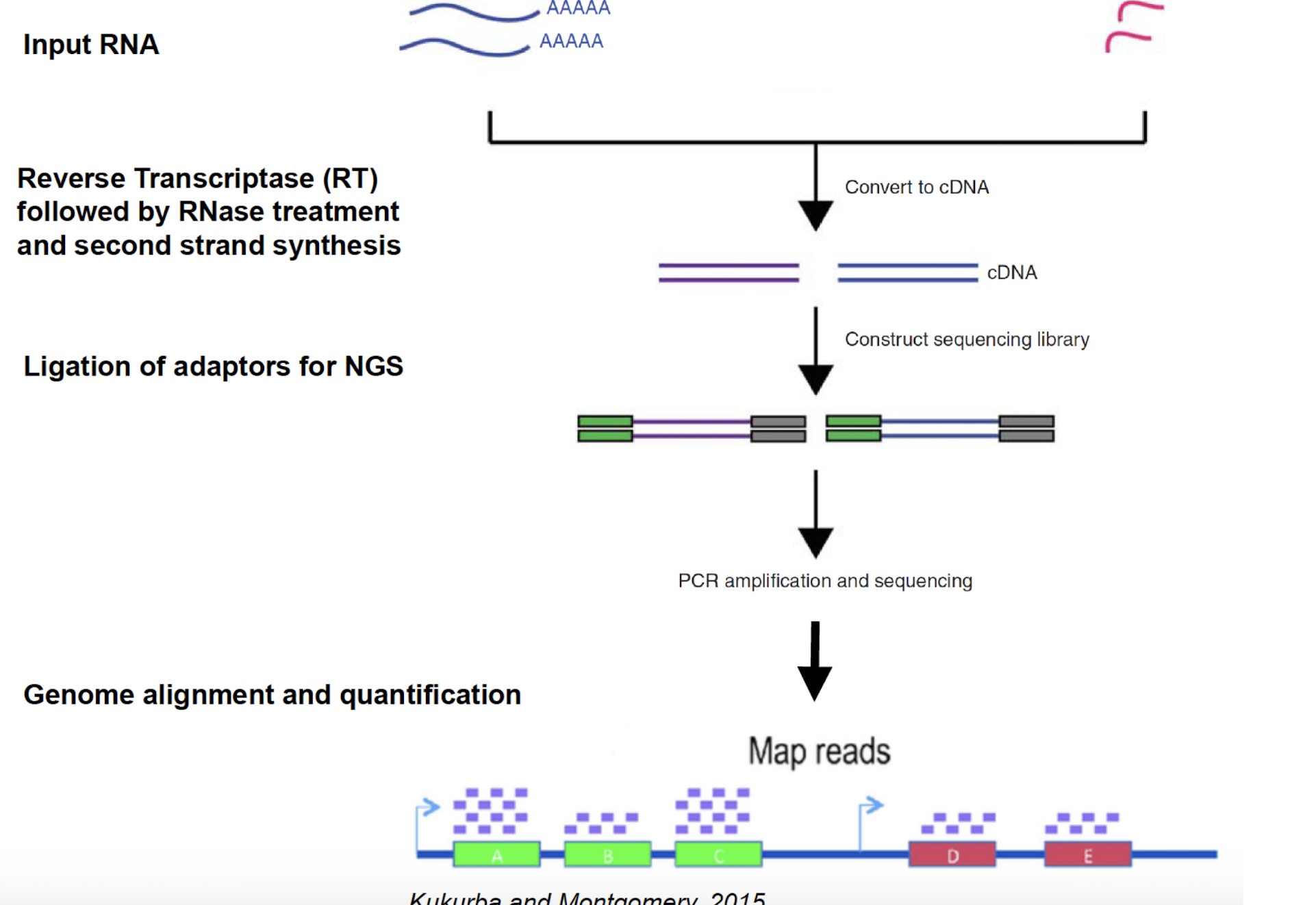
rna sequencing (6 stps)
ngs methos for studying gene eexpression
isolate mrna, rrna, ncrna from sample
used poly A selection or size selection to isolate specific rna species
rna —> cdna
ligate short dna adaptors to each end of cdna to act as primer
optional : pcr to amplify library
use ngs to read fragments and map to genome
main method of regulating gene expression
transcriptional control
3 stages of transcription
intiation - rna pol 2 binds to promoter, locally denatures dna, and catalyzes first phosphodiester linkage
elgongation - rna pol makes rna in 5’ → 3’ direction
temrination - rna pol sees stop siite, releases dna, and dissociates
polycistronic vs monocistronic
polycistronic have multiple genes regulated by the same promoter
seen in prokaryotes
mono had one promoter per gene
eukaryotic
2 key structures of rna pol 2
clamp
CTD with heptapeptide sequence
what is a phosphorylated ctd of an rna pol 2 associated with?
active transcription