TAAP End of Pathway Exam
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
in order for the "five-factor theory" to be implemented effectively, a school must have strong leadership, high expectations, a school mission, a safe and orderly climate, and. . .
monitor student success
the AFT is best described as
professional organization
learning by doing is a foundation of. . .
progressive education
a part of the education amendments of 1972, . . . protected individuals from discrimination based on gender.
gender equality
title IX
accepting that students learn, comprehend, and retain materials differently will help the teacher to. . .
facilitate learning
structure, question, respond, and . . . make up a pedagogical cycle.
react
one of the pioneers in cognitive (learning) development was
piaget
the terms for the ends of the spectrum in bloom's taxonomy are. . .
knowledge and evaluation
undergoing an extensive observation period and portfolio review is a part of. . .
becoming a National Board Certificate Teacher
teachers are often members of a collective bargaining unit which negotiates salary and. . .
benefits
the elementary and secondary education act was passed to. . .
develop the mental resources and technical skills of young people
horace mann was one of the implementers of. . .
public school development
knowledge of the subject area and proper instructional skills are part of. . .
effective teaching
successful teachers require many characteristics. which of the following characteristics is the MOST important for a teacher to possess?
strong work ethic
Schools that are effective tend to have clear expectations, small class sizes, teachers that engage students, and. . .
a belief that all students can learn
effective technology integration is achieved when there is active engagement, participation in groups, frequent interaction, and. . .
feedback
This piece of legislation requires government-run schools that receive federal aid to administer state-wide standardized tests annually for all students:
This Act has impacted the classroom by putting a large amount of funding into ensuring high-quality professional development for teachers.
No Child Left Behind Act
the desegregation of public schools, which took place in 1954, was a landmark case known as. . .
Brown v. Board of Education
Public schools in the United States are funded by which combination of entities?
federal, state, and local
Pickering v. Board of Education protects teachers'. . .
First amendment rights
according to john goodlad's "a place called school" there are four broad goals of public education. They are academic, vocational, social/civic, and. . .
personal
unrealistic expectations for the workplace have been linked to. . .
increased drop-out rates
the improvement of school districts to become more competitive is a by-product of. . .
schools of choice
there are several common methods used in moral education. which is the correct combination of these methods?
moral stages of development, comprehensive values education, character education, and values clarification.
the issue during the lau v. nichols court case was discrimination based on
national origin
Chinese American with limited English proficiency living in California was not receiving aid. DISCRIMINATION BASED ON NATIONAL ORIGIN is unconstitutional. Students should be treated equally among schools.
Claimed students were receiving an unequal education due to lack of English language courses. Supreme Court ruled California was violating the Civil Rights Act of 1964 - equal access to education. Federal $ should be spent for resources for students with limited English proficiency.
cooperative learning is known to be a good technique to use when working with a/an. . . classroom
diverse
the theory that intelligence is differentiated into various specific modalities instead of one is called. . .
multiple intelligences
the fairest way to test a large number of participants for comparison is through the use of. . . tests
standardized
which of the following MOST clearly matches the annual state-based salary of a beginning teacher in Georgia with a four-year degree?
$36,000
high stakes test scores MOST likely contribute. . .
drop-out rates (high stakes test scores)
an example of a zero-tolerance punishment would be. . .
punishing any infraction of a rule regardless of mistakes, ignorance, or extenuating circumstances
fair use allows the use of copyrighted material on a website without first getting permission from the. . .
copyright holder
Accommodating group and individual cultural differences is part of a/an. . .
culturally inclusive classroom
which type of test is used to set a baseline for a student's abilities?
diagnostic
Lemon v. Kurtzman
Nonpublic school teachers were reimbursed for salaries of teachers teaching secular material.
Lemon Law
Test determines if something violates the 1st amendment- Separation of church and state. Public school teachers must agree not to teach courses in religion
Tinker vs. Des Moines 1965
ARM BANDS worn by students to protest Vietnam war. Established that students have FREEDOM OF SPEECH as long as it does not disrupt the school environment. "Students don't shed constitutional rights at the school house gate."
Pickering vs. Board of Education 1968
Teachers have rights to express their concern on matters of public concern.
Tennessee vs. John Scopes
MONKEY trial- trial to decide whether evolution would be taught in public schools
Kalamazoo Michigan 1874
Ruled that taxes could be used to support schools
Civil Rights Act 1964
Outlawed major forms of discrimination in the workplace.
IDEA- Individuals With Disabilities Education Act
Ensures students with disabilities receive a free appropriate education.
504 Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Gives disabled students rights.
PAGE-Professional Association of Georgia Educators
Largest professional organization in Georgia
NAE- National Association of Educators
Largest professional organization and labor union in the U.S.
GAE- Georgia Association of Educators
Supports, protects and strengthens Georgia educators.
AFT- American Foundation of Teachers
American labor union for teachers.
Cognitive Learning
Reasoning, intuition and perception
Emotional Learning
Ability to handle feelings determines success in learning
Social Learning
Includes how to deal with ones self, others and relationships to work effectively.
Loco Parentis
refers to legal responsibility of a person or organization to take on some functions of a parent.
Auditory Learning
Hearing
Visual Learning
Seeing
Kinesthetic Learning
Movement, hands on, doing
Tactile Learner
Similar to Kinesthetic, student always touches things
Social Distractions
Distraction by peers/others preventing learning
Homogenous
Grouping of similar students
Heterogeneous
Grouping of different students
Proficiency
Having knowledge of and passing tests
Mainstreaming
Moving special Ed students into regular Ed classrooms
Open ended questions
Questions requiring more than a yes or no answer
Closed ended questions
Yes or no answer
Rote memory
Memorization, Quick recall
Wait time
time given when a teacher asks a question to answer
Education
Teaching and learning skills and knowledge
Learning
Change in behavior as a result of experience
Curriculum
topics taught within a subject within an area
Head Start
Gov. program provided for medical social, nutritional and educational needs for low income families
Inclusion
mainstreaming - including others
IEP
Individualized plan guarantees each child gets accommodations necessary to learn
Accommodations
Changes to the classroom- deals with the mobility of the body
Modifications
Changes to class work- deals with the academic portion
Essentialism
Traditional "Back to the Basics" approach.
Teacher Centered
Emphasis on structure, routine, rigor and academic
subjects, old school thought - Must make As and pass
everything to be better than other societies (competitive
nature), largely testing focused
Progressivism
Focuses on individual interests
(JOHN DEWEY, key figure)
Student Centered
Problem solving skills, learn by DOING, focuses on
student interests, electives and career experiences
(CTAE), field trips, project based, most popular in
education
Perennialism
Teaches principles, not facts
Teacher Centered
Studies the GREAT BOOKS and focuses on philosophers
and their teachings/morality, focuses on the core
subjects but how literature can be used in all, 3 R's
reading, writing and arithmetic, Socratic Seminars
Existentialism
Learn through play. Focused on feelings actions and natural consequences
Student Centered
Each student finds their own path, what they are
interested in and they are responsible for their own
learning, usually a private school setting
pedagogical cycle
evaluate -> engage -> explain -> explore -> elaborate
Minersville School District v. Gobitis
(1940)
Kids didn't want to do the pledge of allegiance for religious
reasons - false idols. Supreme Court ruled that standing for
the pledge did not violate their religious rights. It was a civic
duty and responsibility. (Kids lost case)
Everson v. BOE
(1947)
Argued that reimbursing parents for transportation costs to
public and private (religious) schools violated 1st amendment
- separation of church and state. (he lost)
Regents of University of California v. Bakke
(1978)
Challenged that he was excluded from admissions on the basis of race.
His application and test scores outranked minorities that were accepted over him.
He won the case - Supreme court ruled that racial quotas
violated equal protection clause, stated that race could not be the sole factor, BUT affirmative action was constitutional and race can be ONE of the aspects used in an application.
-Process of "setting aside" a certain number of admittances for
minorities only is called - Affirmative Action - (in employment, the practice of favoring individuals that have previously been discriminated against)
Plyler v. Doe (1982)
Students originating from Mexico could not provide documentation that they had legally entered Texas; they were denied enrollment into the public school because Texas law stated public funds would not support undocumented children. Supreme Court ruled states cannot deny free public education to students based on their immigration status
Albert Bandura
Social Learning Or Observational Learning Theory
BOBO Doll Experiment in 1961-
Took three groups of children
1 group watched adult be nice to bobo doll
1 group watched adult beat up doll
1 group watched adults ignore the doll
Kids that watched the violence copied and beat
up the doll.
Bandura proved that once you Observed a
behavior you would IMITATE that behavior.
What you See is what you Do!
Attention
Memory (retention)
Imitation
Motivation
Students pay attention to a lesson/topic and
then they retain (memorize) it, choose to imitate
(copy) the action if they are motivated positively.
OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING
Teachers should model the behavior they want
to see from their students.
Erik Erikson
Theory of Psychosocial Development
Psychosocial crisis, Trust vs Mistrust (0-1.5yrs), 2. Autonomy vs Shame (1.5-3yrs), 3. Initiative vs Guilt (3-5yrs), Industry vs Inferiority (6-12yrs), Identity vs Role Confusion (13-18yrs)
-Gives Teachers a schedule of what to
expect from their students.
-Understanding the emotional and
social aspects of a child's
development in the classroom on top
of the academic goals
-How should you react to a student's
continual questions... will you build
them up or tear them down?
Lawrence Kohlberg
moral development, heinz dilemma
-Have students be a part of creating the
classroom rules; by allowing students to
voice, what they think is acceptable behavior they are more likely to abide by them.
-Giving peer/group evaluations holds people
accountable and makes the individual want
to work hard to gain the respect of their peers
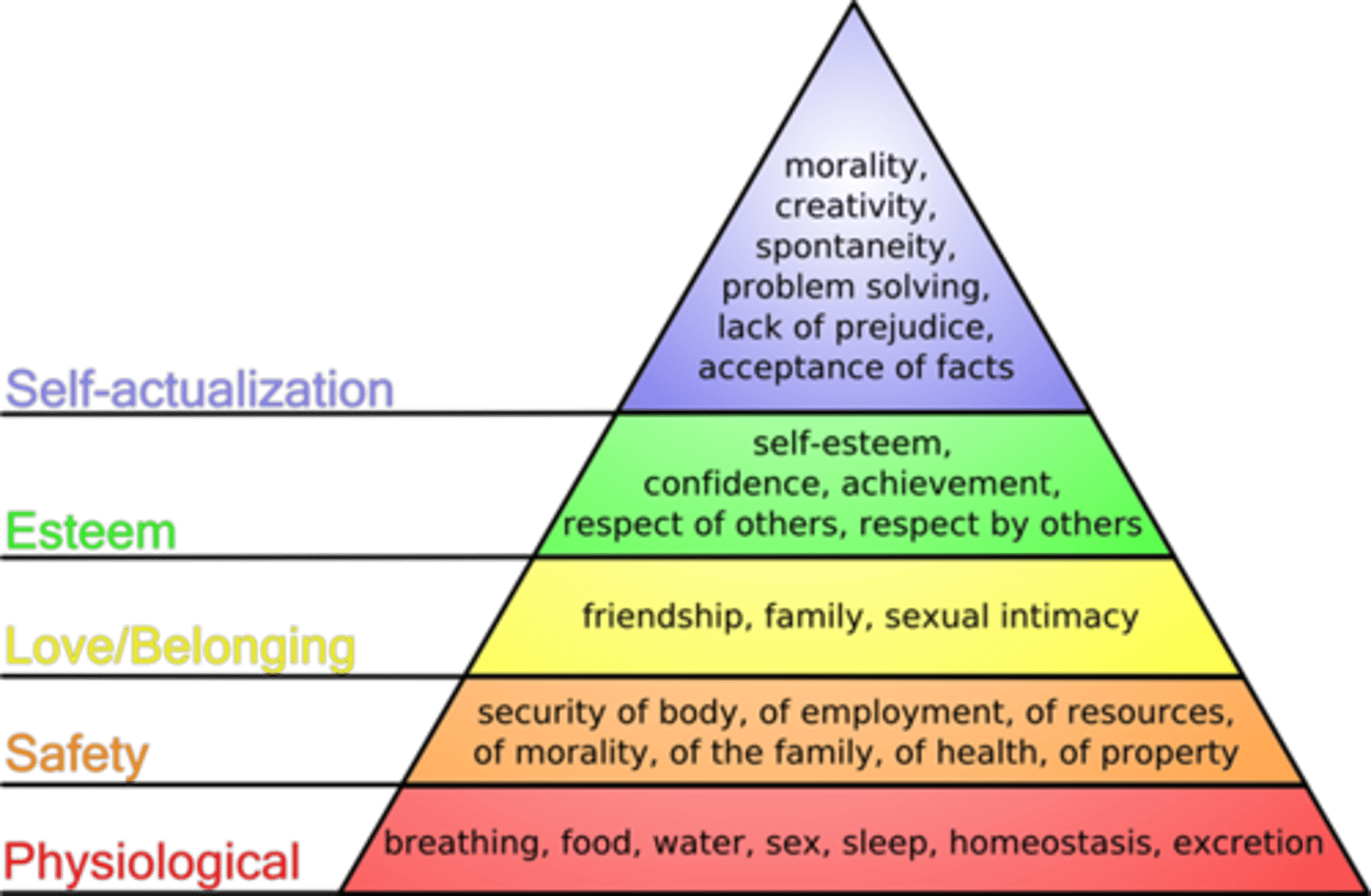
Abraham Maslow
Theory of motivation (hierarchy of needs)
Legal Compliance
An educator gets arrested for a felony - drugs, alcohol,
sexual offenses and found guilty in court
Conduct with Students
An educator puts children in danger, sexual act or
relationship with student, gives or prevents alcohol/drug use by students.
Alcohol and Drugs
An educator is on school property while under the influence
and or brings alcohol or drugs on school grounds. Use of alcohol or drugs while supervising students (like on a field trip).
Honesty
An educator lies about their criminal history, evaluations, reasons for absences or lies about their job requirements/skills.
Public Funds and Property
An educator uses school property for personal
use/gain, steals money from school or joins school money with personal money
Remunerative Conduct
An educator takes a bribe, gift or excess money for
personal gain. Tutoring students for money without school's knowledge.
Confidential Information
An educator shares legal, medical, disciplinary or
personal information about students. An educator uses student information for personal gain.
Required Reports
An educator MUST report a violation or investigation about
them, any arrests and must submit accurate and ALL documents to the PSC.
Professional Conduct
An educator does not fulfill their entire contract, breach
of contract, does not make professional/ good choices. SOCIAL MEDIA POSTS
Testing
An educator shares, changes or breaks test security.
What is the NBPTS?
National Board of Professional Teaching Standards
What is the difference between a disposition and a NBPTS proposition?
A disposition is a personality trait you should have and a proposition is what you learn in school to be highly qualified.
Social Reconstructionism
Student Centered
Problem solving skills, what is wrong in current society
and how can it be fixed, social experiences and group,
people, community interaction, independent thinking
and analyzing
Ivan Pavlov
classical conditioning
Teachers set a structure and a routine to
the class and students know expectations.
Ex: Students walk in to the classroom open
notebooks and begin the warm-up because
they are conditioned to do so.
They know what is expected from them by
the teacher's set routine
Jean Piaget
cognitive development
sensorimotor, pre-operational, concrete operational, formal operational