Biochem HW 5 (CH9)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
A molecule moves across a membrane from a lower to a higher concentration with the aid of a membrane protein. This process is known as…
active transport
Which of the following is not relevant to facilitated (passive) transport across biological membranes?
ATP hydrolysis is required.
Indicate whether the following compounds are likely to cross a membrane by simple diffusion or facilitated diffusion transport:
Term:
Lysine:
Oxygen:
Water:
Definition:
Facilitated
Simple
Lysine: Facilitated
Oxygen: Simple
Water: Facilitated
A pore that simultaneously transports two different molecules in different directions is called a(n)
antiporter.
Which of the following is/are true regarding the glucose transporter?
Both
The glucose transporter is an example of…
Facilitated transport.
Where would you mostly likely find polar charged amino acids (e.g. Asp, Glu, Lys, Arg) in an integral membrane protein?
Near the polar head groups on the extracellular/intracellar membrane surface.
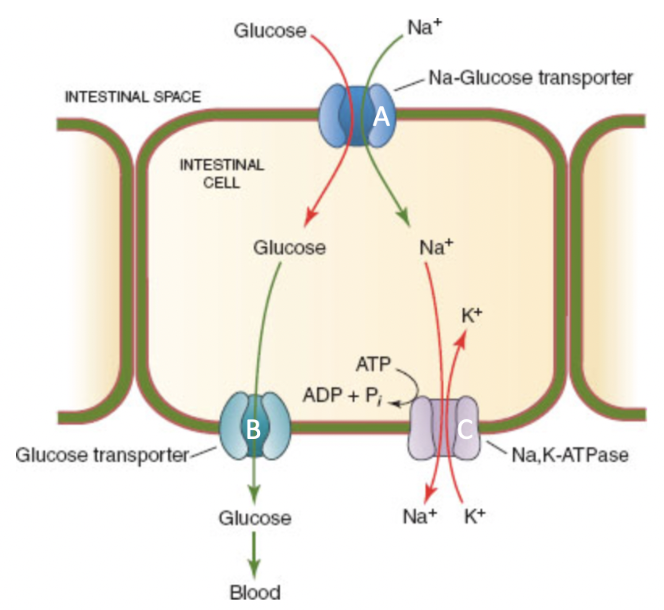
Match the transporter (A- blue, B- green, C- light purple) with it's description.
Term:
A:
B:
C:
Definition
Uniporter
Antiporter
Symporter
A: Symporter
B: Uniporter
C: Antiporter
Which of the following will cause the opening or closing of a gated ion channel?
voltage change
In the sodium-potassium pump:
sodium is transported out of the cell and potassium into the cell, both against concentration gradients
Energy requiring transport mechanisms include…
Active transport
What substance will be transported through an aquaporin?
water
Which amino acid in the aquaporin channel hydrogen bonds with water to prevent the movement of protons? (Hint-consider the characteristics of the amino acids.)
Asn
Active transport is uniquely characterized by:
the tight coupling of an input of energy, with the species going from a lesser concentration to a greater concentration.
Facilitated (Mediated) diffusion across a biological membrane:
is driven by a difference in solute concentration.
The movement of glucose into a cell when blood sugar is high in the extracellular matrix is accomplished by _____ ["active transport", "passive transport", "membrane fusion"] . The movement of K+ against its concentration gradient is accomplished by ____ ["passive transport", "active transport", "membrane fusion"] .
Passive transport, Active transport
Due to the hydrophobicity of the lipid bilayer, small ions like Na+ are unable to leave the cell by simple diffusion.
True
Resting membrane potential depends on:
I. The differential distribution of ions across the membrane.
II. The active transport process.
III. The selective permeability of the phospholipid bilayer.
All of the above
Active diffusion across a biological membrane…
is endergonic.
The sodium-glucose cotransport system is an example of:
secondary active transport
Which of the following is not relevant to facilitated (passive) transport across biological membranes?
ATP hydrolysis is required.
Calculate the membrane potential at 20°C when a. [Na+]in = 10 mM and [Na+]out = 100 mM.
Stop! For full credit:
1. Enter your answer in mV, millivolts.
2. Do not put units in the box.
3. If your calculator permits, do not round until the end for the sake of continuity.
4. If your answer is negative, include the sign and number with no space.
-58
Use the appropriate equation to calculate the free energy change for the movement of Na+ into a cell at the resting potential. The Nain/Naout ratio is 0.063/1, the membrane potential is -70mV. Assume the temperature is 37°C.
Stop! For full credit:
1. Enter your answer in kJ, kilojoules.
2. Do not put units in the box.
3. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. If your calculator permits, do not round until the end for the sake of continuity.
4. If your answer is negative, include the sign and number with no space.
-13.9
Calculate the membrane potential at 20°C when a. [Na+]in = 40 mM and [Na+]out = 25 mM.
Stop! For full credit:
1. Enter your answer in mV, millivolts.
2. Do not put units in the box.
3. Round your answer to the nearest whole number. If your calculator permits, do not round until the end for the sake of continuity.
4. If your answer is negative, include the sign and number with no space.
13
Use the appropriate equation to calculate the free energy change for the movement of Na+ into the depolarized nerve cell where the membrane potential is +50mV and the Nain/Naout ratio is 7.3/1. Assume the temperature is 37°C.
Stop! For full credit:
1. Enter your answer in kJ, kilojoules.
2. Do not put units in the box.
3. Round your answer to the nearest tenth. If your calculator permits, do not round until the end for the sake of continuity.
4. If your answer is negative, include the sign and number with no space.
9.9